Non-Target Effects of Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)-Derived Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA-GFP) Used in Honey Bee RNA Interference (RNAi) Assays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
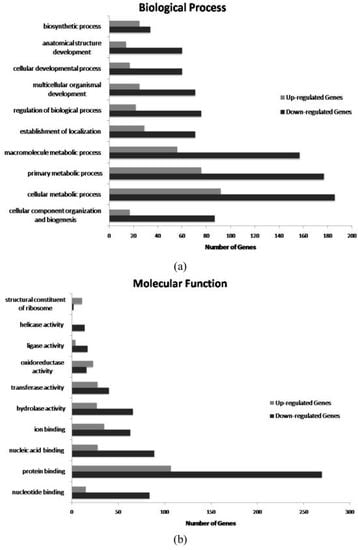
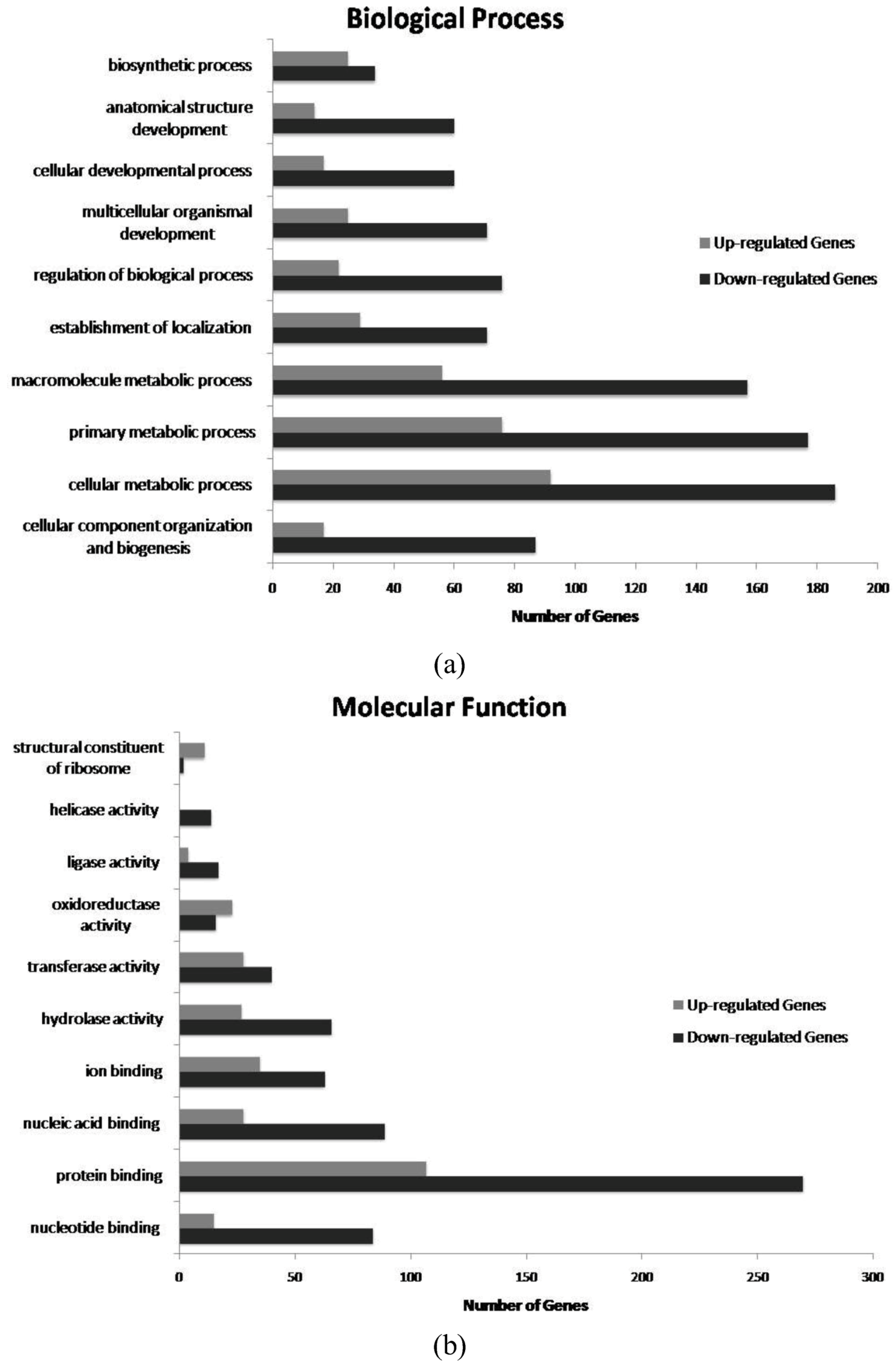
2. Results and Discussion
| Experiment | Upregulated | Downregulated | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 203 | 591 | 794 |
| 2 | 239 | 423 | 662 |
| 3 | 4 | 1 | 5 |
| Total | 446 | 1,015 | 1,461 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bees
3.2. dsRNA Synthesis
3.3. RNAi Treatments, Sampling and RNA Isolation
3.4. Microarrays: Hybridization and Data Analysis
3.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Perrimon, N.; Ni, J.Q.; Perkins, L. In vivo RNAi: today and tomorrow. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a003640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.E., Jr; Gadau, J.; Beye, M. The emergence of hymenopteran genetics. Genetics 2002, 160, 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Beye, M.; Härtel, S.; Hagen, A.; Hasselmann, M.; Omholt, S.W. Specific developmental gene silencing in the honey bee using a homeobox motif. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdam, G.V.; Simões, Z.L.; Guidugli, K.R.; Norberg, K.; Omholt, S.W. Disruption of vitellogenin gene function in adult honeybees by intra-abdominal injection of double-stranded RNA. BMC Biotechnol. 2003, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ament, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.C.; Blatti, C.A.; Hong, F.; Liang, Z.S.; Negre, N.; White, K.P.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Mizzen, C.A.; Sinha, S.; Zhong, S.; Robinson, G.E. The transcription factor ultraspiracle influences honey bee social behavior and behavior-related gene expression. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002596. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.L.; Bartz, S.R.; Schelter, J.; Kobayashi, S.V.; Burchard, J.; Mao, M.; Li, B.; Cavet, G.; Linsley, P.S. Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, Y.; Anderson, E.M.; Birmingham, A.; Reynolds, A.; Karpilow, J.; Robinson, K.; Leake, D.; Marshall, W.S.; Khvorova, A. Off-target effects by siRNA can induce toxic phenotype. RNA 2006, 12, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.M.; Booker, M.; Silver, S.J.; Friedman, A.; Hong, P.; Perrimon, N.; Mathey-Prevot, B. Evidence of off-target effects associated with long dsRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster cell-based assays. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Schüssler, M.D.; Alexandersson, E.; Bienert, G.P.; Kichey, T.; Laursen, K.H.; Johanson, U.; Kjellbom, P.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Jahn, T.P. The effects of the loss of TIP1;1 and TIP1;2 aquaporins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant. J. 2008, 56, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosch, A.; Moritz, R.F. RNA interference in honeybees: Off-target effects caused by dsRNA. Apidologie 2012, 43, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, A.J.; Shi, L.J.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. TRBP and eIF6 homologue in Marsupenaeus. japonicus play crucial roles in antiviral response. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30057. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Söderhäll, I.; Cerenius, L.; Söderhäll, K. Antilipopolysaccharide factor interferes with white spot syndrome virus replication in vitro and in vivo in the crayfish Pacifastacus. leniusculus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10365–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Tang, B.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, W. Identification of 20-hydroxyecdysone late-response genes in the chitin biosynthesis pathway. PLoS One 2010, 5, e14058. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F. Two storage hexamerins from the beet armyworm Spodoptera. exigua: Cloning, characterization and the effect of gene silencing on survival. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutti, N.S.; Park, Y.; Reese, J.C.; Reeck, G.R. RNAi knockdown of a salivary transcript leading to lethality in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon. pisum. J. Insect Sci. 2006, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, S.; Ramirez, J.L.; Dimopoulos, G. Dengue virus infection of the Aedes. aegypti salivary gland and chemosensory apparatus induces genes that modulate infection and blood-feeding behavior. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.N.; Nagaraju, J. Two female-specific DSX proteins are encoded by the sex-specific transcripts of dsx and are required for female sexual differentiation in two wild silkmoth species, Antheraea. assama and Antheraea. mylitta (Lepidoptera, Saturniidae). Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 672–682. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhu, K.Y.; Ma, E.; Zhang, J. Characterization of a midgut-specific chitin synthase gene (LmCHS2) responsible for biosynthesis of chitin of peritrophic matrix in Locusta. migratoria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynant, N.; Verlinden, H.; Breugelmans, B.; Simonet, G.; Vanden Broeck, J. Tissue-dependence and sensitivity of the systemic RNA interference response in the desert locust, Schistocerca. gregaria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuriyanghan, H.; Rosa, C.; Falk, B.W. Oral delivery of double-stranded RNAs and siRNAs induces RNAi effects in the potato/tomato psyllid, Bactericerca. cockerelli. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.M.; Ihle, K.E.; Fondrk, M.K.; Page, R.E.; Amdam, G.V. The gene vitellogenin has multiple coordinating effects on social organization. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maori, E.; Paldi, N.; Shafir, S.; Kalev, H.; Tsur, E.; Glick, E.; Sela, I. IAPV, a bee-affecting virus associated with Colony Collapse Disorder can be silenced by dsRNA ingestion. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.M.F.; Simões, Z.L.P. A non-invasive method for silencing gene transcription in honeybees maintained under natural conditions. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosch, A.; Moritz, R.F. Systemic RNA-interference in the honeybee Apis mellifera: Tissue dependent uptake of fluorescent siRNA after intra-abdominal application observed by laser-scanning microscopy. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamakura, M. Royalactin induces queen differentiation in honeybees. Nature 2011, 473, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutti, N.S.; Wang, Y.; Kaftanoglu, O.; Amdam, G.V. Honey bee PTEN--description, developmental knockdown and tissue-specific expression of splice-variants correlated with alternative social phenotypes. PLoS One 2011, 6, e22195. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, S.D.; Eu, Y.J.; Whyard, S.; Currie, R.W. Reduction in deformed wing virus infection in larval and adult honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) by double-stranded RNA ingestion. Insect Mol. Biol. 2012, 21, 446–455. [Google Scholar]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ruan, X.; Anderson, M.G.; McDowell, J.A.; Kroeger, P.E.; Fesik, S.W.; Shen, Y. siRNA-mediated off-target gene silencing triggered by a 7 nt complementation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 4527–4535. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.L.; Burchard, J.; Schelter, J.; Chau, B.N.; Cleary, M.; Lim, L.; Linsley, P.S. Widespread siRNA "off-target" transcript silencing mediated by seed region sequence complementarity. RNA 2006, 12, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, J.G.; Yoda, M.; Tomari, Y. miRNA-like duplexes as RNAi triggers with improved specificity. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, A.L.; Burchard, J.; Schelter, J.; Chau, BN.; Cleary, M.; Lim, L.; Linsley, P.S. Widespread siRNA "off-target" transcript silencing mediated by seed region sequence complementarity. RNA 2006, 12, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, N.; Marenstein, D.R.; De Angelis, D.A.; Wang, W.Q.; Nelander, S.; Jacobsen, A.; Marks, D.S.; Massagué, J.; Sander, C. Off-target effects dominate a large-scale RNAi screen for modulators of the TGF-β pathway and reveal microRNA regulation of TGFBR2. Silence 2011, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigoillot, F.D.; King, R.W. Vigilance and validation: keys to success in RNAi screening. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Betel, D.; Miller, M.L.; Sander, C.; Leslie, C.S.; Marks, D.S. Transfection of small RNAs globally perturbs gene regulation by endogenous microRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Persengiev, S.P.; Zhu, X.; Green, M.R. Nonspecific, concentration-dependent stimulation and repression of mammalian gene expression by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). RNA 2004, 10, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, M.; Robinson, G.E. Genes of the antioxidant system of the honey bee: Annotation and phylogeny. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, M.; Agaisse, H.; Perrimon, N. Sequential activation of signaling pathways during innate immune responses in Drosophila. Dev. Cell. 2002, 3, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, S.; Wang, X.; Simms, N.; Page-McCaw, A. Drosophila Ninjurin A induces nonapoptotic cell death. PLoS One 2012, 7, e44567. [Google Scholar]
- Casteels, P.; Ampe, C.; Jacobs, F.; Vaeck, M.; Tempst, P. Apidaecins: Antibacterial peptides from honeybees. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 2387–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Lu, R.; Lau, N.; Lai, E.C.; Li, W.X.; Ding, S.W. Virus discovery by deep sequencing and assembly of virus-derived small silencing RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar]
- Zambon, R.A.; Vakharia, V.N.; Wu, L.P. RNAi is an antiviral immune response against a dsRNA virus in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolt, K.; Gimple, O.; Geissendörfer, J.; Reinders, J.; Prusko, C.; Mueller, M.J.; Albert, S.; Tautz, J.; Beier, H. Immune-related proteins induced in the hemolymph after aseptic and septic injury differ in honey bee worker larvae and adults. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2008, 69, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyuki, T.; Matsuzaka, E.; Nakaoka, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Wakamoto, A.; Ohka, S.; Sekimizu, K.; Nomoto, A.; Kubo, T. Distribution of Kakugo virus and its effects on the gene expression profile in the brain of the worker honeybee Apis mellifera L. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11560–11568. [Google Scholar]
- Gätschenberger, H.; Azzami, K.; Gimple, O.; Grimmer, G.; Sumner, S.; Fujiyuki, T.; Tautz, J.; Mueller, M.J. Evidence of a novel immune responsive protein in the Hymenoptera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenius, O.; Papanicolaou, A.; Garbutt, J.S.; Eleftherianos, I.; Huvenne, H.; Kanginakudru, S.; Albrechtsen, M.; An, C.; Aymeric, J.L.; Barthel, A.; Bebas, P.; Bitra, K.; Bravo, A.; Chevalier, F.; Collinge, D.P.; Crava, C.M.; de Maagd, R.A.; Duvic, B.; Erlandson, M.; Faye, I.; Felföldi, G.; Fujiwara, H.; Futahashi, R.; Gandhe, A.S.; Gatehouse, H.S.; Gatehouse, L.N.; Giebultowicz, J.M.; Gómez, I.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.; Groot, A.T.; Hauser, F.; Heckel, D.G.; Hegedus, D.D.; Hrycaj, S.; Huang, L.; Hull, J.J.; Iatrou, K.; Iga, M.; Kanost, M.R.; Kotwica, J.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Lundmark, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Meyering-Vos, M.; Millichap, P.J.; Monteiro, A.; Mrinal, N.; Niimi, T.; Nowara, D.; Ohnishi, A.; Oostra, V.; Ozaki, K.; Papakonstantinou, M.; Popadic, A.; Rajam, M.V.; Saenko, S.; Simpson, R.M.; Soberón, M.; Strand, M.R.; Tomita, S.; Toprak, U.; Wang, P.; Wee, C.W.; Whyard, S.; Zhang, W.; Nagaraju, J.; Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Herrero, S.; Gordon, K.; Swevers, L.; Smagghe, G. RNA interference in Lepidoptera: an overview of successful and unsuccessful studies and implications for experimental design. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 231–245. [Google Scholar]
- Vankoningsloo, S.; de Longueville, F.; Evrard, S.; Rahier, P.; Houbion, A.; Fattaccioli, A.; Gastellier, M.; Remacle, J.; Raes, M.; Renard, P.; Arnould, T. Gene expression silencing with 'specific' small interfering RNA goes beyond specificity - a study of key parameters to take into account in the onset of small interfering RNA off-target effects. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2738–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak, M.; Galka, P.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Sequence-non-specific effects of RNA interference triggers and microRNA regulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, F.L.; Püttmann-Holgado, R.; Thomas, F.; Lamar, D.L.; Hughes, M.; Kondo, M.; Rebel, V.I.; Schmucker, D. Extensive diversity of Ig-superfamily proteins in the immune system of insects. Science 2005, 309, 1874–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Aronstein, K.; Chen, Y.P.; Hetru, C.; Imler, J.L.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.; Thompson, G.J.; Zou, Z.; Hultmark, D. Immune pathways and defence mechanisms in honey bees Apis mellifera. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, H. Blood proteins in insect development. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1960, 89, 490–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, G.; Seeley, D.; Wolf, A.; Kafatos, F.C. Malaria infection of the mosquito Anopheles gambiae activates immune-responsive genes during critical transition stages of the parasite life cycle. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6115–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Rich, N.; Dres, S.T.; Starks, P.T. The ontogeny of immunity: development of innate immune strength in the honey bee (Apis mellifera). J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, A.P.; Martins, J.R.; Guidugli-Lazzarini, K.R.; Macedo, L.M.; Bitondi, M.M.G.; Simões, Z.L.P. Potential costs of bacterial infection on storage protein gene expression and reproduction in queenless Apis mellifera worker bees on distinct dietary regimes. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.R.; Nunes, F.M.F.; Cristino, A.S.; Simões, Z.LP.; Bitondi, M.M.G. The four hexamerin genes in the honey bee: structure, molecular evolution and function deduced from expression patterns in queens, workers and drones. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelette, E.R.F.; Soares, A.E.E. Characterization of preimaginal developmental stages in Africanized honey bee workers (Apis mellifera L). Apidologie 1993, 24, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, S.D.; Richard, F.J.; Tarpy, D.R.; Grozinger, C.M. Genomic analysis of post-mating changes in the honey bee queen (Apis mellifera). BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, S.D.; Ayroles, J.; Stone, E.A.; Grozinger, C.M. Individual variation in pheromone response correlates with reproductive traits and brain gene expression in worker honey bees. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9116. [Google Scholar]
- Barchuk, A.R.; Cristino, A.S.; Kucharski, R.; Costa, L.F.; Simões, Z.L.P.; Maleszka, R. Molecular determinants of caste differentiation in the highly eusocial honeybee Apis mellifera. BMC Dev. Biol. 2007, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bomtorin, A.D.; Barchuk, A.R.; Moda, L.M.; Simões, Z.L.P. Hox gene expression leads to differential hind leg development between honeybee castes. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40111. [Google Scholar]
- Brazma, A. Minimum Information About a Microarray Experiment (MIAME)--successes, failures, challenges. Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsik, C.G.; Mackey, A.J.; Reese, J.T.; Milshina, N.V.; Roos, D.S.; Weinstock, G.M. Creating a honey bee consensus gene set. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeybee Genome Sequencing Consortium. Insights into social insects from the genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nature 2006, 443, 931–949. [Google Scholar]
- Apis mellifera Genome Sequences. Available online: http://hymenopteragenome.org/beebase/?q=download_sequences (accessed on 9 December 2012).
- BLAST Assembled RefSeq Genomes. Available online: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 9 December 2012).
- BLAST resources for Species of Apis. Available online: http://hymenopteragenome.org/beebase/?q=apis_blast (accessed on 9 December 2012).
- Multiple Sequence Alignment by CLUSTALW. Available online: http://www.genome.jp/tools/clustalw/ (accessed on 9 December 2012).
- A Database of Drosophila Genes & Genomes. Available online: http://flybase.org (accessed on 9 December 2012).
- BABELOMICS. v3.2! new release. Available online: http://babelomics3.bioinfo.cipf.es (accessed on 9 December 2012).
Supplementary Materials
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunes, F.M.F.; Aleixo, A.C.; Barchuk, A.R.; Bomtorin, A.D.; Grozinger, C.M.; Simões, Z.L.P. Non-Target Effects of Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)-Derived Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA-GFP) Used in Honey Bee RNA Interference (RNAi) Assays. Insects 2013, 4, 90-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects4010090
Nunes FMF, Aleixo AC, Barchuk AR, Bomtorin AD, Grozinger CM, Simões ZLP. Non-Target Effects of Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)-Derived Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA-GFP) Used in Honey Bee RNA Interference (RNAi) Assays. Insects. 2013; 4(1):90-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects4010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunes, Francis M. F., Aline C. Aleixo, Angel R. Barchuk, Ana D. Bomtorin, Christina M. Grozinger, and Zilá L. P. Simões. 2013. "Non-Target Effects of Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)-Derived Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA-GFP) Used in Honey Bee RNA Interference (RNAi) Assays" Insects 4, no. 1: 90-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects4010090
APA StyleNunes, F. M. F., Aleixo, A. C., Barchuk, A. R., Bomtorin, A. D., Grozinger, C. M., & Simões, Z. L. P. (2013). Non-Target Effects of Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)-Derived Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA-GFP) Used in Honey Bee RNA Interference (RNAi) Assays. Insects, 4(1), 90-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects4010090