Ambient Pressure Laser Desorption—Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Fast and Reliable Detection of Explosives, Drugs, and Their Precursors
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Improved Detection Limits through Design Optimization
3.1.1. Sampling Head Design Optimization
3.1.2. Optimization of Desorption Area
3.1.3. Optimization Results
3.2. Target Compound Enhancement
3.3. Real Sample Measurements
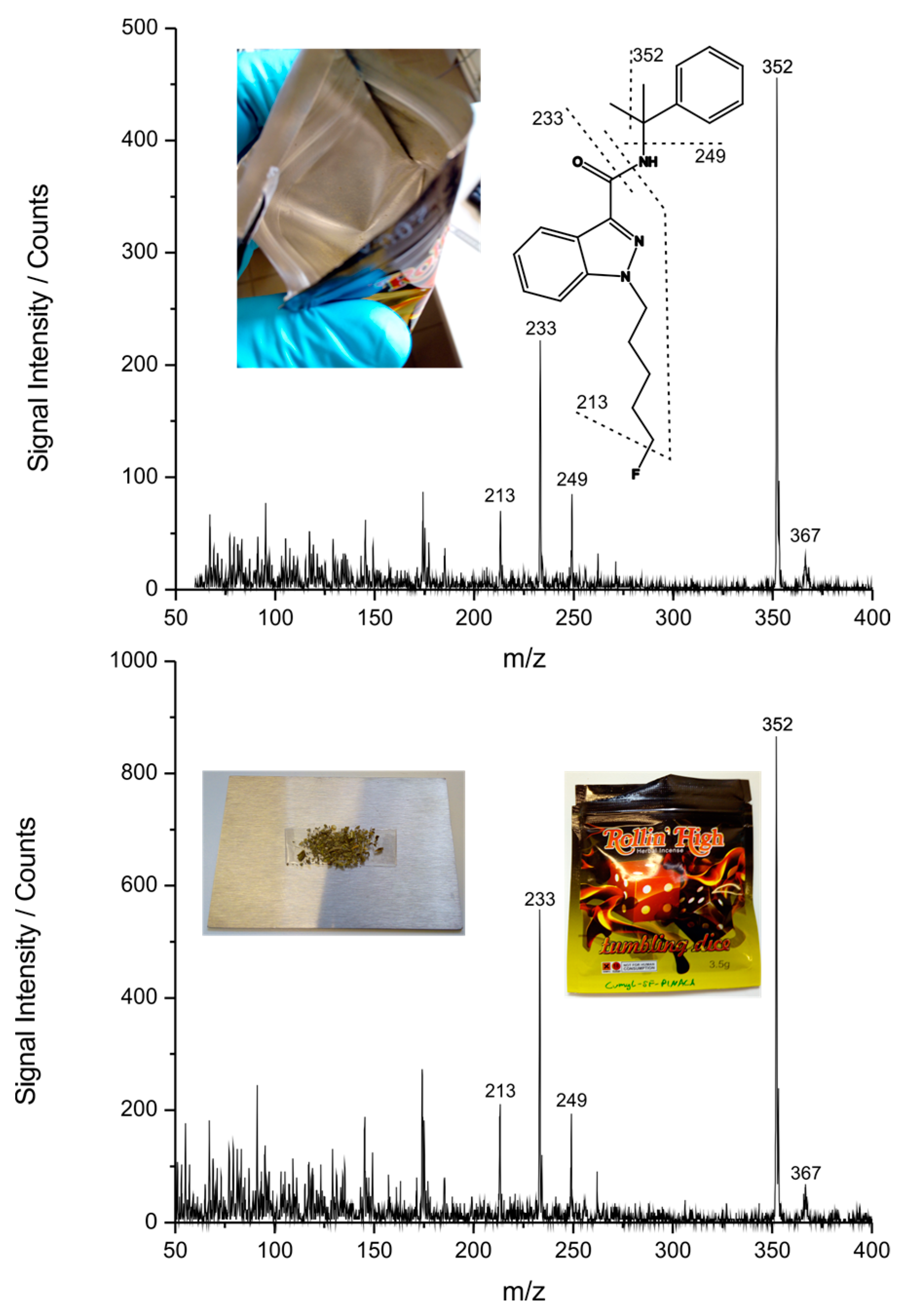
3.3.1. Shrapnel of Defused Bomb
3.3.2. New Psychoactive Substance on Herbal Mixture
3.4. Additional Capabilities of the APLD Approach
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boumsellek, S.; Alajajian, H.; Chutjian, A. Negative-Ion formation in the explosives RDX, PETN, and TNT by using the reversal electron attachment detection technique. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1992, 3, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielsdorf, W. Identifizierung einiger Sprengstoffe mit Hilfe spezieller GC/MS-Techniken, insbesondere der PPNICI-Methode. Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 1981, 308, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, R.G. Chemical ionisation mass spectra of explosives. Org. Mass Spectrom. 1974, 9, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pate, C.T.; Mach, M.H. Analysis of explosives using chemical ionization mass spectroscopy. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Phys. 1978, 26, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Lin, K.-L.; Chen, S.-C.; Chang, Y.-Z. Integration of GC/EI-MS and GC/NCI-MS for simultaneous quantitative determination of opiates, amphetamines, MDMA, ketamine, and metabolites in human hair. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 870, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yinon, J.; McClellan, J.E.; Yost, R.A.; Lifshitz, C. Electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry collision-induced dissociation study of explosives in an ion trap mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 11, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, R.E. An Introduction to Quadrupole Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 32, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schramm, E.; Sklorz, M.; Zimmermann, R.H. Verfahren und Vorrichtung für den Nachweis von organischen Spurenbestandteilen auf Oberflächen. Patent No. DE102007045361, 22 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nilles, J.M.; Connell, T.R.; Stokes, S.T.; Dupont Durst, H. Explosives Detection Using Direct Analysis in Real Time (DART) Mass Spectrometry. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2010, 35, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, F.; Seviour, J.; Lim, A.Y.; Elumbaring-Salazar, C.G.; Loke, J.; Ma, J. Detection of nitro-organic and peroxide explosives in latent fingermarks by DART- and SALDI-TOF-mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 221, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridoux, M.C.; Schwarzenberg, A.; Schramm, S.; Cole, R.B. Combined use of direct analysis in real-time/Orbitrap mass spectrometry and micro-Raman spectroscopy for the comprehensive characterization of real explosive samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5677–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.-H.; Lin, Z.; Garimella, S.; Zheng, L.; Shi, R.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Development of a mass spectrometry sampling probe for chemical analysis in surgical and endoscopic procedures. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11843–11850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justes, D.R.; Talaty, N.; Cotte-Rodriguez, I.; Cooks, R.G. Detection of explosives on skin using ambient ionization mass spectrometry. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2142–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabelli, M.F.; Coviello, G.; Volmer, D.A. Determining fatty acids by desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using thin-layer chromatography substrates. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 4513–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, B.; Walker, G.S.; Kobus, H.; Pigou, P.; Bird, C.; Smith, G. The analysis of dyes in ball point pen inks on single paper fibres using laser desorption ionisation time of flight mass spectrometry (LDI-TOFMS). Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 209, e26–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, M.; Bachmann, D.; Hillenkamp, F. Influence of the Wavelength in High-Irradiance Ultraviolet Laser Desorption Mass Spectrometry of Organic Molecules. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, 2935–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, Z.; Bai, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, R.; Zhao, F. Using molecular recognition of beta-cyclodextrin to determine molecular weights of low-molecular-weight explosives by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 17, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silina, Y.E.; Koch, M.; Volmer, D.A. The role of physical and chemical properties of Pd nanostructured materials immobilized on inorganic carriers on ion formation in atmospheric pressure laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 49, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, L.R.; Reschke, B.; Friend, J.; Powell, M.; Vertes, A. Remote laser ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for non-proximate analysis of biological tissues. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, M.; Ovchinnikova, O.S.; Kertesz, V.; Van Berkel, G.J. Laser microdissection and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry coupled for multimodal imaging. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Solliec, M.; Sinotte, M.; Deblois, C.; Sauvé, S. High resolution/accurate mass (HRMS) detection of anatoxin-a in lake water using LDTD-APCI coupled to a Q-Exactive mass spectrometer. Talanta 2015, 132, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrical, B.D.; Fergenson, D.P.; Prather, K.A. Coupling two-step laser desorption/ionization with aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the analysis of individual organic particles. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1998, 9, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickhardt, C.; Kaiser, N.; Borsdorf, H. Ion mobility spectrometry of laser desorbed pesticides from fruit surfaces. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 2012, 15, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, C.; Cabezas, C.; Mata, S.; Berdakin, M.; Tejedor, J.M.; Alonso, J.L. Analysis of illicit drugs by direct ablation of solid samples. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 21, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J.S.; Bryden, W.A.; Miragliotta, J.A.; Aamodt, L.C. Improved Detection of Explosive Residues by Laser Thermal Desorption. Johns Hopkins APL Tech. Digest 1999, 20, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Sabo, M.; Malásková, M.; Matejčík, Š. Laser desorption with corona discharge ion mobility spectrometry for direct surface detection of explosives. Analyst 2014, 139, 5112–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östmark, H.; Wallin, S.; Ang, H.G. Vapor Pressure of Explosives: A Critical Review. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2012, 37, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindal, A.B.; Jenkins, R.A.; Buchanan, M.V.; Bayne, C.K. Determination of cocaine and heroin vapor pressures using commercial and illicit samples. Analyst 2000, 125, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lubman, D.M. Pulsed laser desorption method for volatilizing thermally labile molecules for supersonic jet spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1988, 59, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlert, S.; Walte, A.; Zimmermann, R. Ambient pressure laser desorption and laser-induced acoustic desorption ion mobility spectrometry detection of explosives. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11047–11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlert, S.; Hölzer, J.; Rittgen, J.; Pütz, M.; Schulte-Ladbeck, R.; Zimmermann, R. Rapid on-site detection of explosives on surfaces by ambient pressure laser desorption and direct inlet single photon ionization or chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 6979–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, A.; Tollefson, E.L. Catalytic reduction of nitric oxide in low concentration high velocity gas streams. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1973, 51, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, L.T.; Berg, J.D. 1-Adamantylamine a simple urine marker for screening for third generation adamantyl-type synthetic cannabinoids by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 53, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, P.-K.; Ng, T.-T.; Wang, H.; Hu, B.; Yao, Z.-P. Rapid detection and quantitation of ketamine and norketamine in urine and oral fluid by wooden-tip electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst 2013, 138, 2239–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, A.; Doi, T.; Tagami, T.; Takeda, A.; Satsuki, Y.; Kawaguchi, M.; Nakamura, A.; Sawabe, Y. Cannabimimetic activities of cumyl carboxamide-type synthetic cannabinoids. Forensic Toxicol. 2017, 31, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Du, H.; Cheng, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Fan, M. Fabrication of SERS swab for direct detection of trace explosives in fingerprints. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21931–21937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabo, M.; Malásková, M.; Matejčík, Š. Ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry studies of ion processes in air at atmospheric pressure and their application to thermal desorption of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, T.P.; Staymates, M.; Sisco, E. Broad spectrum infrared thermal desorption of wipe-based explosive and narcotic samples for trace mass spectrometric detection. Analyst 2017, 142, 3002–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G.; Xu, W. Rapid screening of explosives in ambient environment by aerodynamic assisted thermo desorption mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, F.M.; Salter, T.L.; Stokes, P.; Gilmore, I.S.; O’Connor, G. Ambient mass spectrometry: Advances and applications in forensics. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovska, N.; Kelly, T.; Tahtouh, M.; Beavis, A.; Fu, S. Analysis of amphetamine-type substances and piperazine analogues using desorption electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Reyes, J.F.; Harper, J.D.; Salazar, G.A.; Charipar, N.A.; Ouyang, Z.; Cooks, R.G. Detection of explosives and related compounds by low-temperature plasma ambient ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisco, E.; Forbes, T.P.; Staymates, M.E.; Gillen, G. Rapid Analysis of Trace Drugs and Metabolites Using a Thermal Desorption DART-MS Configuration. Anal. Methods: Adv. Methods Appl. 2016, 8, 6494–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sägmüller, B.; Schwarze, B.; Brehm, G.; Trachta, G.; Schneider, S. Identification of illicit drugs by a combination of liquid chromatography and surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 661–662, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoranville, L.T.; Brewer, T.M. Ambient pressure thermal desorption ionization mass spectrometry for the analysis of substances of forensic interest. Analyst 2013, 138, 5332–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Song, Q.; Patterson, G.E.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Handheld rectilinear ion trap mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5994–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Substance Measured | LOD Original System | LOD Novel System | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNT (trinitrotoluene) | 3 ng | 500 pg | 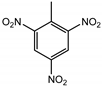 |
| 1,3-Dinitrobenzene | 6 ng | 1.5 ng | 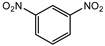 |
| 2,4-DNT (Dinitrotoluene) | 3 ng | 1.5 ng | 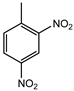 |
| 2,6-DNT | 6 ng | 2 ng | 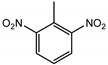 |
| Tetryl (2,4,6-trinitrophenylmethylnitramine) *, m/z 241 | 30 ng | 2 ng | 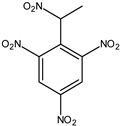 |
| Substances Measured at Novel Systems | LOD | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Explosives | ||
| PA (picric acid) | 15 ng | 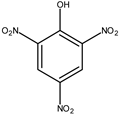 |
| 3,4-DNT | 3 ng | 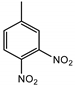 |
| TATP (triacetonetriperoxide) | 800 ng |  |
| AN (ammonia nitrate) *, m/z 63 | 78 ng | 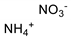 |
| Drug precursors | ||
| Safrole | 100 ng | 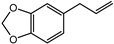 |
| Phenylacetone | 50 ng |  |
| Drugs/drugs of abuse | ||
| Amphetamine | 20 ng | 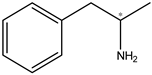 |
| Methamphetamine | 10 ng |  |
| MDMA (3,4-methylendioxy-methamphetamine) hydrochloride | 20 ng | 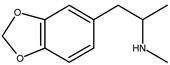 |
| Heroin | 200 ng |  |
| Cocaine hydrochloride | 17 ng |  |
| Ketamine hydrochloride | 6 ng |  |
| Compared Analytical Technique | Measured Substance | LOD Ref. Technique/ng | LOD APLD/ng |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raman spectroscopy | 2,4-DNT | 5 | 1.5 |
| Cocaine HCl | 1000 | 17 | |
| Ion mobility spectrometry | TNT | 0.35 | 0.5 |
| Cocaine HCl | 5 | 5 | |
| Thermal desorption MS | TNT | 5 | 0.5 |
| Cocaine HCl | 388 | 17 | |
| MDMA | 2 | 10 | |
| Desorption spray ionization | TNT | 10 fg | 0.5 |
| Amphetamine | 14 | 20 | |
| Low-temperature plasma probe | Tetryl | 0.25 | 2 |
| DART-TD-MS | Tetryl | 2 | 2 |
| MDMA | 2 | 10 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reiss, R.; Ehlert, S.; Heide, J.; Pütz, M.; Forster, T.; Zimmermann, R. Ambient Pressure Laser Desorption—Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Fast and Reliable Detection of Explosives, Drugs, and Their Precursors. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060933
Reiss R, Ehlert S, Heide J, Pütz M, Forster T, Zimmermann R. Ambient Pressure Laser Desorption—Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Fast and Reliable Detection of Explosives, Drugs, and Their Precursors. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(6):933. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060933
Chicago/Turabian StyleReiss, René, Sven Ehlert, Jan Heide, Michael Pütz, Thomas Forster, and Ralf Zimmermann. 2018. "Ambient Pressure Laser Desorption—Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Fast and Reliable Detection of Explosives, Drugs, and Their Precursors" Applied Sciences 8, no. 6: 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060933
APA StyleReiss, R., Ehlert, S., Heide, J., Pütz, M., Forster, T., & Zimmermann, R. (2018). Ambient Pressure Laser Desorption—Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Fast and Reliable Detection of Explosives, Drugs, and Their Precursors. Applied Sciences, 8(6), 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060933




