Carbon Redistribution in Martensite in High-C Steel: Atomic-Scale Characterization and Modelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
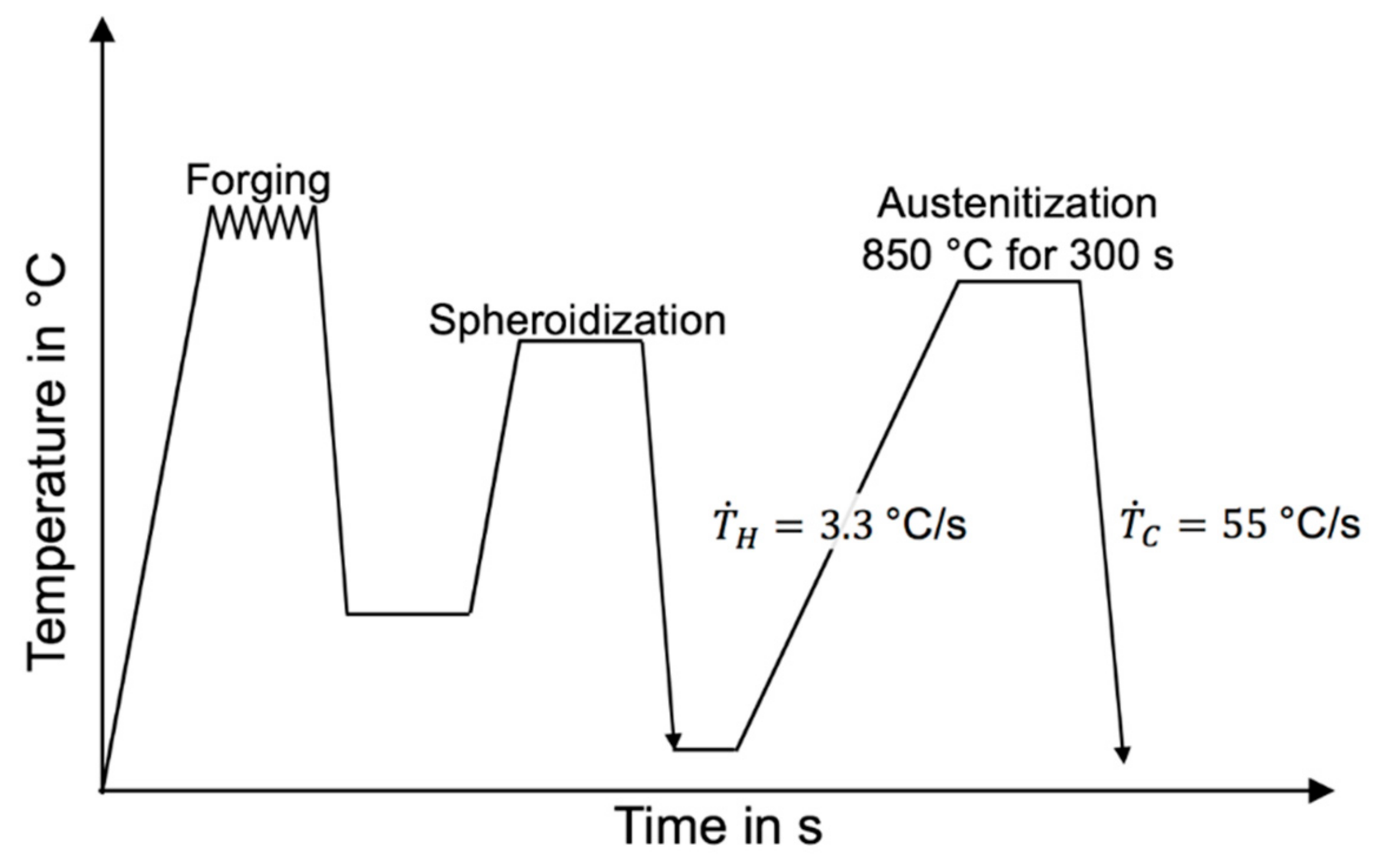
2. Experimental
3. Results
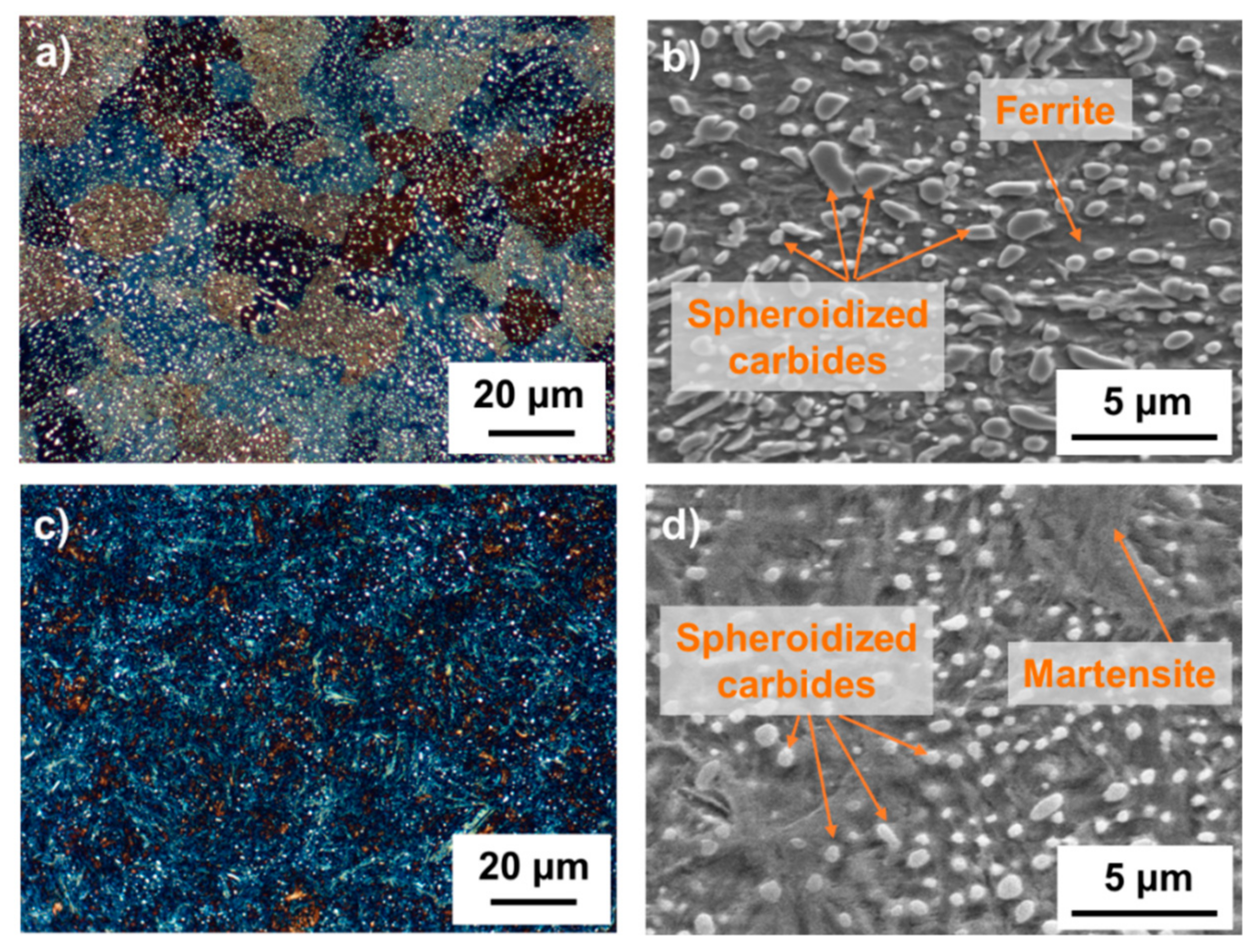
3.1. Metallography and Microstructure
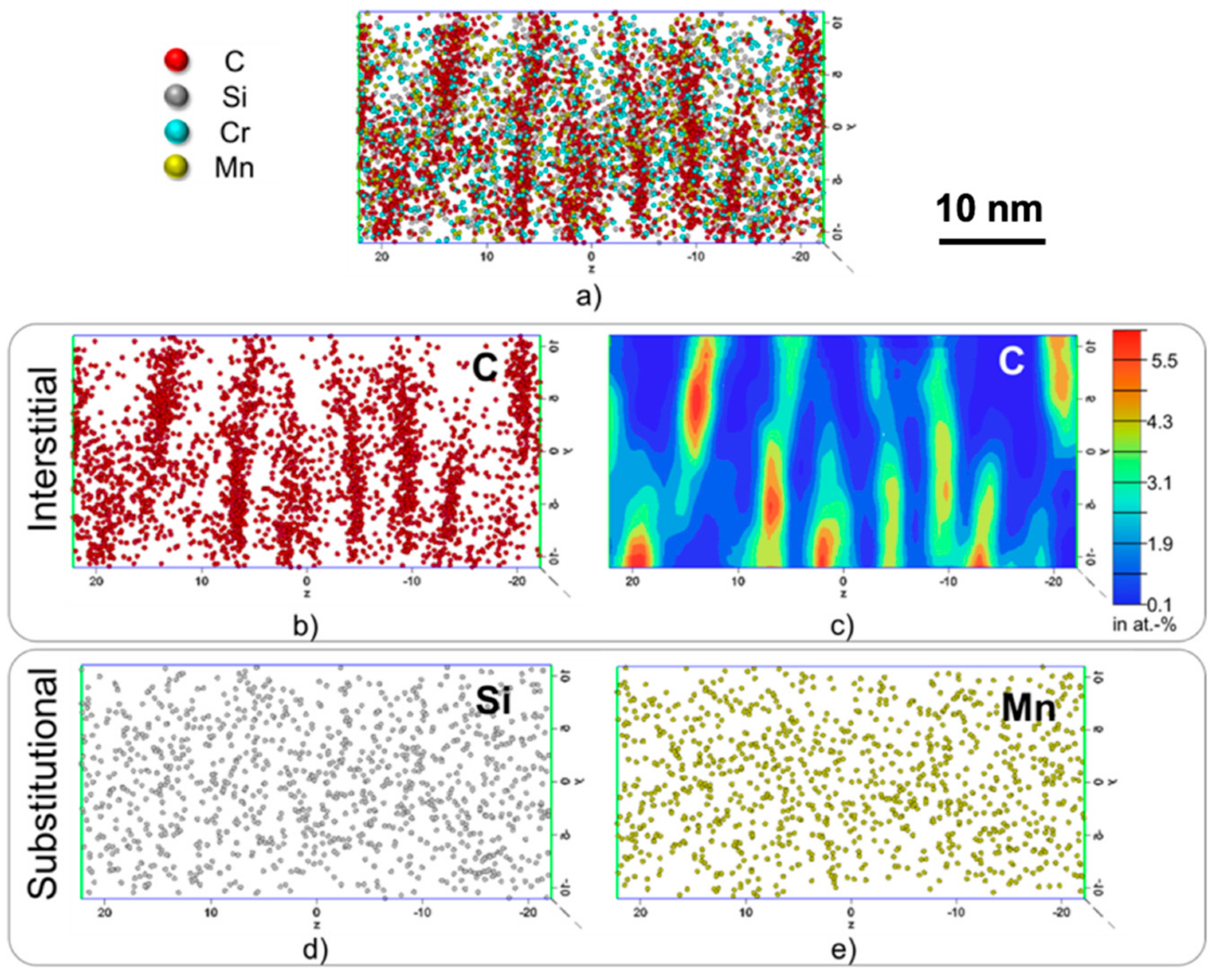
3.2. Atom Probe Tomograpy
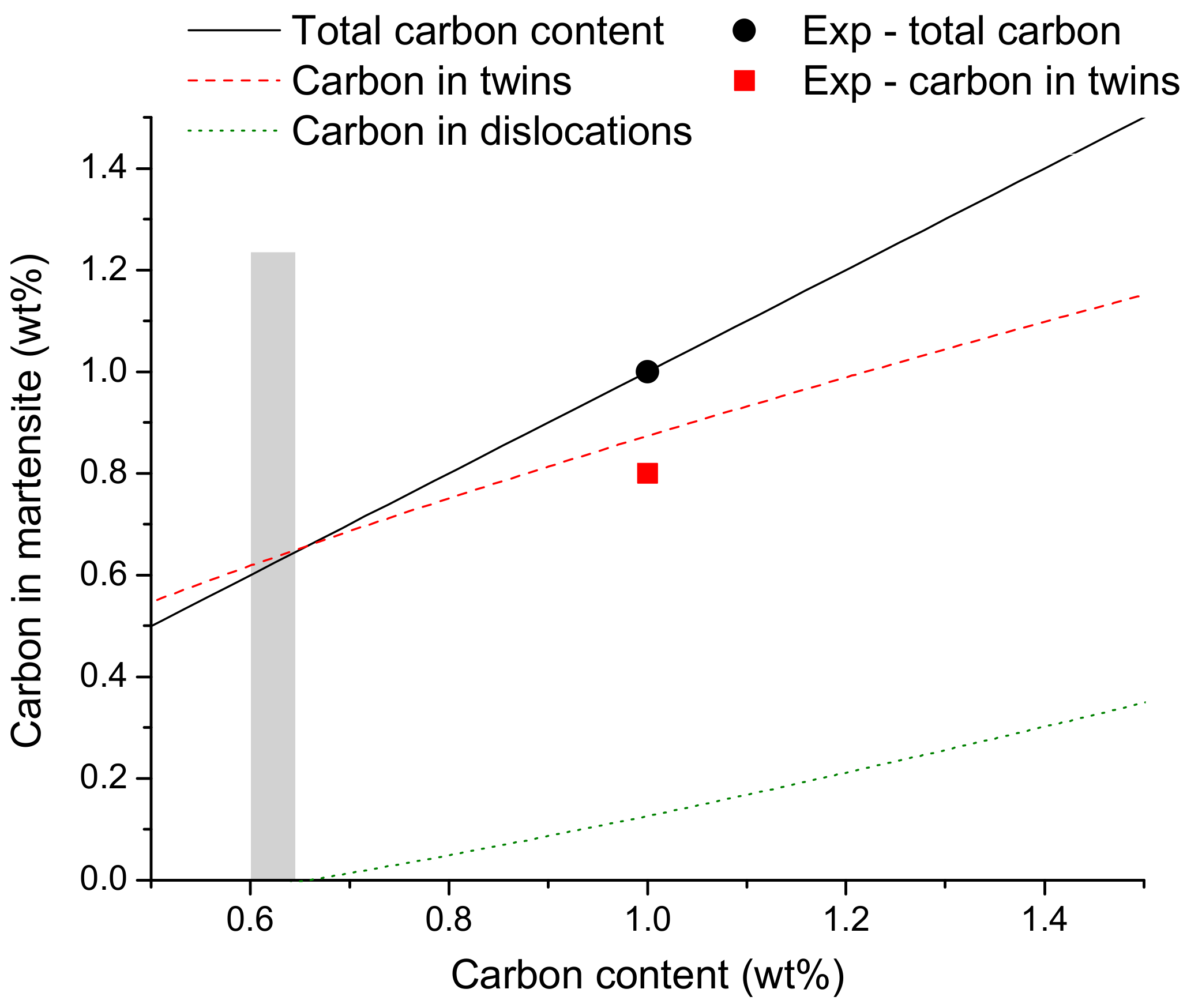
3.3. Modelling Carbon Redistribution in A Martensite Plate
4. Discussion
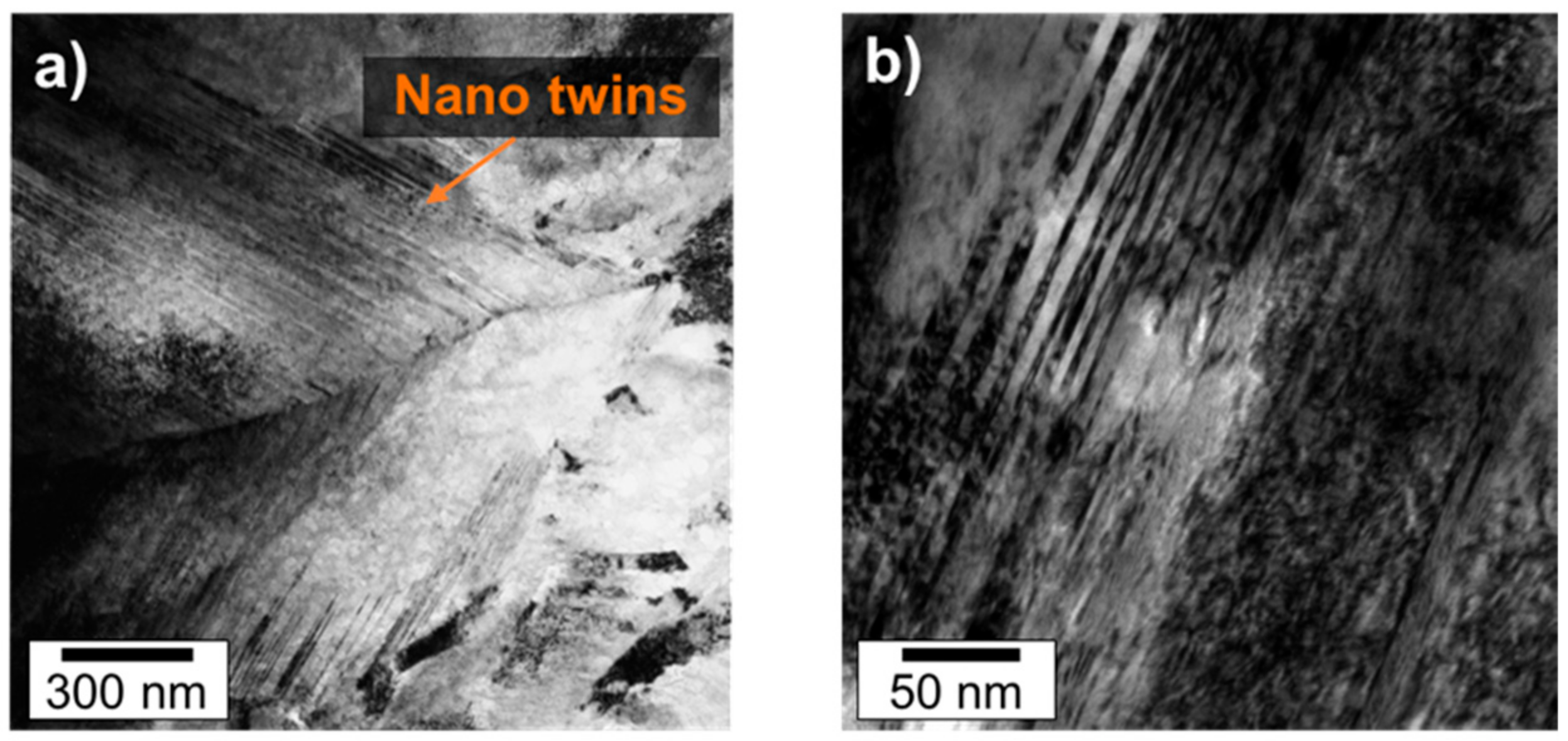
4.1. Carbon Enrichment at Twin Boundary Interfaces in Plate Martensite
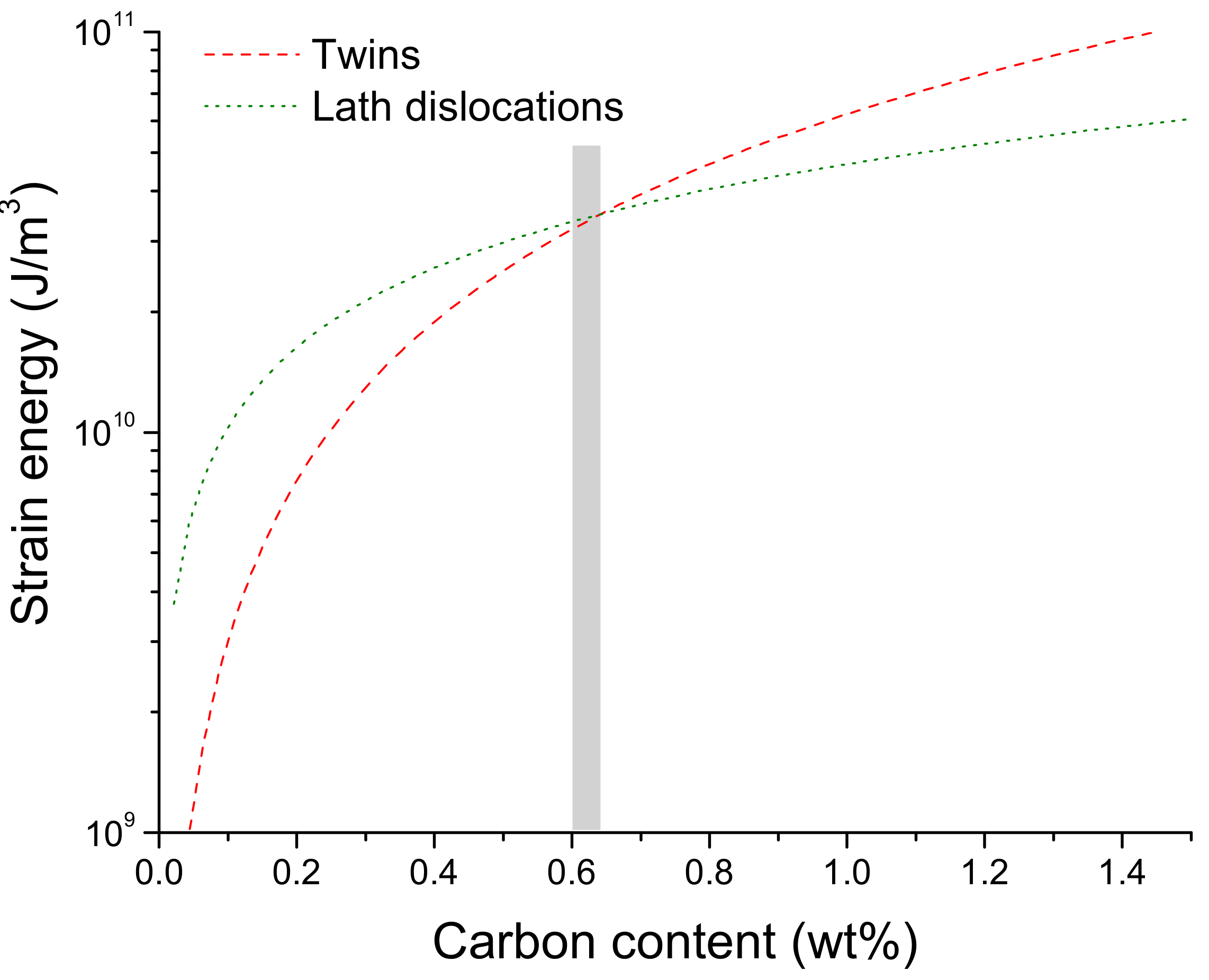
4.2. Strain Energy Accommodated by Martensite Laths and Plates in Fe-C Steels
5. Conclusions
- After quenching, the microstructure exhibits a martensitic matrix with partially dissolved spheroidized carbides with an average size of 0.49 ± 0.02 µm in 100Cr6 bearing steel. The austenitization and the subsequent quenching facilitate the spheroidized particles to become more spherical and smaller.
- The length and thickness of the nano-sized twins in plate martensite in 100Cr6 is in the range of 100–500 nm and 5–10 nm, respectively.
- The C-content at twin boundaries has an approximate average of 4.5 at%, while the substitutional elements, such as Si, Mn and Cr, display no evidence of segregation at the twin boundary.
- It was predicted and validated that most of the carbon atoms segregate to the twins located at the midribs and a low fraction of carbon was located at dislocations in the interior of the plate. It was also shown that the mean spacing of nano-sized twins is dictated by the carbon additions in the steel as twins are able to accommodate the lattice distortions during the transformation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krauss, G. Steels: Processing, Structure, and Performance, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 1915; ISBN 978-1-62708-083-5. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, A.T.W.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Nanoprecipitation in bearing steels. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 7155–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.J.; Miller, M.K.; Field, R.D.; Coughlin, D.R.; Gibbs, P.J.; Clarke, K.D.; Alexander, D.J.; Powers, K.A.; Papin, P.A.; Krauss, G. Atomic and nanoscale chemical and structural changes in quenched and tempered 4340 steel. Acta Mater. 2014, 77, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Choi, P.P.; Inden, G.; Prahl, U.; Raabe, D.; Bleck, W. On the Spheroidized Carbide Dissolution and Elemental Partitioning in High Carbon Bearing Steel 100Cr6. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stormvinter, A.; Hedström, P.; Borgenstam, A. A Transmission Electron Microscopy Study of Plate Martensite Formation in High-carbon Low Alloy Steels. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Herbig, M.; Goto, S.; Raabe, D. Atomic scale characterization of white etching area and its adjacent matrix in a martensitic 100Cr6 bearing steel. Mater. Charact. 2017, 123, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, A.T.W.; Kang, J.H.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. The ϵ→η→θ transition in 100Cr6 and effect on mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2805–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, A.; Murakami, T.; Morito, S.; Furuhara, T.; Maki, T. The Origin of Midrib in Lenticular Martensite. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Yen, H.W.; Chang, H.T. Martensite Midrib in an Fe-1C-17Cr Stainless Steel. Solid State Phenom. 2011, 172–174, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toji, Y.; Miyamoto, G.; Raabe, D. Carbon partitioning during quenching and partitioning heat treatment accompanied by carbide precipitation. Acta Mater. 2015, 86, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Understanding the factors controlling the hardness in martensitic steels. Scr. Mater. 2016, 110, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvesvaran, P. A study on morphology and plate mean dimensions in Fe-Ni and Fe-Ni-Cr alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1996, 27, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherby, O.D.; Wadsworth, J.; Lesuer, D.R.; Syn, C.K. Revisiting the Structure of Martensite in Iron-Carbon Steels. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. A model for the microstructure behaviour and strength evolution in lath martensite. Acta Mater. 2015, 98, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.K.; Beaven, P.A.; Smith, G.D.W. A study of the early stages of tempering of iron-carbon martensites by atom probe field ion microscopy. Metall. Trans. A 1981, 12, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beswick, J.M. The effect of chromium in high carbon bearing steels. Metall. Trans. A 1987, 18, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.A.; Olson, G.B.; Cohen, M.; Sande, J.B.V. Carbide precipitation during stage I tempering of Fe-Ni-C martensites. Metall. Trans. A 1989, 20, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, R.K.W.; Gutierrez-Urrutia, I.; Herbig, M.; Moore, K.L.; Lozano-Perez, S.; Raabe, D. Multi-scale correlative microscopy investigation of both structure and chemistry of deformation twin bundles in Fe-Mn-C steel. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1581–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbig, M.; Raabe, D.; Li, Y.J.; Choi, P.; Zaefferer, S.; Goto, S. Atomic-scale quantification of grain boundary segregation in nanocrystalline material. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 126103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabe, D.; Herbig, M.; Sandlöbes, S.; Li, Y.; Tytko, D.; Kuzmina, M.; Ponge, D.; Choi, P.P. Grain boundary segregation engineering in metallic alloys: A pathway to the design of interfaces. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2014, 18, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stibitz, G.R. Energy of lattice distortion. Phys. Rev. 1936, 49, 859. [Google Scholar]
- Kumosa, M. Strain energy of a mechanical twin in alpha -iron. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 1991, 24, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | Cu | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 0.967 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 1.38 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.026 |
| at% | 4.325 | 0.58 | 0.23 | 0.005 | <0.002 | 1.43 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.052 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, W.; Drouven, C.; Galindo-Nava, E. Carbon Redistribution in Martensite in High-C Steel: Atomic-Scale Characterization and Modelling. Metals 2018, 8, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080577
Song W, Drouven C, Galindo-Nava E. Carbon Redistribution in Martensite in High-C Steel: Atomic-Scale Characterization and Modelling. Metals. 2018; 8(8):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080577
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Wenwen, Carsten Drouven, and Enrique Galindo-Nava. 2018. "Carbon Redistribution in Martensite in High-C Steel: Atomic-Scale Characterization and Modelling" Metals 8, no. 8: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080577
APA StyleSong, W., Drouven, C., & Galindo-Nava, E. (2018). Carbon Redistribution in Martensite in High-C Steel: Atomic-Scale Characterization and Modelling. Metals, 8(8), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080577






