Effects of Boron Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-Co Based Cermets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Development of Cermets
2.2. Chemical, Microstructural, and Physical Characterization
2.3. Mechanical Behavior
3. Results and Discussion
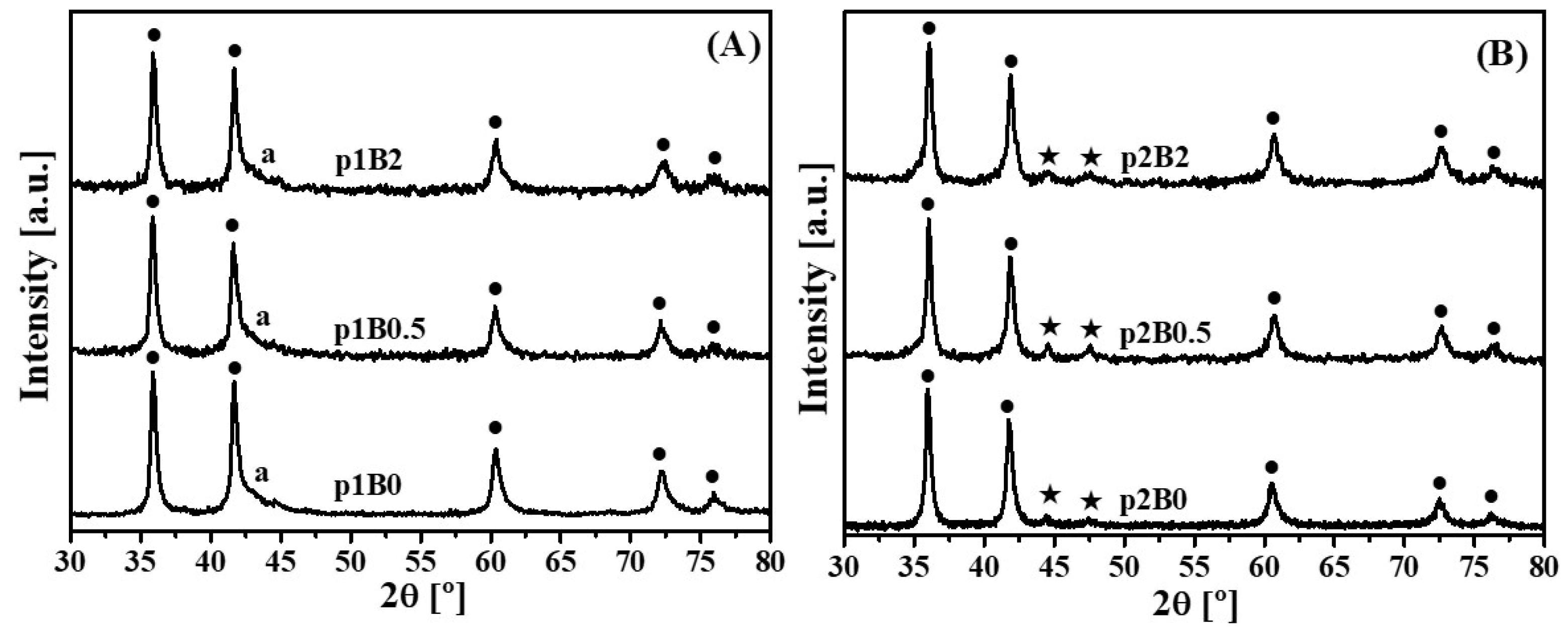
3.1. Synthesis of the Powdered Cermets with Boron Addition
3.2. Sintering of Cermets with Boron Addition
3.3. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Cermets.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The addition of boron to (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-Co based cermets during the sintering step caused the formation of two different boride solid solutions, i.e., (Ti,Ta)B2 and (Ti,Ta)3B4.
- (2)
- The main mechanism of this process seems to be different for both methodologies. While for the first methodology the boron mainly reacts with the Ti and Ta presented in the binder phase prior to the sintering step, for the second methodology, the boron reacted with the Ti and Ta dissolved from the (Ti,Ta)(C,N) ceramic phase.
- (3)
- This reaction of the boride formation allowed for the decrease of the Ti and Ta amounts in the binder phase and, consequently, the modification of the binder nature. Particularly, the (Ti,Ta)Co2 brittle intermetallic compound observed for cermets without boron addition evolved to a new (Ti,Ta)Co3 and α-Co alloy, more ductile and tough than (Ti,Ta)Co2.
- (4)
- As a general trend, the increase of hardness and toughness was due to the formation of new ceramic phases (borides) and tougher and ductile binder phases, respectively.
- (5)
- This new approach for reducing the amount of transition metals (in this case, Ti and Ta) in the binder phase of cermets, based on the reaction with boron to synthesize borides, can be an alternative way to other, already published, approaches focused on reducing the ceramic dissolution during sintering.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellosi, A.; Calzavarini, R.; Faga, M.G.; Monteverde, F.; Zancolò, C.; D’Errico, G.E. Characterisation and application of titanium carbonitride-based cutting tools. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 143–144, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicardi, E.; Córdoba, J.M.; Sayagués, M.J.; Gotor, F.J. Absence of the core–rim microstructure in TixTa1−xCyN1−y-based cermets developed from a pre-sintered carbonitride master alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 33, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicardi, E.; Torres, Y.; Córdoba, J.M.; Sayagués, M.J.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Gotor, F.J. Effect of sintering time on the microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 38, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, S. Properties of titanium carbonitride matrix cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2006, 24, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Obra, G.; Avilés, M.A.; Torres, Y.; Chicardi, E.; Gotor, F.J. A new family of cermets: Chemically complex but microstructurally simple. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 63, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicardi, E.; Gotor, F.J.; Medri, V.; Guicciardi, S.; Lascano, S.; Córdoba, J.M. Hot-pressing of (Ti,Mt)(C,N)–Co–Mo2C (Mt=Ta,Nb) powdered cermets synthesized by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 292, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaSalvia, J.C.; Kim, D.K.; Meyers, M.A. Effect of Mo on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiC—Ni-based cermets produced by combustion synthesis—Impact forging technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 206, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ye, J.; Tu, M. Effect of VC and nano-TiC addition on the microstructure and properties of micrometer grade Ti(CN)-based cermets. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2222–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiong, W.; Yang, Q.; Yao, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, X. Effect of Mo addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ti,W)C solid solution based cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 43, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, N. Effects of ZrC on microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of TiC–ZrC–Co–Ni cermets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 561, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ai, X.; Zhao, J.; Gong, F.; Pang, J.; Wang, Y. Effects of metal binder on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti(C,N)-based cermets. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 644, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicardi, E.; Córdoba, J.M.; Gotor, F.J. High temperature oxidation resistance of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets. Corros. Sci. 2016, 102, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicardi, E.; Córdoba, J.M.; Gotor, F.J. Kinetics of high-temperature oxidation of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets. Corros. Sci. 2016, 102, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicardi, E.; Gotor, F.J.; Córdoba, J.M. Enhanced oxidation resistance of Ti(C,N)-based cermets containing Ta. Corros. Sci. 2014, 84, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, W.; Kim, J. Stability domains of (Ti,W)C and (Ti,W)(CN) during carbothermal reduction of TiO2/WO3 mixture at 1500K. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 1355–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Fan, H.; Qiu, Y. Effects of (Ti,Ta,Nb,W)(C,N) on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behaviors of WC-Co cemented carbides. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Dong, Z.; Xiong, W. Fabrication of Ti(C,N)-based cermets by in situ carbothermal reduction of MoO3 and subsequent liquid sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Obra, A.G.; Gotor, F.J.; Chicardi, E. Effect of the impact energy on the chemical homogeneity of a (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N) solid solution obtained via a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 708, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Córdoba, J.M.; Avilés, M.A.; Sayagués, M.J.; Alcalá, M.D.; Gotor, F.J. Synthesis of complex carbonitride powders TiyMT1−yCxN1−x (MT: Zr, V, Ta, Hf) via a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 482, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.; Sánchez, J.M. Spark plasma sintering of Ti(C,N) cermets with intermetallic binder phases. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2007, 25, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicardi, E.; Torres, Y.; Córdoba, J.M.; Hvizdoš, P.; Gotor, F.J. Effect of tantalum content on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of cermets based on (TixTa1−x)(C0.5N0.5) solid solutions. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicardi, E.; Torres, Y.; Sayagués, M.J.; Medri, V.; Melandri, C.; Córdoba, J.M.; Gotor, F.J. Toughening of complete solid solution cermets by graphite addition. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coric, D.; Curkovic, L. Statistical analysis of Vickers indentation fracture toughness of Y-TZP ceramics. Trans. FAMENA 2017, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegler, R.; Schmauder, S.; Sig, L. Fracture toughness evaluation of WC–Co alloys by indentation testing. J. Hard Met. 1990, 1, 158–174. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, R.; Matzke, H. Indentation Testing of a Broad Range of Cemented Carbides. In Science of Hard Materials; Viswanadham, R.K., Rowcliffe, D.J., Gurland, J., Eds.; Springer Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 563–582. [Google Scholar]
- Chicardi, E.; Córdoba, J.M.; Sayagués, M.J.; Gotor, F.J. Inverse core–rim microstructure in (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets developed by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 31, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, S. Microstructure of Ti(CN)–WC–NbC–Ni Cermets. J Am. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 84, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Nam, S.; Kang, S. Enhanced toughness of titanium carbonitride-based cermets by addition of (Ti,W)C carbides. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 649, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Area | Atomic Percentage (at. %) | Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | Ta | Co | - | |
| 1 | 83.4 ± 2.1 | 16.6 ± 2.1 | - | (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-core |
| 2 | 86.8 ± 1.3 | 13.2 ± 1.3 | - | (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-rim |
| 3 | 83.8 ± 0.5 | 16.2 ± 0.5 | - | (Ti,Ta)(C,N) |
| 4 | 21.5 ± 1.0 | 10.0 ± 1.0 | 68.5 ± 1.0 | (Ti,Ta)Co2 |
| 5 | 21.1 ± 1.2 | 15.3 ± 1.2 | 63.8 ± 1.2 | (Ti,Ta)Co2 |
| 6 | 16.7 ± 0.8 | 8.1 ± 0.8 | 75.2 ± 0.8 | (Ti,Ta)Co3 |
| 7 | 18.4 ± 1.4 | 12.7 ± 1.4 | 68.9 ± 1.4 | (Ti,Ta)Co2 |
| 8 | 15.3 ± 1.0 | 20.2 ± 1.0 | 64.5 ± 1.0 | (Ti,Ta)Co2 |
| 9 | 14.7 ± 1.7 | 10.0 ± 1.7 | 75.3 ± 1.7 | (Ti,Ta)Co3 |
| 10 | 12.4 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 85.4 ± 0.7 | -Co |
| 11 | 96.5 ± 1.1 | 3.5 ± 1.1 | - | (Ti,Ta)B2 or (Ti,Ta)3B4. |
| Cermet | d (μm) | Vb (vol.%) | ρ (vol.%) | HV (GPa) | KIC (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s1B0 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 26 ± 3 | 4.0 ± 0.6 | 11.9 ± 1.2 | 4.0 ± 0.6 |
| s1B0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 21 ± 3 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 12.9 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 1.0 |
| s1B2 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 23 ± 2 | 2.6 ± 1.1 | 12.8 ± 0.5 | 4.0 ± 0.5 |
| s2B0 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 28 ± 2 | 2.2 ± 0.5 | 14.1 ± 1.0 | 2.9 ± 0.3 |
| s2B0.5 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 26 ± 2 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 14.0 ± 1.0 | 5.3 ± 1.0 |
| s2B2 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 26 ± 3 | 2.8 ± 0.7 | 16.2 ± 0.8 | 3.3 ± 0.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chicardi, E.; Gotor Martínez, F.J. Effects of Boron Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-Co Based Cermets. Metals 2019, 9, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070787
Chicardi E, Gotor Martínez FJ. Effects of Boron Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-Co Based Cermets. Metals. 2019; 9(7):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070787
Chicago/Turabian StyleChicardi, Ernesto, and Francisco José Gotor Martínez. 2019. "Effects of Boron Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-Co Based Cermets" Metals 9, no. 7: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070787
APA StyleChicardi, E., & Gotor Martínez, F. J. (2019). Effects of Boron Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-Co Based Cermets. Metals, 9(7), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070787





