Evolution Properties of Tribological Parameters for Steel Wire Rope under Sliding Contact Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evolution of the Coefficient of Friction under Different Strokes and Loads
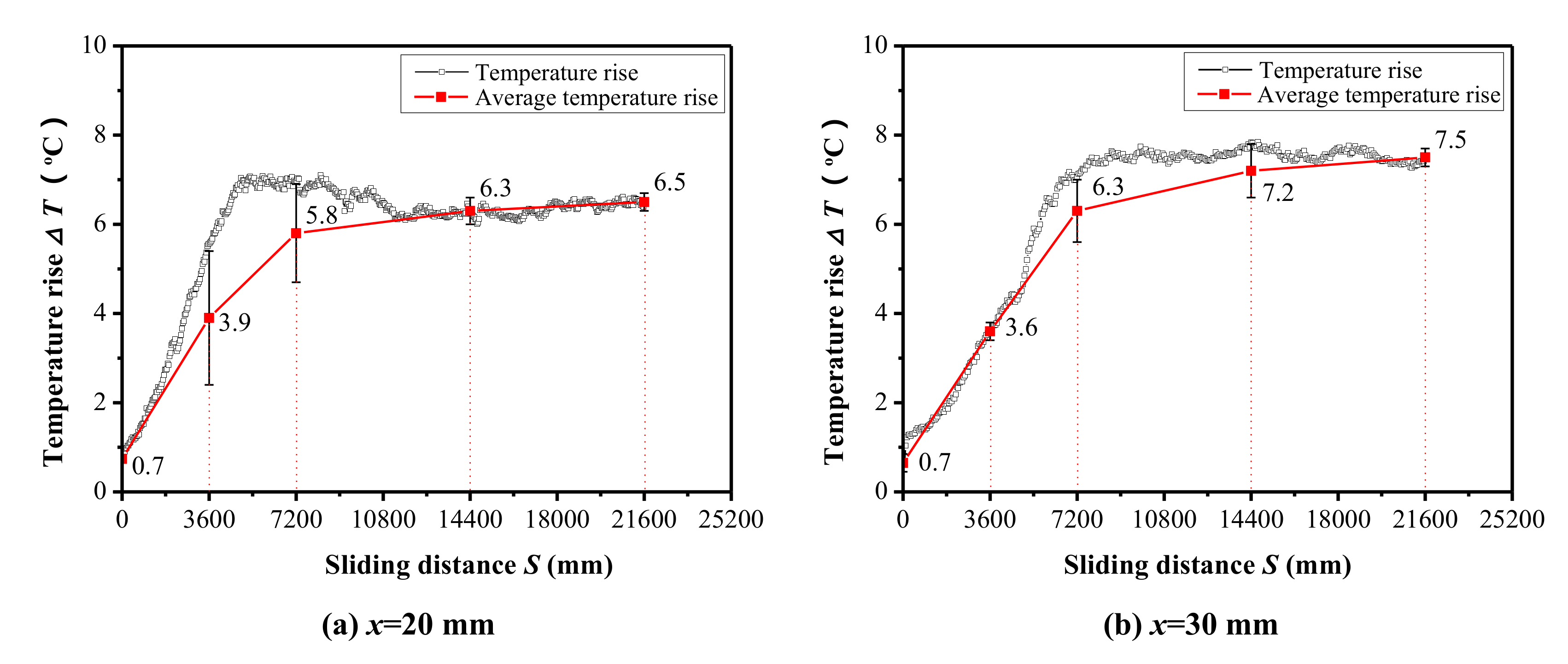
3.2. Evolution of Friction Temperature Rise
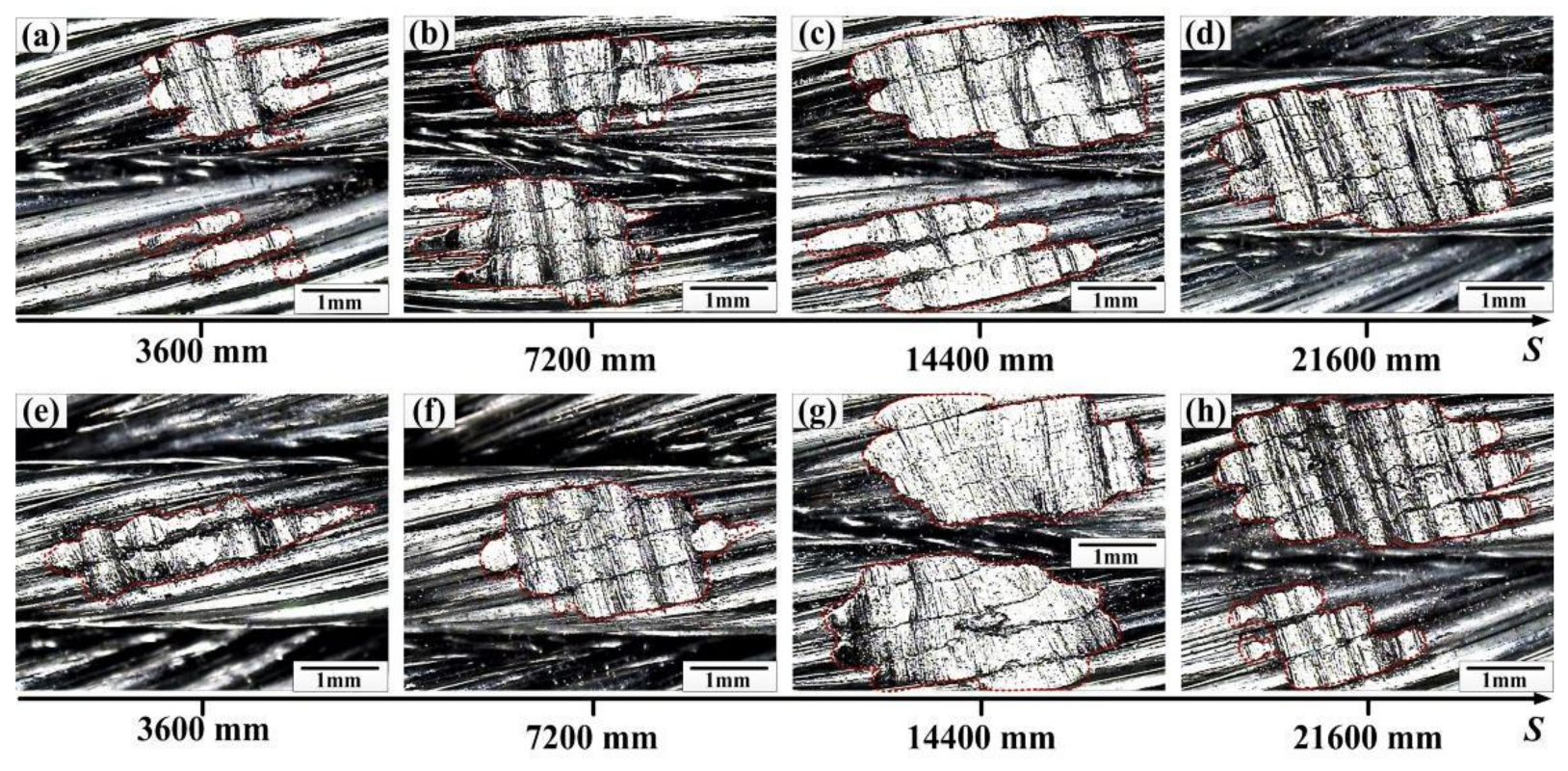
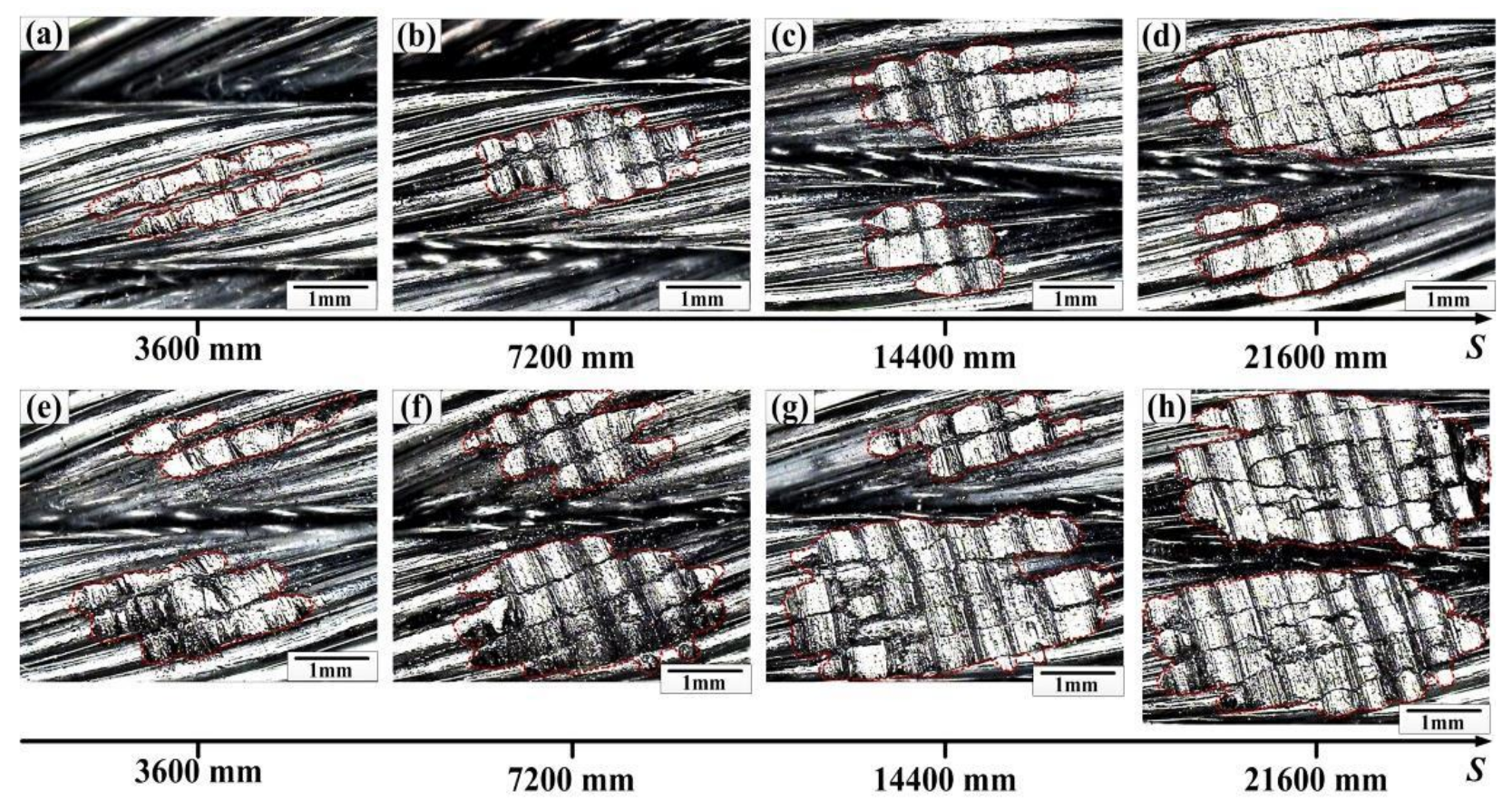
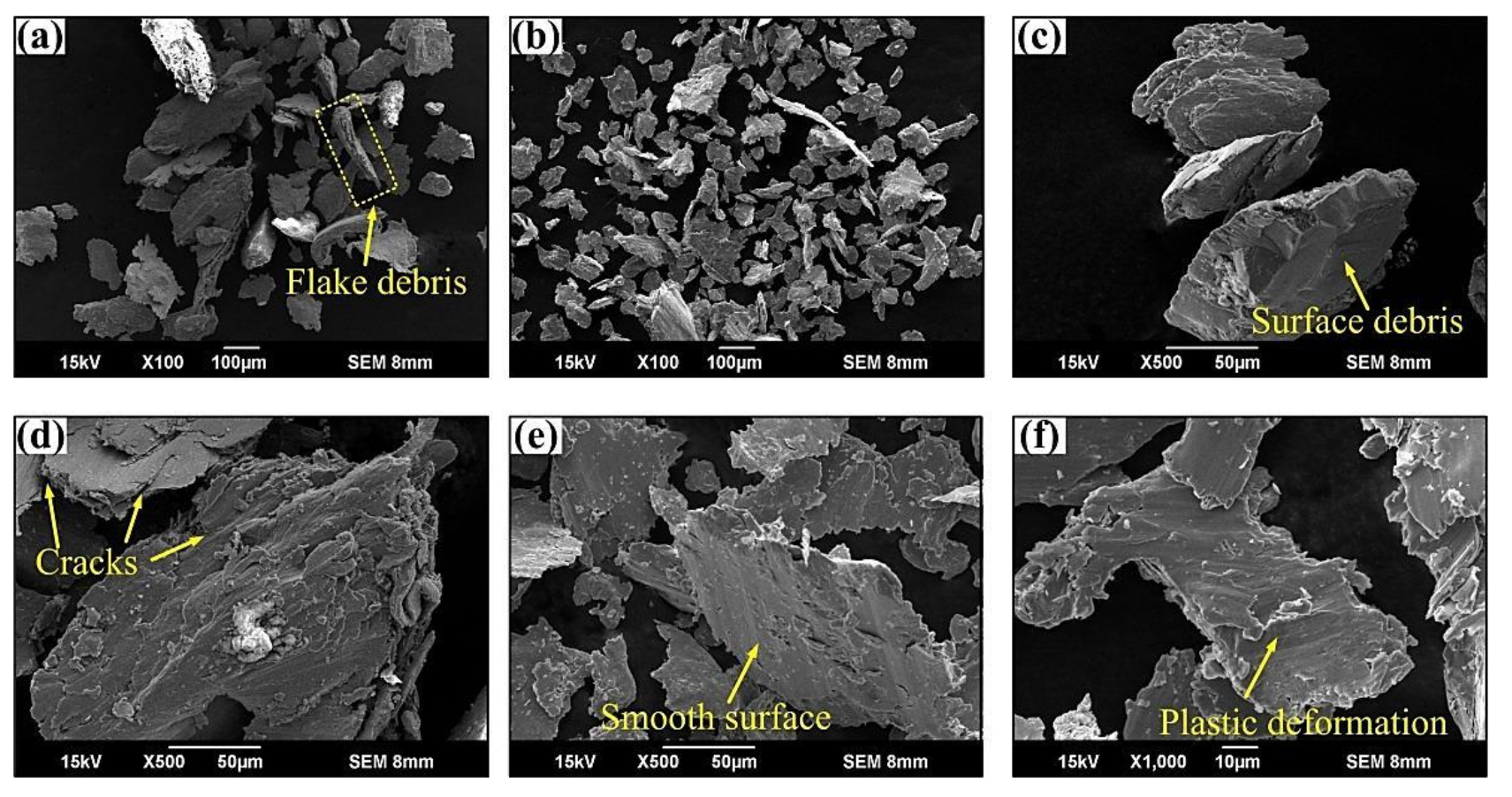
3.3. Wear Charcteristics
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The fluctuation of the friction is larger in the early stage of the experiment, especially around 10 min. The obvious peaks of the curve mainly depend on the stroke. Additionally, there are three strong fluctuation regions for the stroke of 30 mm.
- (2)
- The evolution of the COF can be divided into a rapid-increase stage (before 7200 mm) and a relatively stable stage (after 14,400 mm). The COF increases from approximately 0.48 to 0.61 with the sliding distance when the contact load is 150 N, which is the most rapid growth.
- (3)
- The evolution of temperature rise in the wear region with the sliding distance is obvious. The maximum temperature rises are approximately 7.5 °C and 7.1 °C under the large stroke (30 mm) and contact load (150 N), respectively, which are much larger than those under the small stroke (20 mm) and load (50 N).
- (4)
- The wear scar region increases with the sliding distance, especially from 3600 mm to 14,400 mm. Additionally, the wear loss of the rope is a growing process with the sliding distance and the values under the large stroke and load are much higher. The maximum wear loss is approximately 65.5 mg at the contact load of 150 N.
- (5)
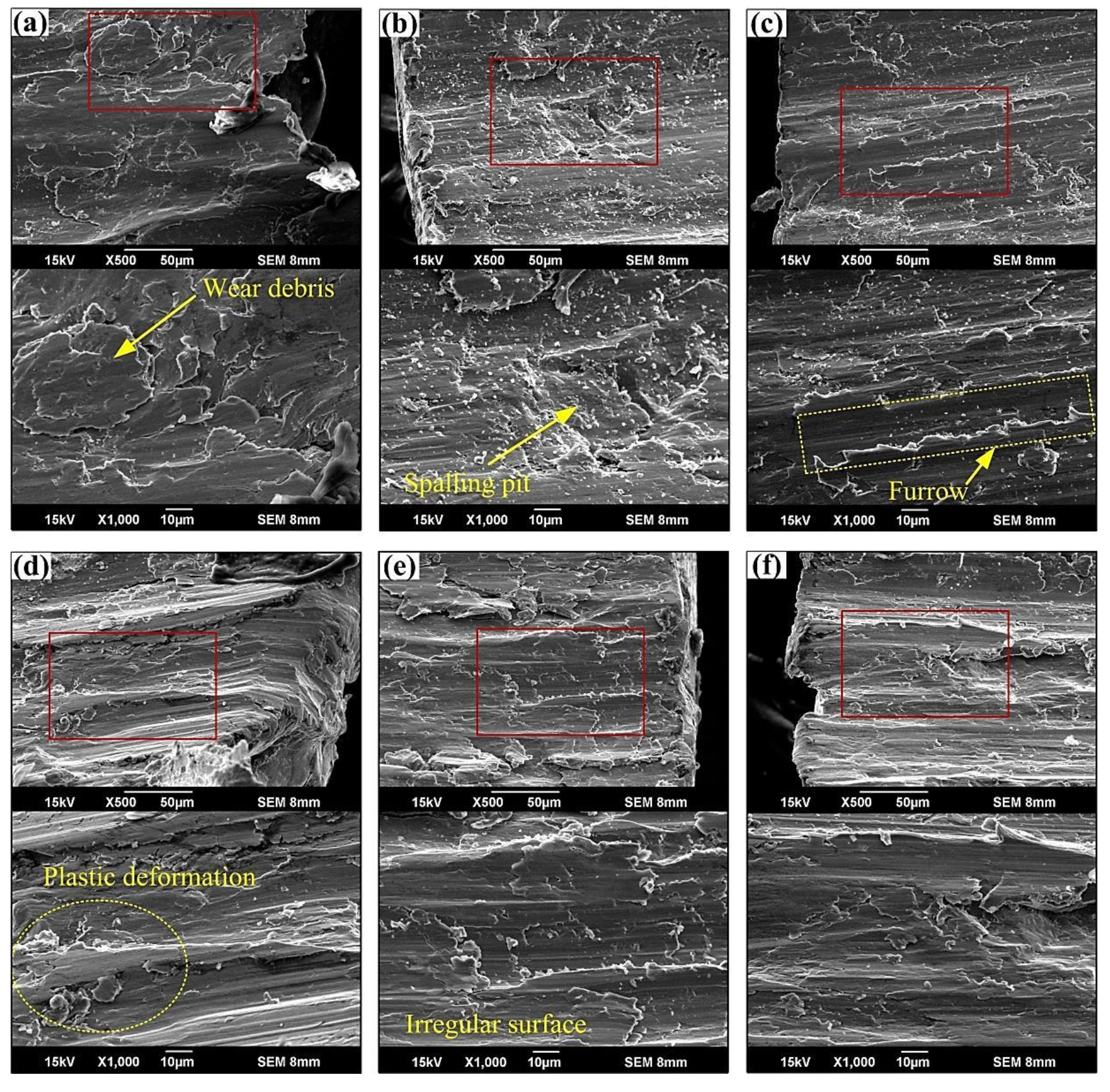
- The wear debris resembles thin flakes and the wear characteristics of the wear surface are cracks, fatigue spalling, furrows, and plastic deformation. Additionally, the wear mechanisms are fatigue and adhesion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, X.D.; Peng, Y.X.; Zhu, Z.C.; Gong, X.S.; Yu, Z.F.; Mi, Z.T.; Xu, C.M. Effects of Strand Lay Direction and Crossing Angle on Tribological Behavior of Winding Hoist Rope. Materials 2017, 10, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.D.; Peng, Y.X.; Zhu, Z.C.; Gong, X.S.; Yu, Z.F.; Mi, Z.T.; Xu, C.M. Experimental investigation of mechanical response and fracture failure behavior of wire rope with different given surface wear. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanari, V.; Benedetti, M.; Monelli, B.D. Elasto-plastic behavior of a Warrington-Seale rope: Experimental analysis and finite element modeling. Eng. Struct. 2015, 82, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Meng, X.B.; Wang, J.X.; Sun, Y.H.; Gao, K. Mathematical modeling and geometric analysis for wire rope strands. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.K.; Ge, S.R.; Qiang, Y.H. Research on the fatigue and fracture behavior due to the fretting wear of steel wire in hoisting rope. Wear 2003, 255, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.X.; Chang, X.D.; Zhu, Z.C.; Wang, D.G.; Gong, X.S.; Zou, S.Y.; Sun, S.S.; Xu, W.X. Sliding friction and wear behavior of winding hoisting rope in ultra-deep coal mine under different conditions. Wear 2016, 368, 423–434. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Mallick, M.; Verma, M.K. Studies on metallurgical properties of wire rope for safe operation in mines. J. Mines Met. Fuels 2011, 59, 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Mallick, M.; Verma, M.K. Studies on failure behavior of wire rope used in underground coal mines. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 70, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Coal Industry. The Coal Mine Safety Rules; Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1986.
- Chaplin, C.R. Failure mechanisms in wire ropes. Eng. Fail. Anal. 1995, 2, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrems, K.; Maclaren, D. Failure analysis of a mine hoist rope. Eng. Fail. Anal. 1997, 4, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterka, P.; Krešák, J.; Kropuch, S.; Fedorko, G.; Molnar, V.; Vojtko, M. Failure analysis of hoisting steel wire rope. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 45, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabay, S.; Ertürk, A.T.; Zeren, M.; Yamanoğlu, R.; Karakulak, E. Failure analysis of wire-breaks in aluminum conductor production and investigation of early failure reasons for transmission lines. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 83, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzado, A.; Hartelt, M.; Wäsche, R.; Urchegui, M.A.; Gómez, X. Fretting wear of thin steel wires Part 1: Influence of contact pressure. Wear 2010, 268, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzado, A.; Hartelt, M.; Wäsche, R.; Urchegui, M.A.; Gómez, X. Fretting wear of thin steel wires Part 2: Influence of crossing angle. Wear 2011, 273, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.G.; Zhang, D.K.; Ge, S.R. Effect of displacement amplitude on fretting fatigue behavior of hoisting rope wires in low cycle fatigue. Tribol. Int. 2012, 52, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.M.; Zhang, D.K.; Yin, Y. Fretting wear behaviors of hoisting rope wires in acid medium. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.G.; Zhang, D.K.; Zhao, W.J.; Ge, S.R. Quantitative analyses of fretting fatigue damages of mine rope wires in different corrosive media. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 596, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.G.; Li, X.W.; Wang, X.R.; Zhang, D.K.; Wang, D.A. Dynamic wear evolution and crack propagation behaviors of steel wires during fretting-fatigue. Tribol. Int. 2016, 101, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Z.F. Fretting fatigue behavior of steel wires contact interface under different crossing angles. Wear 2018, 400, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Wang, D.G.; Zhang, D.K.; Ge, S.R.; Araújo, J.A. Effect of torsion angle on tension-torsion multiaxial fretting fatigue behaviors of steel wires. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 106, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Wang, D.G.; Li, X.W.; Zhang, D.K.; Ge, S.R.; Araújo, J.A. Comparative analyses of torsional fretting, longitudinal fretting and combined longitudinal and torsional fretting behaviors of steel wires. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 85, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, S.R.; Shipway, P.H.; Abere, J.O.; Hewitt, R.A.A. The effect of temperature on wear and friction of a high strength steel in fretting. Wear 2013, 303, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkavrh, I.; Ausserer, F.; Klien, S.; Brenner, J.; Forêt, P.; Diem, A. The effect of gaseous atmospheres on friction and wear of steel–steel contacts. Tribol. Int. 2014, 79, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, M.R.; Neu, R.W. Temperature-dependent fretting damage of high strength stainless steel sheets. Wear 2016, 346, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkavrh, I.; Ausserer, F.; Klien, S.; Voyer, J.; Ristow, A.; Brenner, J.; Forêt, P.; Diem, A. The influence of temperature on friction and wear of unlubricated steel/steel contacts in different gaseous atmospheres. Tribol. Int. 2016, 98, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemani, M.; Gialanella, S.; Straffelini, G.; Ciudin, R.; Olofsson, U.; Perricone, G.; Metinoz, I. Dry sliding of a low steel friction material against cast iron at different loads: Characterization of the friction layer and wear debris. Wear 2017, 376, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, V.; Andersson, P.; Valtonen, K.; Holmberg, K.; Kuokkala, V.T. Characterization of the wear of nodular cast iron rollers in contact with wire ropes. Wear 2013, 308, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, V.; Valtonen, K.; Andersson, P.; Vaajoki, A.; Laukkanen, A.; Holmberg, K.; Kuokkala, V.T. Comparison of laboratory rolling–sliding wear tests with in-service wear of nodular cast iron rollers against wire ropes. Wear 2015, 340, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urchegui, M.A.; Tato, W.; Gómez, X. Wear evolution in a stranded rope subjected to cyclic bending. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2008, 17, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.K.; Feng, C.A.; Chen, K.; Wang, D.G.; Ni, X. Effect of broken wire on bending fatigue characteristics of wire ropes. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 103, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.G.; Zhang, D.K.; Wang, S.Q.; Ge, S.R. Finite element analysis of hoisting rope and fretting wear evolution and fatigue life estimation of steel wires. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 27, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.G.; Zhang, D.K.; Ge, S. Finite element analysis of fretting fatigue behavior of steel wires and crack initiation characteristics. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 28, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzado, A.; Urchegui, M.A.; Gómez, X. Finite element modeling and experimental validation of fretting wear scars in thin steel wires. Wear 2012, 289, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzado, A.; Urchegui, M.A.; Gómez, X. Finite element modeling of fretting wear scars in the thin steel wires: Application in crossed cylinder arrangements. Wear 2014, 318, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.X.; Chang, X.D.; Sun, S.S.; Zhu, Z.C.; Gong, X.S.; Zou, S.Y.; Xu, W.X.; Mi, Z.T. The friction and wear properties of steel wire rope sliding against itself under impact load. Wear 2018, 400, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.D.; Peng, Y.X.; Zhu, Z.C.; Wang, D.G.; Gong, X.S.; Zou, S.Y.; Sun, S.S.; Xu, W.X. Tribological properties of winding hoisting rope between two layers with different sliding parameters. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter of the rope (mm) | 9.3 |
| Diameter of the wires (mm) | 0.6 |
| Strand lay direction | Right |
| Wire lay direction | Left |
| Strand lay angle (°) | 15.5 |
| Strand lay length (mm) | 70 |
| Outer wire lay length (mm) | 35 |
| Internal wire lay length (mm) | 20 |
| Nominal tensile strength (MPa) | 1570 |
| Breaking force (kN) | 52.5 |
| Test Parameter | Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact load (P) | 100 N | 100 N | 50 N | 150 N |
| Stroke (x) | 20 mm | 30 mm | 20 mm | 20 mm |
| Test time (t/min) | 5; 10; 20; 30 | 5; 10; 20; 30 | 5; 10; 20; 30 | 5; 10; 20; 30 |
| Number of cycles (n) | 90; 180; 360; 540 | 60; 120; 240; 360 | 90; 180; 360; 540 | 90; 180; 360; 540 |
| Sliding distance (S/mm) | 3600; 7200; 14,400; 21,600 | 3600; 7200; 14,400; 21,600 | 3600; 7200; 14,400; 21,600 | 3600; 7200; 14,400; 21,600 |
| Velocity (v) | 12 mm/s | 12 mm/s | 12 mm/s | 12 mm/s |
| Crossing angle (α) | 90° | 90° | 90° | 90° |
| Tensile force | 1000 N | 1000 N | 1000 N | 1000 N |
| Lubricant condition | Dry-friction | Dry-friction | Dry-friction | Dry-friction |
| Room temperature | 25 °C | 25 °C | 25 °C | 25 °C |
| Humidity (%) | 65 ± 5 | 65 ± 5 | 65 ± 5 | 65 ± 5 |
| Atmosphere | Laboratory air | Laboratory air | Laboratory air | Laboratory air |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, X.-D.; Peng, Y.-X.; Zhu, Z.-C.; Zou, S.-Y.; Gong, X.-S.; Xu, C.-M. Evolution Properties of Tribological Parameters for Steel Wire Rope under Sliding Contact Conditions. Metals 2018, 8, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100743
Chang X-D, Peng Y-X, Zhu Z-C, Zou S-Y, Gong X-S, Xu C-M. Evolution Properties of Tribological Parameters for Steel Wire Rope under Sliding Contact Conditions. Metals. 2018; 8(10):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100743
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Xiang-Dong, Yu-Xing Peng, Zhen-Cai Zhu, Sheng-Yong Zou, Xian-Sheng Gong, and Chun-Ming Xu. 2018. "Evolution Properties of Tribological Parameters for Steel Wire Rope under Sliding Contact Conditions" Metals 8, no. 10: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100743
APA StyleChang, X.-D., Peng, Y.-X., Zhu, Z.-C., Zou, S.-Y., Gong, X.-S., & Xu, C.-M. (2018). Evolution Properties of Tribological Parameters for Steel Wire Rope under Sliding Contact Conditions. Metals, 8(10), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100743






