Harnessing the Power of Microbiome Assessment Tools as Part of Neuroprotective Nutrition and Lifestyle Medicine Interventions
Abstract
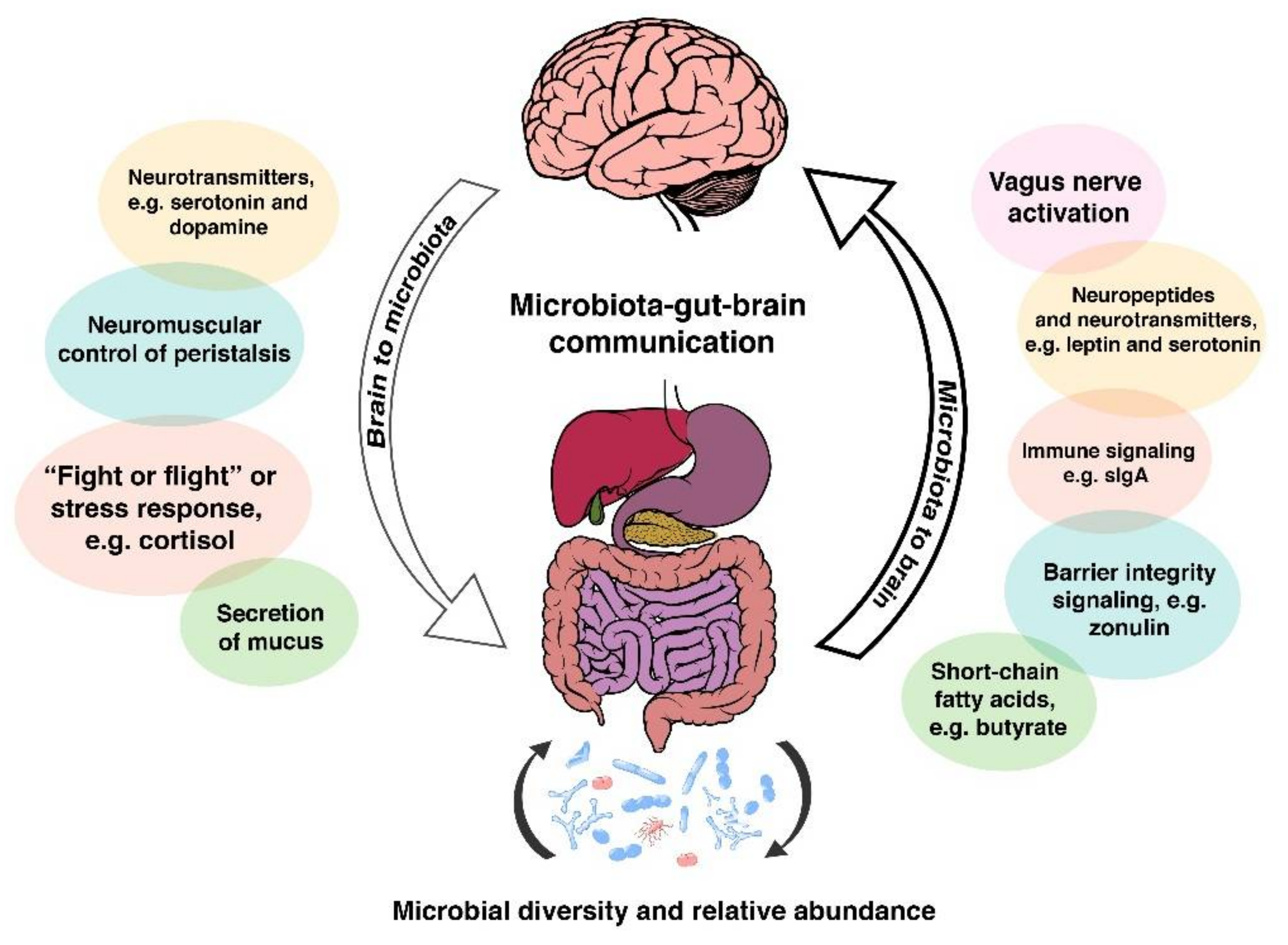
:1. Introducing the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis
Dysbiosis and Leaky Gut
2. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: A Complex Communication System
- (1)
- the composition/diversity of the gut microbiota;
- (2)
- neurotransmitters, hormones, and immune- and neuro-peptides produced in the gut and communication between these and gut microbes;
- (3)
- the integrity of the intestinal wall serving as the physical barrier to the external environment.
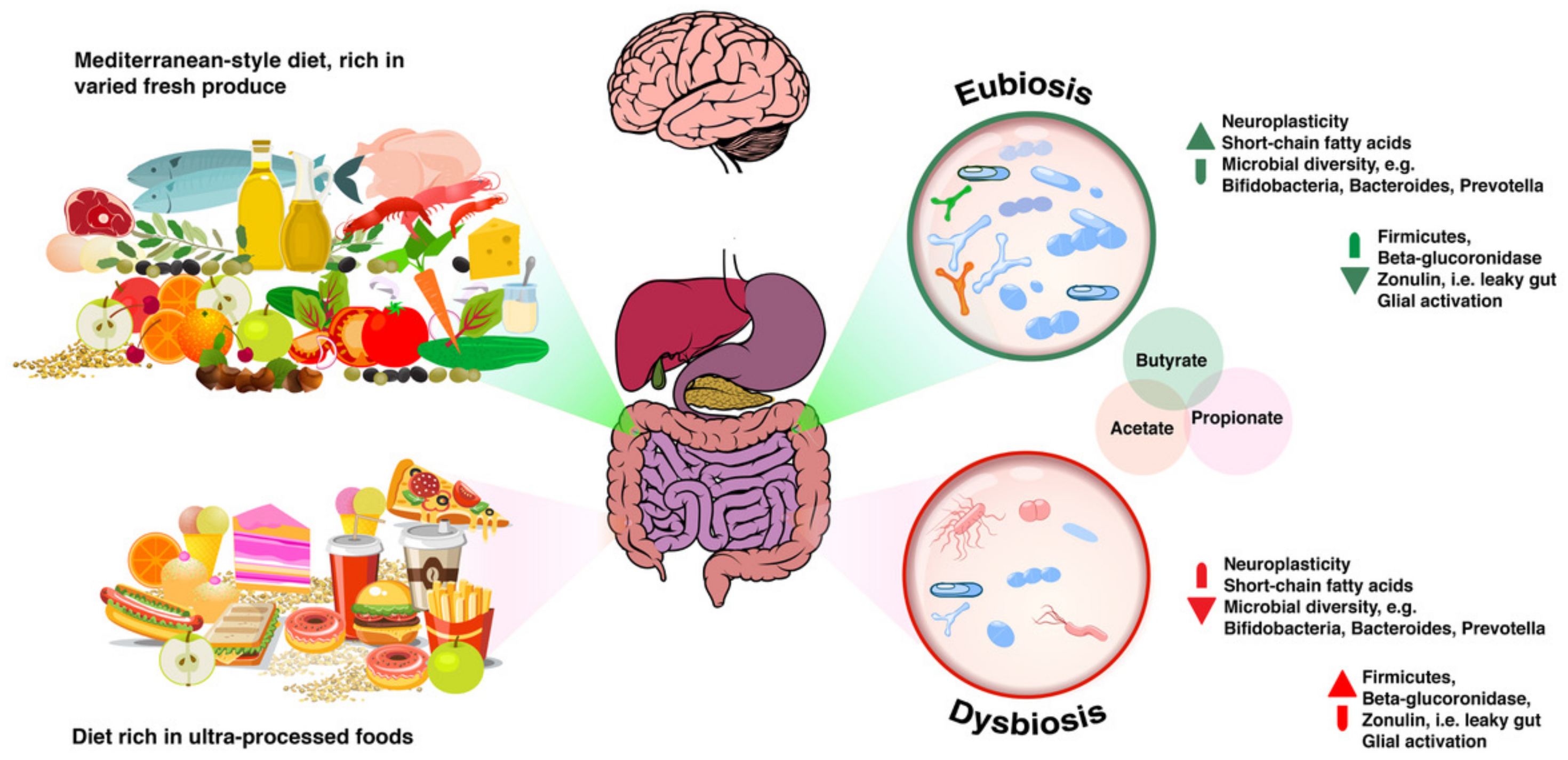
From Eubiosis to Dysbiosis and Back
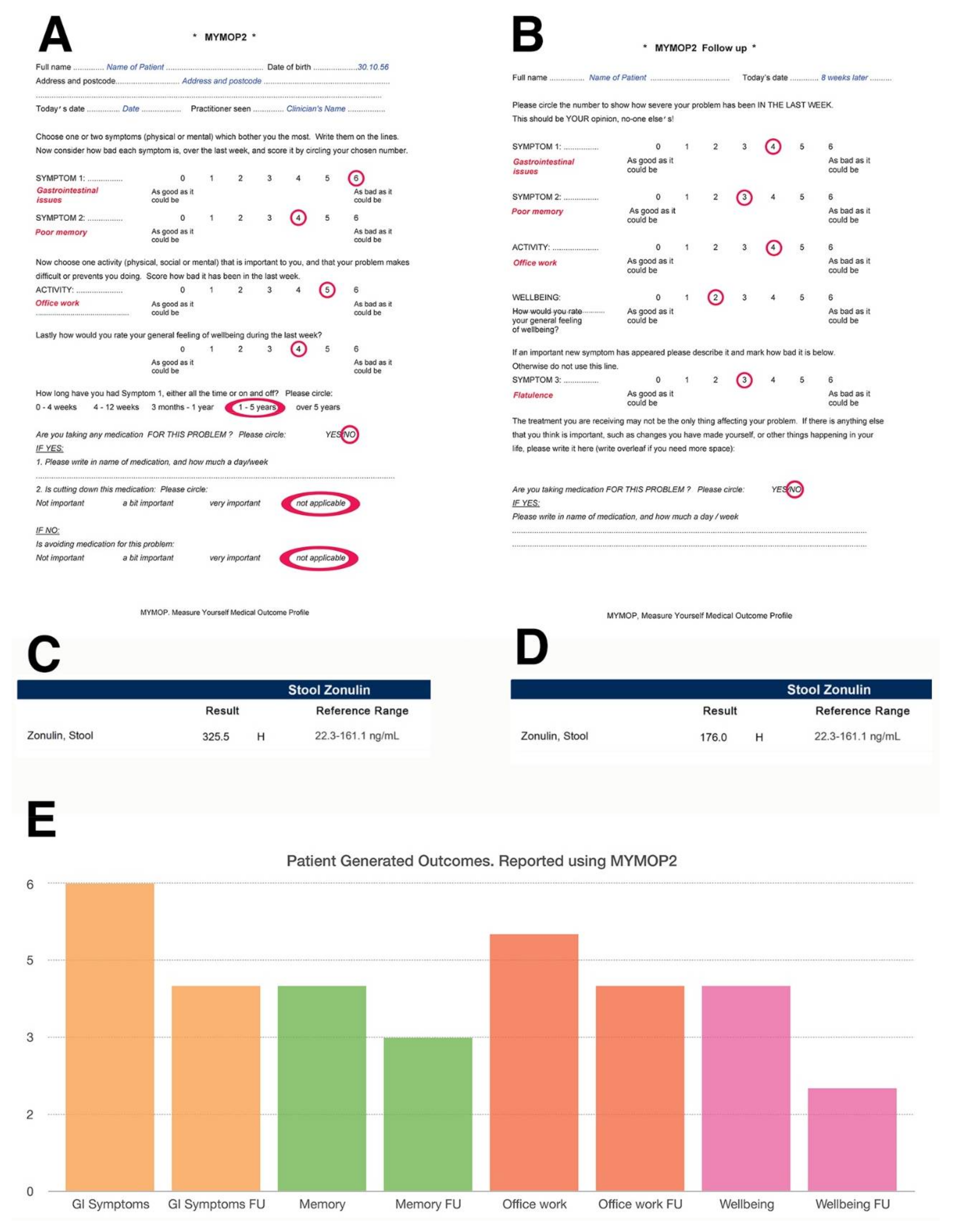
3. Assessing Function by Means of Laboratory Testing and “n = 1 Trials”
4. Helpful Biomarkers in Stool Tests
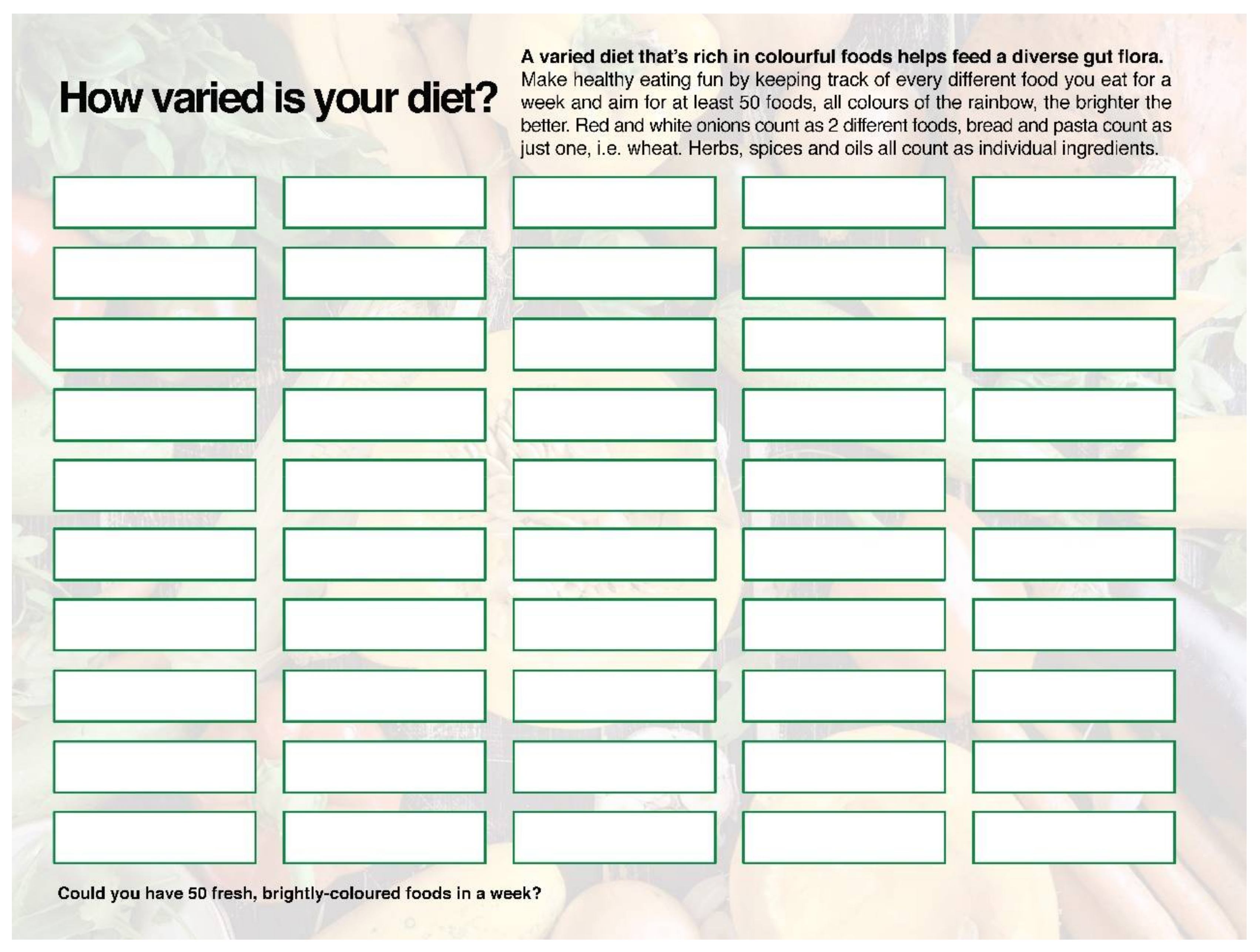
4.1. Microbial Diversity
4.1.1. Getting “a Mediterranean Gut”?
4.1.2. Prebiotics, More Than Just Fibre
4.1.3. Working with Microbial Diversity in Clinical Practice
4.2. Faecal Calprotectin and the Brain
Faecal Calprotectin: Clinical Considerations
4.3. Zonulin and Intestinal Permeability
4.3.1. Zonulin and Gluten
4.3.2. Zonulin and Potential Clinical Presentations: Non-Coeliac Gluten Sensitivity
4.3.3. Zonulin and Parasitic Infections
4.3.4. Reducing Zonulin Levels
4.4. Short Chain Fatty Acids
Clinical Insight on SCFAs
4.5. Beta-Glucuronidase
Clinical Notes on Beta-Glucuronidase
5. Dietary Neuroprotection, from the Gut Up
5.1. Prebiotics, Probiotics and Psychobiotics
5.2. Fermented Foods as Natural Sources of Probiotics
5.3. Assessing Clinical Impact
6. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belkaid, Y.; Naik, S. Compartmentalized and systemic control of tissue immunity by commensals. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.M.; Sadarangani, M.; Finlay, B.B. The role of the immune system in governing host-microbe interactions in the intestine. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.M.; Davy, B.M.; Halliday, T.M.; Hulver, M.W.; Neilson, A.P.; Ponder, M.A.; Davy, K.P. The effect of prebiotic supplementation with inulin on cardiometabolic health: Rationale, design, and methods of a controlled feeding efficacy trial in adults at risk of type 2 diabetes. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yin, A.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Wu, G.; Shen, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Dietary modulation of gut microbiota contributes to alleviation of both genetic and simple obesity in children. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez-Arango, L.F.; Barrett, H.L.; McIntyre, H.D.; Callaway, L.K.; Morrison, M.; Dekker Nitert, M. Increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure is associated with altered gut microbiota composition and butyrate production in early pregnancy. Hypertension 2016, 68, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, C.A.; Cannon, G.; Moubarac, J.C.; Levy, R.B.; Louzada, M.L.C.; Jaime, P.C. Ultra-processing. An odd ‘appraisal’. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiolet, T.; Srour, B.; Sellem, L.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Allès, B.; Méjean, C.; Deschasaux, M.; Fassier, P.; Latino-Martel, P.; Beslay, M.; et al. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and cancer risk: Results from nutrinet-santé prospective cohort. BMJ 2018, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibbo, S.; Ianiro, G.; Giorgio, V.; Scaldaferri, F.; Masucci, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cammarota, G. The role of diet on gut microbiota composition. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. 2016, 20, 4742–4749. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, C.; Ferrario, C.; Turroni, F.; Duranti, S.; Mangifesta, M.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. The human gut microbiota and its interactive connections to diet. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda, P.; Bobe, A.; Dolan, K.; Leone, V.; Martinez, K. Nutritional modulation of gut microbiota—The impact on metabolic disease pathophysiology. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 28, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battson, M.L.; Lee, D.M.; Jarrell, D.K.; Hou, S.; Ecton, K.E.; Weir, T.L.; Gentile, C.L. Suppression of gut dysbiosis reverses western diet-induced vascularr dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battson, M.L.; Lee, D.M.; Weir, T.L.; Gentile, C.L. The gut microbiota as a novel regulator of cardiovascular function and disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, M.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Gut microbial metabolism defines host metabolism: An emerging perspective in obesity and allergic inflammation. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzel, A.; Muller, D.N.; Hafler, D.A.; Erdman, S.E.; Linker, R.A.; Kleinewietfeld, M. Role of “western diet” in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J. Asthma microbiome studies and the potential for new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013, 13, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; Boushey, H.A. The microbiome in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, K.E.; Lynch, S.V. Microbiota in allergy and asthma and the emerging relationship with the gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.L.; Madak-Erdogan, Z. Estrogen and microbiota crosstalk: Should we pay attention? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.M.; Al-Nakkash, L.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Estrogen-gut microbiome axis: Physiological and clinical implications. Maturitas 2017, 103, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkman, A.; Lehtimaki, J.; Ruokolainen, L. The ecology of human microbiota: Dynamics and diversity in health and disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1399, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Bernstein, C.N.; Iliopoulos, D.; Macpherson, A.; Neurath, M.F.; Ali, R.A.R.; Vavricka, S.R.; Fiocchi, C. Environmental triggers in ibd: A review of progress and evidence. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, S.Y.; Kaplan, G.G.; Madsen, K.L. Air pollution effects on the gut microbiota: A link between exposure and inflammatory disease. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehra, V.; Allen, J.M.; Mailing, L.J.; Kashyap, P.C.; Woods, J.A. Gut microbiota: Modulation of host physiology in obesity. Physiology 2016, 31, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monda, V.; Villano, I.; Messina, A.; Valenzano, A.; Esposito, T.; Moscatelli, F.; Viggiano, A.; Cibelli, G.; Chieffi, S.; Monda, M.; et al. Exercise modifies the gut microbiota with positive health effects. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3831972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Gui, Y.; Xu, D. Physical exercise, gut, gut microbiota, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, J.M.; Opp, M.R. Sleep and microbes. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2016, 131, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogendoorn, C.J.; Roy, J.F.; Gonzalez, J.S. Shared dysregulation of homeostatic brain-body pathways in depression and type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2017, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karl, J.P.; Margolis, L.M.; Madslien, E.H.; Murphy, N.E.; Castellani, J.W.; Gundersen, Y.; Hoke, A.V.; Levangie, M.W.; Kumar, R.; Chakraborty, N.; et al. Changes in intestinal microbiota composition and metabolism coincide with increased intestinal permeability in young adults under prolonged physiological stress. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G559–G571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berding, K.; Holscher, H.D.; Arthur, A.E.; Donovan, S.M. Fecal microbiome composition and stability in 4- to 8-year old children is associated with dietary patterns and nutrient intake. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 56, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Ding, G.; Ding, Y.; Deng, C.; Ze, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, L.; Yan, H.; Liu, F.; et al. Effect of probiotics on digestibility and immunity in infants: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2017, 96, e5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergström, A.; Skov, T.H.; Bahl, M.I.; Roager, H.M.; Christensen, L.B.; Ejlerskov, K.T.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Licht, T.R. Establishment of intestinal microbiota during early life: A longitudinal, explorative study of a large cohort of danish infants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutten, N.B.; Gorissen, D.M.; Eck, A.; Niers, L.E.; Vlieger, A.M.; Besseling-van der Vaart, I.; Budding, A.E.; Savelkoul, P.H.; van der Ent, C.K.; Rijkers, G.T. Long term development of gut microbiota composition in atopic children: Impact of probiotics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Vojdani, A.; Blaurock-Busch, E.; Busch, Y.; Friedle, A.; Franco-Lira, M.; Sarathi-Mukherjee, P.; Martinez-Aguirre, X.; Park, S.B.; Torres-Jardon, R.; et al. Air pollution and children: Neural and tight junction antibodies and combustion metals, the role of barrier breakdown and brain immunity in neurodegeneration. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 43, 1039–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulet, M.A.; Puchau, B.; Hermsdorff, H.H.; Navarro, C.; Martinez, J.A. Vitamin a intake is inversely related with adiposity in healthy young adults. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2008, 54, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botella-Carretero, J.I.; Alvarez-Blasco, F.; Villafruela, J.J.; Balsa, J.A.; Vázquez, C.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F. Vitamin d deficiency is associated with the metabolic syndrome in morbid obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozata, M.; Mergen, M.; Oktenli, C.; Aydin, A.; Yavuz Sanisoglu, S.; Bolu, E.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Sayal, A.; Isimer, A.; Ozdemir, I.C. Increased oxidative stress and hypozincemia in male obesity. Clin. Biochem. 2002, 35, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, M.G.; Roemmich, J.N.; Kington, M.L.; Bovbjerg, V.E.; Weltman, A.L.; Holmes, V.F.; Patrie, J.T.; Rogol, A.D.; Nadler, J.L. Magnesium deficiency is associated with insulin resistance in obese children. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet–induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergheim, I.; Weber, S.; Vos, M.; Krämer, S.; Volynets, V.; Kaserouni, S.; McClain, C.J.; Bischoff, S.C. Antibiotics protect against fructose-induced hepatic lipid accumulation in mice: Role of endotoxin. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montassier, E.; Berthelot, L.; Soulillou, J.P. Are the decrease in circulating anti-alpha1,3-gal igg and the lower content of galactosyl transferase a1 in the microbiota of patients with multiple sclerosis a novel environmental risk factor for the disease? Mol. Immunol. 2018, 93, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Berre, L.; Rousse, J.; Gourraud, P.A.; Imbert-Marcille, B.M.; Salama, A.; Evanno, G.; Semana, G.; Nicot, A.; Dugast, E.; Guerif, P.; et al. Decrease of blood anti-alpha1,3 galactose abs levels in multiple sclerosis (ms) and clinically isolated syndrome (cis) patients. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 180, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, S.; Kim, S.; Suda, W.; Oshima, K.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Chihara, N.; Tomita, A.; Sato, W.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Dysbiosis in the gut microbiota of patients with multiple sclerosis, with a striking depletion of species belonging to clostridia xiva and iv clusters. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, A.; Cattane, N.; Galluzzi, S.; Provasi, S.; Lopizzo, N.; Festari, C.; Ferrari, C.; Guerra, U.P.; Paghera, B.; Muscio, C.; et al. Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.L.; Kao, C.H. Irritable bowel syndrome is associated with an increased risk of dementia: A nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0144589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Agnihotri, A.; Pathak, M.K.; Shirazi, A.; Tiwari, R.P.; Sreenivas, V.; Sagar, R.; Makharia, G.K. Psychiatric, somatic and other functional gastrointestinal disorders in patients with irritable bowel syndrome at a tertiary care center. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 18, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Kubera, M.; Leunis, J.C. The gut-brain barrier in major depression: Intestinal mucosal dysfunction with an increased translocation of LPS from gram negative enterobacteria (leaky gut) plays a role in the inflammatory pathophysiology of depression. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2008, 29, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamezaki, F.; Sonoda, S.; Nakata, S.; Okazaki, M.; Tamura, M.; Abe, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Otsuji, Y. Elevated depressive symptoms are associated with hypertriglyceridemia in japanese male workers. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodard, L.D.; Urech, T.; Landrum, C.R.; Wang, D.; Petersen, L.A. Impact of comorbidity type on measures of quality for diabetes care. Med. Care 2011, 49, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Korff, M.; Katon, W.J.; Lin, E.H.; Ciechanowski, P.; Peterson, D.; Ludman, E.J.; Young, B.; Rutter, C.M. Functional outcomes of multi-condition collaborative care and successful ageing: Results of randomised trial. BMJ 2011, 343, d6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cersosimo, M.G.; Benarroch, E.E. Pathological correlates of gastrointestinal dysfunction in parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Disease 2012, 46, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Shannon, K.M.; Kordower, J.H.; Voigt, R.M.; Shaikh, M.; Jaglin, J.A.; Estes, J.D.; Dodiya, H.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early parkinson's disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassani, E.; Barichella, M.; Cancello, R.; Cavanna, F.; Iorio, L.; Cereda, E.; Bolliri, C.; Zampella Maria, P.; Bianchi, F.; Cestaro, B.; et al. Increased urinary indoxyl sulfate (indican): New insights into gut dysbiosis in parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devos, D.; Lebouvier, T.; Lardeux, B.; Biraud, M.; Rouaud, T.; Pouclet, H.; Coron, E.; Bruley des Varannes, S.; Naveilhan, P.; Nguyen, J.-M.; et al. Colonic inflammation in parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Disease 2013, 50, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stilling, R.M.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Collective unconscious: How gut microbes shape human behavior. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The vagus nerve at the interface of the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellissier, S.; Dantzer, C.; Mondillon, L.; Trocme, C.; Gauchez, A.S.; Ducros, V.; Mathieu, N.; Toussaint, B.; Fournier, A.; Canini, F.; et al. Relationship between vagal tone, cortisol, tnf-alpha, epinephrine and negative affects in crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, E.; Chinnock, J.E.; De Daly, M.B.; Murray, J.G. Functional and histological studies of the vagus nerve and its branches to the heart, lungs and abdominal viscera in the cat. J. Physiol. 1957, 135, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundman, M.H.; Chen, N.K.; Subbian, V.; Chou, Y.H. The bidirectional gut-brain-microbiota axis as a potential nexus between traumatic brain injury, inflammation, and disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, L.M.; Galley, J.D.; Hade, E.M.; Schoppe-Sullivan, S.; Kamp Dush, C.; Bailey, M.T. Gut microbiome composition is associated with temperament during early childhood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 45, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfall, S.; Lomis, N.; Kahouli, I.; Dia, S.Y.; Singh, S.P.; Prakash, S. Microbiome, probiotics and neurodegenerative diseases: Deciphering the gut brain axis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3769–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Anderson, J.M.; Bharti, R.; Raes, J.; Rosenstiel, P. The resilience of the intestinal microbiota influences health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto-Sanchez, M.I.; Hall, G.B.; Ghajar, K.; Nardelli, A.; Bolino, C.; Lau, J.T.; Martin, F.P.; Cominetti, O.; Welsh, C.; Rieder, A.; et al. Probiotic bifidobacterium longum ncc3001 reduces depression scores and alters brain activity: A pilot study in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, D.; Quigley, E.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Do interactions between stress and immune responses lead to symptom exacerbations in irritable bowel syndrome? Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonefjall, B.; Ohman, L.; Simren, M.; Strid, H. Ibs-like symptoms in patients with ulcerative colitis in deep remission are associated with increased levels of serum cytokines and poor psychological well-being. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2630–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiman, S.C.; Watson, H.J.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.C.; Huh, E.Y.; Tarantino, L.M.; Bulik, C.M.; Carroll, I.M. The intestinal microbiota in acute anorexia nervosa and during renourishment: Relationship to depression, anxiety, and eating disorder psychopathology. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sareen, J.; Jacobi, F.; Cox, B.J.; Belik, S.L.; Clara, I.; Stein, M.B. Disability and poor quality of life associated with comorbid anxiety disorders and physical conditions. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, B.; Williams, K.C.; Gorrindo, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Lee, E.B.; Levitt, P.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. Rigid-compulsive behaviors are associated with mixed bowel symptoms in autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dansie, E.J.; Furberg, H.; Afari, N.; Buchwald, D.; Edwards, K.; Goldberg, J.; Schur, E.; Sullivan, P.F. Conditions comorbid with chronic fatigue in a population-based sample. Psychosomatics 2012, 53, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy-Szakal, D.; Williams, B.L.; Mishra, N.; Che, X.; Lee, B.; Bateman, L.; Klimas, N.G.; Komaroff, A.L.; Levine, S.; Montoya, J.G.; et al. Fecal metagenomic profiles in subgroups of patients with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. Microbiome 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumont, M.; Goodrich, J.K.; Jackson, M.A.; Yet, I.; Davenport, E.R.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Debelius, J.; Pallister, T.; Mangino, M.; Raes, J.; et al. Heritable components of the human fecal microbiome are associated with visceral fat. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Bose, S.; Seo, J.G.; Chung, W.S.; Lim, C.Y.; Kim, H. The effects of co-administration of probiotics with herbal medicine on obesity, metabolic endotoxemia and dysbiosis: A randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, B.N.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yao, S.K. Visceral and somatic hypersensitivity, autonomic cardiovascular dysfunction and low-grade inflammation in a subset of irritable bowel syndrome patients. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2014, 15, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlsson, B.; Orho-Melander, M.; Nilsson, P.M. Higher levels of serum zonulin may rather be associated with increased risk of obesity and hyperlipidemia, than with gastrointestinal symptoms or disease manifestations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassaian, N.; Aminorroaya, A.; Feizi, A.; Jafari, P.; Amini, M. The effects of probiotic and synbiotic supplementation on metabolic syndrome indices in adults at risk of type 2 diabetes: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonucci, L.B.; Olbrich Dos Santos, K.M.; Licursi de Oliveira, L.; Rocha Ribeiro, S.M.; Duarte Martino, H.S. Clinical application of probiotics in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zohar, A.; Cohen, A.D.; Bitterman, H.; Feldhamer, I.; Greenberg-Dotan, S.; Lavi, I.; Comanesther, D.; Batat, E.; Zisman, D. Gastrointestinal comorbidities in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2679–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casellas, D.F.; Arenas, J.I.; Baudet, J.S.; Fábregas, S.; García, N.; Gelabert, J.; Medina, C.; Ochotorena, I.; Papo, M.; Rodrigo, L.; et al. Impairment of health-related quality of life in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A spanish multicenter study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2005, 11, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, T.H.; Andreoulakis, E.; Alves, G.S.; Miranda, H.L.; Braga, L.L.; Hyphantis, T.; Carvalho, A.F. Associations of sense of coherence with psychological distress and quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6713–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaz, B.L.; Bernstein, C.N. Brain-gut interactions in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Savidge, T.; Shulman, R.J. Brain-gut microbiome interactions and functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1500–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lartigue, G.; de La Serre, C.B.; Raybould, H.E. Vagal afferent neurons in high fat diet-induced obesity; intestinal microflora, gut inflammation and cholecystokinin. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 105, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M.K.; Raybould, H.E. Bugs, guts and brains, and the regulation of food intake and body weight. Int. J. Obes. Suppl. 2016, 6, S8–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kentish, S.J.; Page, A.J. The role of gastrointestinal vagal afferent fibres in obesity. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P.; Farzi, A. Neuropeptides and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockray, G.J. Enteroendocrine cell signalling via the vagus nerve. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockray, G.J. Gastrointestinal hormones and the dialogue between gut and brain. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 2927–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.M.; Brummer, R.J.; Derrien, M.; MacDonald, T.T.; Troost, F.; Cani, P.D.; Theodorou, V.; Dekker, J.; Meheust, A.; de Vos, W.M.; et al. Homeostasis of the gut barrier and potential biomarkers. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G171–G193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Gate-keeper function of the intestinal epithelium. Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinler, J.K.; Sontakke, A.; Hollister, E.B.; Venable, S.F.; Oh, P.L.; Balderas, M.A.; Saulnier, D.M.; Mistretta, T.A.; Devaraj, S.; Walter, J.; et al. From prediction to function using evolutionary genomics: Human-specific ecotypes of lactobacillus reuteri have diverse probiotic functions. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 1772–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B.; Tomar, S.K.; Mandal, S. Phenotypic and genotypic screening of human-originated lactobacilli for vitamin b12 production potential: Process validation by micro-assay and uflc. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6791–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, T.M.; Wall, R.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. Programming infant gut microbiota: Influence of dietary and environmental factors. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.Y.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, A.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, H.J.; Yang, S.J. Nutritional factors affecting mental health. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2016, 5, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hodgson, N.W.; Trivedi, M.S.; Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Fournier, M.; Cuenod, M.; Do, K.Q.; Deth, R.C. Decreased brain levels of vitamin b12 in aging, autism and schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Serino, M.; Blasco, G.; Puig, J.; Daunis-i-Estadella, J.; Ricart, W.; Burcelin, R.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Portero-Otin, M. Gut microbiota interacts with brain microstructure and function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 4505–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillisch, K.; Labus, J.; Kilpatrick, L.; Jiang, Z.; Stains, J.; Ebrat, B. Consumption of fermented milk product with probiotic modulates brain activity. Gastroenterology 2013, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeevi, D.; Korem, T.; Zmora, N.; Israeli, D.; Rothschild, D.; Weinberger, A. Personalized nutrition by prediction of glycemic responses. Cell 2015, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, A.; Denizot, J.; Thevenot, J.; Martinez-Medina, M.; Massier, S.; Sauvanet, P.; Bernalier-Donadille, A.; Denis, S.; Hofman, P.; Bonnet, R.; et al. Western diet induces a shift in microbiota composition enhancing susceptibility to adherent-invasive E. coli infection and intestinal inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Fei, N.; Pang, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; et al. A gut microbiota-targeted dietary intervention for amelioration of chronic inflammation underlying metabolic syndrome. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, J.R.; Tomas, J.; Brenner, C.; Sansonetti, P.J. Impact of high-fat diet on the intestinal microbiota and small intestinal physiology before and after the onset of obesity. Biochimie 2017, 141, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labus, J.S.; Hollister, E.B.; Jacobs, J.; Kirbach, K.; Oezguen, N.; Gupta, A.; Acosta, J.; Luna, R.A.; Aagaard, K.; Versalovic, J.; et al. Differences in gut microbial composition correlate with regional brain volumes in irritable bowel syndrome. Microbiome 2017, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Ridlon, J.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Thacker, L.R.; Heuman, D.M.; Smith, S.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Linkage of gut microbiome with cognition in hepatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G168–G175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Heuman, D.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Sanyal, A.J.; Puri, P.; Sterling, R.K.; Luketic, V.; Stravitz, R.T.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Fuchs, M.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Lactobacillus GG modulates gut microbiome, metabolome and endotoxemia in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, V.; Wade, J.B.; Heuman, D.M.; Hammeke, T.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sterling, R.K.; Stravitz, R.T.; Luketic, V.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Puri, P.; et al. Enhancement of functional connectivity, working memory and inhibitory control on multi-modal brain mr imaging with rifaximin in cirrhosis: Implications for the gut-liver-brain axis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parbo, P.; Ismail, R.; Hansen, K.V.; Amidi, A.; Marup, F.H.; Gottrup, H.; Braendgaard, H.; Eriksson, B.O.; Eskildsen, S.F.; Lund, T.E.; et al. Brain inflammation accompanies amyloid in the majority of mild cognitive impairment cases due to alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2017, 140, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, L.; Lim, W.S.; Chan, M.; Ye, R.J.; Chong, M.S. The independent role of inflammation in physical frailty among older adults with mild cognitive impairment and mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrenz, F.; Wrede, K.; Forsting, M.; Engler, H.; Schedlowski, M.; Elsenbruch, S.; Benson, S. Alterations in functional connectivity of resting state networks during experimental endotoxemia—An exploratory study in healthy men. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 54, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laparra Llopis, J.M.; Sanz Herranz, Y. Gliadins induce tnfalpha production through camp-dependent protein kinase a activation in intestinal cells (caco-2). J. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 66, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyonouchi, H.; Sun, S.; Itokazu, N. Innate immunity associated with inflammatory responses and cytokine production against common dietary proteins in patients with autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychobiology 2002, 46, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaussen, R.W.; Karlsson, M.R.; Lundin, K.E.; Jahnsen, J.; Brandtzaeg, P.; Farstad, I.N. Reduced chemokine receptor 9 on intraepithelial lymphocytes in celiac disease suggests persistent epithelial activation. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2371–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; DiSilvio, B.; Fernstrom, M.H.; Fernstrom, J.D. Meal ingestion, amino acids and brain neurotransmitters: Effects of dietary protein source on serotonin and catecholamine synthesis rates. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 98, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beshai, S.; Mishra, S.; Mishra, S.; Carleton, R.N. Personal relative deprivation associated with functional disorders via stress: An examination of fibromyalgia and gastrointestinal symptoms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Urrutia, A.; Eiroa-Orosa, F.J.; Accarino, A.; Malagelada, C.; Azpiroz, F. The role of incongruence between the perceived functioning by patients and clinicians in the detection of psychological distress among functional and motor digestive disorders. J. Psychosom. Res. 2017, 99, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, P.; Agarwal, N.; Khanna, D.; Hays, R.D.; Chang, L.; Bolus, R.; Melmed, G.; Whitman, C.B.; Kaplan, R.M.; Ogawa, R.; et al. Development of an online library of patient-reported outcome measures in gastroenterology: The gi-pro database. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azpiroz, F.; Dubray, C.; Bernalier-Donadille, A.; Cardot, J.M.; Accarino, A.; Serra, J.; Wagner, A.; Respondek, F.; Dapoigny, M. Effects of scfos on the composition of fecal microbiota and anxiety in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hustoft, T.N.; Hausken, T.; Ystad, S.O.; Valeur, J.; Brokstad, K.; Hatlebakk, J.G.; Lied, G.A. Effects of varying dietary content of fermentable short-chain carbohydrates on symptoms, fecal microenvironment, and cytokine profiles in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drakoularakou, A.; Tzortzis, G.; Rastall, R.A.; Gibson, G.R. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized human study assessing the capacity of a novel galacto-oligosaccharide mixture in reducing travellers’ diarrhoea. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Cao, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; You, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Chronic stress promotes colitis by disturbing the gut microbiota and triggering immune system response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2960–E2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langgartner, D.; Peterlik, D.; Foertsch, S.; Fuchsl, A.M.; Brokmann, P.; Flor, P.J.; Shen, Z.; Fox, J.G.; Uschold-Schmidt, N.; Lowry, C.A.; et al. Individual differences in stress vulnerability: The role of gut pathobionts in stress-induced colitis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 64, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, A.P.; Hutch, W.; Borre, Y.E.; Kennedy, P.J.; Temko, A.; Boylan, G.; Murphy, E.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G. Bifidobacterium longum 1714 as a translational psychobiotic: Modulation of stress, electrophysiology and neurocognition in healthy volunteers. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Costacurta, M.; Merra, G.; Gualtieri, P.; Cioccoloni, G.; Marchetti, M.; Varvaras, D.; Docimo, R.; Di Renzo, L. Can psychobiotics intake modulate psychological profile and body composition of women affected by normal weight obese syndrome and obesity? A double blind randomized clinical trial. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, V. Gut microbiome profiling tests propelled by customer demand. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P. Dynamics and stabilization of the human gut microbiome during the first year of life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Saarinen, A.; Mikkola, T.M.; Tenhunen, J.; Martinmaki, S.; Rahikainen, A.; Cheng, S.; Eklund, N.; Pekkala, S.; Wiklund, P.; et al. Effects of exercise and diet interventions on obesity-related sleep disorders in men: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2013, 14, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankelma, J.M.; van Vught, L.A.; Belzer, C.; Schultz, M.J.; van der Poll, T.; de Vos, W.M.; Wiersinga, W.J. Critically ill patients demonstrate large interpersonal variation in intestinal microbiota dysregulation: A pilot study. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, M.B.; Firek, B.; Shi, M.; Yeh, A.; Brower-Sinning, R.; Aveson, V.; Kohl, B.L.; Fabio, A.; Carcillo, J.A.; Morowitz, M.J. Disruption of the microbiota across multiple body sites in critically ill children. Microbiome 2016, 4, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, V.J.; Kim, S.; Blanchard, E.T.; Luo, M.; Jazwinski, S.M.; Taylor, C.M.; Welsh, D.A. Biological aging and the human gut microbiota. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, R.; Song, Y.; Garg, S.; Girotra, M.; Sinha, A.; Sivaraman, A.; Phillips, L.; Dutta, S.K. Effect of aging on the composition of fecal microbiota in donors for FMT and its impact on clinical outcomes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.A.; Jeffery, I.B.; Beaumont, M.; Bell, J.T.; Clark, A.G.; Ley, R.E.; O’Toole, P.W.; Spector, T.D.; Steves, C.J. Signatures of early frailty in the gut microbiota. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, P.A.B.; Aho, V.T.E.; Paulin, L.; Pekkonen, E.; Auvinen, P.; Scheperjans, F. Oral and nasal microbiota in parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 38, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopfner, F.; Kunstner, A.; Muller, S.H.; Kunzel, S.; Zeuner, K.E.; Margraf, N.G.; Deuschl, G.; Baines, J.F.; Kuhlenbaumer, G. Gut microbiota in parkinson disease in a northern german cohort. Brain Res. 2017, 1667, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiman, S.C.; Glenny, E.M.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.C.; Huh, E.Y.; Tsilimigras, M.C.B.; Fodor, A.A.; Bulik, C.M.; Carroll, I.M. Daily changes in composition and diversity of the intestinal microbiota in patients with anorexia nervosa: A series of three cases. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2017, 25, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, C.; Tsuji, H.; Hata, T.; Gondo, M.; Takakura, S.; Kawai, K.; Yoshihara, K.; Ogata, K.; Nomoto, K.; Miyazaki, K.; et al. Gut dysbiosis in patients with anorexia nervosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgo, F.; Riva, A.; Benetti, A.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Bertelli, S.; Garbossa, S.; Anselmetti, S.; Scarone, S.; Pontiroli, A.E.; Morace, G.; et al. Microbiota in anorexia nervosa: The triangle between bacterial species, metabolites and psychological tests. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Clavero, P.; Toledo, E.; San Julian, B.; Sanchez-Tainta, A.; Corella, D.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Martinez, J.A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. Virgin olive oil supplementation and long-term cognition: The predimed-navarra randomized, trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Sala-Vila, A.; Serra-Mir, M.; Corella, D.; de la Torre, R.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Martinez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Fito, M.; Perez-Heras, A.; Salas-Salvado, J.; et al. Mediterranean diet and age-related cognitive decline: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Barfoot, K.L.; May, G.; Lamport, D.J.; Reynolds, S.A.; Williams, C.M. Effects of acute blueberry flavonoids on mood in children and young adults. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Pase, M.; Pipingas, A.; Raubenheimer, J.; Thurgood, M.; Villalon, L.; Macpherson, H.; Gibbs, A.; Scholey, A. Switching to a 10-day mediterranean-style diet improves mood and cardiovascular function in a controlled crossover study. Nutrition 2015, 31, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamport, D.J.; Pal, D.; Macready, A.L.; Barbosa-Boucas, S.; Fletcher, J.M.; Williams, C.M.; Spencer, J.P.; Butler, L.T. The effects of flavanone-rich citrus juice on cognitive function and cerebral blood flow: An acute, randomised, placebo-controlled cross-over trial in healthy, young adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroix, L.; Tonoli, C.; Soares, D.D.; Tagougui, S.; Heyman, E.; Meeusen, R. Acute cocoa flavanol improves cerebral oxygenation without enhancing executive function at rest or after exercise. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.F.; Loizzo, M.R.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Nabavi, S.M. Flavonoids and dementia: An update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.A.; Havlik, J.; Cong, W.; Mullen, W.; Preston, T.; Morrison, D.J.; Combet, E. Polyphenols and health: Interactions between fibre, plant polyphenols and the gut microbiota. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics (isapp) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.Y.; Summanen, P.H.; Lee, R.P.; Huang, J.; Henning, S.M.; Heber, D.; Finegold, S.M.; Li, Z. Prebiotic potential and chemical composition of seven culinary spice extracts. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1807–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selma, M.V.; Espin, J.C.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. Interaction between phenolics and gut microbiota: Role in human health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6485–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Hyde, E.R.; Debelius, J.W.; Morton, J.T.; Gonzalez, A.; Ackermann, G.; Aksenov, A.A.; Behsaz, B.; Brennan, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. American gut: An open platform for citizen-science microbiome research. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheflin, A.M.; Melby, C.L.; Carbonero, F.; Weir, T.L. Linking dietary patterns with gut microbial composition and function. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, E.; Munoz-Gonzalez, I.; Jimenez, E.; Bartolome, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Pelaez, C.; Del Carmen Martinez-Cuesta, M.; Requena, T. Phylogenetic profile of gut microbiota in healthy adults after moderate intake of red wine. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmos, E.P.; Christophersen, C.T.; Bird, A.R.; Shepherd, S.J.; Gibson, P.R.; Muir, J.G. Diets that differ in their fodmap content alter the colonic luminal microenvironment. Gut 2015, 64, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duenas, M.; Munoz-Gonzalez, I.; Cueva, C.; Jimenez-Giron, A.; Sanchez-Patan, F.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Bartolome, B. A survey of modulation of gut microbiota by dietary polyphenols. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 850902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavel, T.; Fallani, M.; Lepage, P.; Levenez, F.; Mathey, J.; Rochet, V.; Serezat, M.; Sutren, M.; Henderson, G.; Bennetau-Pelissero, C.; et al. Isoflavones and functional foods alter the dominant intestinal microbiota in postmenopausal women. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, L.; Florez, A.B.; Guadamuro, L.; Mayo, B. Effect of soy isoflavones on growth of representative bacterial species from the human gut. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Beltran, C.E.; Calderon-Oliver, M.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Chirino, Y.I. Protective effect of sulforaphane against oxidative stress: Recent advances. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Nieves, J.W.; Stern, Y.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Scarmeas, N. Food combination and alzheimer disease risk: A protective diet. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argollo, M.; Fiorino, G.; Hindryckx, P.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Novel therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel disease. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 85, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblhuber, F.; Geisler, S.; Steiner, K.; Fuchs, D.; Schütz, B. Elevated fecal calprotectin in patients with alzheimer’s dementia indicates leaky gut. J. Neural Transm. 2015, 122, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, I.; Jia, X.; Johansson, P.; Wang, C.; Moskalenko, R.; Steinau, A.; Forsgren, L.; Wagberg, T.; Svensson, J.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Pro-inflammatory s100a9 protein as a robust biomarker differentiating early stages of cognitive impairment in alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Campo, R.; Garriga, M.; Perez-Aragon, A.; Guallarte, P.; Lamas, A.; Maiz, L.; Bayon, C.; Roy, G.; Canton, R.; Zamora, J.; et al. Improvement of digestive health and reduction in proteobacterial populations in the gut microbiota of cystic fibrosis patients using a lactobacillus reuteri probiotic preparation: A double blind prospective study. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014, 13, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzese, E.; Callegari, M.L.; Raia, V.; Viscovo, S.; Scotto, R.; Ferrari, S.; Morelli, L.; Buccigrossi, V.; Lo Vecchio, A.; Ruberto, E.; et al. Disrupted intestinal microbiota and intestinal inflammation in children with cystic fibrosis and its restoration with lactobacillus Gg: A randomised clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1258, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Intestinal permeability and its regulation by zonulin: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollon, J.; Puppa, E.L.; Greenwald, B.; Goldberg, E.; Guerrerio, A.; Fasano, A. Effect of gliadin on permeability of intestinal biopsy explants from celiac disease patients and patients with non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobjova, T.; Raikkerus, H.; Kadaja, L.; Talja, I.; Uibo, O.; Heilman, K.; Uibo, R. Circulating zonulin correlates with density of enteroviruses and tolerogenic dendritic cells in the small bowel mucosa of celiac disease patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daulatzai, M.A. Non-celiac gluten sensitivity triggers gut dysbiosis, neuroinflammation, gut-brain axis dysfunction, and vulnerability for dementia. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 14, 110–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, R.D.; Zawahir, S. Celiac disease and nonceliac gluten sensitivity. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 64, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volta, U.; Caio, G.; Karunaratne, T.B.; Alaedini, A.; De Giorgio, R. Non-coeliac gluten/wheat sensitivity: Advances in knowledge and relevant questions. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czaja-Bulsa, G. Non coeliac gluten sensitivity—A new disease with gluten intolerance. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardella, M.T.; Elli, L.; Ferretti, F. Non celiac gluten sensitivity. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J. Non-coeliac gluten or wheat sensitivity: Emerging disease or misdiagnosis? Med. J. Aust. 2017, 207, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Salhy, M.; Hatlebakk, J.G.; Gilja, O.H.; Hausken, T. The relation between celiac disease, nonceliac gluten sensitivity and irritable bowel syndrome. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catassi, C. Gluten sensitivity. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 67 (Suppl. 2), 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, G.; Pozzi, R.; Cigognetti, M.; Bachetti, F.; Torti, G.; Cadei, M.; Villanacci, V.; Baldini, V.; Bassotti, G. Mood disorders and non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2017, 63, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionetti, E.; Leonardi, S.; Franzonello, C.; Mancardi, M.; Ruggieri, M.; Catassi, C. Gluten psychosis: Confirmation of a new clinical entity. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5532–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagci, H.; Ustun, S.; Taner, M.S.; Ersoz, G.; Karacasu, F.; Budak, S. Protozoon infections and intestinal permeability. Acta Trop. 2002, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boorom, K.F.; Smith, H.; Nimri, L.; Viscogliosi, E.; Spanakos, G.; Parkar, U.; Li, L.-H.; Zhou, X.-N.; Ok, Ü.Z.; Leelayoova, S.; et al. Oh my aching gut: Irritable bowel syndrome, blastocystis, and asymptomatic infection. Parasites Vectors 2008, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.; Stark, D.; Harkness, J.; Ellis, J. Update on the pathogenic potential and treatment options for Blastocystis sp. Gut Pathogens 2014, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinleyici, E.C.; Eren, M.; Dogan, N.; Reyhanioglu, S.; Yargic, Z.A.; Vandenplas, Y. Clinical efficacy of saccharomyces boulardii or metronidazole in symptomatic children with blastocystis hominis infection. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, L.; Larocca, L.; Massarelli, L.; Patamia, I.; Minniti, S.; Palermo, F.; Cacopardo, B. A placebo-controlled treatment trial of blastocystis hominis infection with metronidazole. J. Travel Med. 2003, 10, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamprecht, M.; Bogner, S.; Steinbauer, K.; Schuetz, B.; Greilberger, J.F.; Leber, B.; Wagner, B.; Zinser, E.; Petek, T.; Wallner-Liebmann, S.; et al. Effects of zeolite supplementation on parameters of intestinal barrier integrity, inflammation, redoxbiology and performance in aerobically trained subjects. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halasa, M.; Maciejewska, D.; Baskiewicz-Halasa, M.; Machalinski, B.; Safranow, K.; Stachowska, E. Oral supplementation with bovine colostrum decreases intestinal permeability and stool concentrations of zonulin in athletes. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H.; Huang, M.J.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, L.; Huang, N.Q.; Peng, H.; Lan, P.; Peng, J.S.; Yang, Z.; Xia, Y.; et al. The effects of perioperative probiotic treatment on serum zonulin concentration and subsequent postoperative infectious complications after colorectal cancer surgery: A double-center and double-blind randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, W.R.; Hoyles, L.; Flint, H.J.; Dumas, M.E. Colonic bacterial metabolites and human health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Bacteria, colonic fermentation, and gastrointestinal health. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, S.; Macfarlane, G.T. Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Goncalves, D.; Vinera, J.; Zitoun, C.; Duchampt, A.; Backhed, F.; Mithieux, G. Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 2014, 156, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segain, J.P.; Raingeard de la Bletiere, D.; Bourreille, A.; Leray, V.; Gervois, N.; Rosales, C.; Ferrier, L.; Bonnet, C.; Blottiere, H.M.; Galmiche, J.P. Butyrate inhibits inflammatory responses through nfkappab inhibition: Implications for crohn’s disease. Gut 2000, 47, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Lahham, S.H.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Roelofsen, H.; Vonk, R.J.; Venema, K. Biological effects of propionic acid in humans; metabolism, potential applications and underlying mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.R. Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 2003, 361, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, T.; Kishimoto, A. Cellular distributions of monocarboxylate transporters: A review. Biomed. Res. 2015, 36, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, T.; Sharma, R.; Frost, G. Propionate. Anti-obesity and satiety enhancing factor? Appetite 2011, 56, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stilling, R.M.; van de Wouw, M.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The neuropharmacology of butyrate: The bread and butter of the microbiota-gut-brain axis? Neurochem. Int. 2016, 99, 110–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courchesne-Loyer, A.; Croteau, E.; Castellano, C.A.; St-Pierre, V.; Hennebelle, M.; Cunnane, S.C. Inverse relationship between brain glucose and ketone metabolism in adults during short-term moderate dietary ketosis: A dual tracer quantitative positron emission tomography study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 2485–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunnane, S.C.; Courchesne-Loyer, A.; St-Pierre, V.; Vandenberghe, C.; Pierotti, T.; Fortier, M.; Croteau, E.; Castellano, C.A. Can ketones compensate for deteriorating brain glucose uptake during aging? Implications for the risk and treatment of alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1367, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulnier, D.M.; Ringel, Y.; Heyman, M.B.; Foster, J.A.; Bercik, P.; Shulman, R.J.; Versalovic, J.; Verdu, E.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Hecht, G.; et al. The intestinal microbiome, probiotics and prebiotics in neurogastroenterology. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattal, K.M.; Barrett, R.M.; Wood, M.A. Systemic or intrahippocampal delivery of histone deacetylase inhibitors facilitates fear extinction. Behav. Neurosci. 2007, 121, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braniste, V.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Kowal, C.; Anuar, F.; Abbaspour, A.; Toth, M.; Korecka, A.; Bakocevic, N.; Ng, L.G.; Kundu, P.; et al. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 263ra158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraca, M.; Putignani, L.; Fierabracci, A.; Teti, A.; Perilongo, G. Gut microbiota-derived outer membrane vesicles: Under-recognized major players in health and disease? Discov. Med. 2015, 19, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi Badi, S.; Moshiri, A.; Fateh, A.; Rahimi Jamnani, F.; Sarshar, M.; Vaziri, F.; Siadat, S.D. Microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles as new systemic regulators. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Ge, S.; Singh, R.; Basu, S.; Shatzer, K.; Zen, M.; Liu, J.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, J.; et al. Glucuronidation: Driving factors and their impact on glucuronide disposition. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 105–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, M.S.; Pellock, S.J.; Walton, W.G.; Tripathy, A.; Redinbo, M.R. Structural basis for the regulation of beta-glucuronidase expression by human gut enterobacteriaceae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E152–E161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellock, S.J.; Redinbo, M.R. Glucuronides in the gut: Sugar-driven symbioses between microbe and host. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8569–8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, R.; Shi, J.; Fuhrman, B.; Xu, X.; Veenstra, T.D.; Gail, M.H.; Gajer, P.; Ravel, J.; Goedert, J.J. Fecal microbial determinants of fecal and systemic estrogens and estrogen metabolites: A cross-sectional study. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrocco, J.; McEwen, B.S. Sex in the brain: Hormones and sex differences. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 18, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patterson, E.; Cryan, J.F.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P.; Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C. Gut microbiota, the pharmabiotics they produce and host health. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, D.G.; Um, Y.J.; Seo, C.S.; Han, J.W.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, G.H.; Jeong, T.C.; et al. The effect of gut microbiota on drug metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umbrello, G.; Esposito, S. Microbiota and neurologic diseases: Potential effects of probiotics. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzelani, A.; Landini, M.; Facchiano, F.; Raggi, M.E.; Villa, L.; Molteni, M.; De Santis, B.; Brera, C.; Caroli, A.M.; Milanesi, L.; et al. Environment, dysbiosis, immunity and sex-specific susceptibility: A translational hypothesis for regressive autism pathogenesis. Nutr. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Liu, Y.; Zou, H.; Son, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Shao, J. Determination of d-glucaric acid and/or d-glucaro-1,4-lacton in different apple varieties through hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, J.L.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Yoo, K.S.; Patil, B.S. Development of a method for the quantification of d-glucaric acid in different varieties of grapefruits by high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectra. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1190, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.K.; Dong, N.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Le, P.H. Lactic acid bacteria: Promising supplements for enhancing the biological activities of kombucha. Springerplus 2015, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanausek, M.; Walaszek, Z.; Slaga, T.J. Detoxifying cancer causing agents to prevent cancer. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, G.S.; Sathishkumar, M.; Jayabalan, R.; Binupriya, A.R.; Swaminathan, K.; Yun, S.E. Hepatoprotective and curative properties of kombucha tea against carbon tetrachloride-induced toxicity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battikh, H.; Chaieb, K.; Bakhrouf, A.; Ammar, E. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of black and green kombucha teas. J. Food Biochem. 2013, 37, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Bhattacharya, S.; Patra, M.M.; Chakravorty, S.; Sarkar, S.; Chakraborty, W.; Koley, H.; Gachhui, R. Antibacterial activity of polyphenolic fraction of kombucha against enteric bacterial pathogens. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J.; Tzortzis, G.; Errington, S.; Burnet, P.W. Prebiotic intake reduces the waking cortisol response and alters emotional bias in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Psychobiotics: A novel class of psychotropic. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Lehto, S.M.; Harty, S.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Burnet, P.W. Psychobiotics and the manipulation of bacteria-gut-brain signals. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.; Reid, G. Distant site effects of ingested prebiotics. Nutrients 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; Zieliński, H. Buckwheat as a functional food and its effects on health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7896–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Darko, K.O.; Huang, Y.; He, C.; Yang, H.; He, S.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Hocher, B.; Yin, Y.; et al. Resistant starch regulates gut microbiota: Structure, biochemistry and cell signalling. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.A.; Jazayeri, S.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Solati, Z.; Mohammadpour, N.; Asemi, Z.; Adab, Z.; Djalali, M.; Tehrani-Doost, M.; Hosseini, M.; et al. The effects of probiotics on mental health and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in petrochemical workers. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, R.; DiMarco, D.M.; Putt, K.K.; Martin, D.A.; Gu, Q.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; White, H.M.; Scarlett, C.O.; Bruno, R.S.; Bolling, B.W. Low-fat yogurt consumption reduces biomarkers of chronic inflammation and inhibits markers of endotoxin exposure in healthy premenopausal women: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, D.D.; Dias, M.M.S.; Grzeskowiak, L.M.; Reis, S.A.; Conceicao, L.L.; Peluzio, M. Milk kefir: Nutritional, microbiological and health benefits. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, M.R.; Blandón, L.M.; Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; Rodrigues, C.; Castro, G.R.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Milk kefir: Composition, microbial cultures, biological activities, and related products. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yüksekdağ, Z.N.; Beyatli, Y.; Aslim, B. Determination of some characteristics coccoid forms of lactic acid bacteria isolated from turkish kefirs with natural probiotic. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanirati, D.F.; Abatemarco, M., Jr.; Sandes, S.H.; Nicoli, J.R.; Nunes, A.C.; Neumann, E. Selection of lactic acid bacteria from brazilian kefir grains for potential use as starter or probiotic cultures. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witthuhn, R.C.; Schoeman, T.; Britz, T.J. Characterisation of the microbial population at different stages of kefir production and kefir grain mass cultivation. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diosma, G.; Romanin, D.E.; Rey-Burusco, M.F.; Londero, A.; Garrote, G.L. Yeasts from kefir grains: Isolation, identification, and probiotic characterization. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carasi, P.; Racedo, S.M.; Jacquot, C.; Romanin, D.E.; Serradell, M.A.; Urdaci, M.C. Impact of kefir derived lactobacillus kefiri on the mucosal immune response and gut microbiota. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 361604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, S.T.; Nisa, M.; Ahmad, H.; Afreen, A. Kefir and health: A contemporary perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, B.; Gurakan, G.C.; Unlu, G. Kefir: A multifaceted fermented dairy product. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2014, 6, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzel-Seydim, Z.B.; Kok-Tas, T.; Greene, A.K.; Seydim, A.C. Review: Functional properties of kefir. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishina, A.; Kulikova, I.; Alieva, L.; Dodson, A.; Rowland, I.; Jin, J. Antigenotoxic effect of kefir and ayran supernatants on fecal water-induced DNA damage in human colon cells. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.Y.; Lee, P.; Denney, D.R.; Spaeth, K.; Nast, O.; Ptomey, L.; Roth, A.K.; Lierman, J.A.; Sullivan, D.K. Dairy intake is associated with brain glutathione concentration in older adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, M.; Dinleyici, E.C. The history of probiotics: The untold story. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunick, M.H.; Van Hekken, D.L. Dairy products and health: Recent insights. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9381–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bau, T.R.; Garcia, S.; Ida, E.I. Optimization of a fermented soy product formulation with a kefir culture and fiber using a simplex-centroid mixture design. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bau, T.R.; Garcia, S.; Ida, E.I. Changes in soymilk during fermentation with kefir culture: Oligosaccharides hydrolysis and isoflavone aglycone production. Int. J. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureys, D.; De Vuyst, L. Microbial species diversity, community dynamics, and metabolite kinetics of water kefir fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureys, D.; De Vuyst, L. The water kefir grain inoculum determines the characteristics of the resulting water kefir fermentation process. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulitz, A.; Stadie, J.; Wenning, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. The microbial diversity of water kefir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco, M.L.; Heeney, D.; Binda, S.; Cifelli, C.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Foligne, B.; Ganzle, M.; Kort, R.; Pasin, G.; Marco, M.L.; et al. Health benefits of fermented foods: Microbiota and beyond. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Fermented food in the context of a healthy diet: How to produce novel functional foods? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Marotta, F.; Dominguez, L.J. Oxidative stress in patients with alzheimer’s disease: Effect of extracts of fermented papaya powder. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 624801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruoma, O.I.; Hayashi, Y.; Marotta, F.; Mantello, P.; Rachmilewitz, E.; Montagnier, L. Applications and bioefficacy of the functional food supplement fermented papaya preparation. Toxicology 2010, 278, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, C. Measuring outcomes in primary care: A patient generated measure, mymop, compared with the sf-36 health survey. BMJ 1996, 312, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, C.; Britten, N. In pursuit of patient-centred outcomes: A qualitative evaluation of the ‘measure yourself medical outcome profile’. J. Health Serv. Res. Policy 2000, 5, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, C. Seeking the patient’s perspective: A qualitative assessment of euroqol, coop-wonca charts and mymop. Qual. Life Res. 2004, 13, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, S.; Mercer, S.W.; MacPherson, H. Practitioner empathy, patient enablement and health outcomes: A prospective study of acupuncture patients. Patient Educ. Couns. 2006, 63, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schork, N.J. Personalized medicine: Time for one-person trials. Nature 2015, 520, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toribio-Mateas, M.A.; Spector, T. Could food act as personalized medicine for chronic disease? Personal. Med. 2017, 14, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toribio-Mateas, M. Harnessing the Power of Microbiome Assessment Tools as Part of Neuroprotective Nutrition and Lifestyle Medicine Interventions. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6020035
Toribio-Mateas M. Harnessing the Power of Microbiome Assessment Tools as Part of Neuroprotective Nutrition and Lifestyle Medicine Interventions. Microorganisms. 2018; 6(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleToribio-Mateas, Miguel. 2018. "Harnessing the Power of Microbiome Assessment Tools as Part of Neuroprotective Nutrition and Lifestyle Medicine Interventions" Microorganisms 6, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6020035




