Current Trends and Applications of PET/MRI Hybrid Imaging in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Normal Aging
Abstract
1. Introduction
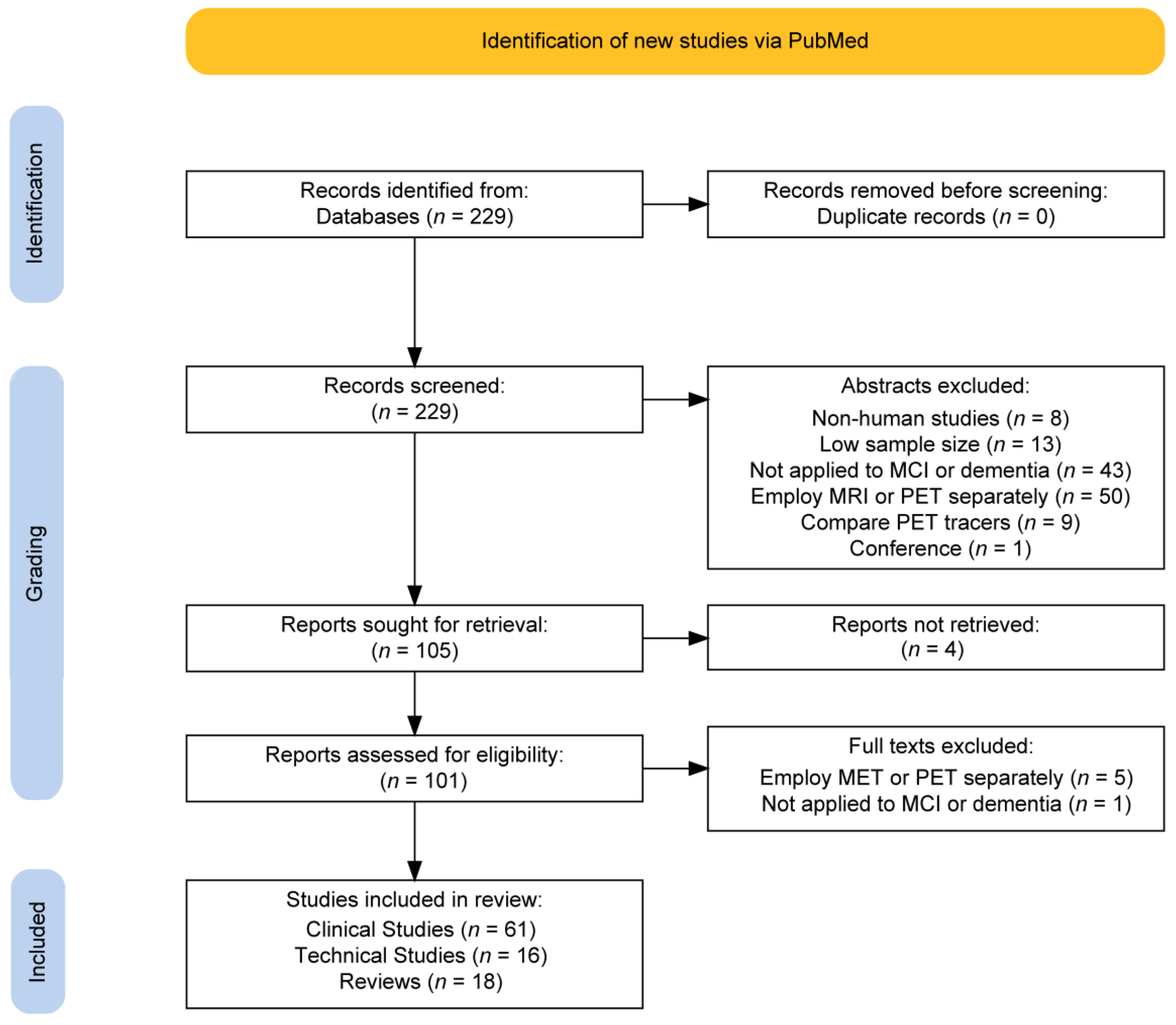
2. Methods
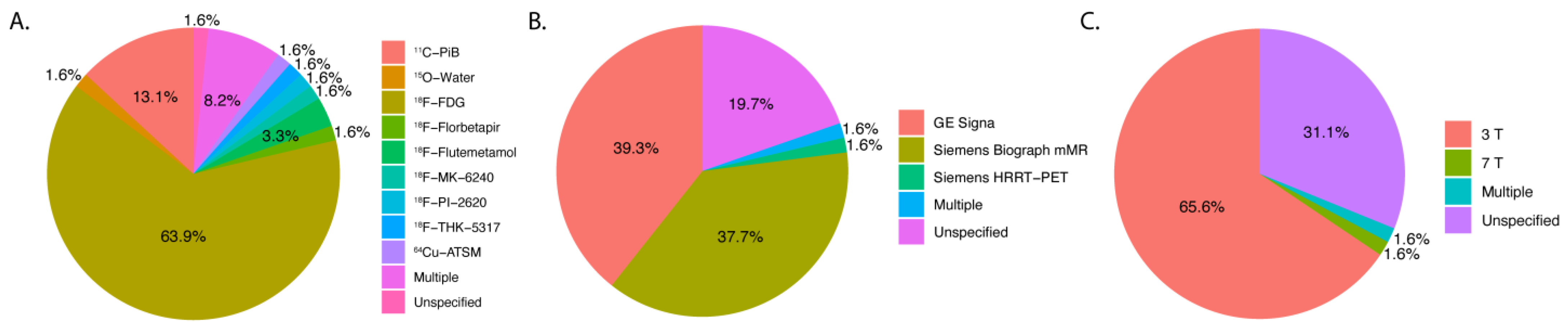
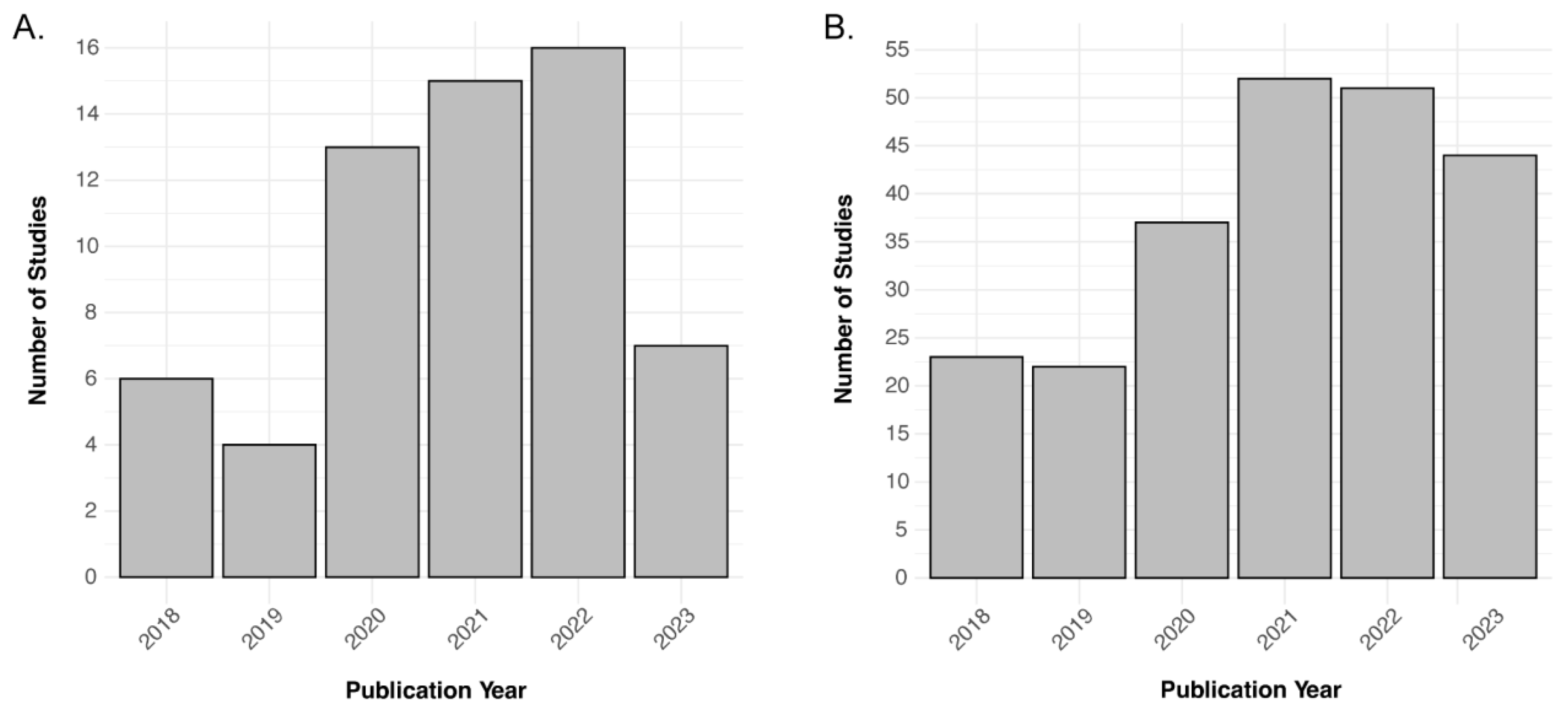
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Artificial Intelligence
4.2. Technical Improvements
4.2.1. Attenuation Correction
4.2.2. Motion Correction
4.2.3. Tracer and Imaging Techniques
4.3. Functional Connectivity
4.4. Brain Regions of Interest and Biomarkers
4.4.1. Hippocampus
4.4.2. Gray and White Matter
4.4.3. Biomarker Evaluation
4.5. Associated Illnesses
4.6. Scanners
4.7. Comparison to MRI or PET
4.8. Limitations
4.9. Ongoing Challenges and Future Directions of Hybrid Imaging
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MRI-ASL | MRI-Arterial Spin Labeling |
| FDG-PET | Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron-Emission Tomography |
| FTD | Frontotemporal Dementia |
| HC | Healthy Control |
| Aß | Amyloid Beta |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| DLB | Dementia with Lewy Bodies |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| P-tau181 | Phosphorylated Tau at position 181 |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| MCI | Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| TOF-MRI | Time-of-Flight MRI |
| DTI | Diffusion Tensor Imaging |
| LBD | Lewy Body Dementia |
| CI | Cognitive Impairment |
| eAD | Early Alzheimer’s Disease |
| bvFTD | Behavioral variant Frontotemporal Dementia |
| preAD | Pre-Alzheimer’s Disease |
| DKI | Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging |
| AWF | Axonal Water Fraction |
| CBD | Corticobasal Degeneration |
| FTLD/PPA | Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration/Primary Progressive Aphasia |
| FC | Functional Connectivity |
| PCA | Posterior Cortical Atrophy |
| SD | Semantic Dementia |
| aMCI | Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| SCD | Subjective Cognitive Decline |
| BOLD-FC | Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent Functional Connectivity |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| NPH | Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus |
| RS-fMRI | Resting-State Functional MRI |
| SUVR | Standardized Uptake Value Ratio |
| EOFAD | Early Onset Familial Alzheimer’s Disease |
| PD-MCI | Parkinson’s Disease with Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| FCSRT | Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test |
| R-MEG | Resting-State Magnetoencephalography |
| FAD | Familial Alzheimer’s Disease |
| WMHV | White Matter Hyperintensity Volume |
| ALS | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
References
- Hebert, L.E.; Weuve, J.; Scherr, P.A.; Evans, D.A. Alzheimer Disease in the United States (2010–2050) Estimated Using the 2010 Census. Neurology 2013, 80, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, C.P.; Prince, M.; Brayne, C.; Brodaty, H.; Fratiglioni, L.; Ganguli, M.; Hall, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Hendrie, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Global Prevalence of Dementia: A Delphi Consensus Study. Lancet 2005, 366, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustani, M.; Peterson, B.; Hanson, L.; Harris, R.; Lohr, K.N.; U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Dementia in Primary Care: A Summary of the Evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Howard, R.S.; Schneider, L.S. The Current Landscape of Prevention Trials in Dementia. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2022, 19, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, J.R. Neuroimaging and the Search for a Cure for Alzheimer Disease. Radiology 2013, 269, 671–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Lowe, V.J.; Weigand, S.D.; Wiste, H.J.; Senjem, M.L.; Knopman, D.S.; Shiung, M.M.; Gunter, J.L.; Boeve, B.F.; Kemp, B.J.; et al. Serial PIB and MRI in Normal, Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Sequence of Pathological Events in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain 2009, 132, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casamitjana, A.; Petrone, P.; Tucholka, A.; Falcon, C.; Skouras, S.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Vilaplana, V.; Gispert, J.D. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative MRI-Based Screening of Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease for Prevention Clinical Trials. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shan, Y.; Ding, J. A Literature Review of MRI Techniques Used to Detect Amyloid-Beta Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 10062–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kas, A.; Rozenblum, L.; Pyatigorskaya, N. Clinical Value of Hybrid PET/MR Imaging: Brain Imaging Using PET/MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2023, 31, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorking, N.; Murray, A.D.; O’Brien, J.T. The Use of Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Dementia: A Literature Review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2021, 36, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anazodo, U.C.; Finger, E.; Kwan, B.Y.M.; Pavlosky, W.; Warrington, J.C.; Günther, M.; Prato, F.S.; Thiessen, J.D.; St Lawrence, K.S. Using Simultaneous PET/MRI to Compare the Accuracy of Diagnosing Frontotemporal Dementia by Arterial Spin Labelling MRI and FDG-PET. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 17, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biundo, R.; Weis, L.; Fiorenzato, E.; Pistonesi, F.; Cagnin, A.; Bertoldo, A.; Anglani, M.; Cecchin, D.; Antonini, A. The Contribution of Beta-Amyloid to Dementia in Lewy Body Diseases: A 1-Year Follow-up Study. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessing, E.M.; Parekh, A.; Betensky, R.A.; Babb, J.; Saba, N.; Debure, L.; Varga, A.W.; Ayappa, I.; Rapoport, D.M.; Butler, T.A.; et al. Association between Lower Body Temperature and Increased Tau Pathology in Cognitively Normal Older Adults. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 171, 105748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.S.G.; Mak, E.; Clare, I.; Grigorova, M.; Beresford-Webb, J.; Walpert, M.; Jones, E.; Hong, Y.T.; Fryer, T.D.; Coles, J.P.; et al. Support Vector Machine Learning and Diffusion-Derived Structural Networks Predict Amyloid Quantity and Cognition in Adults with Down’s Syndrome. Neurobiol. Aging 2022, 115, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanholo, K.R.; Pitombeira, M.S.; Rimkus, C.M.; Mendes, M.F.; Apóstolos-Pereira, S.L.; Busatto Filho, G.; Callegaro, D.; Buchpiguel, C.A.; Duran, F.; De Paula Faria, D. Myelin Imaging Measures as Predictors of Cognitive Impairment in MS Patients: A Hybrid PET-MRI Study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 57, 103331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; DiGiacomo, P.S.; Fan, A.P.; Goubran, M.; Khalighi, M.M.; Chao, S.Z.; Vasanawala, M.; Wintermark, M.; Mormino, E.; Zaharchuk, G.; et al. Simultaneous FDG-PET/MRI Detects Hippocampal Subfield Metabolic Differences in AD/MCI. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.L.; Toueg, T.N.; Khalighi, M.M.; Castillo, J.; Shen, B.; Azevedo, E.C.; DiGiacomo, P.; Mouchawar, N.; Chau, G.; Zaharchuk, G.; et al. Hippocampal Subfield Imaging and Fractional Anisotropy Show Parallel Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease Tau Progression Using Simultaneous Tau-PET/MRI at 3T. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 13, e12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarini, J.; Bourgeois, S.; Van Weehaeghe, D.; Goffin, K.; Vandenberghe, R.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Sunaert, S.; Van Laere, K. Direct Prospective Comparison of 18F-FDG PET and Arterial Spin Labelling MR Using Simultaneous PET/MR in Patients Referred for Diagnosis of Dementia. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 2142–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, C.; Su, Y.; Jing, D.; Wu, L.; Liang, P.; Liang, Z. Evaluating the Association between Brain Atrophy, Hypometabolism, and Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease: A PET/MRI Study. Aging 2021, 13, 7228–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Bi, S.; Shan, Y.; Cui, B.; Yang, H.; Qi, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Han, Y.; Yan, S.; Lu, J. Multiparametric Hippocampal Signatures for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Using 18 F-FDG PET/MRI Radiomics. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023. prepint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, M.; Peng, G. Characterizing Differences in Functional Connectivity Between Posterior Cortical Atrophy and Semantic Dementia by Seed-Based Approach. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 850977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; Son, Y.D.; Noh, Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Park, K.H. Glucose Hypometabolism in Hippocampal Subdivisions in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pilot Study Using High-Resolution 18F-FDG PET and 7.0-T MRI. J. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 14, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Kong, Y.; Jing, D.; Xie, K.; Cui, Y.; Cui, B.; Zhang, J.; et al. Investigating the Roles of Anterior Cingulate in Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia: A PET/MRI Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 84, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Du, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Jiang, J. Coupling Relationship between Glucose and Oxygen Metabolisms to Differentiate Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease and Normal Individuals. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 5051–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.W.; Jelescu, I.O.; Ades-Aron, B.; Novikov, D.S.; Friedman, K.; Babb, J.S.; Osorio, R.S.; Galvin, J.E.; Shepherd, T.M.; Fieremans, E. Diffusion MRI Biomarkers of White Matter Microstructure Vary Nonmonotonically with Increasing Cerebral Amyloid Deposition. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 89, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, A.M.; Clifton, M.A.; Naser-Tavakolian, K.; Ahmed, O.; Bangiyev, L.; Clouston, S.; Franceschi, D. FDG PET/MRI for Visual Detection of Crossed Cerebellar Diaschisis in Patients With Dementia. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, A.M.; Naser-Tavakolian, K.; Clifton, M.; Ahmed, O.; Stoffers, K.; Bangiyev, L.; Cruciata, G.; Clouston, S.; Franceschi, D. Hybrid Imaging in Dementia: A Semi-Quantitative (18F)-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging Approach in Clinical Practice. World J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 20, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, A.M.; Clifton, M.; Naser-Tavakolian, K.; Ahmed, O.; Cruciata, G.; Bangiyev, L.; Clouston, S.; Franceschi, D. (18F)-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging Assessment of Hypometabolism Patterns in Clinical Phenotypes of Suspected Corticobasal Degeneration. World J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 20, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, A.M.; Naser-Tavakolian, K.; Clifton, M.; Bangiyev, L.; Cruciata, G.; Clouston, S.; Franceschi, D. Metabolic Positron-Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Primary Progressive Aphasia and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration Subtypes: Reassessment of Expected [18F]-Fluorodeoxyglucose Uptake Patterns. World J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 20, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, R. Functional Abnormality Associated With Tau Deposition in Alzheimer’s Disease—A Hybrid Positron Emission Tomography/MRI Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 758053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, M.; Weis, L.; Fiorenzato, E.; Pistonesi, F.; Cagnin, A.; Bertoldo, A.; Anglani, M.; Cecchin, D.; Antonini, A.; Biundo, R. Quantification of Brain β-Amyloid Load in Parkinson’s Disease With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A PET/MRI Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 760518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttler, J.; Preibisch, C.; Riederer, I.; Pasquini, L.; Alexopoulos, P.; Bohn, K.P.; Yakushev, I.; Beller, E.; Kaczmarz, S.; Zimmer, C.; et al. Reduced Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent Connectivity Is Related to Hypoperfusion in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 1314–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstege, H.; Beker, N.; Dijkstra, T.; Pieterse, K.; Wemmenhove, E.; Schouten, K.; Thiessens, L.; Horsten, D.; Rechtuijt, S.; Sikkes, S.; et al. The 100-plus Study of Cognitively Healthy Centenarians: Rationale, Design and Cohort Description. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 1229–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.-N.; Manning, E.N.; Storey, M.; Nicholas, J.M.; Coath, W.; Keuss, S.E.; Cash, D.M.; Lane, C.A.; Parker, T.; Keshavan, A.; et al. Neuroimaging, Clinical and Life Course Correlates of Normal-Appearing White Matter Integrity in 70-Year-Olds. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.-N.; Nicholas, J.M.; Lu, K.; Keshavan, A.; Lane, C.A.; Parker, T.; Buchanan, S.M.; Keuss, S.E.; Murray-Smith, H.; Wong, A.; et al. Adulthood Cognitive Trajectories over 26 Years and Brain Health at 70 Years of Age: Findings from the 1946 British Birth Cohort. Neurobiol. Aging 2023, 122, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltoft, N.S.; Marner, L.; Larsen, V.A.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Law, I.; Henriksen, O.M. Hybrid FDG PET/MRI vs. FDG PET and CT in Patients with Suspected Dementia—A Comparison of Diagnostic Yield and Propagated Influence on Clinical Diagnosis and Patient Management. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.M.; Sohn, C.-H.; Byun, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, D.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Sohn, B.K.; Yoo, R.-E.; et al. Prediction of Amyloid Positivity in Mild Cognitive Impairment Using Fully Automated Brain Segmentation Software. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kritikos, M.; Franceschi, A.M.; Vaska, P.; Clouston, S.A.P.; Huang, C.; Salerno, M.; Deri, Y.; Tang, C.; Pellecchia, A.; Santiago-Michels, S.; et al. Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease Imaging Biomarkers in World Trade Center Responders with Cognitive Impairment at Midlife. World J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 21, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladefoged, C.N.; Hansen, A.E.; Henriksen, O.M.; Bruun, F.J.; Eikenes, L.; Øen, S.K.; Karlberg, A.; Højgaard, L.; Law, I.; Andersen, F.L. AI-Driven Attenuation Correction for Brain PET/MRI: Clinical Evaluation of a Dementia Cohort and Importance of the Training Group Size. NeuroImage 2020, 222, 117221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, J.; Olivieri, P.; Tonietto, M.; Tissot, C.; Rivals, I.; Gervais, P.; Caillé, F.; Moussion, M.; Bottlaender, M.; Sarazin, M. Tau-PET Imaging Predicts Cognitive Decline and Brain Atrophy Progression in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chu, M.; Nie, B.; Liu, L.; Xie, K.; Cui, Y.; Kong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Nan, H.; Chen, K.; et al. Reconfigured Metabolism Brain Network in Asymptomatic Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau Mutation Carriers: A Graph Theoretical Analysis. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chu, M.; Nie, B.; Jiang, D.; Xie, K.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Kong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Nan, H.; et al. Altered Metabolic Connectivity within the Limbic Cortico-Striato-Thalamo-Cortical Circuit in Presymptomatic and Symptomatic Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Chu, M.; Wang, J.; Xie, K.; Cui, Y.; Ma, J.; Nan, H.; Cui, C.; Qiao, H.; et al. Involvement of Striatal Motoric Subregions in Familial Frontotemporal Dementia with Parkinsonism Harboring the C9orf72 Repeat Expansions. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Nicholas, J.M.; Weston, P.S.J.; Stout, J.C.; O’Regan, A.M.; James, S.-N.; Buchanan, S.M.; Lane, C.A.; Parker, T.D.; Keuss, S.E.; et al. Visuomotor Integration Deficits Are Common to Familial and Sporadic Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki Balajoo, S.; Rahmani, F.; Khosrowabadi, R.; Meng, C.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Grimmer, T.; Zarei, M.; Drzezga, A.; Sorg, C.; Tahmasian, M. Decoupling of Regional Neural Activity and Inter-Regional Functional Connectivity in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Simultaneous PET/MR Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 3173–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangalore, S.; Vankayalapati, S.; Gupta, A.K. Hydrocephalic Dementia: Revisited with Multimodality Imaging and toward a Unified Imaging Approach. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2021, 12, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchitelli, R.; Aiello, M.; Cachia, A.; Quarantelli, M.; Cavaliere, C.; Postiglione, A.; Tedeschi, G.; Montella, P.; Milan, G.; Salvatore, M.; et al. Simultaneous Resting-State FDG-PET/fMRI in Alzheimer Disease: Relationship between Glucose Metabolism and Intrinsic Activity. NeuroImage 2018, 176, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukku, S.S.R.; Sivakumar, P.T.; Nagaraj, C.; Mangalore, S.; Harbishettar, V.; Varghese, M. Clinical Utility of 18F-FDG-PET/MRI Brain in Dementia: Preliminary Experience from a Geriatric Clinic in South India. Asian J. Psychiatry 2019, 44, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazawa, H.; Ikawa, M.; Jung, M.; Maruyama, R.; Tsujikawa, T.; Mori, T.; Rahman, M.G.M.; Makino, A.; Kiyono, Y.; Kosaka, H. Multimodal Analysis Using [11C]PiB-PET/MRI for Functional Evaluation of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazawa, H.; Ikawa, M.; Tsujikawa, T.; Mori, T.; Makino, A.; Kiyono, Y.; Nakamoto, Y.; Kosaka, H.; Yoneda, M. Cerebral Oxidative Stress in Early Alzheimer’s Disease Evaluated by 64Cu-ATSM PET/MRI: A Preliminary Study. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazawa, H.; Ikawa, M.; Tsujikawa, T.; Makino, A.; Mori, T.; Kiyono, Y.; Kosaka, H. Noninvasive Measurement of [11C]PiB Distribution Volume Using Integrated PET/MRI. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, T.D.; Cash, D.M.; Lane, C.A.S.; Lu, K.; Malone, I.B.; Nicholas, J.M.; James, S.-N.; Keshavan, A.; Murray-Smith, H.; Wong, A.; et al. Hippocampal Subfield Volumes and Pre-Clinical Alzheimer’s Disease in 408 Cognitively Normal Adults Born in 1946. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttaert, D.; Coquelet, N.; Wens, V.; Peigneux, P.; Fery, P.; Rovai, A.; Trotta, N.; Sadeghi, N.; Coolen, T.; Bier, J.-C.; et al. Alterations in Resting-State Network Dynamics along the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttaert, D.; Wens, V.; Fery, P.; Rovai, A.; Trotta, N.; Coquelet, N.; De Breucker, S.; Sadeghi, N.; Coolen, T.; Goldman, S.; et al. Decreased Alpha Peak Frequency Is Linked to Episodic Memory Impairment in Pathological Aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 711375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Fu, L.; Wang, R.; Lyu, J.; Ma, H.; Zhan, M.; Zhou, A.; Wang, F.; Zuo, X.; Wei, C. Prominent Striatum Amyloid Retention in Early-Onset Familial Alzheimer’s Disease With PSEN1 Mutations: A Pilot PET/MR Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 732159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riederer, I.; Bohn, K.P.; Preibisch, C.; Wiedemann, E.; Zimmer, C.; Alexopoulos, P.; Förster, S. Alzheimer Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: Integrated Pulsed Arterial Spin-Labeling MRI and 18F-FDG PET. Radiology 2018, 288, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saka, E.; Atay, L.O.; Akdemir, U.O.; Yetim, E.; Balci, E.; Arsava, E.M.; Topcuoglu, M.A. Cerebral Vasomotor Reactivity across the Continuum of Subjective Cognitive Impairment, Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and Probable Alzheimer’s Dementia: A Transcranial Doppler and PET/MRI Study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherr, M.; Utz, L.; Tahmasian, M.; Pasquini, L.; Grothe, M.J.; Rauschecker, J.P.; Grimmer, T.; Drzezga, A.; Sorg, C.; Riedl, V. Effective Connectivity in the Default Mode Network Is Distinctively Disrupted in Alzheimer’s Disease-A Simultaneous Resting-State FDG-PET/fMRI Study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 4134–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, T.; Buck, A.; Delso, G.; Kemp, B.; Ter Voert, E.E.G.W.; Huellner, M.; Veit-Haibach, P.; Kaushik, S.; Wiesinger, F.; Warnock, G.; et al. The Impact of Atlas-Based MR Attenuation Correction on the Diagnosis of FDG-PET/MR for Alzheimer’s Diseases- A Simulation Study Combining Multi-Center Data and ADNI-Data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssali, T.; Narciso, L.; Hicks, J.; Liu, L.; Jesso, S.; Richardson, L.; Günther, M.; Konstandin, S.; Eickel, K.; Prato, F.; et al. Concordance of Regional Hypoperfusion by pCASL MRI and 15O-Water PET in Frontotemporal Dementia: Is pCASL an Efficacious Alternative? NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 33, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiepolt, S.; Rullmann, M.; Jochimsen, T.H.; Gertz, H.-J.; Schroeter, M.L.; Patt, M.; Sabri, O.; Barthel, H. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping in β-Amyloid PET-Stratified Patients with Dementia and Healthy Controls—A Hybrid PET/MRI Study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 131, 109243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bergen, J.M.G.; Li, X.; Quevenco, F.C.; Gietl, A.F.; Treyer, V.; Meyer, R.; Buck, A.; Kaufmann, P.A.; Nitsch, R.M.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; et al. Simultaneous Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping and Flutemetamol-PET Suggests Local Correlation of Iron and β-Amyloid as an Indicator of Cognitive Performance at High Age. NeuroImage 2018, 174, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderlinden, G.; Ceccarini, J.; Vande Casteele, T.; Michiels, L.; Lemmens, R.; Triau, E.; Serdons, K.; Tournoy, J.; Koole, M.; Vandenbulcke, M.; et al. Spatial Decrease of Synaptic Density in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment Follows the Tau Build-up Pattern. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4244–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaute, H.; Ceccarini, J.; Michiels, L.; Koole, M.; Sunaert, S.; Lemmens, R.; Triau, E.; Emsell, L.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Van Laere, K. In Vivo Synaptic Density Loss Is Related to Tau Deposition in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neurology 2020, 95, e545–e553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Brendel, M.; Rominger, A.; Shi, K.; Han, Y.; Jiang, J. A Metabolism-Functional Connectome Sparse Coupling Method to Reveal Imaging Markers for Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Simultaneous PET/MRI Scans. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 44, 6020–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zheng, C.; Cui, B.; Qi, Z.; Zhao, Z.; An, Y.; Qiao, L.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J. Multiparametric Imaging Hippocampal Neurodegeneration and Functional Connectivity with Simultaneous PET/MRI in Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 2440–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, J.; Alberts, I.; Wang, M.; Li, T.; Sun, X.; Rominger, A.; Zuo, C.; Shi, K. Combining PET with MRI to Improve Predictions of Progression from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease: An Exploratory Radiomic Analysis Study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanovello, M.; Sorarù, G.; Campi, C.; Anglani, M.; Spimpolo, A.; Berti, S.; Bussè, C.; Mozzetta, S.; Cagnin, A.; Cecchin, D. Brain Stem Glucose Hypermetabolism in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Frontotemporal Dementia and Shortened Survival: An 18F-FDG PET/MRI Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Li, B.; Ye, G.; Meng, H.; Huang, X.; et al. Disrupted Coupling between Salience Network Segregation and Glucose Metabolism Is Associated with Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease—A Simultaneous Resting-State FDG-PET/fMRI Study. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 34, 102977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, W.; Guan, Z.; Hu, J.; Li, B.; Ye, G.; Meng, H.; Huang, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Simultaneous PET/fMRI Detects Distinctive Alterations in Functional Connectivity and Glucose Metabolism of Precuneus Subregions in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 737002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, G.; Cecchin, D.; Bussè, C.; Perini, G.; Corbetta, M.; Cagnin, A. Changes of Metabolic Connectivity in Dementia with Lewy Bodies with Visual Hallucinations: A 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Study. Brain Connect. 2021, 11, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, F.S.; Pavlosky, W.F.; Foster, S.C.; Thiessen, J.D.; Beaujot, R.P. Screening for Dementia Caused by Modifiable Lifestyle Choices Using Hybrid PET/MRI. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2019, 3, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, P. A Role of PET/MR Imaging in Dementia? Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantellizzi, V.; Conte, M.; De Vincentis, G. Hybrid Imaging of Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainta, I.C.; Vargas, M.I.; Trombella, S.; Frisoni, G.B.; Unschuld, P.G.; Garibotto, V. Hybrid PET-MRI in Alzheimer’s Disease Research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1750, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, T.M.; Nayak, G.K. Clinical Use of Integrated Positron Emission Tomography-Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Dementia Patients. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 28, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, F.; Leporace, M.; Cimini, A.; Ricci, M.; Travascio, L.; Bagnato, A. Positron Emission Tomography Molecular Imaging of the Major Neurodegenerative Disorders: Overview and Pictorial Essay, from a Nuclear Medicine Center’s Perspective. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Du, X.; Feng, H.; Zhang, S. Application of Deep Learning for Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease in PET/MR Imaging. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoshima, S.; Cross, D. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Brain Molecular Imaging. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2022, 36, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, R.; Williams, B.G.; Ferreira da Silva, M.; Indani, A.; Schcolnicov, N.; Ganguly, A.; Miller, S.J. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks With Ensemble Learning and Generative Adversarial Networks for Alzheimer’s Disease Image Data Classification. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 720226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgard, B.; Khalifé, M.; Bouchut, A.; Fernandez, B.; Soret, M.; Giron, A.; Zaslavsky, C.; Delso, G.; Habert, M.-O.; Kas, A. ZTE MR-Based Attenuation Correction in Brain FDG-PET/MR: Performance in Patients with Cognitive Impairment. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Øen, S.K.; Keil, T.M.; Berntsen, E.M.; Aanerud, J.F.; Schwarzlmüller, T.; Ladefoged, C.N.; Karlberg, A.M.; Eikenes, L. Quantitative and Clinical Impact of MRI-Based Attenuation Correction Methods in [18F]FDG Evaluation of Dementia. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ying, C.; Binkley, M.M.; Juttukonda, M.R.; Flores, S.; Laforest, R.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; An, H. Deep Learning-Based T1-Enhanced Selection of Linear Attenuation Coefficients (DL-TESLA) for PET/MR Attenuation Correction in Dementia Neuroimaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 86, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc-Durand, P.; Khalife, M.; Sgard, B.; Kaushik, S.; Soret, M.; Tiss, A.; El Fakhri, G.; Habert, M.-O.; Wiesinger, F.; Kas, A. Attenuation Correction Using 3D Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Brain 18F-FDG PET/MR: Comparison with Atlas, ZTE and CT Based Attenuation Correction. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, A.M.; Abballe, V.; Raad, R.A.; Nelson, A.; Jackson, K.; Babb, J.; Vahle, T.; Fenchel, M.; Zhan, Y.; Valadez, G.H.; et al. Visual Detection of Regional Brain Hypometabolism in Cognitively Impaired Patients Is Independent of Positron Emission Tomography-Magnetic Resonance Attenuation Correction Method. World J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 17, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, K.; Han, P.K.; Johnson, K.A.; El Fakhri, G.; Ma, C.; Li, Q. Attenuation Correction Using Deep Learning and Integrated UTE/Multi-Echo Dixon Sequence: Evaluation in Amyloid and Tau PET Imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberghe, S.; Marsden, P.K. PET-MRI: A Review of Challenges and Solutions in the Development of Integrated Multimodality Imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladefoged, C.N.; Benoit, D.; Law, I.; Holm, S.; Kjær, A.; Højgaard, L.; Hansen, A.E.; Andersen, F.L. Region Specific Optimization of Continuous Linear Attenuation Coefficients Based on UTE (RESOLUTE): Application to PET/MR Brain Imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarparvar, B.; Shamsaei, M.; Rajabi, H. Correction of Head Movements in Positron Emission Tomography Using Point Source Tracking System: A Simulation Study. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2012, 26, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiss, A.; Marin, T.; Chemli, Y.; Spangler-Bickell, M.; Gong, K.; Lois, C.; Petibon, Y.; Landes, V.; Grogg, K.; Normandin, M.; et al. Impact of Motion Correction on [18F]-MK6240 Tau PET Imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.T.; Salcedo, S.; Chonde, D.B.; Izquierdo-Garcia, D.; Levine, M.A.; Price, J.C.; Dickerson, B.C.; Catana, C. MR-Assisted PET Motion Correction in Simultaneous PET/MRI Studies of Dementia Subjects. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coath, W.; Modat, M.; Cardoso, M.J.; Markiewicz, P.J.; Lane, C.A.; Parker, T.D.; Keshavan, A.; Buchanan, S.M.; Keuss, S.E.; Harris, M.J.; et al. Operationalizing the Centiloid Scale for [18F]Florbetapir PET Studies on PET/MRI. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 15, e12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, J.N.; Sweeney, E.M.; Skafida, M.; Glynn, S.; Amoashiy, M.; Lange, D.J.; Lin, E.; Chiang, G.C.; Osborne, J.R.; Pahlajani, S.; et al. Heuristic Scoring Method Utilizing FDG-PET Statistical Parametric Mapping in the Evaluation of Suspected Alzheimer Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 11, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hinge, C.; Henriksen, O.M.; Lindberg, U.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Højgaard, L.; Law, I.; Andersen, F.L.; Ladefoged, C.N. A Zero-Dose Synthetic Baseline for the Personalized Analysis of [18F]FDG-PET: Application in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1053783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, S.C.; Bahroos, E.; Hawkins, R.A.; Nardo, L.; Ravanfar, V.; Capbarat, E.V.; Seo, Y. Quantitative and Visual Assessments toward Potential Sub-mSv or Ultrafast FDG PET Using High-Sensitivity TOF PET in PET/MRI. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 20, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.T.; Tesfay, R.; Koran, M.E.I.; Ouyang, J.; Shams, S.; Young, C.B.; Davidzon, G.; Liang, T.; Khalighi, M.; Mormino, E.; et al. Generative Adversarial Network-Enhanced Ultra-Low-Dose [18F]-PI-2620 τ PET/MRI in Aging and Neurodegenerative Populations. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2023, 44, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.T.; Gong, E.; de Carvalho Macruz, F.B.; Xu, J.; Boumis, A.; Khalighi, M.; Poston, K.L.; Sha, S.J.; Greicius, M.D.; Mormino, E.; et al. Ultra–Low-Dose 18F-Florbetaben Amyloid PET Imaging Using Deep Learning with Multi-Contrast MRI Inputs. Radiology 2019, 290, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Bocchetta, M.; Chételat, G.; Rabinovici, G.D.; de Leon, M.J.; Kaye, J.; Reiman, E.M.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Black, S.E.; et al. Imaging Markers for Alzheimer Disease: Which vs. How. Neurology 2013, 81, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, T.A. Aging and Measures of Processing Speed. Biol. Psychol. 2000, 54, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Li, C.; Liu, C.-S.J.; Shiroishi, M.; Carmichael, J.D.; Zada, G.; Patel, V. Ultra-High Field 7 T MRI Localizes Regional Brain Volume Recovery Following Corticotroph Adenoma Resection and Hormonal Remission in Cushing’s Disease: A Case Series. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2022, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Cheong, E.-N.; Jung, D.E.; Shim, W.H.; Lee, J.S. Utility of 7 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients With Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 621936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, E.F.; O’Brien, J.T. 7T MRI for Neurodegenerative Dementias in Vivo: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemmer, H.-P.W.; Pichler, B.J.; Schmand, M.; Burbar, Z.; Michel, C.; Ladebeck, R.; Jattke, K.; Townsend, D.; Nahmias, C.; Jacob, P.K.; et al. Simultaneous MR/PET Imaging of the Human Brain: Feasibility Study. Radiology 2008, 248, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavese, N.; Simpson, B.S.; Metta, V.; Ramlackhansingh, A.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Brooks, D.J. [18F]FDOPA Uptake in the Raphe Nuclei Complex Reflects Serotonin Transporter Availability. A Combined [18F]FDOPA and [11C]DASB PET Study in Parkinson’s Disease. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszek, A.; Bladowska, J.; Pokryszko-Dragan, A.; Podemski, R.; Sąsiadek, M.J. Evaluation of the Degradation of the Selected Projectile, Commissural and Association White Matter Tracts Within Normal Appearing White Matter in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Using Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging—A Preliminary Study. Pol. J. Radiol. 2015, 80, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukart, J.; Mueller, K.; Horstmann, A.; Barthel, H.; Möller, H.E.; Villringer, A.; Sabri, O.; Schroeter, M.L. Combined Evaluation of FDG-PET and MRI Improves Detection and Differentiation of Dementia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.L.; Petrella, J.R.; Sheldon, F.C.; Choudhury, K.R.; Calhoun, V.D.; Coleman, R.E.; Doraiswamy, P.M.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Predicting Cognitive Decline in Subjects at Risk for Alzheimer Disease by Using Combined Cerebrospinal Fluid, MR Imaging, and PET Biomarkers. Radiology 2013, 266, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunari, I.; Samuraki, M.; Chen, W.-P.; Yanase, D.; Takeda, N.; Ono, K.; Yoshita, M.; Matsuda, H.; Yamada, M.; Kinuya, S. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET and Optimized Voxel-Based Morphometry for Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease: Aging Effect on Diagnostic Performance. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Smith, R.; Ohlsson, T.; Strandberg, O.; Mattsson, N.; Insel, P.S.; Palmqvist, S.; Hansson, O. Associations between Tau, Aβ, and Cortical Thickness with Cognition in Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2019, 92, e601–e612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppiah, S.; Didier, M.-A.; Vinjamuri, S. The Who, When, Why, and How of PET Amyloid Imaging in Management of Alzheimer’s Disease—Review of Literature and Interesting Images. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthel, H.; Schroeter, M.L.; Hoffmann, K.-T.; Sabri, O. PET/MR in Dementia and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 45, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuel, D.G.; Garner, R.; Finès, P.; Bancej, C.; Flanagan, W.; Tu, K.; Reimer, K.; Chambers, L.W.; Bernier, J. Alzheimer’s and Other Dementias in Canada, 2011 to 2031: A Microsimulation Population Health Modeling (POHEM) Study of Projected Prevalence, Health Burden, Health Services, and Caregiving Use. Popul. Health Metr. 2016, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Title | Lead | Aims | Sample Size | Imaging | Journal | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Using simultaneous PET/MRI to compare the accuracy of diagnosing frontotemporal dementia by arterial spin labeling MRI and FDG-PET | Anazodo et al. [11] | Compare MRI-arterial spin labeling (MRI-ASL) with FDG-PET in diagnosing frontotemporal dementia (FTD) | 10 FTD patients/10 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph | NeuroImage: Clinical | 2018 |
| The contribution of beta-amyloid to dementia in Lewy body diseases: a 1-year follow-up study | Biundo et al. [12] | Explore the contribution of Aß in Lewy body disease, especially in Parkinson’s disease patients with and without amyloid | 40 PD patients (13 with dementia, 22 MCI, 5 normal) and 10 DLB patients | 18F-Flutemetamol PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | Brain Communications | 2021 |
| Association between lower body temperature and increased tau pathology in cognitively normal older adults | Blessing et al. [13] | Cross-sectionally evaluate the association between body temperature (as a proxy for brain temperature) and tau pathology in cognitively normal older adults using plasma and CSF P-tau181 and PET-MR | 21 patients | 18F-MK-6240 PET/MRI | Neurobiology of Disease | 2022 |
| Support vector machine learning and diffusion-derived structural networks predict amyloid quantity and cognition in adults with Down’s syndrome | Brown et al. [14] | Assess the effectiveness of hybrid imaging to predict brain amyloid plaque burden, baseline cognition, and longitudinal cognitive change using support vector regression | 95 patients with Down’s syndrome | 11C-PiB PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Neurobiology of Aging | 2022 |
| Myelin imaging measures as predictors of cognitive impairment in MS patients: A hybrid PET-MRI study | Campanholo et al. [15] | Highlight differences in myelin imaging modalities that can be used as predictors of cognitive dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) | 51 MS patients/24 HC | 11C-PiB PET/MRI on GE Signa | Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders | 2022 |
| Simultaneous FDG-PET/MRI detects hippocampal subfield metabolic differences in AD/MCI | Carlson et al. [16] | Study changes in FDG-PET and time-of-flight MRI (TOF-MRI) in Alzheimer’s disease, focusing on the hippocampus and its subregions | 9 AD and 6 MCI patients/17 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Scientific Reports | 2020 |
| Hippocampal subfield imaging and fractional anisotropy show parallel changes in Alzheimer’s disease tau progression using simultaneous tau-PET/MRI at 3 T | Carlson et al. [17] | Examine the development of tau pathology on PET and its relationship with hippocampal connectivity changes on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) | 5 AD and MCI patients/13 HC | 18F-PI-2620 PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Alzheimer’s & Dementia (Amsterdam) | 2021 |
| Direct prospective comparison of (18)F-FDG PET and arterial spin labeling MR using simultaneous PET/MR in patients referred for diagnosis of dementia | Ceccarini et al. [18] | Conduct a head-to-head comparison of FDG-PET and MRI-ASL in diagnosing cognitive impairment (Alzheimer’s disease [AD], Lewy Body Dementia [LBD], FTD) in patients with suspected cognitive impairment | 27 suspected CI patients/30 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on GE Signa | European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging | 2020 |
| Evaluating the association between brain atrophy, hypometabolism, and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease: a PET/MRI study | Chen et al. [19] | Evaluate changes in the hippocampus and default mode network as biomarkers for the diagnosis of AD | 23 AD patients/24 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Aging (Albany NY) | 2021 |
| Multiparametric hippocampal signatures for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using (18)F-FDG PET/MRI Radiomics | Chen et al. [20] | Explore the utility of hippocampal radiomic data to conduct early diagnosis of AD | 51 AD patients and 55 aMCI patients/53 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on GE Signa | CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics | 2023 |
| Characterizing Differences in Functional Connectivity Between Posterior Cortical Atrophy and Semantic Dementia by Seed-Based Approach | Chen et al. [21] | Demonstrate the existence of abnormal functional connectivity (FC) with an unaffected network in posterior cortical atrophy (PCA) and semantic dementia (SD) using neuropsychological assessments and PET/MRI scans | 12 SD patients/11 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | 2022 |
| Glucose Hypometabolism in Hippocampal Subdivisions in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Pilot Study Using High-Resolution 18F-FDG PET and 7.0-T MRI | Choi et al. [22] | Compare the glucose metabolism of hippocampal divisions, a clinical diagnostic marker of AD, in mild-AD patients and healthy controls | 9 eAD patients/10 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 7 T Siemens HRRT-PET | Journal of Clinical Neurology | 2018 |
| Investigating the Roles of Anterior Cingulate in Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia: A PET/MRI Study | Chu et al. [23] | Explore the role that the anterior cingulate cortex plays in behavioral deficits and executive dysfunction using hybrid imaging | 21 bvFTD patients/21 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease | 2021 |
| Coupling relationship between glucose and oxygen metabolisms to differentiate preclinical Alzheimer’s disease and normal individuals | Ding et al. [24] | Explore the relationship between fMRI and FDG-PET signals in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), using biomarkers for early detection | 15 CI and 20 preAD patients/27 HC | 18F-FDG-PET/MRI and 18F-AV45-PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Human Brain Mapping | 2021 |
| Diffusion MRI biomarkers of white matter microstructure vary nonmonotonically with increasing cerebral amyloid deposition | Dong et al. [25] | Cross-sectionally characterize the pathological white matter changes in AD and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) using integrated PET/MR imaging, kurtosis imaging (DKI), and axonal water fraction (AWF) | 21 MCI or early AD patients/23 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | Neurobiology of Aging | 2020 |
| FDG PET/MRI for Visual Detection of Crossed Cerebellar Diaschisis in Patients With Dementia | Franceschi et al. [26] | To evaluate the presence of crossed cerebellar diaschisis in patients with suspected neurodegenerative disease | 75 patients with neurodegenerative disease | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | American Journal of Roentgenology | 2021 |
| Hybrid imaging in dementia: A semi-quantitative ((18)F)-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging approach in clinical practice | Franceschi et al. [27] | Retrospectively assess the relationship between semi-quantitative changes in lobar-specific gray matter volumes and corresponding regions of brain fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) hypometabolism in patients with dementia and neurodegenerative disease using FDG PET/MRI, NeuroQuant morphometric analysis, and z-scores | 89 dementia patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | World Journal of Nuclear Medicine | 2020 |
| ((18)F)-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging assessment of hypometabolism patterns in clinical phenotypes of suspected corticobasal degeneration | Franceschi et al. [28] | Retrospectively evaluate the metabolic and volumetric abnormalities in patients with clinically suspected corticobasal degeneration (CBD) using FDG PET/MRI | 75 suspected CBD patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | World Journal of Nuclear Medicine | 2020 |
| Metabolic positron-emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging in primary progressive aphasia and frontotemporal lobar degeneration subtypes: Reassessment of expected [(18)F]-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake patterns | Franceschi et al. [29] | Evaluate FDG uptake patterns in patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration/primary progressive aphasia (FTLD/PPA) subtypes | 51 FTLD/PPA patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | World Journal of Nuclear Medicine | 2021 |
| Functional Abnormality Associated With Tau Deposition in Alzheimer’s Disease—A Hybrid Positron Emission Tomography/MRI Study | Fu et al. [30] | Investigate the characteristics of tau deposition and its impact on functional connectivity (FC) in AD using neuropsychological assessments and FDG PET/MRI scans | 26 AD patients/19 HC | 18F-THK5317 PET/MRI | Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | 2021 |
| Quantification of Brain β-Amyloid Load in Parkinson’s Disease With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A PET/MRI Study | Garon et al. [31] | Study how Aβ affects clinical presentation and regional brain volumes in PD-MCI | 25 PD-MCI patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T | Frontiers in Neurology | 2022 |
| Reduced blood oxygenation level dependent connectivity is related to hypoperfusion in Alzheimer’s disease | Göttler et al. [32] | Investigate the relationship between functional connectivity in the posterior default mode network (pDMN) using resting-state fMRI blood oxygenation level-dependent signal fluctuations (BOLD-FC) and PET/MRI in patients with AD | 42 AD patients/27 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism | 2019 |
| The 100-plus Study of cognitively healthy centenarians: rationale, design and cohort description | Holstege et al. [33] | Cohort study identifying characteristics associated with escape/delay of cognitive decline in centenarians enrolled in the 100-plus Study using MMSE tests, PET/MRI or PET/CT, feces collection, and post-mortem brain donation | 300 patients | Unspecified PET/MRI | European Journal of Epidemiology | 2018 |
| Neuroimaging, clinical and life course correlates of normal-appearing white matter integrity in 70-year-olds | James et al. [34] | Explore how changes in normal-appearing white matter relate to brain health and modifiable lifestyle factors, considering confounders such as sex, white matter hyperintensity volume, and ApoE4 status | 502 patients | 18F-Florbetapir PET/MRI on Siemens Biograph mMR | Brain Communications | 2023 |
| Adulthood cognitive trajectories over 26 years and brain health at 70 years of age: findings from the 1946 British Birth Cohort | James et al. [35] | Characterize individual changes in cognitive function through mid- and later life in relation to brain health measures using PET/MRI, amyloid PET, whole-brain volume, hippocampal volume, and white matter hyperintensity volume (WMHV) | 468 patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | Neurobiology of Aging | 2023 |
| Hybrid FDG PET/MRI vs. FDG PET and CT in patients with suspected dementia—A comparison of diagnostic yield and propagated influence on clinical diagnosis and patient management | Kaltoft et al. [36] | Retrospectively compare simultaneous FDG-PET/MRI with PET/CT in identifying cognitive impairment features, evaluating the clinical impact of adding MRI to CT | 78 patients | 18F-FDG-PET on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | PLoS One | 2019 |
| Prediction of Amyloid Positivity in Mild Cognitive Impairment Using Fully Automated Brain Segmentation Software | Kang et al. [37] | To score the predictive ability of regional volume information extracted from PET/MRI images using FreeSurfer for cerebral amyloid positivity in patients with MCI | 130 aMCI patients | 11C-PiB PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment | 2020 |
| Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease Imaging Biomarkers in World Trade Center Responders with Cognitive Impairment at Midlife | Kritikos et al. [38] | Analyze preliminary results of FDG-PET and amyloid PET scans in World Trade Center first responders, assessing the risk of dementia | 6 CI and 6 MCI patients | 18F-FBB-PET and 18F-FTP-PET on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | World Journal of Nuclear Medicine | 2022 |
| Estimation of brain amyloid accumulation using deep learning in clinical [(11)C]PiB PET imaging | Ladefoged et al. [39] | Develop a deep learning model for predicting SUVR and Amyloid Status in 11C PiB PET scans, using MRI in the test set | 1309 CI patients | 11C-PiB-PET/MRI | EJNMMI Physics | 2023 |
| Tau-PET imaging predicts cognitive decline and brain atrophy progression in early Alzheimer’s disease | Lagarde et al. [40] | Explore regional tau binding measured at baseline is associated with AD progression over 2 years using PET/MRI and CSF biomarkers | 36 AD patients/15 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T | Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry | 2022 |
| Reconfigured metabolism brain network in asymptomatic microtubule-associated protein tau mutation carriers: a graph theoretical analysis | Liu et al. [41] | Explore patterns of metabolism topology reconfiguration in microtubule-associated protein tau MAPT mutation carriers during presymptomatic stages of genetic frontotemporal dementia (FDT) using neuropsychological testing, genetic testing, and PET/MRI | 32 bvFTD/33 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy | 2022 |
| Altered metabolic connectivity within the limbic cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuit in presymptomatic and symptomatic behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia | Liu et al. [42] | Characterize the metabolic connectivity between areas of the limbic cortico–striatal–thalamic–cortical (CSTC) circuit in presymptomatic and symptomatic bvFTD patients | 33 bvFTD patients/33 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy | 2023 |
| Involvement of striatal motoric subregions in familial frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism harboring the C9orf72 repeat expansions | Liu et al. [43] | Explore the roles of striatal motor subdivisions in the pathogenesis of parkinsonism resulting from C9ORF72 repeat expansions in patients with FTDP (frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism) using PET/MRI and PET/CT | 2 FTDP patients/17 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | NPJ Parkinson’s Disease | 2022 |
| Visuomotor integration deficits are common to familial and sporadic preclinical Alzheimer’s disease | Lu et al. [44] | Investigate the discernibility of subtle visuomotor deficits in familial and sporadic preclinical AD using β-amyloid-PET/MRI, whole-brain volume, and white matter hyperintensity volume in presymptomatic familial AD patients | 31 FAD patients/390 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | Brain Communications | 2021 |
| Decoupling of regional neural activity and inter-regional functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease: a simultaneous PET/MR study | Maleki et al. [45] | Explore the effect of AD and MCI on the coupling between regional neural activity and inter-regional functional connectivity | 33 AD patients/26 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on Siemens Biograph mMR | European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging | 2022 |
| Hydrocephalic Dementia: Revisited with Multimodality Imaging and toward a Unified Imaging Approach | Mangalore et al. [46] | Study the correlation between normal pressure hydrocephalus and dementia, analyzing imaging findings and clinical symptoms | 13 NPH patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI | Journal of Neuroscience in Rural Practice | 2021 |
| Simultaneous resting-state FDG-PET/fMRI in Alzheimer Disease: Relationship between glucose metabolism and intrinsic activity | Marchitelli et al. [47] | Investigate how early AD-related local changes in resting-state glucose consumption relate to the changes in functional activity observed in stand-alone RS-fMRI studies | 23 MCI or AD patients/23 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | NeuroImage | 2018 |
| Clinical utility of 18F-FDG-PET/MRI brain in dementia: Preliminary experience from a geriatric clinic in South India | Mukku et al. [48] | Further explore the use of hybrid imaging to subtype dementia in groups such as semantic-frontotemporal dementia and mixed AD | 21 MCI patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on Siemens Biograph mMR | Asian Journal of Psychiatry | 2019 |
| Multimodal analysis using [(11)C]PiB-PET/MRI for functional evaluation of patients with Alzheimer’s disease | Okazawa et al. [49] | Evaluate neurofunctional changes in dementia with multiple parameters (perfusion, SUV of 11C-PiB PET, neurofunctional connectivity using RS-fMRI) reflecting neurophysiologic activity | 58 MCI patients/16 HC | 11C-PiB PET/MRI on GE Signa | EJNMMI Research | 2020 |
| Cerebral Oxidative Stress in Early Alzheimer’s Disease Evaluated by (64)Cu-ATSM PET/MRI: A Preliminary Study | Okazawa et al. [50] | Evaluate the degree of oxidative stress and amyloid burden in the brains of AD patients | 10 eAD patients/10 HC | 64Cu-ATSM PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Antioxidants (Basel) | 2022 |
| Noninvasive Measurement of [(11)C]PiB Distribution Volume Using Integrated PET/MRI | Okazawa et al. [51] | Explore the utility of a non-invasive method for determining the arterial concentration of radioactive tracer in PET image reconstruction | 19 MCI patients/16 HC | 11C-PiB PET/MRI on GE Signa | Diagnostics (Basel) | 2020 |
| Hippocampal subfield volumes and pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease in 408 cognitively normal adults born in 1946 | Parker et al. [52] | Cross-sectionally analyze the relationship between cerebral β-amyloid deposition and volume of individual hippocampal subfields in cognitively normal older adults using MMSE, PET/MRI | 408 patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | PLoS One | 2019 |
| Alterations in resting-state network dynamics along the Alzheimer’s disease continuum | Puttaert et al. [53] | Investigate the relationships between MEG and FDG PET/MRI signals, focusing on network connectivity and dynamics in Alzheimer’s disease and MCI | 10 AD, 10 aMCI, and 10 SCD patients/10 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Scientific Reports | 2020 |
| Decreased Alpha Peak Frequency Is Linked to Episodic Memory Impairment in Pathological Aging | Puttaert et al. [54] | Investigate the link between alpha brain activity and alterations in episodic memory as assessed by PET/MRI, FCSRT (Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test), and R-MEG (Resting-State Magnetoencephalography) | 37 AD patients/19 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | 2021 |
| Prominent Striatum Amyloid Retention in Early-Onset Familial Alzheimer’s Disease With PSEN1 Mutations: A Pilot PET/MR Study | Qin et al. [55] | Investigate amyloid deposition in Early Onset Familial Alzheimer’s Disease (EOFAD) and its correlation with clinical symptoms | 5 EOFAD and 15 AD patients/12 HC | 11C-PiB-PET/MRI on Siemens Biograph mMR | Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | 2021 |
| Alzheimer Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: Integrated Pulsed Arterial Spin-Labeling MRI and (18)F-FDG PET | Riederer et al. [56] | Compare PET/MR hypoperfusion and hypometabolism in patients with AD and MCI with healthy controls | 45 AD patients and 20 MCI patients/11 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI | Radiology | 2018 |
| Cerebral vasomotor reactivity across the continuum of subjective cognitive impairment, amnestic mild cognitive impairment and probable Alzheimer’s dementia: A transcranial Doppler and PET/MRI study | Saka et al. [57] | Study the relationship between cerebrovascular dysfunction and AD-associated neuronal degeneration | 43 sMCI, aMCI, or probable AD patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI; 18F-Flutemetamol PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism | 2023 |
| Effective connectivity in the default mode network is distinctively disrupted in Alzheimer’s disease-A simultaneous resting-state FDG-PET/fMRI study | Scherr et al. [58] | Investigate patterns of effective connectivity (EC) within the default mode network in patients with early AD using metabolic connectivity mapping (MCM) utilizing functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and FDG PET | 35 eAD patients/18 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | Human Brain Mapping | 2021 |
| The impact of atlas-based MR attenuation correction on the diagnosis of FDG-PET/MR for Alzheimer’s diseases—A simulation study combining multi-center data and ADNI-data | Sekine et al. [59] | Assess the impact of vendor-provided atlases on FDG PET/MRI evaluation of AD | 47 AD patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | PLoS One | 2020 |
| Concordance of regional hypoperfusion by pCASL MRI and (15)O-water PET in frontotemporal dementia: Is pCASL an efficacious alternative? | Ssali et al. [60] | Help elucidate biomarkers on hybrid imaging that can differentiate frontotemporal dementia subtypes and psychiatric disorders | 9 FTD patients/13 HC | 15O-Water PET/MRI on Siemens Biograph mMR | NeuroImage: Clinical | 2022 |
| Quantitative susceptibility mapping in β-Amyloid PET-stratified patients with dementia and healthy controls—A hybrid PET/MRI study | Tiepolt et al. [61] | Study the amount of iron accumulation and Aβ in patients with AD using hybrid imaging | 16 AD patients/10 non-AD patients/11 HC | 11C-PiB PET/MRI on 3 T | European Journal of Radiology | 2020 |
| Simultaneous quantitative susceptibility mapping and Flutemetamol-PET suggests local correlation of iron and β-amyloid as an indicator of cognitive performance at high age | van et al. [62] | Investigate local correlations between iron and Aß plaque deposition and their impact on cognitive function | 116 HC | 18F-Flutemetamol PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | NeuroImage | 2018 |
| Spatial decrease of synaptic density in amnestic mild cognitive impairment follows the tau build-up pattern | Vanderlinden et al. [63] | Investigate tau distribution and its relation to synaptic density in amnestic mild cognitive impairment | 12 aMCI patients/12 HC | 18F-MK-6240 PET/MRI and 11C-UCB-J PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Molecular Psychiatry | 2022 |
| In vivo synaptic density loss is related to tau deposition in amnestic mild cognitive impairment | Vanhaute et al. [64] | Study whether synaptic loss and neurofibrillary tangle load spatially overlap and correlate with the clinical presentation of patients with aMCI | 10 aMCI patients/10 HC | 11C-UCB-J PET/MRI and 18F-MK-6240 PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa; 11C-PiB on Siemens Truepoint | Neurology | 2020 |
| A metabolism-functional connectome sparse coupling method to reveal imaging markers for Alzheimer’s disease based on simultaneous PET/MRI scans | Wang et al. [65] | Develop a metabolic connectome and functional connectome coupling method to explore how abnormal glucose metabolism and oxygen utilization relates to SCD and AD | 54 SCD patients and 27 AD patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | Human Brain Mapping | 2023 |
| Multiparametric imaging hippocampal neurodegeneration and functional connectivity with simultaneous PET/MRI in Alzheimer’s disease | Yan et al. [66] | To investigate the association between hippocampal neurodegeneration and MCI and AD | 22 AD patients and 38 MCI patients/42 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T GE Signa | European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging | 2020 |
| Combining PET with MRI to improve predictions of progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease: an exploratory radiomic analysis study | Yang et al. [67] | Investigate if 18F-FDG PET/MRI could predict the progression of MCI into AD | 377 MCI patients/94 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI | Annals of Translational Medicine | 2022 |
| Brain Stem Glucose Hypermetabolism in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Frontotemporal Dementia and Shortened Survival: An (18)F-FDG PET/MRI Study | Zanovello et al. [68] | Further investigate the presence of brain hypermetabolism in the brain and cervical spine cord of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontal temporal dementia continuum | 28 ALS/FTD patients/13 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI | Journal of Nuclear Medicine | 2022 |
| Disrupted coupling between salience network segregation and glucose metabolism is associated with cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease—A simultaneous resting-state FDG-PET/fMRI study | Zhang et al. [69] | Investigate the correlation between network segregation (functional connectivity) of core neurocognitive networks and glucose metabolism in cognitive decline | 21 AD and 21 MCI patients/24 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR | NeuroImage: Clinical | 2022 |
| Simultaneous PET/fMRI Detects Distinctive Alterations in Functional Connectivity and Glucose Metabolism of Precuneus Subregions in Alzheimer’s Disease | Zhang et al. [70] | Explore the involvement of the precuneus in Alzheimer’s disease, focusing on glucose metabolism and functional connectivity | 20 AD and 23 MCI patients/27 HC | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on Siemens Biograph mMR | Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | 2021 |
| Changes of Metabolic Connectivity in Dementia with Lewy Bodies with Visual Hallucinations: A (18)F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Study | Zorzi et al. [71] | Examine the changes in neuronal activity between cortical regions in patients with visual hallucinations in dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) using FDG PET/MRI scans and graph theory | 26 DLB patients | 18F-FDG PET/MRI on 3 T | Brain Connectivity | 2021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Renslo, J.; Wong, K.; Clifford, T.G.; Beutler, B.D.; Kim, P.E.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Current Trends and Applications of PET/MRI Hybrid Imaging in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Normal Aging. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060585
Lee J, Renslo J, Wong K, Clifford TG, Beutler BD, Kim PE, Gholamrezanezhad A. Current Trends and Applications of PET/MRI Hybrid Imaging in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Normal Aging. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(6):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060585
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jonathan, Jonathan Renslo, Kasen Wong, Thomas G. Clifford, Bryce D. Beutler, Paul E. Kim, and Ali Gholamrezanezhad. 2024. "Current Trends and Applications of PET/MRI Hybrid Imaging in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Normal Aging" Diagnostics 14, no. 6: 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060585
APA StyleLee, J., Renslo, J., Wong, K., Clifford, T. G., Beutler, B. D., Kim, P. E., & Gholamrezanezhad, A. (2024). Current Trends and Applications of PET/MRI Hybrid Imaging in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Normal Aging. Diagnostics, 14(6), 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14060585






