-
 Diagnosis of Peritonsillar Abscess—A Prospective Study Comparing Clinical with CT Findings in 133 Consecutive Patients
Diagnosis of Peritonsillar Abscess—A Prospective Study Comparing Clinical with CT Findings in 133 Consecutive Patients -
 The Dynamic Evolution of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
The Dynamic Evolution of Eosinophilic Esophagitis -
 Echocardiography with Strain Assessment in Psychiatric Diseases: A Narrative Review
Echocardiography with Strain Assessment in Psychiatric Diseases: A Narrative Review -
 How to Effectively Communicate Dismal Diagnoses in Dermatology and Venereology: From Skin Cancers to Sexually Transmitted Infections
How to Effectively Communicate Dismal Diagnoses in Dermatology and Venereology: From Skin Cancers to Sexually Transmitted Infections -
 Transforming Microbiological Diagnostics in Nosocomial Lower Respiratory Tract Infections: Innovations Shaping the Future
Transforming Microbiological Diagnostics in Nosocomial Lower Respiratory Tract Infections: Innovations Shaping the Future
Journal Description
Diagnostics
Diagnostics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on medical diagnosis published semimonthly online by MDPI. The British Neuro-Oncology Society (BNOS), the International Society for Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynaecology (ISIDOG) and the Swiss Union of Laboratory Medicine (SULM) are affiliated with Diagnostics and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Medicine, General and Internal) / CiteScore - Q2 (Internal Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Diagnostics include: LabMed and AI in Medicine.
Impact Factor:
3.0 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.1 (2023)
Latest Articles
Retinal Microvascular Characteristics—Novel Risk Stratification in Cardiovascular Diseases
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1073; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091073 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are responsible for 32.4% of all deaths across the European Union (EU), and several CVD risk scores have been developed, with variable results. Retinal microvascular changes have been proposed as potential biomarkers for cardiovascular risk, especially in coronary heart
[...] Read more.
Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are responsible for 32.4% of all deaths across the European Union (EU), and several CVD risk scores have been developed, with variable results. Retinal microvascular changes have been proposed as potential biomarkers for cardiovascular risk, especially in coronary heart diseases (CHDs). This study aims to identify the retinal microvascular features associated with CHDs and evaluate their potential use in a CHD screening algorithm in conjunction with traditional risk factors. Methods: We performed a two-center cross-sectional study on 120 adult participants—36 patients previously diagnosed with severe CHDs and scheduled for coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CHD group) and 84 healthy controls. A brief medical history and a clinical profile were available for all cases. All patients benefited from optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA), the use of which allowed several parameters to be quantified for the foveal avascular zone and superficial and deep capillary plexuses. We evaluated the precision of several classification models in identifying patients with CHDs based on traditional risk factors and OCTA characteristics: a conventional logistic regression model and four machine learning algorithms: k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN), Naive Bayes, Support Vector Machine (SVM) and supervised logistic regression. Results: Conventional multiple logistic regression had a classification accuracy of 78.7% based on traditional risk factors and retinal microvascular features, while machine learning algorithms had higher accuracies: 81% for K-NN and supervised logistic regression, 85.71% for Naive Bayes and 86% for SVM. Conclusions: Novel risk scores developed using machine learning algorithms and based on traditional risk factors and retinal microvascular characteristics could improve the identification of patients with CHDs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Advances in Cardiovascular Risk Prediction)
Open AccessReview
Developments in Deep Learning Artificial Neural Network Techniques for Medical Image Analysis and Interpretation
by
Olamilekan Shobayo and Reza Saatchi
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1072; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091072 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
Deep learning has revolutionised medical image analysis, offering the possibility of automated, efficient, and highly accurate diagnostic solutions. This article explores recent developments in deep learning techniques applied to medical imaging, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for classification and segmentation, recurrent neural networks
[...] Read more.
Deep learning has revolutionised medical image analysis, offering the possibility of automated, efficient, and highly accurate diagnostic solutions. This article explores recent developments in deep learning techniques applied to medical imaging, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for classification and segmentation, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for temporal analysis, autoencoders for feature extraction, and generative adversarial networks (GANs) for image synthesis and augmentation. Additionally, U-Net models for segmentation, vision transformers (ViTs) for global feature extraction, and hybrid models integrating multiple architectures are explored. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) process were used, and searches on PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus databases were conducted. The findings highlight key challenges such as data availability, interpretability, overfitting, and computational requirements. While deep learning has demonstrated significant potential in enhancing diagnostic accuracy across multiple medical imaging modalities—including MRI, CT, US, and X-ray—factors such as model trust, data privacy, and ethical considerations remain ongoing concerns. The study underscores the importance of integrating multimodal data, improving computational efficiency, and advancing explainability to facilitate broader clinical adoption. Future research directions emphasize optimising deep learning models for real-time applications, enhancing interpretability, and integrating deep learning with existing healthcare frameworks for improved patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence in Biomedical Imaging and Signal Processing)
Open AccessInteresting Images
A Rare Case of Severe Aortic Regurgitation Secondary to Tenting of Chordae Tendineae Strands: A Multimodality Imaging Approach for a Challenging Diagnosis
by
Dario Catapano, Santo Dellegrottaglie, Alessandra Scatteia, Carlo Maria Gallinoro, Carmine Emanuele Pascale, Luigi Falco, Emilio Di Lorenzo and Daniele Masarone
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1071; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091071 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
We discuss a case of a patient who was referred to our department for an in-depth evaluation of aortic regurgitation severity and its underlying causes. By employing a multimodal imaging strategy that combined transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), and cardiac magnetic resonance
[...] Read more.
We discuss a case of a patient who was referred to our department for an in-depth evaluation of aortic regurgitation severity and its underlying causes. By employing a multimodal imaging strategy that combined transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (cMRI), we successfully identified a particularly rare cause of aortic regurgitation: chordae tendineae that lead to asymmetric retraction of the aortic cusps. Furthermore, this approach provided a clearer understanding of the aortic root anatomy and the hemodynamic effects of the regurgitant flow on the ventricle. This case demonstrates the diagnostic effectiveness of various imaging techniques and emphasizes the crucial importance of multimodal imaging for a thorough assessment of aortic valvular issues.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medical Imaging and Theranostics)
►▼
Show Figures
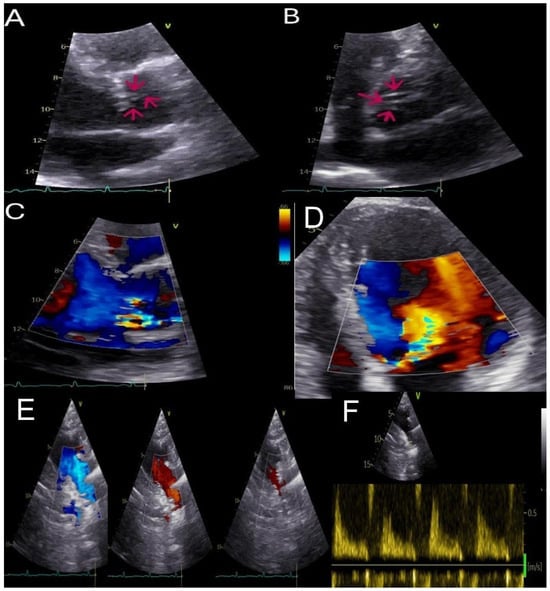
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Will PET/MR Imaging Replace PET/CT for Pediatric Applications?
by
Gabriele Masselli and Chiara Di Bella
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1070; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091070 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
The combination of positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a modern, highly advanced diagnostic tool that offers numerous advantages in the treatment and management of some pediatric pathologies. The use of PET/MR in children provides high-resolution images with outstanding
[...] Read more.
The combination of positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a modern, highly advanced diagnostic tool that offers numerous advantages in the treatment and management of some pediatric pathologies. The use of PET/MR in children provides high-resolution images with outstanding tissue characterization, as well as important metabolic and physiological information; it is not only essential for early diagnosis, but also for the assessment and management of oncological, neurological, and cardiovascular diseases. The hybrid PET/MR is a multimodal approach that reduces the need for separate examinations, minimizes radiation exposure, and improves the overall experience for pediatric patients. In addition, PET/MR, by combining functional data, allows for more precise therapeutic planning and monitoring of treatment responses, optimizing clinical interventions especially with regard to staging and follow-up. This review will explore the benefits, weaknesses, and emerging applications of PET/MR in pediatric patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medical Imaging and Theranostics)
Open AccessArticle
Investigating Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Under Detector-Based Spectral Computed Tomography
by
Hsien-Fu Cheng, Yu-Pin Chang and Jyh-Wen Chai
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1069; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091069 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is characterized by elevated pressure in the pulmonary artery. Currently, most dual-energy CT (DECT) research focuses on the application of iodine mapping in pulmonary embolism. However, little attention is paid to the parametric mapping of the lung parenchyma
[...] Read more.
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is characterized by elevated pressure in the pulmonary artery. Currently, most dual-energy CT (DECT) research focuses on the application of iodine mapping in pulmonary embolism. However, little attention is paid to the parametric mapping of the lung parenchyma of PH. Methods: In total, 156 cases undergoing thoracic DECT from 2021 August to 2023 February were surveyed. For each case, the iodine density (Iod) and effective atomic number (Zeff) of four different levels of the lung, along with the iodine density of the pulmonary artery and aorta, were measured. The measured parameters and their derivatives were compared between PH cases and normal controls and between chronic thromboembolic PH (CTEPH) and non-CTEPH cases. Results: Region of interest (ROI)-Zeff was statistically lower in the PH group as compared to the normal controls on each level. The ratio of PA-iod/ROI-iod was significantly higher in the PH group than in the normal controls. ROI-iod was statistically lower in the CTEPH cases as compared with the non-CTEPH cases on each level. The CTEPH cases demonstrated a higher PA-iod/ROI-iod value as compared with the non-CTEPH cases. Conclusions: The PA-iodine density and effective Z of spectrum CT could serve as valuable imaging parameters for the diagnosis and characterization of PH and CTEPH.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Computed Tomography Imaging for Clinical Diagnosis—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
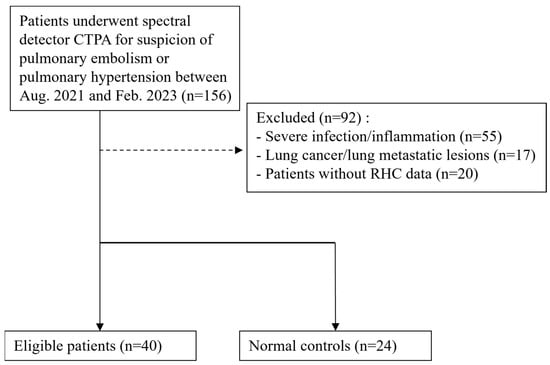
Figure 1
Open AccessInteresting Images
Muscle Infiltration in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Diagnostic Challenge
by
Jiro Ichikawa, Keita Kirito, Tomonori Kawasaki, Kojiro Onohara, Masanori Wako and Hirotaka Haro
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1068; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091068 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia in adults but is rare in Asia. Extramedullary and extranodal manifestations in CLL are generally uncommon, and muscle involvement is extremely rare. A 70-year-old male with CLL presented with bilateral plantar pain, predominantly on
[...] Read more.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common leukemia in adults but is rare in Asia. Extramedullary and extranodal manifestations in CLL are generally uncommon, and muscle involvement is extremely rare. A 70-year-old male with CLL presented with bilateral plantar pain, predominantly on the left side. Anemia and reduced platelet count prompted ibrutinib treatment. MRI revealed high-signal areas in the muscles, suggesting inflammation. Anemia and thrombocytopenia improved, but the pain persisted for 8 months. Histopathological findings confirmed CLL infiltration of the muscles. Radiotherapy alleviated the pain, and the patient remains under observation. Careful caution was needed because (1) MRI findings suggested an inflammatory lesion, broadening differential diagnosis, and (2) CLL may coexist with inflammatory diseases. Histopathological examination is essential for correct diagnosis and treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medical Imaging and Theranostics)
►▼
Show Figures
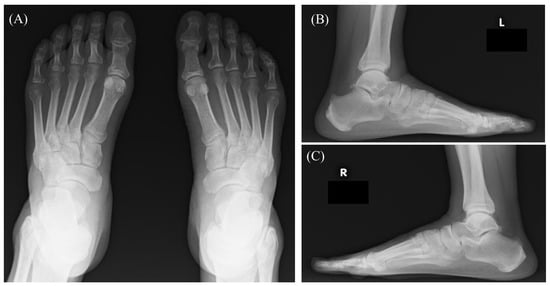
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Innovative Discrete Multi-Wavelength Near-Infrared Spectroscopic (DMW-NIRS) Imaging for Rapid Breast Lesion Differentiation: Feasibility Study
by
Jiyoung Yoon, Kyunghwa Han, Min Jung Kim, Heesun Hong, Eunice S. Han and Sung-Ho Han
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1067; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091067 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study evaluated the role of a discrete multi-wavelength near-infrared spectroscopic (DMW-NIRS) imaging device for rapid breast lesion differentiation. Methods: A total of 62 women (mean age, 49.9 years) with ultrasound (US)-guided biopsy-confirmed breast lesions (37 malignant, 25 benign) were
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study evaluated the role of a discrete multi-wavelength near-infrared spectroscopic (DMW-NIRS) imaging device for rapid breast lesion differentiation. Methods: A total of 62 women (mean age, 49.9 years) with ultrasound (US)-guided biopsy-confirmed breast lesions (37 malignant, 25 benign) were included. A handheld probe equipped with five pairs of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photodiodes (PDs) measured lesion-to-normal tissue (L/N) ratios of four chromophores, THC (Total Hemoglobin Concentration), StO2, and the Tissue Optical Index (TOI: log10(THC × Water/Lipid)). Lesions were localized using US. Diagnostic performance was assessed for each L/N ratio, with subgroup analysis for BI-RADS 4A lesions. Two adaptive BI-RADS models were developed: Model 1 used TOIL/N thresholds (Youden index), while Model 2 incorporated radiologists’ reassessments of US findings integrated with DMW-NIRS results. These models were compared to the initial BI-RADS assessments, conducted by breast-dedicated radiologists. Results: All L/N ratios significantly differentiated malignant from benign lesions (p < 0.05), with TOIL/N achieving the highest AUC-ROC (0.901; 95% CI: 0.825–0.976). In BI-RADS 4A lesions, all L/N ratios except Lipid significantly differentiated malignancy (p < 0.05), with TOIL/N achieving the highest AUC-ROC (0.902; 95% CI: 0.788–1.000). Model 1 and Model 2 showed superior diagnostic performance (AUC-ROCs: 0.962 and 0.922, respectively), significantly outperforming initial BI-RADS assessments (prospective AUC-ROC: 0.862; retrospective AUC-ROC: 0.866; p < 0.05). Conclusions: Integrating DMW-NIRS findings with US evaluations enhances diagnostic accuracy, particularly for BI-RADS 4A lesions. This novel device offers a rapid, non-invasive, and efficient method to reduce unnecessary biopsies and improve breast cancer diagnostics. Further validation in larger cohorts is warranted.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medical Imaging and Theranostics)
►▼
Show Figures
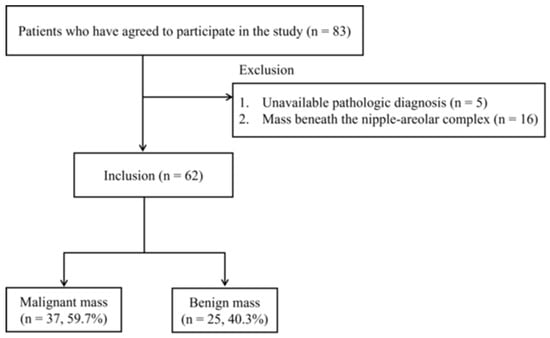
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Convolutional Neural Network-Based Approach for Cobb Angle Measurement Using Mask R-CNN
by
Marcos Villar García, José-Benito Bouza-Rodríguez and Alberto Comesaña-Campos
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1066; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091066 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Scoliosis is a disorder characterized by an abnormal spinal curvature, which can lead to negative effects on patients, affecting their quality of life. Given its progressive nature, the classification of the scoliosis severity requires an accurate diagnosis and effective monitoring. The Cobb
[...] Read more.
Background: Scoliosis is a disorder characterized by an abnormal spinal curvature, which can lead to negative effects on patients, affecting their quality of life. Given its progressive nature, the classification of the scoliosis severity requires an accurate diagnosis and effective monitoring. The Cobb angle measurement method has been widely considered as the gold standard for a scoliosis assessment. Commonly, an expert assesses scoliosis severity manually by identifying the most tilted vertebrae of the spine. However, this method requires time, effort, and presents limitations in measurement accuracy, such as the intra- and inter-observer variability. Artificial intelligence provides more objective tools that are less sensitive to manual intervention aiming to transform the diagnosis of scoliosis. Objectives: The objective of this study was to address three key research questions regarding automated Cobb angle quantification: “Where is the spine in this radiograph?”, “What is its exact shape?”, and “Is the proposed method accurate?”. We propose the use of Mask R-CNN architecture for spine detection and segmentation in response to the first two questions, and a set of algorithms to tackle the third. Methods: The network’s detection and segmentation performance was evaluated through various metrics. An automated workflow for Cobb angle quantification and severity classification was developed. Finally, statistical methods provided the agreement between manual and automated measurements. Results: A high segmentation accuracy was achieved, highlighting the following: mIoU of 0.8012, and a mean precision of 0.9145. MAE was 2.96° ± 2.60° demonstrating a high agreement. Conclusions: The results obtained in this study demonstrate the potential of the proposed automated approach in clinical scenarios, which provides experts with a clear visualization of each stage in the scoliosis assessment by overlaying the results onto the X-ray image.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Deep Learning Techniques for Medical Image Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
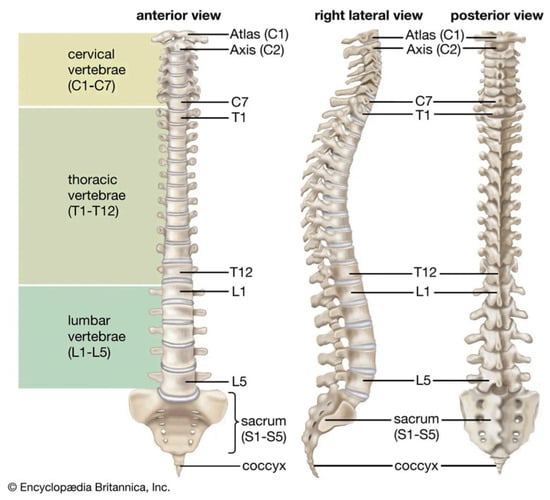
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Emotional Disorders, Risk Factors, and Correlations of Post-Partum Depression and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder with Sexual Function During Post-Partum Period
by
Panagiotis Eskitzis, Vasiliki Michou, Christiana Arampatzi, Ioannis Tsakiridis and Dimitrios Papoutsis
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1065; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091065 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the presence of emotional disorders, the risk factors associated with these disorders, and the level of sexual function observed after childbirth. Additionally, the study aimed to explore how sexual function affects post-partum depression and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aimed to investigate the presence of emotional disorders, the risk factors associated with these disorders, and the level of sexual function observed after childbirth. Additionally, the study aimed to explore how sexual function affects post-partum depression and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), as well as how these emotional disorders, in turn, impact sexual function. Methodology: A total of 336 women participated in the study, who were asked to complete four questionnaires: a general women’s personal information questionnaire, the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS), the PTSD Scale (PCL-5), and the Female Sexual Functioning Index (FSFI). Results: The results showed that 33% of mothers scored on the EPDS above 14 points, which was considered a threshold value for the prognosis of post-partum depression. In addition, the women scored an average of 20.8 points on the FSFI, and thus, their level of sexual functioning was characterized as moderate. According to the total score of the PCL-5 scale, it was observed that 17.6% of the mothers show post-traumatic stress after childbirth and satisfy all four criteria of this scale. Lastly, multiple regression analysis showed that factors such as annual family income and negative body image had a significant contribution to the models. Conclusions: Finally, it was observed that reduced sexual functionality in women is linked to post-partum depression and post-traumatic stress after childbirth. In conclusion, our research emphasizes the need for further exploration of the psychological and emotional challenges women face during the puerperium, which can negatively affect sexual health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Mental Health Diagnosis and Screening, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
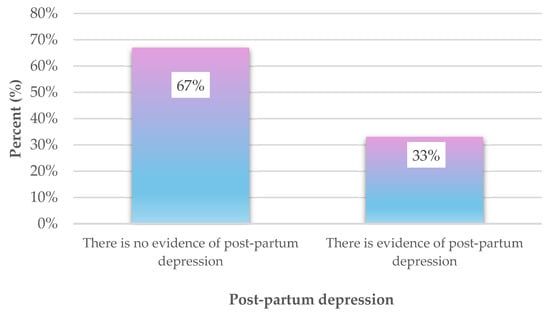
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High-Quality Samples for Next-Generation Sequencing and PD-L1 Assessment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Role of Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration
by
Marta Rodríguez González, Juan Carlos Montero González, José María Sayagués Manzano, Tamara Clavero Sánchez, Jonnathan Roldán Ruiz, Miguel Iglesias Heras, María Belén Rivas Marcos, Mar Abad Hernández and Rosa Cordovilla Pérez
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1064; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091064 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Recent advances in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have shifted from conventional chemotherapy to targeted therapies aimed at specific genetic mutations, particularly in the adenocarcinoma subtype. These therapies have improved overall survival and quality of life. However, some
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Recent advances in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have shifted from conventional chemotherapy to targeted therapies aimed at specific genetic mutations, particularly in the adenocarcinoma subtype. These therapies have improved overall survival and quality of life. However, some patients still face barriers to accessing these treatments due to challenges in diagnosing advanced-stage NSCLC. Limited tumor cellularity in small biopsies and cytological samples hinders the ability to perform further molecular analyses. Additionally, the increasing number of genetic alterations requiring testing complicates the diagnostic process. To overcome this challenge, we propose combining endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) with next-generation sequencing (NGS) and immunohistochemistry for PD-L1. Methods: A total of 120 EBUS-TBNA samples were consecutively collected during the first year of integrating NGS at a reference hospital in Castilla y León, Spain. Depending on the histology and patient characteristics, a total of 67 NGS analyses and 116 PD-L1 determinations were performed. Results: The cytological sample obtained in these cases successfully achieved the triple objective proposed by the NCCN for lung cancer (diagnosis, staging, and molecular analysis in a single procedure) in 97% of instances. Conclusions: Our study highlights the effectiveness of EBUS-TBNA as a comprehensive, cost-effective, and safe diagnostic tool for NSCLC, successfully achieving the triple objective of diagnosis, staging, and molecular analysis in 97% of cases. The procedure consistently provided high-quality samples for NGS and PD-L1 testing, with minimal complications, reinforcing its value as a reliable approach for optimizing personalized treatment strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinical Diagnosis and Prognosis)
►▼
Show Figures
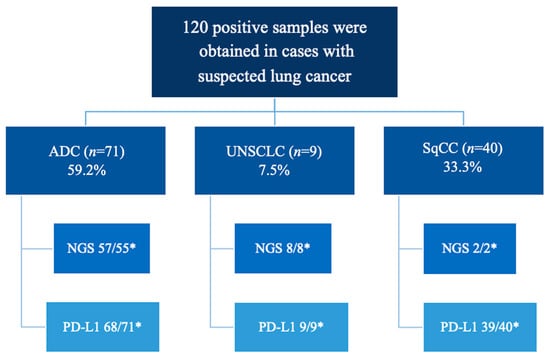
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning in Predicting Cardiac Events for ESRD Patients: A Framework for Clinical Decision Support
by
Chien-Wei Chuang, Chung-Kuan Wu, Chao-Hsin Wu, Ben-Chang Shia and Mingchih Chen
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1063; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091063 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) are at an increased risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs), highlighting the need for accurate risk prediction and personalized interventions. This study aims to develop and evaluate machine learning (ML) models to identify key predictive
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) are at an increased risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACEs), highlighting the need for accurate risk prediction and personalized interventions. This study aims to develop and evaluate machine learning (ML) models to identify key predictive features and enhance clinical decision-making in MACE risk assessment. Methods: A dataset comprising 84 variables, including patient demographics, laboratory findings, and comorbidities, was analyzed using CatBoost, XGBoost, and LightGBM. Feature selection, cross-validation, and SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) analyses were employed to improve model interpretability and clinical relevance. Results: CatBoost exhibited the highest predictive performance among the models tested, achieving an AUC of 0.745 (0.605–0.83) with balanced sensitivity and specificity. Key predictors of MACEs included antiplatelet use, the grade of left ventricular hypertrophy, and serum albumin levels. SHAP analysis enhanced the interpretability of model outputs, supporting clinician-led risk stratification. Conclusions: This study highlights the potential of ML-based predictive modeling to improve MACE risk assessment in patients with ESRD. The findings support the adoption of ML models in clinical workflows by integrating explainable AI methods to enable individualized treatment planning. Future integration with electronic health record systems may facilitate real-time decision-making and enhance patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics)
►▼
Show Figures
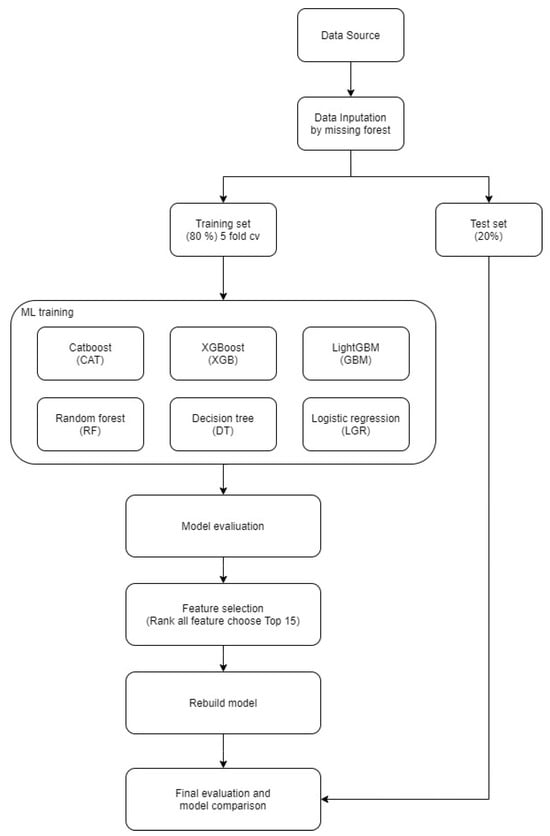
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mapping Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from Complicated Urinary Tract Infections in Oman: Phenotypic and Genotypic Insights
by
Nawal AL Shizawi, Zaaima AL Jabri, Fatima Khan, Hiba Sami, Turkiya AL Siyabi, Zakariya AL Muharrmi, Srinivasa Rao Sirasanagandla and Meher Rizvi
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1062; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091062 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Mapping the local etiology and susceptibility of common pathogens causing complicated urinary tract infection (cUTI) is important for promoting evidence-based antimicrobial prescribing. Evaluating the prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL), AmpC beta-lactamase (AmpC), and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPEs) is equally important as it informs
[...] Read more.
Background: Mapping the local etiology and susceptibility of common pathogens causing complicated urinary tract infection (cUTI) is important for promoting evidence-based antimicrobial prescribing. Evaluating the prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL), AmpC beta-lactamase (AmpC), and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPEs) is equally important as it informs treatment guidelines and empiric management. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) enhances antimicrobial resistance (AMR) surveillance by complementing phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing, offering deeper insights into resistance mechanisms, transmissions, and evolutions. Integrating it into routine AMR monitoring can significantly improve global efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance. Methods: Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of isolates from cUTI were collected from patients presenting with Sultan Qaboos University Hospital, Muscat and Suhar Hospital, Suhar, Oman. Automated systems as well as manual methods were used for detection of ESBL, AmpC, and CPE. ESBLs, AmpC β-lactamases, and CPEs were further detected by manual methods: double-disk synergy test for ESBL; disk approximation assay and D69C AmpC detection set for AmpC, and mCIM and KPC/IMP/NDM/VIM/OXA-48 Combo test kit for CPE. WGS was carried out in 11 FOX-resistant E. coli and (22 carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae) isolates with varying susceptibilities to identify circulating clades, AMR genes, and plasmids. Bioinformatic analysis was performed using online tools. Results: The susceptibility patterns of E. coli from cUTI were as follows: nitrofurantoin (96%), fosfomycin (100%), fluoroquinolones (44%), aminoglycosides (93%), piperacillin-tazobactam (95%), and carbapenems (98%). In comparison, susceptibility rates of K. pneumoniae were far lower: nitrofurantoin (38%), fosfomycin (89%), aminoglycosides (82%), piperacillin-tazobactam (72%), and carbapenems (83%). K. pneumoniae, however, was more susceptible to fluoroquinolones at 47% in comparison to E. coli. The prevalence of ESBL among E. coli and K. pneumoniae was 37.2% and CRE was 6.2% while the estimated prevalence of AmpC was 5.4%. It was observed that E. coli was the predominant ESBL and AmpC producer, while K. pneumoniae was the major carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CREs) producer. No predominant multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) lineage was observed in AmpC-producing E. coli with nine E. coli MLST lineages being identified from eleven isolates: ST-10, ST-69, ST-77, ST-131, ST-156, ST-167, ST-361, ST-1125, and ST-2520. On the other hand, a less diverse MLST spectrum (ST-2096, ST-231, ST-147, ST-1770, and ST-111) was observed in the CRE K. pneumoniae. Among the five MLST lineages, ST-2096 (twelve isolates) and ST-147 (seven isolates) predominated. WGS revealed that DHA-1 was the predominant plasmid-mediated AmpC gene in E. coli, while OXA-232 and NDM-5 were the most common carbapenemase genes in K. pneumoniae. All E. coli DHA-1-positive isolates co-harbored the quinolone resistance gene qnrB4 and the sulfonamide resistance gene sul1 while no aminoglycoside resistance genes were detected. The majority of CPE CRE K. pneumoniae carried other β-lactamase genes, such as blaCTX-M-15, blaSHV, and blaTEM; all co-harbored the quinolone resistance gene OqxAB; and 77% carried the aminoglycoside resistance gene armA. Conclusions: Our results suggest that fosfomycin is an excellent empiric choice for treating complicated cystitis caused by both E. coli and K. pneumoniae, while nitrofurantoin is an appropriate choice for E. coli cystitis but not for K. pneumoniae. Aminoglycosides and piperacillin-tazobactam are excellent intravenous alternatives that spare carbapenems. DHA-1 was the predominant AmpC in E. coli, while OXA-232 and NDM-5 were the predominant carbapenemases in K. pneumoniae. In AmpC-producing E. coli, no MLST predominated, suggesting a significant flux in E. coli with lack of stable clades in this region. In contrast, ST-2096 and ST-147 predominated in CRE Klebsiella pneumoniae, suggesting a stable circulation of these in Oman. WGS profiling provides a deeper understanding of the genetic basis of resistance and enhances surveillance and offers comprehensive insights into pathogen evolution and transmission patterns.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Editorial Board Members' Collection Series: Molecular Diagnostics of Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
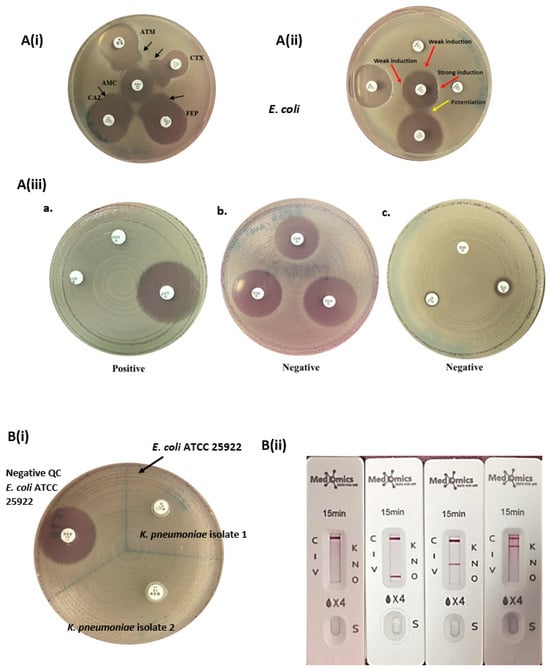
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Cardiac Troponin as a Prognostic Indicator for Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Non-Cardiac Surgery: A Narrative Review
by
Syarifah Noor Nazihah Sayed Masri, Fadzwani Basri, Siti Nadzrah Yunus and Saw Kian Cheah
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1061; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091061 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
A major adverse cardiac event (MACE) following non-cardiac surgery encompasses critical postoperative cardiovascular complications such as myocardial infarction or injury, cardiac arrest, or stroke that are associated with increased perioperative morbidity, mortality, and healthcare resource utilisation. Cardiac troponin (cTn), particularly high-sensitivity cardiac troponin
[...] Read more.
A major adverse cardiac event (MACE) following non-cardiac surgery encompasses critical postoperative cardiovascular complications such as myocardial infarction or injury, cardiac arrest, or stroke that are associated with increased perioperative morbidity, mortality, and healthcare resource utilisation. Cardiac troponin (cTn), particularly high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn), has emerged as a key biomarker for prediction of MACE. Despite its recognised utility, there is no consensus on how cTn levels should be used for standardised postoperative surveillance. Interpretation of the cTn levels may vary depending on sex-specific reference values and baseline comorbidities such as chronic kidney disease, sepsis, critical illness, and non-ischaemic conditions. The balance between cost-effectiveness and clinical benefit in implementing universal versus targeted postoperative hs-cTn screening remains to be fully explored. This review examines the prognostic value of cardiac troponin (cTn) levels in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery, with a focus on perioperative cTn elevations—particularly those associated with myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery (MINS)—as potential early indicators of increased cardiovascular risk.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Efficacy and Safety of Percutaneous Transhepatic Lithotripsy Using SpyGlassDSTM Cholangioscopy for the Treatment of Difficult Stones
by
Salvatore Alessio Angileri, Giuseppe Pellegrino, Carolina Lanza, Jacopo Pozzi, Marco Costa, Matilde Pavan, Pierpaolo Biondetti, Serena Carriero, Velio Ascenti, Gaetano Valerio Davide Amato, Pierluca Torcia, Anna Maria Ierardi and Gianpaolo Carrafiello
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1060; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091060 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: the aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of percutaneous transhepatic lithotripsy using the SpyGlassDSTM cholangioscopy system for the treatment of difficult stones. Methods: Retrospectively, all patients treated with percutaneous transhepatic lithotripsy using SpyGlassDSTM cholangioscopy system
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: the aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of percutaneous transhepatic lithotripsy using the SpyGlassDSTM cholangioscopy system for the treatment of difficult stones. Methods: Retrospectively, all patients treated with percutaneous transhepatic lithotripsy using SpyGlassDSTM cholangioscopy system were analyzed. As primary outcome measures, the following data were assessed: the presence of a previous history of the hepatobiliary disease, location of stones, reasons for the choice of the procedure, previous balloon bilioplasty, type of pre-procedural imaging, procedural time, technical success, clinical success, and post-procedural complications (according to CIRSE classification). Clinical success was considered “primary” when achieved with a single treatment, and “secondary” if more than one treatment was required in the duration of follow-up. Results: 10 patients (6 males and 4 females, mean age = 64 years, SD = 22), all with cholangitis due to gallstones, underwent 11 PTL procedures using SpyGlassDSTM. Technical and clinical successes were achieved in all patients (100%). Primary success was observed in 4/10 (40%) patients, while the remaining 6/10 (60%) patients undergoing re-treatment, and all showed secondary success (100%). No periprocedural complications were observed. In 10/11 procedures (90%), no relevant adverse events were recorded within the first thirty days of follow-up. In 1/11 case (9%), mild complications (grade I according to CIRSE classification) were registered in the following days after the procedure (<30 days). Conclusions: in conclusion, the treatment of percutaneous transhepatic lithotripsy using SpyGlassDSTM cholangioscopy of difficult stones has been demonstrated as efficient and safe treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Endoscopic Diagnostics for Pancreatobiliary Disorders 2025)
►▼
Show Figures
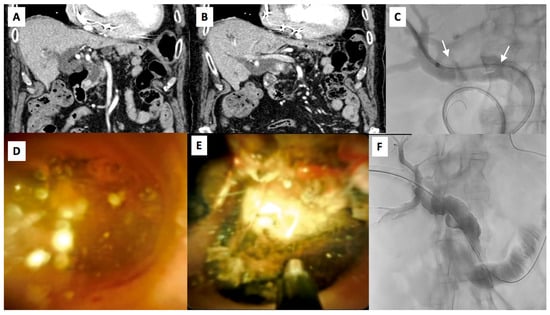
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Classification of Intraoral Photographs with Deep Learning Algorithms Trained According to Cephalometric Measurements
by
Sultan Büşra Ay Kartbak, Mehmet Birol Özel, Duygu Nur Cesur Kocakaya, Muhammet Çakmak and Enver Alper Sinanoğlu
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1059; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091059 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Clinical intraoral photographs are important for orthodontic diagnosis, treatment planning, and documentation. This study aimed to evaluate deep learning algorithms trained utilizing actual cephalometric measurements for the classification of intraoral clinical photographs. Methods: This study was executed on lateral cephalograms
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Clinical intraoral photographs are important for orthodontic diagnosis, treatment planning, and documentation. This study aimed to evaluate deep learning algorithms trained utilizing actual cephalometric measurements for the classification of intraoral clinical photographs. Methods: This study was executed on lateral cephalograms and intraoral right-side images of 990 patients. IMPA, interincisal angle, U1–palatal plane angle, and Wits appraisal values were measured utilizing WebCeph. Intraoral photographs were divided into three groups based on cephalometric measurements. A total of 14 deep learning models (DenseNet 121, DenseNet 169, DenseNet 201, EfficientNet B0, EfficientNet V2, Inception V3, MobileNet V2, NasNetMobile, ResNet101, ResNet152, ResNet50, VGG16, VGG19, and Xception) were employed to classify the intraoral photographs. Performance metrics (F1 scores, accuracy, precision, and recall) were calculated and confusion matrices were formed. Results: The highest accuracy rates were 98.33% for IMPA groups, 99.00% for interincisal angle groups, 96.67% for U1–palatal plane angle groups, and 98.33% for Wits measurement groups. Lowest accuracy rates were 59% for IMPA groups, 53% for interincisal angle groups, 33.33% for U1–palatal plane angle groups, and 83.67% for Wits measurement groups. Conclusions: Although accuracy rates varied among classifications and DL algorithms, successful classification could be achieved in the majority of cases. Our results may be promising for case classification and analysis without the need for lateral cephalometric radiographs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics)
►▼
Show Figures
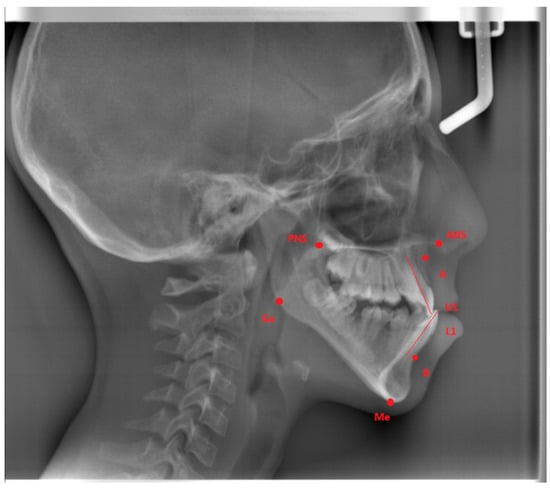
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Human Epididymis Protein 4 Expression in Breast Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
by
Nah Ihm Kim, Min Ho Park and Ji Shin Lee
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1058; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091058 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Elevated expression of human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) has been observed in breast cancer and is associated with cancer progression; however, its role in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate HE4 levels in serum and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Elevated expression of human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) has been observed in breast cancer and is associated with cancer progression; however, its role in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate HE4 levels in serum and tissue from patients with DCIS and their correlation with clinicopathological features. Methods: Preoperative serum HE4 levels were measured in 59 DCIS patients. HE4 mRNA and protein expression in DCIS and adjacent normal tissues were assessed using RNAscope in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry, respectively. An additional independent tissue microarray of 41 DCIS cases was also analyzed for HE4 expression in tumor tissue only. Furthermore, the BreastMark database was applied to assess the prognostic significance of HE4 expression in a larger cohort of breast cancer. Results: Serum HE4 levels (mean ± SD: 39.4 ± 11.9 pmol/L) were within the normal range and showed no significant correlation with clinicopathological parameters except menopausal status. HE4 expression was significantly higher in DCIS tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues, with a positive correlation between mRNA and protein levels (r = 0.771, p < 0.001). High HE4 mRNA and protein expression was associated with ER positivity, HER2 negativity, low stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density, and HR+/HER2− subtypes, but was not predictive of DCIS recurrence. In breast cancer patients, high HE4 expression was significantly correlated with improved survival outcomes. Conclusions: Although serum HE4 is not elevated in DCIS, high HE4 expression in tissue is associated with favorable clinicopathological features. These findings highlight the need for further investigation into the potential prognostic role of HE4.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pathology and Molecular Diagnostics)
►▼
Show Figures
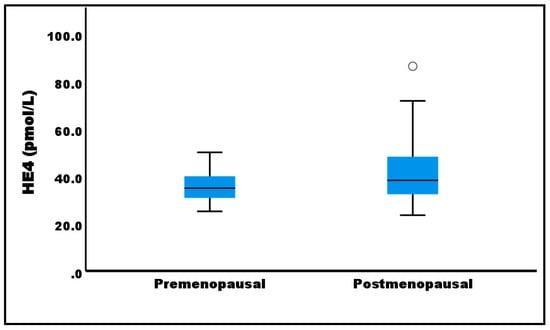
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Pediatric Cutaneous Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Histiocytosis with DCTN1::ALK Fusion: A Case Report and Literature Search
by
Kristóf Levente Korpás, Attila Mokánszki, Lívia Beke, Gábor Méhes and Yi-Che Chang Chien
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1057; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091057 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background and Clinical Significance: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive histiocytosis is a relatively novel entity, affecting single or multiple organ systems; it is characterized by aggregates of neoplastic cells of the histiocytic lineage, harboring molecular alterations in the ALK gene and exhibiting excellent
[...] Read more.
Background and Clinical Significance: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive histiocytosis is a relatively novel entity, affecting single or multiple organ systems; it is characterized by aggregates of neoplastic cells of the histiocytic lineage, harboring molecular alterations in the ALK gene and exhibiting excellent response to systemic tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Case presentation: Herein, we present a pediatric case with cutaneous-only involvement: the 6-month-old male patient presented with an elevated, tan-colored lesion on his left forearm. Following surgical excision, histopathological evaluation reported spindle cells with wide eosinophilic cytoplasm and Touton-type giant cells. The tumor cells were positive for CD163, ALK, phosphorylated ERK, and cyclin D1. Fluorescent in situ hybridization revealed ALK rearrangement, whereas, upon next-generation sequencing, a DCTN1::ALK fusion was identified. Conclusion: Our case serves as a great addition to the limited number of cases reported in the literature, and it represents the first published pediatric case with the rare DCTN1::ALK fusion. The novelty of this genetic alteration and the lack of knowledge about its potential effects on the clinical aspects of ALK-positive histiocytosis highlight the importance of ancillary molecular testing, when available.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pathology and Molecular Diagnostics)
►▼
Show Figures
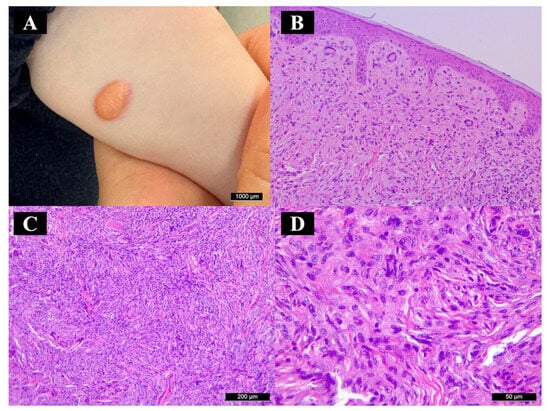
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Pulmonary Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma, a Multifaceted Disease—Case Report and Literature Review
by
Ancuța-Alina Constantin, Antonio Andrei Cotea and Florin-Dumitru Mihălțan
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1056; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091056 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background and Clinical Significance: This article explores the complexity of large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) by presenting a clinical case involving a 17-year-old admitted for persistent wheezing, with no history of respiratory toxin exposure, a background of atopy, and a suspected diagnosis of bronchial
[...] Read more.
Background and Clinical Significance: This article explores the complexity of large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) by presenting a clinical case involving a 17-year-old admitted for persistent wheezing, with no history of respiratory toxin exposure, a background of atopy, and a suspected diagnosis of bronchial asthma. Given the patient’s age and the nature of the symptoms, the condition was initially diagnosed as asthma, leading to the initiation of maximum inhalation therapy. Case Presentation: Despite proper adherence and correct administration, symptoms persisted, necessitating the use of oral corticosteroids. Imaging revealed an extensive inhomogeneous mass in the cervical esophagus and trachea, along with a similar tumor in the right hilum, prompting bronchoscopy. The diagnosis of LCNEC was confirmed through imaging, histopathological findings, and a detailed immunohistochemical profile. Initially misdiagnosed as adenoid cystic carcinoma, this case highlights the diagnostic challenges and the importance of rigorous evaluation. Conclusions: It emphasizes that recurrent wheezing in adolescents is not always indicative of asthma and requires careful differential diagnosis to uncover less common causes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medical Imaging and Theranostics)
►▼
Show Figures
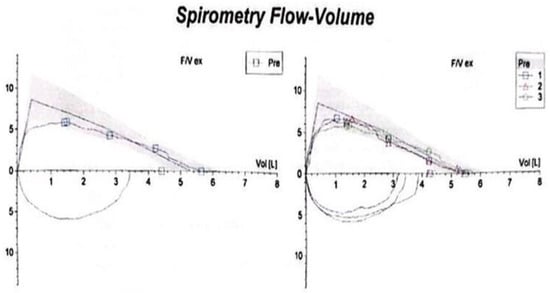
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparing the National Early Warning Score and the Manchester Triage System in Emergency Department Triage: A Multi-Outcome Performance Evaluation
by
Arian Zaboli, Serena Sibilio, Gloria Brigiari, Magdalena Massar, Norbert Pfeifer, Francesco Brigo and Gianni Turcato
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1055; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091055 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Emergency department (ED) triage systems aim to prioritize patients based on clinical severity, ensuring timely intervention for high-risk cases. Recently, the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) has been proposed as an alternative to traditional triage systems, but its efficacy across multiple clinical
[...] Read more.
Background: Emergency department (ED) triage systems aim to prioritize patients based on clinical severity, ensuring timely intervention for high-risk cases. Recently, the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) has been proposed as an alternative to traditional triage systems, but its efficacy across multiple clinical outcomes remains unclear. This study aimed to compare the predictive performance of the NEWS and the Manchester Triage System (MTS) across multiple clinical outcomes. Methods: We conducted a retrospective, single-center study at Merano Hospital, Italy, from 1 June 2022 to 30 June 2023, comparing the performance of the NEWS and the Manchester Triage System (MTS). All adult ED patients (≥18 years) were included, while exclusions applied to those on fast-track pathways, non-residents, and pregnant patients. Primary outcomes included 30-day mortality, hospitalization, and ICU admission. A random 5% subgroup was analyzed for secondary outcomes, including the need for life-saving interventions (LSIs), physician-defined clinical priority, and severity. Predictive performance was assessed using Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves, area under the ROC curve (AUROC) comparisons, and Decision Curve Analysis (DCA). Results: Among 27,238 patients, the NEWS predicted 30-day mortality more accurately than the MTS (AUROC 0.745 vs. 0.701, p < 0.001). However, the MTS outperformed the NEWS for hospitalization (AUROC 0.733 vs. 0.609, p < 0.001), ICU admission (AUROC 0.862 vs. 0.672, p < 0.001), and all secondary outcomes. DCA further confirmed MTS’s superiority across clinically relevant ED probability thresholds (20–40%). Conclusions: The NEWS, while effective for predicting mortality, it is inadequate in comprehensive triage decision-making. The MTS remains the superior system for prioritizing high-risk patients based on clinical severity. Rather than replacing triage with the NEWS, efforts should focus on refining existing systems to improve risk stratification. Future multi-center prospective studies are necessary to validate these findings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnostic Tool and Healthcare in Emergency Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Radiomics Analysis of Breast MRI to Predict Oncotype Dx Recurrence Score: Systematic Review
by
Nathan Kim, Richard Adam, Takouhie Maldjian and Tim Q. Duong
Diagnostics 2025, 15(9), 1054; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091054 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The Oncotype DX recurrence score (ODXRS) has emerged as an important tool for predicting recurrence risk and guiding treatment decisions in estrogen receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early-stage breast cancer. This review summarizes the current evidence on the clinical
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The Oncotype DX recurrence score (ODXRS) has emerged as an important tool for predicting recurrence risk and guiding treatment decisions in estrogen receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early-stage breast cancer. This review summarizes the current evidence on the clinical utility of the Oncotype DX RS and explores emerging research on potential imaging-based alternatives. The 21-gene assay provides a recurrence score that stratifies patients into low, intermediate, and high-risk groups, helping to identify patients who may benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy. Multiple validation studies have demonstrated the prognostic and predictive value of the ODXRS. However, the test is costly and requires tumor tissue samples. Methods: This paper systemically reviewed the current literature on the use of radiomic analysis of breast MRI to predict Oncotype DX. The literature search was performed from 2016 to 2024 using PubMed. We compared different image types, methods of analysis, sample size, numbers of high/intermediate and low scores, MRI image types, performance indices, among others. We also discussed lessons learned and suggested future research directions. Results: Recent studies have investigated the potential of radiomics applied to breast MRI to non-invasively predict the Oncotype DX RS. Quantitative imaging features extracted from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, diffusion-weighted imaging, and T2-weighted sequences have shown promise for distinguishing between low and high RS groups. Multiparametric MRI-based models integrating multiple sequences have achieved the highest performance. Conclusions: While further validation is needed, MRI radiomics may offer a non-invasive, cost-effective alternative for assessing recurrence risk.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Breast Cancer Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Diagnostics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
2 April 2025
MDPI INSIGHTS: The CEO's Letter #21 - Annual Report, Swiss Consortium, IWD, ICARS, Serbia
MDPI INSIGHTS: The CEO's Letter #21 - Annual Report, Swiss Consortium, IWD, ICARS, Serbia
1 April 2025
Meet us at the 11th Congress of the European Academy of Neurology, 21–24 June 2025, Helsinki, Finland
Meet us at the 11th Congress of the European Academy of Neurology, 21–24 June 2025, Helsinki, Finland

Topics
Topic in
Cancers, Current Oncology, Diagnostics, Diseases, Onco
Artificial Intelligence in Cancer Pathology and Prognosis
Topic Editors: Hamid Khayyam, Ali Hekmatnia, Rahele Kafieh, Ali JamaliDeadline: 1 May 2025
Topic in
Diagnostics, JCTO, JCM, JPM, Tomography
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and OCT Angiography – Recent Advances
Topic Editors: Sumit Randhir Singh, Jay ChhablaniDeadline: 26 May 2025
Topic in
Biology, JCM, Diagnostics, Dentistry Journal
Assessment of Craniofacial Morphology: Traditional Methods and Innovative Approaches
Topic Editors: Nikolaos Gkantidis, Carlalberta VernaDeadline: 20 June 2025
Topic in
JCM, JPM, JVD, Diagnostics, Cancers
Diagnosis, Management, and Prognostic Assessment of Chronic Disease
Topic Editors: Xiude Fan, Enfa Zhao, Yang Xia, Shanshan Shao, Tatsunori Miyata, Dongxing XieDeadline: 5 July 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Diagnostics
Novel Imaging Techniques in Infection and Inflammation
Guest Editors: Maria Ricci, Andrea Cimini, Ennio LubranoDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Diagnostics
Current Diagnosis and Treatment in Sports Medicine
Guest Editor: Du-Han KimDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Diagnostics
Latest Advances in Diagnosis and Management of Skin Cancer
Guest Editor: Choon Chiat OhDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Diagnostics
Advances in the Diagnosis and Management of Breast Cancer
Guest Editors: Fulvio Borella, Isabella CastellanoDeadline: 30 April 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Diagnostics
Clinical Guidelines/Expert Consensus on Diagnostics
Collection Editor: Zhongheng Zhang






