-
 Extraction Methods for Annual Bluegrass Weevil Larval Populations
Extraction Methods for Annual Bluegrass Weevil Larval Populations -
 How Mediterranean Oaks Defend Their Acorns from Insect Seed Predators
How Mediterranean Oaks Defend Their Acorns from Insect Seed Predators -
 Predation Pressure on Kenyan Tea Planatations
Predation Pressure on Kenyan Tea Planatations -
 Lysine and Isoleucine as Limiting Amino Acids for Mealworm
Lysine and Isoleucine as Limiting Amino Acids for Mealworm -
 Modeling the Phenology and Establishment Risk of the Spotted Lanternfly
Modeling the Phenology and Establishment Risk of the Spotted Lanternfly
Journal Description
Insects
Insects
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on entomology, published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, PubAg, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Entomology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Insect Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Animal Science: Animals, Arthropoda, Birds, Insects, Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens, Pets, Poultry, Ruminants and Veterinary Sciences.
Impact Factor:
2.9 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
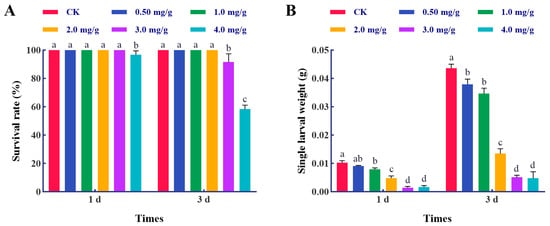
Growth Inhibition, Mortality Induction, Adverse Impacts of Development, and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms of Thymol Against Spodoptera frugiperda
Insects 2026, 17(1), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010069 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
The global migratory pest, Spodoptera frugiperda, has garnered widespread attention due to the serious damage it inflicts on agricultural productivity, particularly in maize. Thymol is a phytochemical that exhibits functional diversification in plant defense, encompassing antibacterial activities and insect pest management. However,
[...] Read more.
The global migratory pest, Spodoptera frugiperda, has garnered widespread attention due to the serious damage it inflicts on agricultural productivity, particularly in maize. Thymol is a phytochemical that exhibits functional diversification in plant defense, encompassing antibacterial activities and insect pest management. However, the impact of thymol on S. frugiperda is still undetermined. This study examined the growth inhibition and mortality induction in S. frugiperda larvae after thymol exposure. The detrimental effects of 2.0 and 4.0 mg/g thymol treatments on the growth and development of S. frugiperda were also examined. RNA-Seq was used to investigate the probable toxicological mechanism of thymol on S. frugiperda, resulting in the identification of 1754 and 1022 DEGs impacted by 2.0 and 4.0 mg/g thymol treatments, respectively. The DEGs associated with chitin metabolism and cuticle synthesis, hormone biosynthesis, and protein and fat digestion were subjected to additional analysis. Our findings demonstrate the efficacy of thymol in controlling S. frugiperda and lay the groundwork for understanding the molecular toxicological mechanisms of thymol on larvae.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Insects Ecology and Biological Control Applications)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Preliminary Evaluation of the Toxic Effects of Essential Oils as Natural Pesticides Against Maize Weevil (Sitophilus zeamais) and Its Fungal Pathogens
by
Ompelege Jacqueline Phokwe, Kabelo Magoro, Mametsi Rahab Maseme and Madira Coutlyne Manganyi
Insects 2026, 17(1), 68; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010068 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
To control maize weevils (Sitophilus zeamais), a major pest of stored grains, this study explores the use of essential oils from Eucalyptus globulus and Lantana camara as natural biopesticides. Given the risks of synthetic pesticides, these oils offer a sustainable alternative.
[...] Read more.
To control maize weevils (Sitophilus zeamais), a major pest of stored grains, this study explores the use of essential oils from Eucalyptus globulus and Lantana camara as natural biopesticides. Given the risks of synthetic pesticides, these oils offer a sustainable alternative. The research first identified ten fungal pathogens associated with the weevils, including the dominant species, Fusarium solani. Preliminary results showed that both oils were then tested for their ability to kill the fungi and the weevils. Eucalyptus globulus oil proved to be a superior antifungal agent, inhibiting fungal growth by up to 93%, significantly outperforming Lantana camara oil. Both oils demonstrated potent insecticidal properties, achieving 100% weevil mortality at a 10% concentration within 24 hrs. However, Eucalyptus oil was more effective, maintaining 100% mortality even at a lower 5% concentration, unlike Lantana oil. Chemical analysis showed that Eucalyptus oil’s high effectiveness may be associated with its main component, eucalyptol (52.8%). Lantana oil had a more varied composition, with caryophyllene (31%) as its primary constituent. The findings suggest that Eucalyptus globulus essential oil is a promising, two-in-one biopesticide capable of controlling both maize weevils and their associated fungal pathogens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Efficacy of Insecticides and Botanicals Against Pests—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
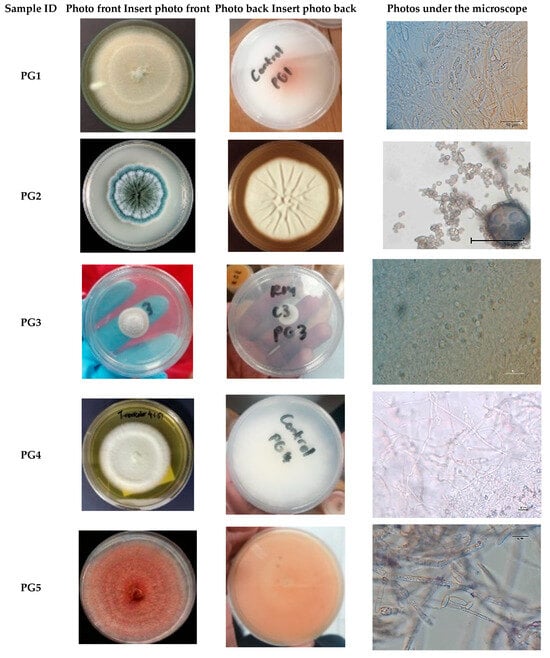
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Microwave on Mortality and Detection Efficiency of Three Stored Grain Insect Adults in Stored Paddy, and on Grain Quality
by
Shiyuan Miao, Yiting Zhou, Suisui Wang, Zhipeng Yang, Adrien Guverinoma, Yaru Zhao and Yujie Lu
Insects 2026, 17(1), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010067 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
Microwave heating has been widely used for disinfestation in the food industry due to its selective heating. However, research on the effects of microwave heating on stored product insects is still relatively limited, which has restricted its broader application in grain pest control
[...] Read more.
Microwave heating has been widely used for disinfestation in the food industry due to its selective heating. However, research on the effects of microwave heating on stored product insects is still relatively limited, which has restricted its broader application in grain pest control storage. Therefore, this study evaluated the lethal effects of different microwave powers and exposure times on three major pests in paddy and investigated the impact of microwave treatment on improving adult detection efficiency, intending to develop a rapid and efficient detection method for stored grain insects. The results showed that the mortality of Sitophilus oryzae, Tribolium castaneum, and Oryzaephilus surinamensis increased with the increase in microwave power and exposure time. Specifically, 100% mortality was achieved for both S. oryzae and T. castaneum at 700 W for 60 s exposure. However, higher power levels and longer exposure durations exacerbated the non-uniformity of grain temperature distribution and adversely affected the germination rate. In addition, microwave treatment at 350 W, 490 W, and 700 W significantly reduced fungal load in paddy. The moisture content and water activity of rice decreased with the increase in microwave power and exposure time, while the percentage of grain breakage remained largely unaffected. These findings indicated that microwave treatment can effectively control insects and fungi without significantly altering the main physical properties of paddy. Notably, microwave treatment with short exposure durations (20–30 s) at all three power levels is conducive to increasing the recovery percentage of S. oryzae adults, while microwave treatment at low power (350 W) with exposure durations of 25–40 s helps improve that of T. castaneum. Accordingly, microwave heating is not only a promising strategy for protecting stored grains but also has potential for development as a rapid detection method for specific insect pests.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Integrated Pest Management in Stored Products)
►▼
Show Figures
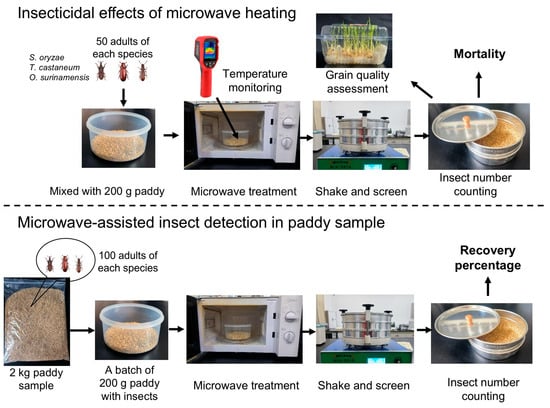
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
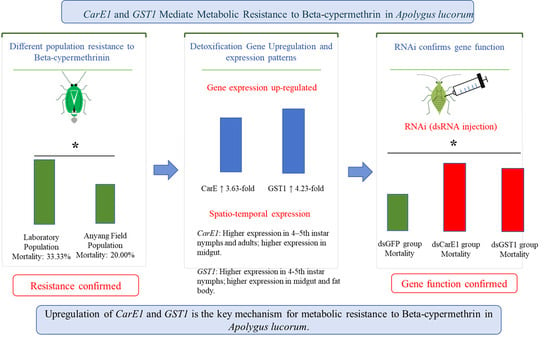
CarE1 and GST1 Are Involved in Beta-Cypermethrin Resistance in Field Populations of the Mirid Bug, Apolygus lucorum
by
Haojie Wang, Weicheng Song, Qiyuan Wu, Liming Xu, Lin Niu and Qingbo Tang
Insects 2026, 17(1), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010066 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
The widespread cultivation of transgenic Bt cotton has elevated Apolygus lucorum (Meyer-Dür) to a major pest in cotton agroecosystems. Its rapidly developing resistance to insecticides poses a serious challenge to sustainable agriculture. In this study, we assessed the susceptibility of a field-collected population
[...] Read more.
The widespread cultivation of transgenic Bt cotton has elevated Apolygus lucorum (Meyer-Dür) to a major pest in cotton agroecosystems. Its rapidly developing resistance to insecticides poses a serious challenge to sustainable agriculture. In this study, we assessed the susceptibility of a field-collected population from Anyang, Henan Province, in relation to a laboratory-susceptible strain, to elucidate the present status and molecular basis of resistance to beta-cypermethrin. First, the toxicity of beta-cypermethrin to A. lucorum was assessed through a diet-incorporation method. Subsequently, the enzymatic activities of carboxylesterase (CarE) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) were measured, and the expression levels of CarE1 and GST1 were quantified by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Finally, the function of candidate genes was confirmed using RNA interference (RNAi) technology. The bioassays results indicated that the median lethal concentration (LC50) for the laboratory and Anyang field strain were 343.34 mg/L and 700.45 mg/L, respectively. Following 48 h of exposure to the LC30 of the susceptible strain, the mortality rate of the field population (20.00%) was significantly lower than that of the laboratory population (33.33%), suggesting an increase in resistance. The field population of A. lucorum exhibited significantly higher activities of CarE (1.61-fold) and GST (1.71-fold) compared to the laboratory strain, accompanied by 3.63- and 4.23-fold overexpression of the corresponding genes CarE1 and GST1. Spatiotemporal expression profiling revealed that CarE1 expression was highest in 4th–5th instar nymphs and adults, with predominant localization in the midgut, while GST1 expression peaked in 4th–5th instar nymphs and was abundant in the midgut and fat body. RNAi-mediated knockdown of CarE1 and GST1 significantly enhanced susceptibility to beta-cypermethrin in field populations, resulting in elevated mortality 48 h post-treatment compared to controls. In conclusion, the field population of A. lucorum has developed considerable resistance to beta-cypermethrin, strongly correlated with overexpression of CarE1 and GST1. These results deepen our understanding of metabolic resistance mechanisms and offer valuable insights for developing targeted pest control strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Insecticide Resistance and Toxicology: Challenges in Pest Management and Basic Research—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Terpenoid Mixtures as Repellents Against the American Cockroach: Their Synergy and Low Toxicity Against Non-Target Species
by
Hataichanok Passara, Tanapoom Moungthipmalai, Chamroon Laosinwattana, Sirawut Sittichok, Kouhei Murata and Mayura Soonwera
Insects 2026, 17(1), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010065 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
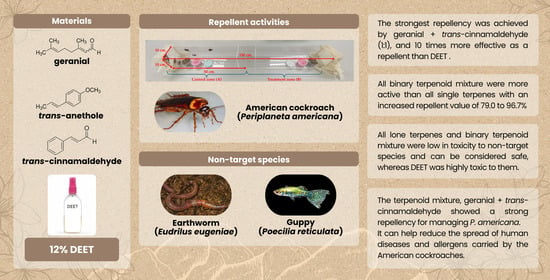
The repellent activities (Periplaneta americana) of lone and binary mixtures of terpenoids—geranial, trans-anethole, and trans-cinnamaldehyde—against adult American cockroaches were evaluated in this study. The respective efficacies of these mixtures were compared with that of 12% (w/w
[...] Read more.
The repellent activities (Periplaneta americana) of lone and binary mixtures of terpenoids—geranial, trans-anethole, and trans-cinnamaldehyde—against adult American cockroaches were evaluated in this study. The respective efficacies of these mixtures were compared with that of 12% (w/w) DEET. Safety bioassays for all formulations on non-target species, namely, earthworms (Eudrilus eugeniae) and guppy fish (Poecilia reticulata), were conducted to identify natural compounds with repellent efficacy equal to or surpassing that of DEET while ensuring ecological safety for non-target organisms such as fish and earthworms. All mixtures (RC50 of 0.3 to 1.6 µL/cm3) were more effective than all lone terpenoids (RC50 of 6.2 to 9.1 µL/cm3) and DEET (RC50 of 3.0 µL/cm3), demonstrating strong synergy, with an increased repellent value (IV) of 79 to 96%. The strongest repellency, 98.0% at 72 h and an RC50 of 0.3 µL/cm3, was achieved using geranial + trans-cinnamaldehyde (1:1). This mixture was 5.9 to 10 times more effective as a repellent than DEET. The toxicity of every lone terpenoid and terpenoid mixture to non-target species was low; hence, these mixtures can be considered safe, whereas DEET was highly toxic to non-target species (100% mortality). The terpenoid mixture geranial + trans-cinnamaldehyde showed strong repellency against P. americana.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urban Entomology and One Health)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Isolation and Identification of the Sex Pheromone of Evergestis extimalis Scopoli (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)
by
Mingang Qin, Youhua Ma, Youpeng Lai, Siyu Liu and Gui Zhang
Insects 2026, 17(1), 64; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010064 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
In Qinghai Province, Evergestis extimalis is an important pest of spring rape and is primarily controlled using chemical pesticides. Sex pheromones offer an alternative method for pest management in relatively non-polluted environments. In this study, the sex of E. extimalis pupae was identified,
[...] Read more.
In Qinghai Province, Evergestis extimalis is an important pest of spring rape and is primarily controlled using chemical pesticides. Sex pheromones offer an alternative method for pest management in relatively non-polluted environments. In this study, the sex of E. extimalis pupae was identified, followed by isolation and structural characterization of female pheromone components using GC-EAD and GC-MS. A field attraction assay was then performed. The results showed that female pupae possess a longitudinal crack on the upper central ventral surface of the eighth abdominal segment, which connects the seventh and ninth abdominal segments. The two sides of this crack are open and flat, without protruding semicircles. Male pupae lack this longitudinal crack on the eighth abdominal segment but display one on the central ninth ventral segment, accompanied by semicircular tubercles on each side. The primary component extracted from female sex glands was identified as E11-14Ac. In field trials, E11-14 displayed a stronger attractive effect on E. extimalis males than the other tested attractants. In conclusion, E11-14Ac was preliminarily identified as the main component of the sex pheromone of E. extimalis, providing a foundation for its control using sex pheromones.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Insect Pest and Vector Management)
►▼
Show Figures
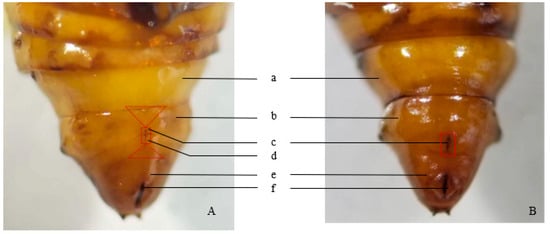
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Next-Generation Precision Breeding in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) for Disease and Pest Resistance: From Multi-Omics to AI-Driven Innovations
by
Xue Pei, Jinhui Xie, Chunhao Liang and Aleksandra O. Utkina
Insects 2026, 17(1), 63; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010063 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is a globally important oilseed and food legume, yet its productivity is persistently constrained by devastating diseases and insect pests that thrive under changing climates. This review aims to provide a comprehensive synthesis of advances in precision breeding
[...] Read more.
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is a globally important oilseed and food legume, yet its productivity is persistently constrained by devastating diseases and insect pests that thrive under changing climates. This review aims to provide a comprehensive synthesis of advances in precision breeding and molecular approaches for enhancing disease and pest resistance in peanut. Traditional control measures ranging from crop rotation and cultural practices to chemical protection have delivered only partial and often unsustainable relief. The narrow genetic base of cultivated peanut and its complex allotetraploid genome further hinder the introgression of durable resistance. Recent advances in precision breeding are redefining the possibilities for resilient peanut improvement. Multi-omics platforms genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics have accelerated the identification of resistance loci, effector-triggered immune components, and molecular cross-talk between pathogen, pest, and host responses. Genome editing tools such as CRISPR-Cas systems now enable the precise modification of susceptibility genes and defense regulators, overcoming barriers of conventional breeding. Integration of these molecular innovations with phenomics, machine learning, and remote sensing has transformed resistance screening from manual assessment to real-time, data-driven prediction. Such AI-assisted breeding pipelines promise enhanced selection accuracy and faster deployment of multi-stress-tolerant cultivars. This review outlines current progress, technological frontiers, and persisting gaps in leveraging precision breeding for disease and pest resistance in peanut, outlining a roadmap toward climate-resilient, sustainable production systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Insect Pests Management: Securing Food Security, Human Health, and Natural Resources)
►▼
Show Figures
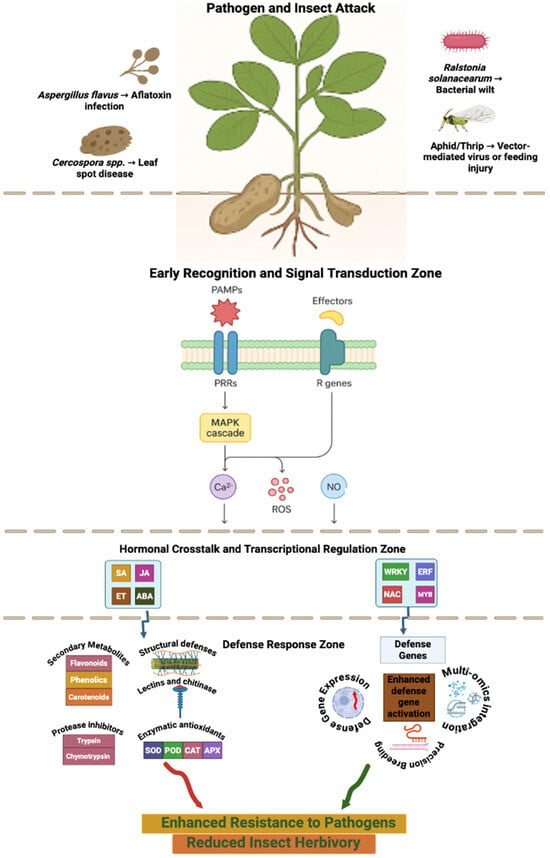
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Corcyra cephalonica Egg Consumption on Population Fitness and Reproduction of the Whitefly Predator Serangium japonicum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae)
by
Jianfeng Liang, Jing Peng, Huiyi Cao, Yuxia Hu, Muhammad Irfan Ullah, Shaukat Ali and Xingmin Wang
Insects 2026, 17(1), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010062 - 3 Jan 2026
Abstract
Ladybird beetle, Serangium japonicum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), is an important predatory natural enemy of whiteflies, and its mass rearing is crucial for biological control. This study evaluated the suitability of Corcyra cephalonica (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) eggs as an alternative diet for adult S. japonicum by
[...] Read more.
Ladybird beetle, Serangium japonicum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), is an important predatory natural enemy of whiteflies, and its mass rearing is crucial for biological control. This study evaluated the suitability of Corcyra cephalonica (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) eggs as an alternative diet for adult S. japonicum by directly comparing it to the natural prey, Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) nymphs. Results showed that, compared to a B. tabaci diet, feeding on C. cephalonica eggs supported normal development and significantly extended the lifespan of adult S. japonicum, without compromising offspring quality (hatching rate, development, survival, or predatory capacity). However, the moth egg diet significantly impaired reproduction, causing delayed ovarian development, reduced vitellogenesis, and altered gene expression: downregulation of methoprene-tolerant, Juvenile hormone acid O-methyltransferase, Vitellogenin, and Vitellogenin receptor, and upregulation of Juvenile hormone esterase and Copper/zinc superoxide dismutase. Practically, this work defines C. cephalonica eggs as a suboptimal but viable supplementary diet for colony maintenance, but unsuitable as a sole diet for mass-rearing reproductively robust populations. Our findings explain the physiological and molecular mechanisms underlying the “reproduction–lifespan trade-off” in S. japonicum induced by feeding on C. cephalonica eggs, providing a mechanistic basis for its rational application in the mass production of natural enemies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Insect Physiology, Reproduction and Development)
►▼
Show Figures
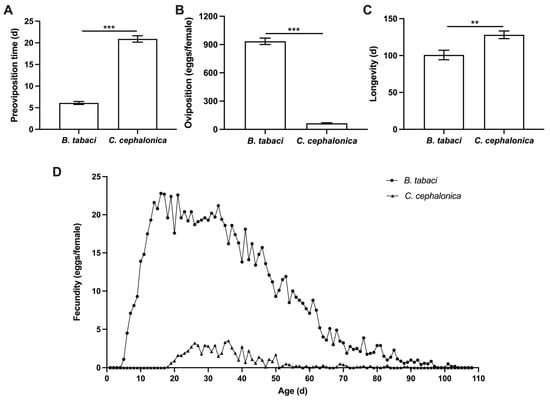
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Role of Biological Control in Management of Invasive Exotic Arthropod Pests and Weeds in India
by
Rangaswamy Muniappan, Kesavan Subaharan, Krishnan Selvaraj, Muthusamy Sampathkumar and Satya Nand Sushil
Insects 2026, 17(1), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010061 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Classical biological control of exotic invasive weeds first took place in India in 1795. Thus far, a total of 174 natural enemies have been imported into India, and out of these, 77 have established themselves in the field. Twelve exotic insect pests and
[...] Read more.
Classical biological control of exotic invasive weeds first took place in India in 1795. Thus far, a total of 174 natural enemies have been imported into India, and out of these, 77 have established themselves in the field. Twelve exotic insect pests and four weeds were successfully controlled with a combination of classical, augmentative, and conservation biological control. Additionally, eight insect pests and one weed were substantially controlled. Augmentative biological control has been adopted as per the needs and availability of resources. Conservation biological control is ubiquitous and has been facilitated by the adoption of integrated pest management. In the past, biological control activities were sporadic; however, since 1977, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research—National Bureau for Agricultural Insect Resources has been regularly implementing classical biological control of invasive agricultural insect pests of economic importance. Unfortunately, the importance given to invasive weeds and insect pests of natural resources has fallen behind in recent years.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Insect Pest and Vector Management)
Open AccessArticle
Decoding Biodiversity in Baiyangdian Lake: A DNA Barcode Reference Library for Aquatic Insects
by
Ya-Jun Qiao, Ze-Peng Wang, Meng-Yu Lv, Pei-Dong Su, Tong Wu, Hai-Feng Xu, Yu-Fan Li, Xiao-Long Lin and Chun-Hui Zhang
Insects 2026, 17(1), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010060 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Freshwater ecosystems are among the most vulnerable habitats worldwide, and reliable biodiversity assessment is essential for their conservation. Baiyangdian Lake, the largest freshwater lake in northern China, has undergone severe ecological degradation but is now experiencing recovery through restoration efforts. To provide a
[...] Read more.
Freshwater ecosystems are among the most vulnerable habitats worldwide, and reliable biodiversity assessment is essential for their conservation. Baiyangdian Lake, the largest freshwater lake in northern China, has undergone severe ecological degradation but is now experiencing recovery through restoration efforts. To provide a molecular basis for monitoring biodiversity, we constructed a COI DNA barcode reference library of aquatic insects from Baiyangdian Lake. From January 2023 to May 2025, systematic sampling across representative habitats yielded 315 high-quality sequences covering 104 species, 74 genera, and 33 families within eight insect orders. Diptera, particularly Chironomidae, showed the highest diversity, followed by Odonata. Phylogenetic analysis using maximum likelihood resolved all orders and families as well-supported monophyletic groups, demonstrating strong congruence with morphological taxonomy. Genetic distance analysis revealed a pronounced barcode gap, with mean intraspecific divergence of 0.46% and nearest-neighbor divergence exceeding 15%, confirming the discriminatory power of COI for species identification. Accumulation curves indicated that genus-level diversity is largely captured, while species-level diversity, especially among Diptera, remains incompletely revealed. This study provides the first comprehensive DNA barcode reference library for Baiyangdian aquatic insects, supporting ecological restoration evaluation, eDNA applications, and regional biodiversity conservation strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Aquatic Insects Biodiversity and eDNA Monitoring)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptomic Analysis of the Cold Resistance Mechanisms During Overwintering in Apis mellifera
by
Xiaoyin Deng, Yali Du, Jiaxu Wu, Jinming He, Haibin Jiang, Yuling Liu, Qingsheng Niu and Kai Xu
Insects 2026, 17(1), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010059 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Safe overwintering is a challenging issue in rearing management that is inevitably faced by beekeepers in high-latitude regions. Under the combined influence of multiple factors, the overwintering loss rate of Western honey bees has risen continuously, and investigating the molecular mechanisms related to
[...] Read more.
Safe overwintering is a challenging issue in rearing management that is inevitably faced by beekeepers in high-latitude regions. Under the combined influence of multiple factors, the overwintering loss rate of Western honey bees has risen continuously, and investigating the molecular mechanisms related to safe overwintering has become key. The Hunchun bee, an Apis mellifera ecotype in Jilin Province, China, exhibits strong overwintering ability during an overwintering period of more than five months. To investigate the molecular mechanisms of its cold resistance, we conducted a comparative transcriptomic analysis between the summer breeding period (July) and different overwintering intervals (November, December, January, and February), and then systematically identified key genes and signaling pathways related to cold resistance. The results showed that the highest number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was found between December and July. Compared with July, the upregulated genes in Hunchun bee in December were significantly enriched in several pathways, such as ion transport and neuroactive ligand–receptor interactions, and the downregulated genes were significantly enriched in pathways related to fatty acid metabolism, glutathione metabolism, and the peroxisome. Notably, a total of 378 shared DEGs were obtained from the four comparison groups, and several candidate cold-resistant gene families, such as AFPs, HSPs, C2H2-ZFPs, STKs, and LRRCs, were identified among the shared DEGs of the winter season. Additionally, 749 shared DEGs related to protein modification and metabolic process regulation were identified between the four successive overwintering intervals. Four shared genes, including sensory neuron membrane protein 1 (SNMP1), were revealed by pairwise comparison of the four intervals. The above results collectively indicate that the Hunchun bee attenuates winter-induced stress responses during the overwintering process by maintaining osmotic pressure balance, reducing fatty acid metabolism, increasing antioxidant capacity, and synthesizing cold-resistant macromolecular proteins. It was also found that chemical signal perception may serve a role in maintaining the stability of the overwintering bee colony. The key genes and pathways related to cold resistance identified in this study not only provide a basis for explaining the overwintering molecular mechanism for Apis mellifera of Hunchun bee but also offer key data to improve overwintering management strategies for Western honey bees.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Insect Transcriptomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seasonal Dynamics and Nest Characterization of Vespa orientalis (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in Apiaries: Insights from Bait Trap Capture Efficiency
by
Sabreen G. El-Gohary, Abd El-Aziz M. A. Mohsen, Mohammed A. I. Youssif, Lamya Ahmed Alkeridis, Laila A. Al-Shuraym, Samy Sayed, Mustafa Shukry and Sherin M. M. Y. Helaly
Insects 2026, 17(1), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010058 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study investigated the population dynamics of Vespa orientalis L. (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) across two consecutive seasons (2023–2024) in selected apiaries, with a focus on nest composition (eggs, larvae, and pupae) and the effectiveness of various bait traps for capturing the species. Monthly monitoring
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the population dynamics of Vespa orientalis L. (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) across two consecutive seasons (2023–2024) in selected apiaries, with a focus on nest composition (eggs, larvae, and pupae) and the effectiveness of various bait traps for capturing the species. Monthly monitoring revealed the highest population peaks in October and the lowest in December. Notable inter-seasonal variations in population density were observed across the studied sites. The average number of individuals per nest varied between seasons, reflecting fluctuations in colony development and environmental factors. In 2023, the mean counts of cells, eggs, larvae, and pupae per nest were 30.14, 18.77, 13.33, and 20.88, respectively, while in 2024, they were 10.55, 14.81, 18.02, and 30.43. Among the tested attractants, grape juice proved the most effective, capturing an average of 511.67 hornets, followed by black honey (422.33 hornets), whereas the capturing trap caught only 5 hornets. These findings provide insights into the seasonal activity and reproductive status of V. orientalis and support the development of environmentally friendly capture strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Systematic and Biological Studies on Hymenoptera: Vespidae)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Validation of Stable Reference Genes for RT-qPCR Normalization in Oxycetonia jucunda (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae)
by
Shi-Hang Zhao, Yang Yue, Rui-Tao Yu, Qi Gao, Jia-Qiang Zhao, Sheng-Ping Zhang, Nan Zhou and Guo-Liang Xu
Insects 2026, 17(1), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010057 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
The polyphagous pest Oxycetonia jucunda Faldermann can cause substantial damage to a range of economically important crops, with the adult beetles feeding directly on floral tissues and young leaves. RT-qPCR is widely used to analyze gene expression, for which the selection of stable
[...] Read more.
The polyphagous pest Oxycetonia jucunda Faldermann can cause substantial damage to a range of economically important crops, with the adult beetles feeding directly on floral tissues and young leaves. RT-qPCR is widely used to analyze gene expression, for which the selection of stable reference genes is essential for enabling an accurate normalization of expression. However, no systematic evaluations of suitable reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis using different tissues of O. jucunda have been conducted. To assess their applicability as reliable normalization controls, we used five computational methods to examine the stability of seven potential reference genes (GAPDH, EF1α, RPS3, RPS18, RPL18, RPS31, and UBC5A) across six adult tissues, with three biological replicates per tissue. The findings revealed RPS3 and RPS31 to be the most stably expressed. This pair of reference genes was further validated by normalizing the expression of the odorant-binding protein 3 (OBP3) target gene. Our findings will provide important foundational data for the accurate analysis of functional gene expression in O. jucunda.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Insect Molecular Biology and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Modeling Pine Caterpillar, Dendrolimus spectabilis (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae), Population Dynamics with a Stage-Structured Matrix Model Based on Field Observations
by
Young-Kyu Park, Youngwoo Nam and Won Il Choi
Insects 2026, 17(1), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010056 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Population models offer insights into both theoretical and practical aspects of insect population dynamics. Among the models, stage-structured matrix models are used to describe the population dynamics of insects because the development of insects is by nature stage-structured. Field populations of the pine
[...] Read more.
Population models offer insights into both theoretical and practical aspects of insect population dynamics. Among the models, stage-structured matrix models are used to describe the population dynamics of insects because the development of insects is by nature stage-structured. Field populations of the pine caterpillar, Dendrolimus spectabilis (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae) were monitored in a pine stand located in Dorak-ri, Cheongsan-myeon, Wando-gun, Jeollanam-do, from May 1998 to March 1999, and the pest density was measured as the number of larvae, pupae, or eggs at one-month intervals, excluding the winter season. Life tables and matrix models were constructed based on field observations, and the most vulnerable life stage was identified through sensitivity analysis. The density of the pine caterpillar (number per 1000 cm2 branch) was 7.9 on 8 May 1998, and subsequently decreased to 0.5 on 14 March 1999, showing a decreasing trend of caterpillar density. The population growth rate was 0.74, a decreasing trend. The most vulnerable stages were (1) the larvae immediately after hatching and (2) again during overwintering, probably due to indirect mortality caused by humid conditions and activities of natural enemies during winter. Given the significant damage caused by mature larvae in the spring and that the density of the caterpillar after overwintering typically remains stable, forest management requires that the pest density be monitored soon after overwintering to allow decisions about control measures to be taken. Our results showed that a matrix model is useful to describe the population dynamics of the pine caterpillar and to construct suitable management strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Integrated Pest Management: New Tools and Tactics for Pest Control)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrative Analysis of Antennal Morphology and Olfactory Receptor Gene Expression Across the Three Castes of Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae)
by
Yu Zhang, Lina Guo and Yuan Guo
Insects 2026, 17(1), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010055 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
To systematically investigate how the olfactory system of Bombus terrestris adapts to its social division of labor and reproductive strategies, this study integrated the micromorphology of antennal sensilla and the expression profiles of olfactory receptor (OR) genes from the heads of its three
[...] Read more.
To systematically investigate how the olfactory system of Bombus terrestris adapts to its social division of labor and reproductive strategies, this study integrated the micromorphology of antennal sensilla and the expression profiles of olfactory receptor (OR) genes from the heads of its three castes (workers, drones, and queens) for a multi-level analysis. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed that drones possess significantly longer chaetic sensilla (Sch), sensilla trichodea (Str A/B), and sensilla basiconica (Sba A), as well as larger-diameter sensilla coeloconica (Sco) compared to workers and queens, indicating structural and functional specialization for sensitive detection of single key signals (e.g., queen pheromones). In contrast, workers and queens exhibited a more complete composition of sensilla types and a higher sensilla distribution density, suggesting the construction of a perceptual system capable of processing multiple chemical signals simultaneously. RNA-seq combined with qRT-PCR confirmed the significant upregulation of seven OR genes (e.g., BterOR3, BterOR4) in drones, while workers showed upregulation of BterOR3/5/7 accompanied by enrichment of P450 detoxification pathways. Phylogenetic analysis suggested that BterOR5 serves as a conserved co-receptor, and some OR genes may originate from recent duplication events. In summary, distinct differences were observed in the morphological structure and molecular expression of the olfactory system among B. terrestris castes. Drones exhibited structural and gene expression features consistent with specialization in queen pheromone detection, while workers and queens demonstrated sensilla diversity and olfactory receptor expression patterns indicative of a broader response capacity to diverse chemical signals. These findings support the view that the olfactory system has undergone multi-level adaptive evolution driven by social division of labor and reproductive roles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bumblebee Biology and Ecology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Deciphering Morphological Variability: Addressing Taxonomic Ambiguities in Contemporary Species Delimitation (Hymenoptera, Figitidae)
by
Mar Ferrer-Suay, George E. Heimpel, Ehsan Rakhshani and Jesús Selfa
Insects 2026, 17(1), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010054 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Species delimitation in Charipinae hyperparasitoids (Hymenoptera: Figitidae) is notoriously difficult due to their minute size and limited morphological variability. Traditional diagnostic characters sometimes show intraspecific variation, raising concerns about their reliability. Here, we applied an integrative taxonomic framework to evaluate species boundaries among
[...] Read more.
Species delimitation in Charipinae hyperparasitoids (Hymenoptera: Figitidae) is notoriously difficult due to their minute size and limited morphological variability. Traditional diagnostic characters sometimes show intraspecific variation, raising concerns about their reliability. Here, we applied an integrative taxonomic framework to evaluate species boundaries among six species of Alloxysta Förster and four species of Phaenoglyphis Förster. We combined a morphological dataset of 53 characters with data from three molecular markers (COI, ITS2, and 16S rRNA) and reconstructed phylogenies under maximum-likelihood criteria. Phylogenies consistently recovered morphologically defined taxa as well-supported clades, confirming the overall reliability of traditional characters (pronotal and propodeal carinae, radial cell shape, and flagellomere proportions). On the other hand, molecular evidence refined certain species limits and highlighted cases of potential cryptic variation. Our results demonstrate that morphology still provides a strong baseline for Charipinae taxonomy, but integration with molecular data yields more robust and stable classifications. This study underscores the value of multi-locus approaches for resolving taxonomic ambiguities and provides a framework for future ecological and evolutionary research on these hyperparasitoid wasps.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Selected Papers from the Second International Electronic Conference on Entomology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Honey Bee Body Surface as a Microbial Hub: Connectivity Shaped by Monoculture vs. Polyculture Farming
by
Baobei Guo, Xueyan Yi, Qihang Sun, Ke Sun, Lina Guo and Yuan Guo
Insects 2026, 17(1), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010053 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Honey bees, as vital pollinators and essential contributors to terrestrial ecosystems, play a critical role in maintaining biodiversity and ecological stability. Beyond their role as pollinators, honey bees are increasingly recognized as bioindicators of environmental health, with their microbiomes reflecting habitat quality, agricultural
[...] Read more.
Honey bees, as vital pollinators and essential contributors to terrestrial ecosystems, play a critical role in maintaining biodiversity and ecological stability. Beyond their role as pollinators, honey bees are increasingly recognized as bioindicators of environmental health, with their microbiomes reflecting habitat quality, agricultural practices, and broader ecological conditions. This study examines the impact of monoculture and polyculture systems on bee-associated microbiomes, focusing on microbial diversity, composition, and functional roles. Microbial communities from floral surfaces, pollen, nectar, foraging bees, hive matrices, and bioaerosols were analyzed across three agricultural plots: a rape monoculture, a pear monoculture, and a polyculture plot. Using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing, network co-occurrence analysis, and microbial source tracking, the findings reveal that plant species and cultivation methods significantly shape microbial dynamics (Adonis = 0.67 ***). Floral microbiomes exhibit host specificity (Adonis = 0.73 ***), while the honey bee body surface functions as a microbial hub linking environmental, floral, and hive microbial networks (average degree pear: 21.86; rape: 21.96). The polyculture system improves microbial diversity due to the diversity of nectar plants, enhancing ecosystem connectivity and potentially benefiting honey bee health. These results highlight the ecological importance of optimizing agricultural practices to preserve microbial diversity, enhance honey bee health, and maintain ecological stability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Advances in Pollinator Insects)
►▼
Show Figures
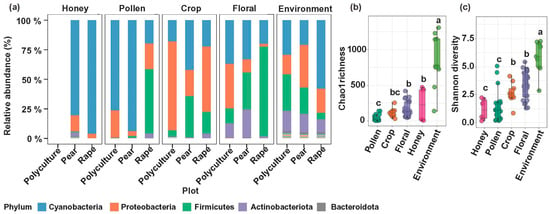
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Characterization of the Bacteriome of Culicoides reevesi from Chihuahua, Northern Mexico: Symbiotic and Pathogenic Associations
by
Rodolfo González-Peña, David Orlando Hidalgo-Martínez, Stephanie V. Laredo-Tiscareño, Herón Huerta, Erick de Jesús de Luna-Santillana, Jaime R. Adame-Gallegos, Carlos A. Rodríguez-Alarcón, Ezequiel Rubio-Tabares, Julián E. García-Rejón, Zilia Y. Muñoz-Ramírez, Chandra Tangudu and Javier A. Garza-Hernández
Insects 2026, 17(1), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010052 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Culicoides biting midges are vectors of veterinary and zoonotic pathogens, yet the bacteriome of several species remains unexplored. Culicoides reevesi, a poorly studied species in northern Mexico, represents an opportunity to investigate microbial associations that may influence vector biology. Adults of C.
[...] Read more.
Culicoides biting midges are vectors of veterinary and zoonotic pathogens, yet the bacteriome of several species remains unexplored. Culicoides reevesi, a poorly studied species in northern Mexico, represents an opportunity to investigate microbial associations that may influence vector biology. Adults of C. reevesi were analyzed using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing, followed by functional prediction with PICRUSt2. Heatmaps and pathway summaries were generated to highlight dominant taxa and functions. The bacteriome was dominated by Pseudomonadota, followed by Actinomycetota, Bacillota, and Bacteroidota. Symbiotic taxa such as Asaia and Cardinium were identified alongside potentially pathogenic bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Mycobacterium avium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Enterococcus faecalis. Functional predictions indicated metabolic versatility, with abundant pathways related to aerobic respiration, the TCA cycle, amino acid biosynthesis, and quorum sensing. Despite all samples being collected from the same site and date, apparent differences in bacterial composition were observed across pools, suggesting microhabitat or host-related variability. This study provides the first taxonomic and functional baseline of the C. reevesi bacteriome. The detection of both symbiotic and pathogenic bacteria highlights the dual ecological role of the microbiome in host fitness and pathogen transmission potential. In conclusion, we suggest that these microbial associations influence vector physiology and competence, providing a basis for future microbiome-based control strategies. These findings emphasize the importance of integrating microbiome analyses into entomological surveillance and vector control strategies in endemic regions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Diversity of Insect-Associated Microorganisms)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Compound Fungicide Impairs Cognitive Performance in Honey Bees (Apis mellifera)
by
Xufeng Zhang, Qian Cao, Qihang Sun, Yuting Tian, Yinyin Du and Yuan Guo
Insects 2026, 17(1), 51; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010051 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
Fungicides play a critical role in crop protection, yet their potential threats to pollinator remain a concern. This study investigated the sublethal effects of a commercial fungicide, Chunmanchun® (a suspension-emulsion of 7% propiconazole and 28% carbendazim), on cognitive functions of the honey
[...] Read more.
Fungicides play a critical role in crop protection, yet their potential threats to pollinator remain a concern. This study investigated the sublethal effects of a commercial fungicide, Chunmanchun® (a suspension-emulsion of 7% propiconazole and 28% carbendazim), on cognitive functions of the honey bee (Apis mellifera). Using the proboscis extension reflex (PER) assay, we evaluated sucrose sensitivity and olfactory learning and memory in workers exposed to the recommended field concentration (PC), along with sublethal (LD10) and semi-lethal (LD50) concentrations. Fungicide exposure significantly reduced sucrose sensitivity across all concentrations tested (0.1%, 1%, and 3%), with the strongest reductions occurring at the LD10 and LD50 levels. While olfactory associative learning was not significantly impaired, memory retention was adversely affected. Bees in the LD50 group showed significantly reduced PER rates at both1 h and 6 h post-training, and LD10 and LD50 groups exhibited significant memory deficits by 1 h and 6 h relative to the control. These results demonstrate that Chunmanchun® impairs both sucrose responsiveness and olfactory memory in honey bees, which may impair foraging efficiency and ultimately affect colony performance. This study highlights a potential ecological risk posed by this fungicide to pollinators in agricultural environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biology and Conservation of Honey Bees)
►▼
Show Figures
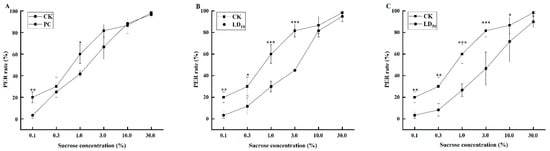
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The First Record of Whitefly (Hemiptera, Sternorrhyncha, Aleyrodidae) from Bitterfeld Amber
by
Jowita Drohojowska, Anita Gorzelańczyk, Natalia Tomanek, Małgorzata Kalandyk-Kołodziejczyk and Jacek Szwedo
Insects 2026, 17(1), 50; https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010050 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
A male specimen of whitefly Pudrica christianottoi Drohojowska et Szwedo, 2024, of subfamily Aleyrodinae, previously known from the sole female specimen from Lower Lusatia succinite, is here described, based on an inclusion from Bitterfeld amber. This fossil is contributing new data to our
[...] Read more.
A male specimen of whitefly Pudrica christianottoi Drohojowska et Szwedo, 2024, of subfamily Aleyrodinae, previously known from the sole female specimen from Lower Lusatia succinite, is here described, based on an inclusion from Bitterfeld amber. This fossil is contributing new data to our understanding of morphological disparity, sexual dimorphism, taxonomic diversity and palaeobiogeographic distribution of the whiteflies in the Eocene fossil resins. It is also a contribution to the ongoing discussions on age, similarities, dissimilarities and taphonomic differences among Eocene resins of Europe collectively known as ‘Baltic amber’.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fossil Insects: Diversity and Evolutionary History)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Insects Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Animals, Arthropoda, Diversity, Insects, Life, Pathogens
Arthropod Biodiversity: Ecological and Functional Aspects, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Paolo Solari, Roberto M. Crnjar, Anita Giglio, Gianluca TettamantiDeadline: 31 January 2026
Topic in
Applied Microbiology, Forests, Insects, JoF, Microorganisms
Diversity of Insect-Associated Microorganisms
Topic Editors: Dilnora E. Gouliamova, Teun BoekhoutDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
Animals, Arthropoda, Insects, Vaccines, Veterinary Sciences, Pathogens
Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogens: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Alina Rodriguez-Mallon, Alejandro Cabezas-CruzDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Crops, Insects, Plants, Agrochemicals, IJPB
Exploring Plant-Derived Compounds for Effective Insect Pest Management in Agriculture
Topic Editors: Ian Scott, Roselyne M. LabbéDeadline: 31 May 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Insects
Insect Mouthparts: Evolution, Biomechanics, and Ecological Significance
Guest Editor: Matthew LehnertDeadline: 15 January 2026
Special Issue in
Insects
Taxonomy and Phylogeny and Evolution of Parasitic Hymenoptera and Biological Control
Guest Editors: Pu Tang, Deqiang Pu, Shu-Jun WeiDeadline: 15 January 2026
Special Issue in
Insects
Bee Conservation: Behavior, Health and Pollination Ecology
Guest Editor: Kit S. PrendergastDeadline: 15 January 2026
Special Issue in
Insects
Advances in the Health, Behavior, and Physiology of Honeybees and Other Pollinators
Guest Editors: Giovanni Formato, Franco MutinelliDeadline: 15 January 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Insects
Cultural Entomology: Our Love-hate Relationship with Insects
Collection Editor: Joseph R. Coelho
Topical Collection in
Insects
Integrated Management and Impact of Stored-Product Pests
Collection Editor: Georgina V. Bingham
Topical Collection in
Insects
Edible Insects and Circular Economy
Collection Editors: Costanza Jucker, Sara Savoldelli, Thomas Spranghers