Stellate Ganglion Block Reduces Anxiety Symptoms by Half: A Case Series of 285 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
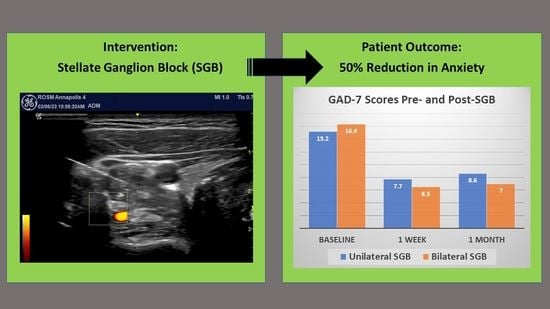
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szuhany, K.L.; Simon, N.M. Anxiety Disorders: A Review. JAMA 2022, 328, 2431–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, R.D.; Weinberger, A.H.; Kim, J.H.; Wu, M.; Galea, S. Trends in anxiety among adults in the United States, 2008–2018: Rapid increases among young adults. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 130, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Petukhova, M.; Sampson, N.A.; Zalavsky, A.M.; Wittchen, H.U. Twelve month and lifetime prevalence and lifetime morbid risk of anxiety disorders in the United States. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 21, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and Injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for Global burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harder, H.G.; Wagner, S.; Rash, J. Mental Illness in the Workplace. Psychological Disability Management; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, J.K.; Andrews, L.A.; Witcraft, S.M.; Powers, M.B.; Smits, J.A.J.; Hofmann, S.G. Cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and related disorders: A meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Depress. Anxiety 2018, 35, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cardemil, E. Effective psychotherapy with low-income clients: The importance of attending to social class. J. Contemp. Psychother. 2012, 42, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, D.A.; Barksdale, C.L.; Beckel-Mitchener, A.C. A call to action to address rural mental health disparities. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 4, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegría, A.A.; Hasin, D.S.; Nunes, E.V.; Liu, S.M.; Davies, C.; Grant, B.F.; Blanco, C. Comorbidity of generalized anxiety disorder and substance use disorders: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 1187–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelow, B.; Lichte, T.; Rudolf, S.; Wiltnik, J.; Beutel, M.E. The diagnosis of and treatment recommendations for anxiety disorder. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2014, 111, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Springer, K.S.; Levy, H.C.; Tolin, D.F. Remission in CBT for adult anxiety disorders: A meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2018, 61, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.C. Stellate Ganglion Block: Techniques, Indications, Uses; Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.C.; Bridenbaugh, L.D. The anterior approach to the stellate ganglion: Use without a serious complication in two thousand blocks. JAMA 1956, 160, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, M.R.; Nevin, R.L. Stellate ganglion block in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder: A review of historical and recent literature. Pain Pract. 2017, 4, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovits, A.H.; Yarmush, J.; Lefkowitz, M. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy and posttraumatic stress disorder. Multidisciplinary evaluation and treatment. Clin. J. Pain 1990, 6, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, S.W.; McLean, B.; De Leeuw, J. The use of stellate ganglion block in the treatment of panic/anxiety symptoms with combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder; preliminary results of long-term follow-up: A case series. Pain Pract. 2010, 10, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicky, A.; Hanling, S.; Pevney, E.; Allen, R.; McLay, R.N. Stellate ganglion block for PTSD. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipov, E.G.; Burkhardt, K.; Smith, J.C. A novel application of stellate ganglion block: Preliminary observations for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. Mil. Med. 2012, 177, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alino, J.; Kosatka, D.; McLean, B.; Hirsch, K. Efficacy of stellate ganglion block in the treatment of anxiety symptoms from combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder: A case series. Mil. Med. 2013, 178, e473–e476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulvaney, S.W.; Lynch, J.H.; Hickey, M.J.; Rahman-Rawlins, T.; Schroeder, M.; Kane, S.; Lipov, E. Stellate ganglion block used to treat symptoms associated with combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder: A case series of 166 patients. Mil. Med. 2014, 179, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLean, B.; McLean, B.C. Safety and patient acceptability of stellate ganglion blockade as a treatment adjunct for combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder: A quality assurance initiative. Cureus 2015, 7, e320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulvaney, S.W.; Lynch, J.H.; de Leeuw, J.; Schroeder, M.; Kane, S. Neurocognitive performance is not degraded after stellate ganglion block treatment for post-traumatic stress disorder: A case series. Mil. Med. 2015, 180, e601–e604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, J.H.; Mulvaney, S.W.; Kim, E.H.; de Leeuw, J.B.; Schroeder, M.J.; Kane, S.F. Effect of stellate ganglion block on specific symptom clusters for treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. Mil. Med. 2016, 181, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanling, S.R.; Hickey, A.; Lesnik, I.; Hackworth, R.J.; Stedje-Larsen, E.; Drastal, C.A.; McLay, R.N. Stellate ganglion block for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2016, 41, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.; Mulvaney, S. Self-reported combat-related symptom scores change after witnessing a teammate’s improvement following stellate ganglion block for post-traumatic stress symptoms. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmsted, K.L.R.; Bartoszek, M.; Mulvaney, S.; McLean, B.; Turabi, A.; Young, R.; Kim, E.; Vandermaas-Peeler, R.; Morgan, J.K.; Constantinescu, O.; et al. Effect of stellate ganglion block treatment on posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvaney, S.W.; Curtis, K.E.; Ibrahim, T.S. Comparison C6 stellate ganglion versus c6 and c4 cervical sympathetic chain blocks for treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (ptsd): Analysis of 147 patients. J. Neurol. Disord. Stroke 2020, 7, 1163. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, J.H.; Muench, P.D.; Okiishi, J.C.; Means, G.E.; Mulvaney, S.W. Behavioral health clinicians endorse stellate ganglion block as a valuable intervention in the treatment of trauma-related disorders. J. Investig. Med. 2021, 69, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odosso, R.J.; Petta, L. The efficacy of the stellate ganglion block as a treatment modality for posttraumatic stress disorder among active duty combat veterans: A pilot program evaluation. Mil. Med. 2021, 186, e796–e803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.L.; Straud, C.L.; Young-McCaughan, S.; McCallin, J.P.; Hoch, M.; Roux, N.P.; Koch, L.; Lara-Ruiz, J.; Roache, J.D.; Hein, J.M.; et al. Combining a stellate ganglion block with prolonged exposure therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder: A nonrandomized clinical trial. J. Trauma. Stress 2022, 35, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, S.W.; Lynch, J.H.; Curtis, K.E.; Ibrahim, T.S. The successful use of left-sided stellate ganglion block in patients that fail to respond to right-sided stellate ganglion block for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms: A retrospective analysis of 205 patients. Mil. Med. 2022, 187, e826–e829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipov, E.G.; Jacobs, R.; Springer, S.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. Utility of Cervical Sympathetic Block in Treating Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Multiple Cohorts: A Retrospective Analysis. Pain Physician 2022, 25, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. ICD-11: International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision. Available online: https://icd.who.int/en (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, S.W.; Lynch, J.H.; Kotwal, R.S. Clinical guidelines for stellate ganglion block to treat anxiety associated with posttraumatic stress disorder. J. Spec. Oper. Med. 2015, 15, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, G.R.; Sloan, J.A.; Wyrwich, K.W. Interpretation of changes in health-related quality of life: The remarkable universality of half a standard deviation. Med. Care 2003, 41, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, A.; Hüsing, P.; Gumz, A.; Wingenfeld, K.; Härter, M.; Schramm, E.; Löwe, B. Sensitivity to change and minimal clinically important difference of the 7-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire (GAD-7). J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 265, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, R.L.; Kroenke, K.; Williams, J.B.; Löwe, B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, J.H. Stellate ganglion block treats posttraumatic stress: An example of precision mental health. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averill, C.L.; Averill, L.A.; Fan, S.; Abdallah, C.G. Of forests and trees: Bridging the gap between neurobiology and behavior in posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2020, 5, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burback, L.; Brémault-Phillips, S.; Nijdam, M.J.; McFarlane, A.; Vermetten, E. Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A State-of-the-art Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, R.A. Sympathetic nerve blocks: In search of a role. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 1998, 23, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Johnson, K.A.; Ilstrup, D.M. Sympathetic blocks for reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Pain 1985, 23, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Peng, P.W.H. Suprascapular nerve block: A narrative review. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2001, 36, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lynch, J.H.; Mulvaney, S.W.; Bryan, C.J.; Hernandez, D. Stellate Ganglion Block Reduces Anxiety Symptoms by Half: A Case Series of 285 Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13060958
Lynch JH, Mulvaney SW, Bryan CJ, Hernandez D. Stellate Ganglion Block Reduces Anxiety Symptoms by Half: A Case Series of 285 Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(6):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13060958
Chicago/Turabian StyleLynch, James H., Sean W. Mulvaney, Craig J. Bryan, and David Hernandez. 2023. "Stellate Ganglion Block Reduces Anxiety Symptoms by Half: A Case Series of 285 Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 6: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13060958