Overexpression of llm1 Affects the Synthesis of Secondary Metabolites of Aspergillus cristatus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Cloning and Overexpression of the llm1 Gene
2.3. Fungal Transformation
2.4. Phenotypic Analysis
2.5. LC–MS-Based Metabolite Profiling
2.6. Transcriptome Data Analysis
2.7. RT-qPCR Detection
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
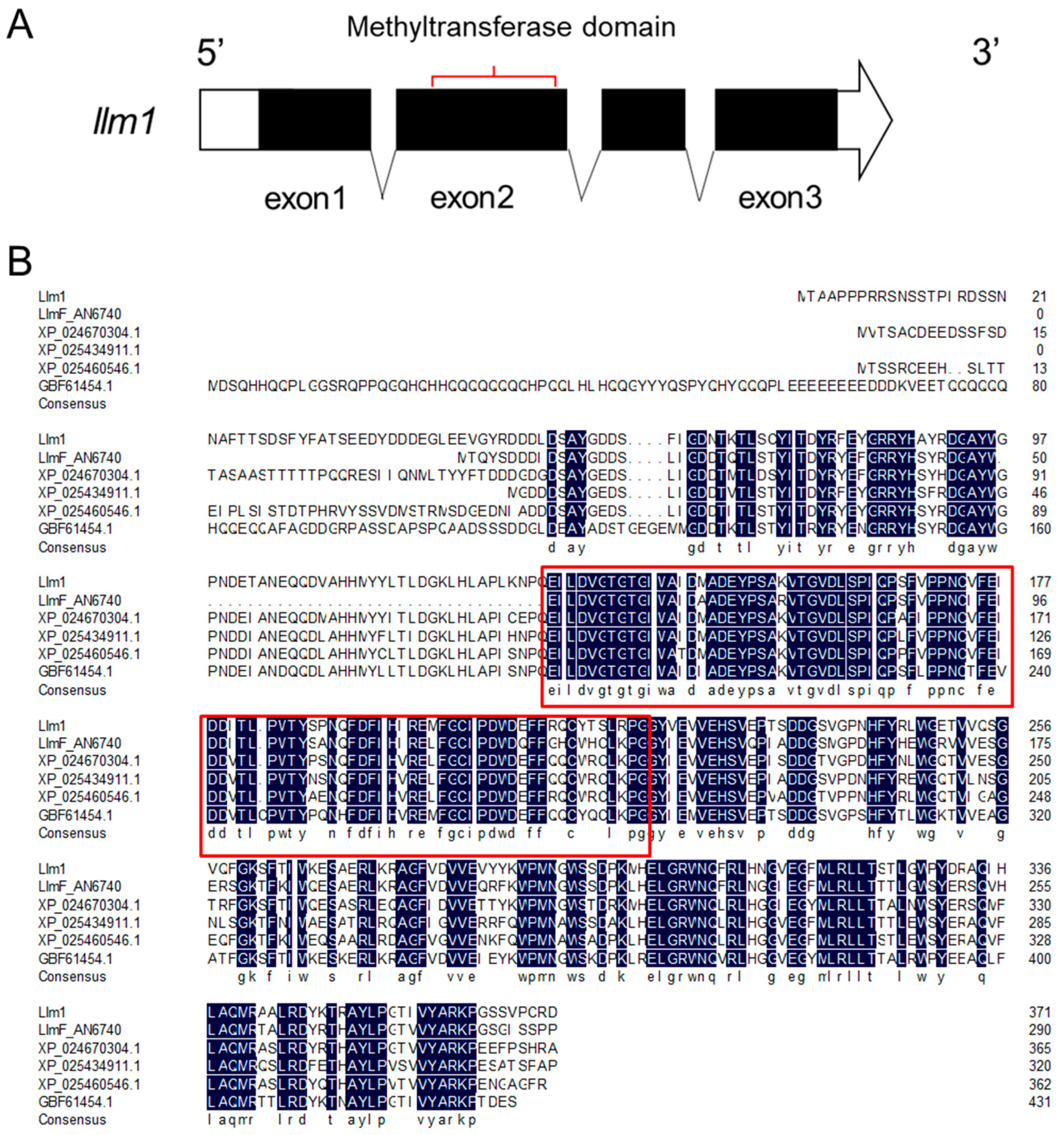
3.1. Cloning and Analysis of the Gene llm1 in A. cristatus
3.2. Construction and Screening of llm1-Overexpressing Strain
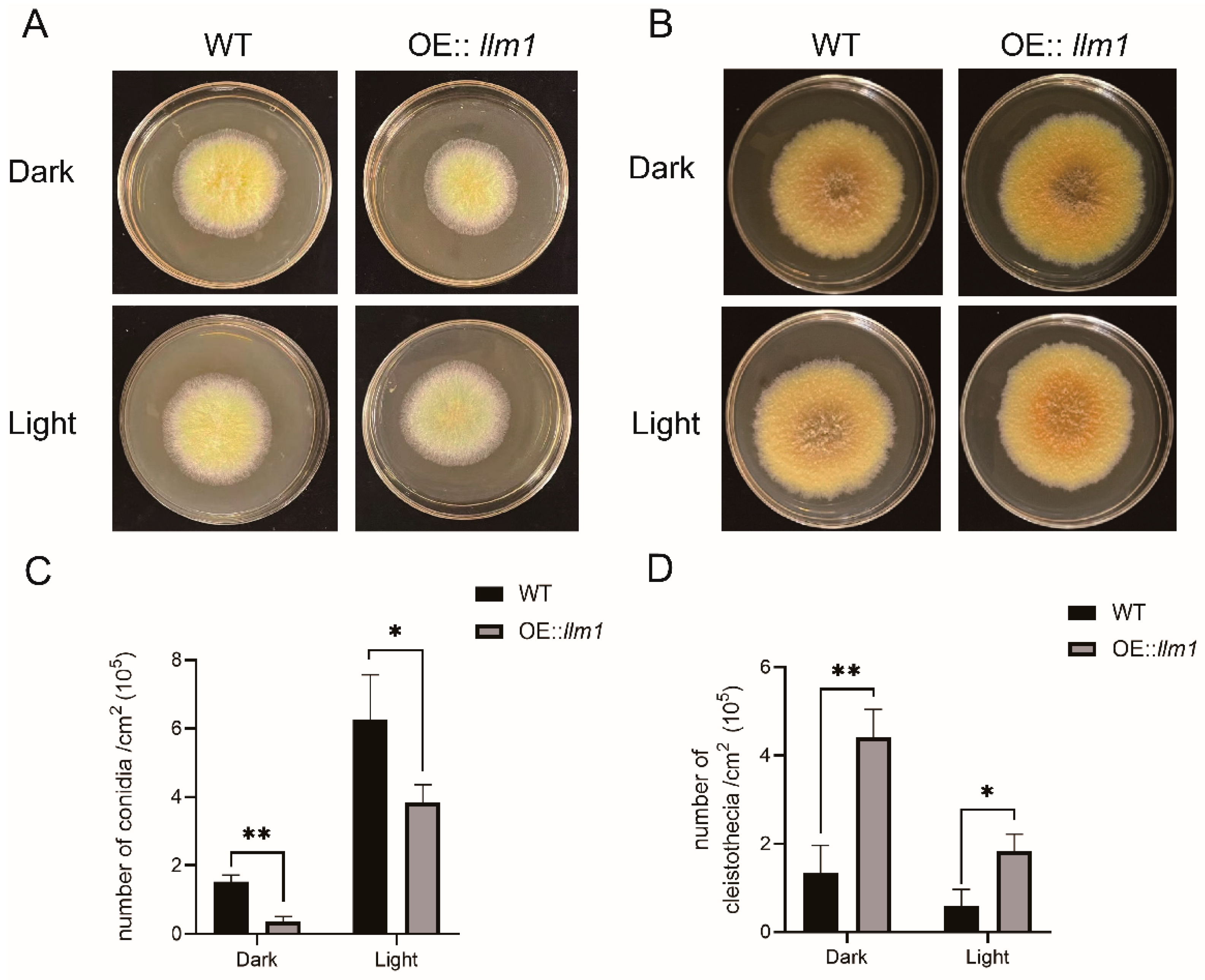
3.3. Effects of Overexpression of llm1 on Sex Development
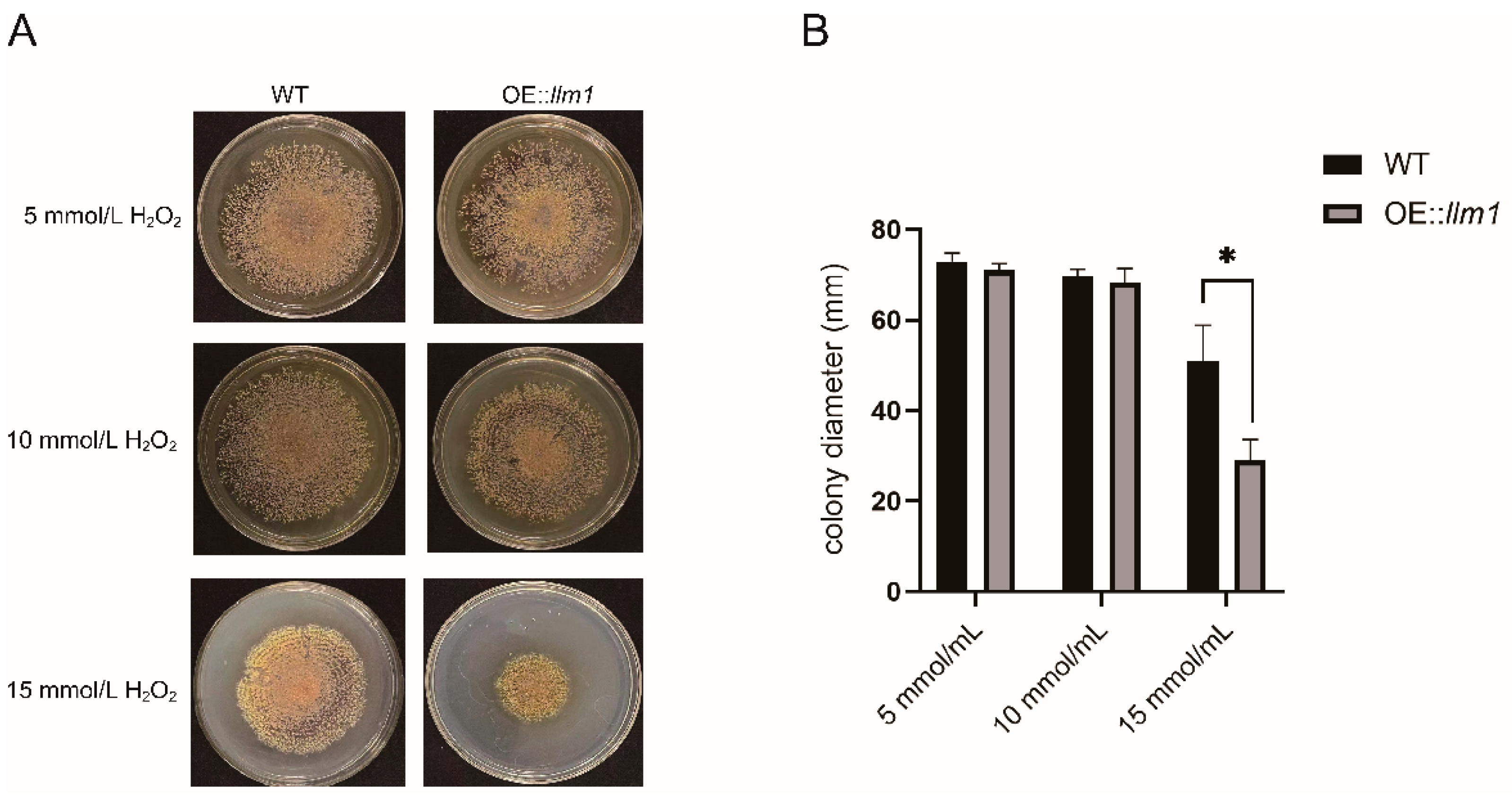
3.4. Overexpression of the Gene llm1 Decreased Oxidative Stress Tolerance of A. cristatus
3.5. Effects of llm1 Overexpression on Metabolites Production
3.6. Transcriptome Data Analysis
3.7. Expression of Secondary Metabolite-Related Gene Clusters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, D.; Su, M.; Duan, Y.; Huang, Y. Eurotium cristatum, a potential probiotic fungus from Fuzhuan brick tea, alleviated obesity in mice by modulating gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5032–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, K.; Gao, H. Eurotium cristatumStructural Characteristics and Hypolipidemic Activity of Theabrownins from Dark Tea Fermented by Single Species PW-1. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Xu, S.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z. Eurotium cristatum Fermented Loose Dark Tea Ameliorates Cigarette Smoke-Induced Lung Injury by MAPK Pathway and Enhances Hepatic Metabolic Detoxification by/Pathway in Mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6635080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Li, N.; Zhou, F.; Ouyang, J.; Lu, D.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J.; et al. Microbial bioconversion of the chemical components in dark tea. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Chen, M.; Zu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Lu, H.; Yue, P.; Gao, X. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics reveal changes in the chemical constituents of instant dark tea during liquid-state fermentation by Eurotium cristatum. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.; Takahashi, M.; Lim, P.; Aoyama, S.; Makino, S.; Ferdinandus, F.; Ng, S.; Arai, S.; Fujita, H.; Tan, H.; et al. Eurotium Cristatum Fermented Okara as a Potential Food Ingredient to Combat Diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wu, X.; Yao, X.; Chen, Y.; Ho, C.; He, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Metabolite profiling, antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of buckwheat processed by solid-state fermentation with Eurotium cristatum YL-1. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Xia, H.; Huang, L.; Dong, M. On-line screening and identification of free radical scavenging compounds in Angelica dahurica fermented with Eurotium cristatum using an HPLC-PDA-Triple-TOF-MS/MS-ABTS system. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X.; Hyde, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analyses of the Fuzhuan brick tea-fermentation fungus Aspergillus cristatus. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brakhage, A. Regulation of fungal secondary metabolism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.; Oakley, C.; Ahuja, M.; Entwistle, R.; Schultz, A.; Chang, S.; Sung, C.; Wang, C.; Oakley, B. An efficient system for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite genes in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7720–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaegashi, J.; Oakley, B.; Wang, C. Recent advances in genome mining of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters and the development of heterologous expression systems in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bok, J.; Balajee, S.; Marr, K.; Andes, D.; Nielsen, K.; Frisvad, J.; Keller, N. LaeA, a regulator of morphogenetic fungal virulence factors. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Hao, S.; Chai, S.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Shi, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, C. Overexpression of global regulator LaeA increases secondary metabolite production in Monascus purpureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 3049–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Kim, N.; Lee, D.; Kim, W.; Lee, I. Overexpression of the laeA gene leads to increased production of cyclopiazonic acid in Aspergillus fumisynnematus. Fungal Biol. 2015, 119, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, X.; Tabudravu, J.; Wang, S.; Deng, H.; Pan, L. The chemical profile of activated secondary metabolites by overexpressing LaeA in Aspergillus niger. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 248, 126735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.; Theisen, J.; Duran, R.; Grayburn, W.; Calvo, A.; Keller, N. Secondary metabolism and development is mediated by LlmF control of VeA subcellular localization in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, Q.; Wu, D.; Zhu, X.; Gillian Turgeon, B. Cochliobolus heterostrophus Llm1—A Lae1-like methyltransferase regulates T-toxin production, virulence, and development. Fungal Genet. Biol. FG B 2013, 51, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, M.; Entwistle, R.; Oakley, C.; Wang, C.; Oakley, B. Aspergillus nidulans Overexpression of an LaeA-like Methyltransferase Upregulates Secondary Metabolite Production in. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Z.; Zhu, H.J.; Yang, C.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Jiang, N.; Xiao, Y.S.; Shi, L.Y.; Jiao, R.H.; Ge, H.M.; Tan, R.X. Dalestones A and B, two anti-inflammatory cyclopentenones from Daldinia eschscholzii with an edited strong promoter for the global regulator LaeA-like gene. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, Z. Role of AcndtA in cleistothecium formation, osmotic stress response, pigmentation and carbon metabolism of Aspergillus cristatus. Fungal Biol. 2021, 125, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 6.0: Improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estiarte, N.; Lawrence, C.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.; Crespo-Sempere, A. LaeA and VeA are involved in growth morphology, asexual development, and mycotoxin production in Alternaria alternata. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 238, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, P.; Ghosh, S.; Roy-Barman, S. MoLAEA Regulates Secondary Metabolism in Magnaporthe oryzae. mSphere 2020, 5, e00936-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maor, U.; Barda, O.; Sadhasivam, S.; Bi, Y.; Levin, E.; Zakin, V.; Prusky, D.; Sionov, E. Functional roles of LaeA, polyketide synthase, and glucose oxidase in the regulation of ochratoxin A biosynthesis and virulence in Aspergillus carbonarius. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, O.; Krappmann, S.; Ni, M.; Bok, J.; Helmstaedt, K.; Valerius, O.; Braus-Stromeyer, S.; Kwon, N.; Keller, N.; Yu, J.; et al. VelB/VeA/LaeA complex coordinates light signal with fungal development and secondary metabolism. Science 2008, 320, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikaya-Bayram, Ö.; Palmer, J.; Keller, N.; Braus, G.; Bayram, Ö. One Juliet and four Romeos: VeA and its methyltransferases. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Qu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Qu, Y.; Qin, Y. Penicillium oxalicum putative methyltransferase Mtr23B has similarities and differences with LaeA in regulating conidium development and glycoside hydrolase gene expression. Fungal Genet. Biol. FG B 2020, 143, 103445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Yue, Y.; Fu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ma, G.; Wang, S. Aspergillus flavus Exploration of the Regulatory Mechanism of Secondary Metabolism by Comparative Transcriptomics in. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fréalle, E.; Aliouat-Denis, C.; Delhaes, L.; Hot, D.; Dei-Cas, E. Transcriptomic insights into the oxidative response of stress-exposed Aspergillus fumigatus. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 3713–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Ren, X.; Ren, C.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. The role of the veA gene in adjusting developmental balance and environmental stress response in Aspergillus cristatus. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Du, H.; Wang, N.; Huang, L. Valsa maliLaeA Controls Virulence and Secondary Metabolism in Apple Canker Pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 581203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Huang, C.; Shi, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhu, X. Recycling of Chinese herb residues by endophytic and probiotic fungus Aspergillus cristatus CB10002 for the production of medicinal valuable anthraquinones. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khabthani, S.; Rolain, J.M.; Merhej, V. In Silico/In Vitro Strategies Leading to the Discovery of New Nonribosomal Peptide and Polyketide Antibiotics Active against Human Pathogens. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duban, M.; Cociancich, S.; Leclère, V. Nonribosomal Peptide Synthesis Definitely Working Out of the Rules. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, S.; Mesarich, C.; Saccomanno, B.; Vaisberg, A.; De Wit, P.; Cox, R.; Collemare, J. Elucidation of cladofulvin biosynthesis reveals a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase required for anthraquinone dimerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6851–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Lv, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Deng, H.; Pan, L. Profiling of secondary metabolite gene clusters regulated by LaeA in Aspergillus niger FGSC A1279 based on genome sequencing and transcriptome analysis. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Accession | Description | Cluster | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated | SI65_08318 | Acyl-CoA ligase | 8 |
| SI65_08405 | Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | 9 | |
| SI65_09733 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase | 17 | |
| SI65_10096 | Diacylglycerol lipase | 21 | |
| SI65_03722 | Polyketide synthase | 24 | |
| SI65_05234 | Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | 30 | |
| SI65_05768 | Atrochrysone carboxylic acid synthase | 32 | |
| SI65_05770 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase | 32 | |
| SI65_05771 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase | 32 | |
| SI65_05772 | Oxidoreductase | 32 | |
| SI65_07252 | Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | 36 | |
| Down-regulated | SI65_09735 | Polyketide synthase | 17 |
| SI65_03276 | Polyketide synthase | 23 | |
| SI65_05416 | Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | 31 | |
| SI65_06672 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase | 34 | |
| SI65_06673 | Polyketide synthase | 34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C. Overexpression of llm1 Affects the Synthesis of Secondary Metabolites of Aspergillus cristatus. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091707
Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhang C. Overexpression of llm1 Affects the Synthesis of Secondary Metabolites of Aspergillus cristatus. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(9):1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091707
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yunsheng, Yincui Chen, Jin Zhang, and Chuanbo Zhang. 2022. "Overexpression of llm1 Affects the Synthesis of Secondary Metabolites of Aspergillus cristatus" Microorganisms 10, no. 9: 1707. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091707






