Recognition of American Sign Language Gestures in a Virtual Reality Using Leap Motion
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The Leap Motion Device and Gesture Recognition
2.2. Network Service Gesture Identification System
2.3. Gesture Identification
2.4. Feature Extraction and Pre-Processing
2.5. Markov Classification
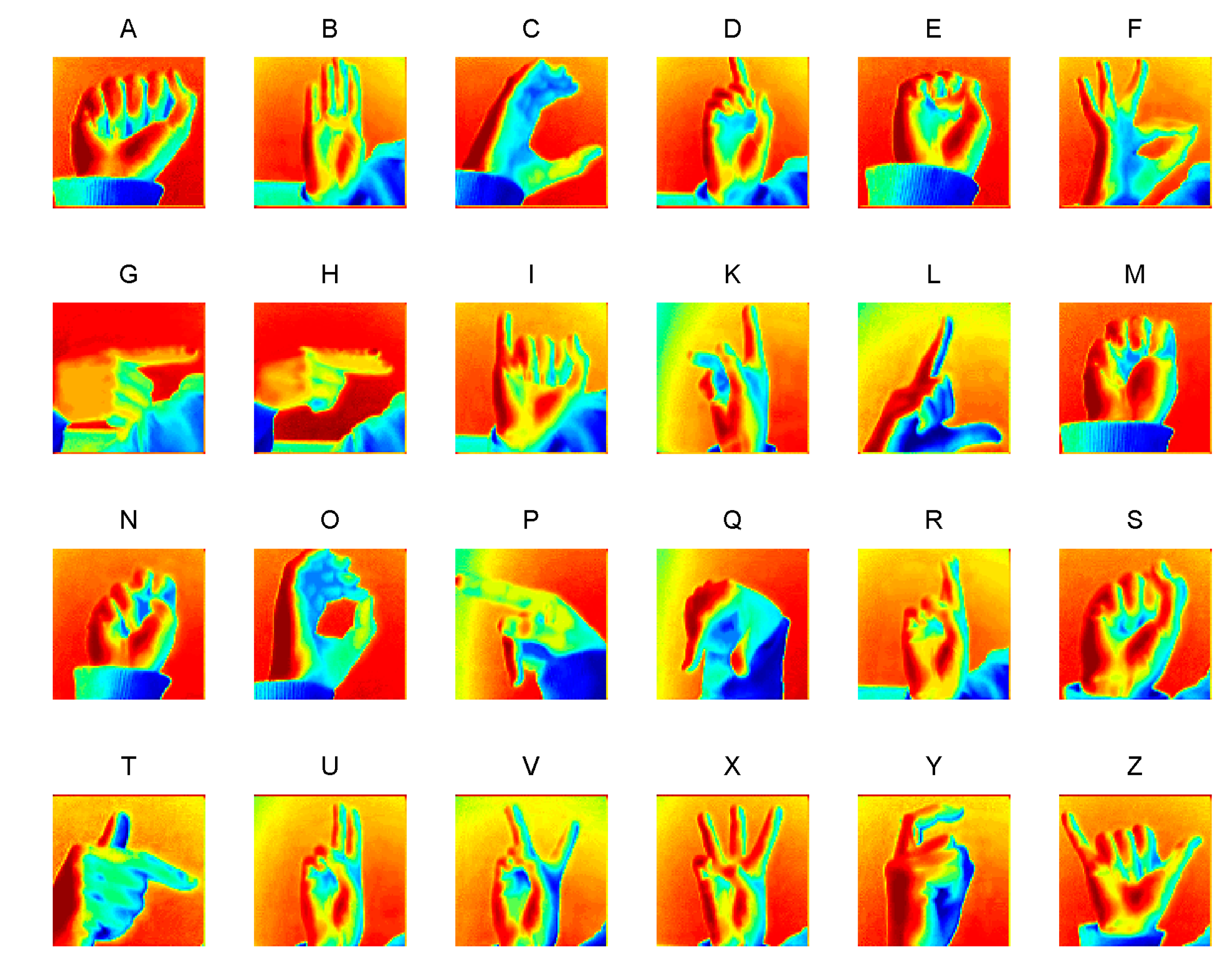
3. Experiment and Results
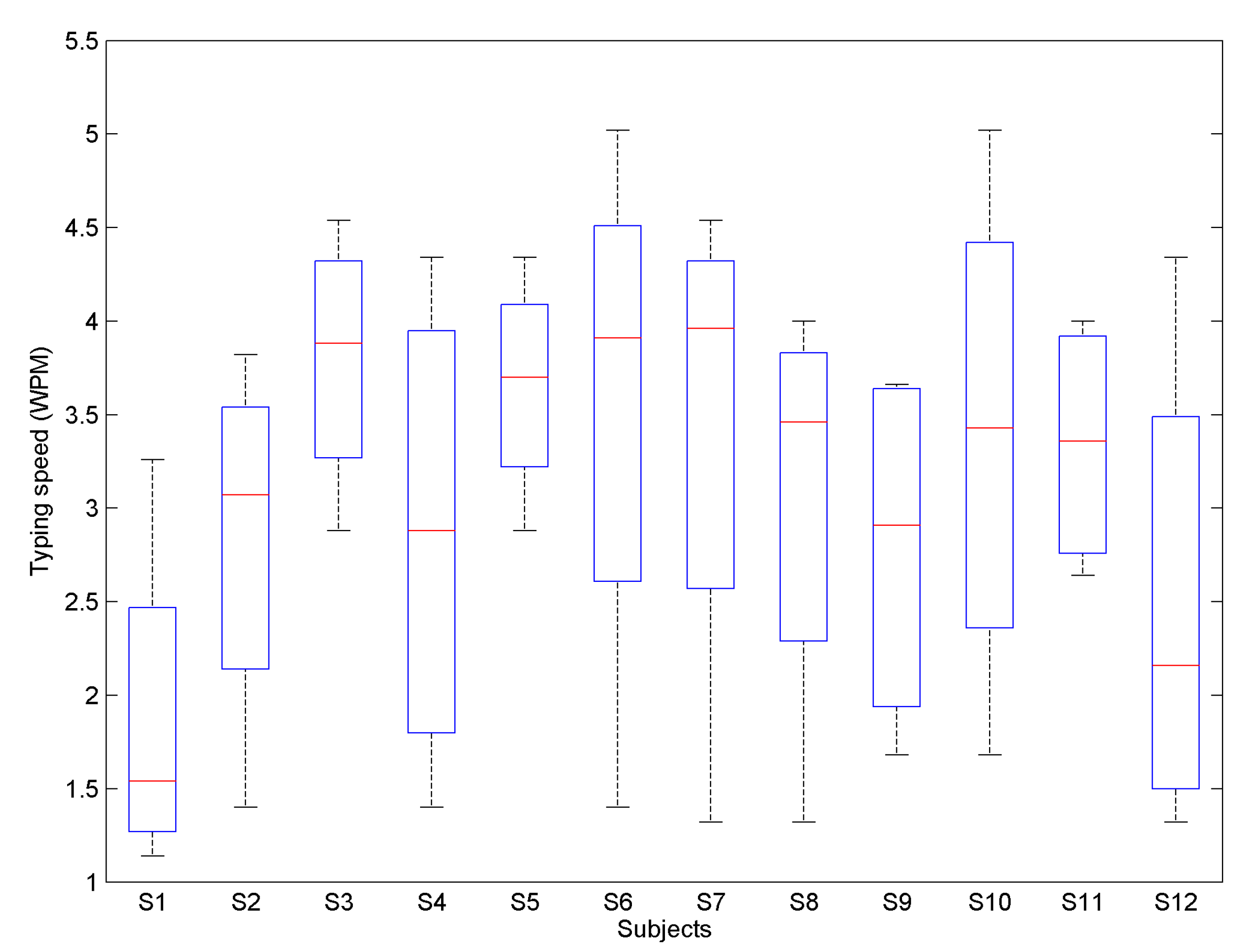
3.1. Settings and Data
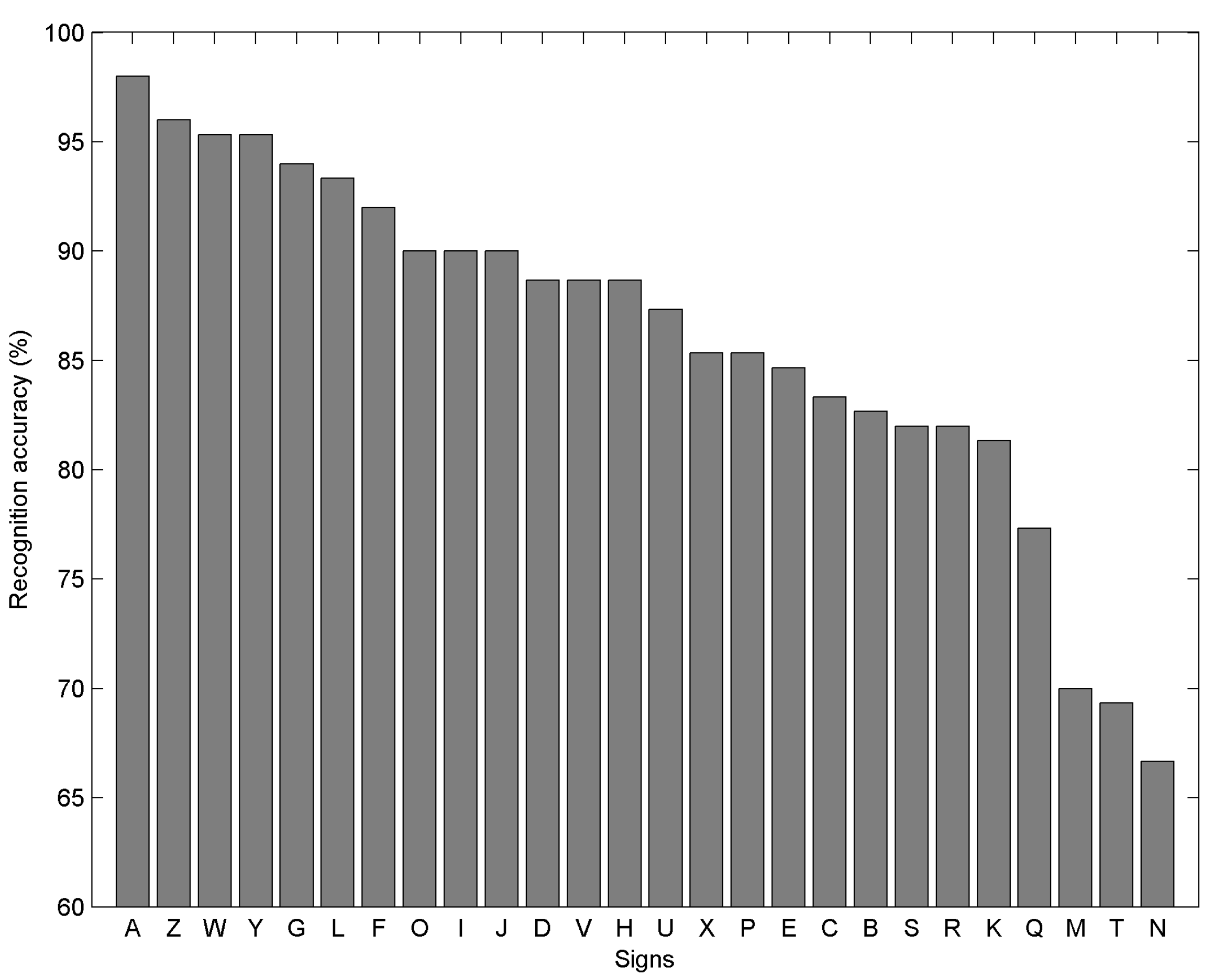
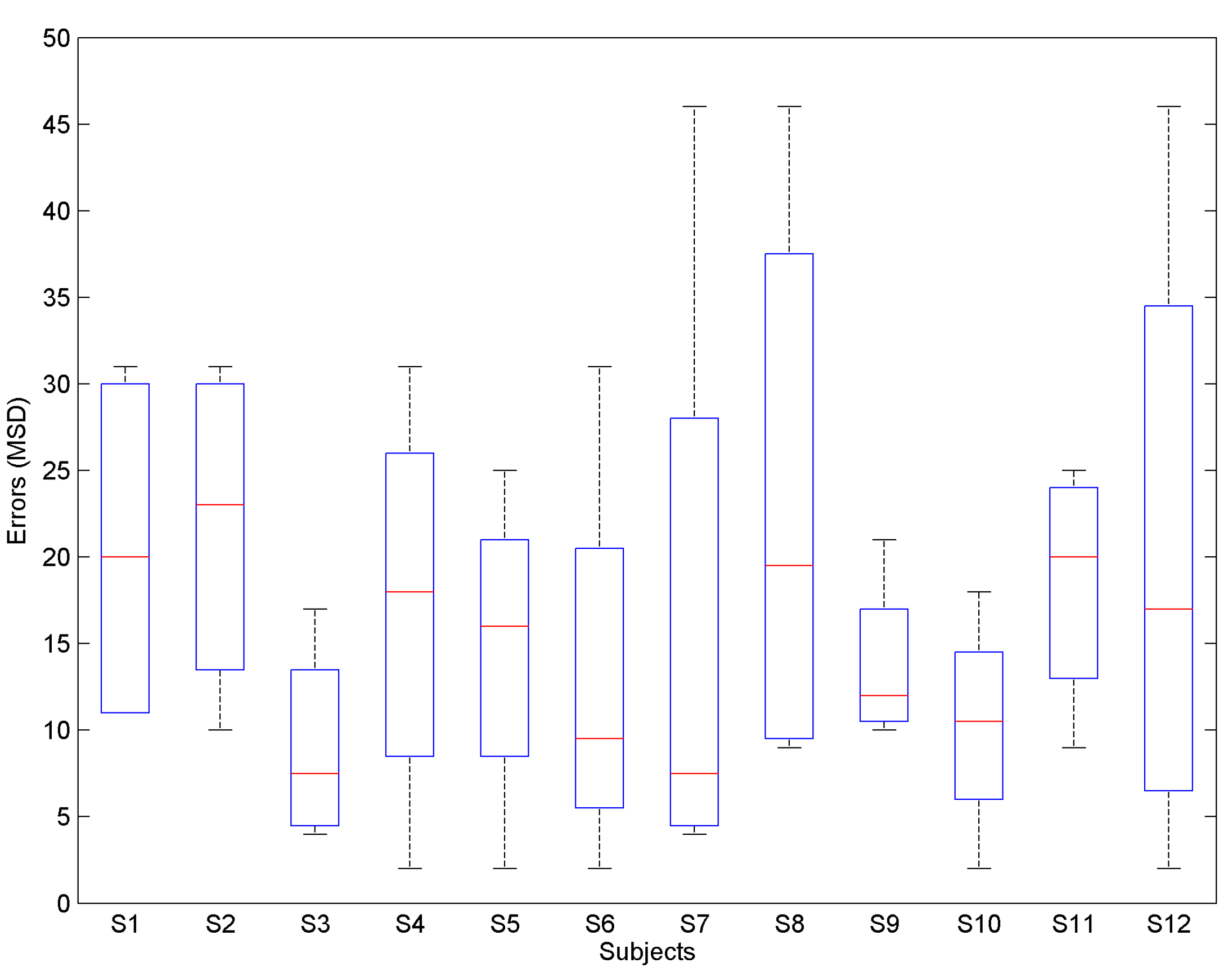
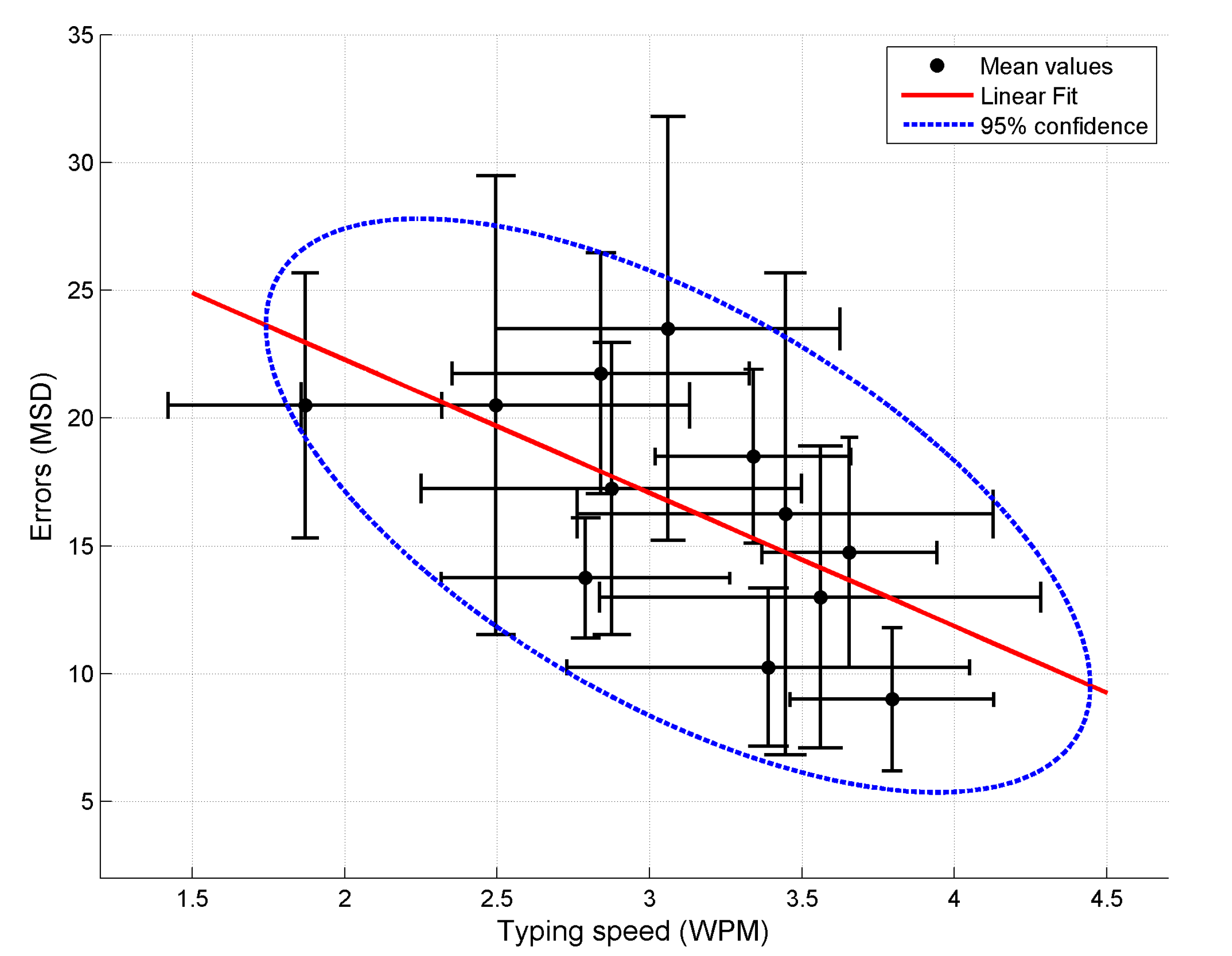
3.2. Results
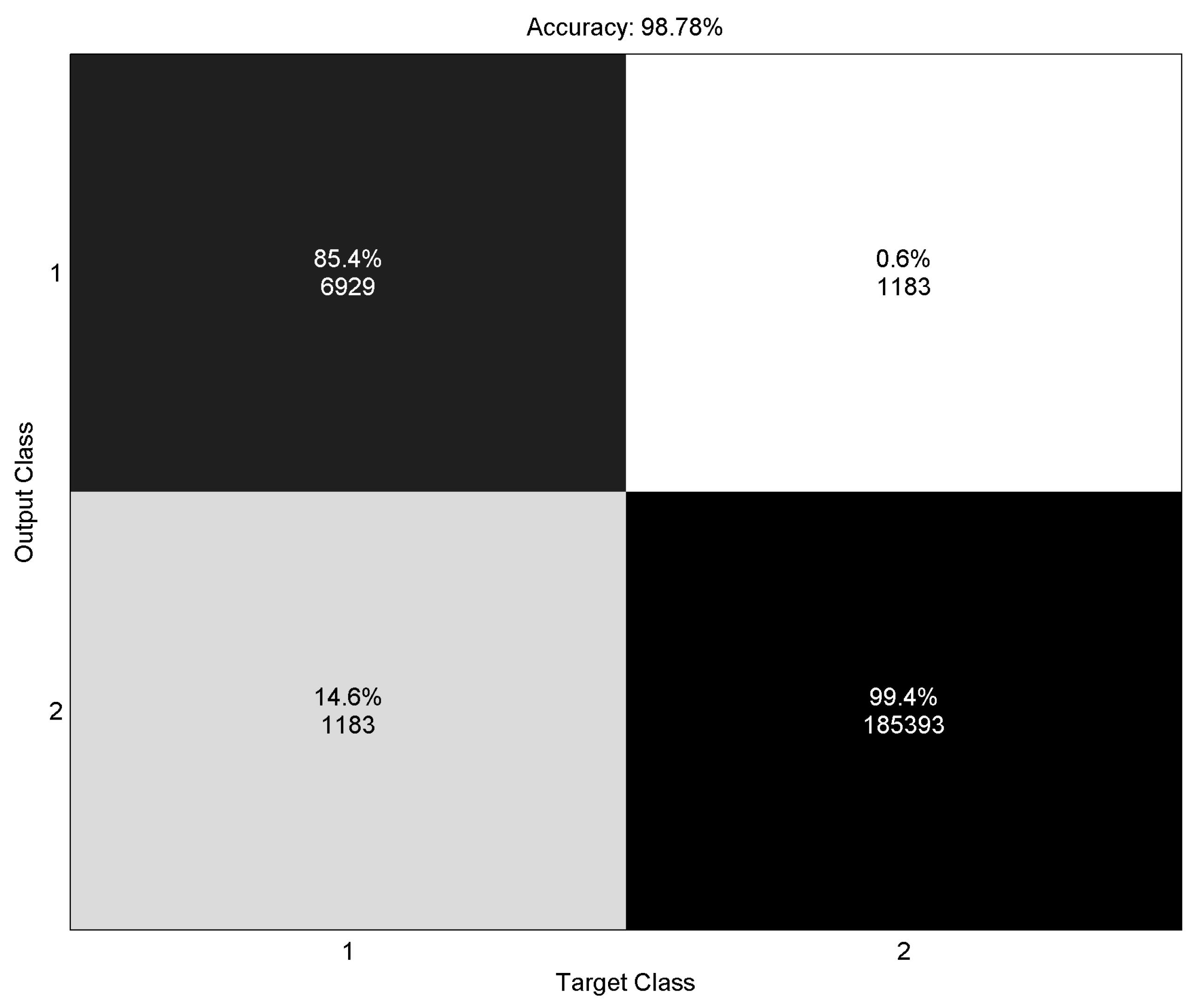
3.3. Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachmann, D.; Weichert, F.; Rinkenauer, G. Review of three-dimensional human-computer interaction with focus on the leap motion controller. Sensors 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, F.; Penders, J.; Carbone, G. Remote Control of a Robotic Hand Using a Leap Sensor. In The International Conference of IFToMM ITALY; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccetti, M.; Marfia, G.; Semeraro, A. Playing into the wild: A gesture-based interface for gaming in public spaces. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2012, 23, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabkh, K.A.; Alturk, F.H.; Sweidan, S.Z. VRCDEA-TCS: 3D virtual reality cooperative drawing educational application with textual chatting system. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2018, 26, 1677–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-D. Sign Language Recognition with the Kinect Sensor Based on Conditional Random Fields. Sensors 2015, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.H.; Rovini, E.; Dolciotti, C.; De Petris, G.; Bongioanni, P.; Carboncini, M.C.; Cavallo, F. Objective and automatic classification of parkinson disease with leap motion controller. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, E.; Hu, X. A case study of gesture-based games in enhancing the fine motor skills and recognition of children with autism. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2018, 26, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.W.; Voldman, I.; Regazzoni, D.; Vitali, A. Hand rehabilitation via gesture recognition using leap motion controller. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Human System Interaction, HIS, Gdansk, Poland, 4–6 July 2018; pp. 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morando, M.; Ponte, S.; Ferrara, E.; Dellepiane, S. Definition of motion and biophysical indicators for home-based rehabilitation through serious games. Information 2018, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingchao, X.; Jiangang, C. The application of leap motion in astronaut virtual training. Iop Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulijala, Y.; Ma, M.; Ayoub, A. VR surgery: Interactive virtual reality application for training oral and maxillofacial surgeons using oculus rift and leap motion. Serious Games Edut. Appl. 2017, II, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, B.; MacLean, K.; Haddadi, A.; Croft, E.; Alcazar, J. Gestures for industry: Intuitive human-robot communication from human observation. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI ’13), Tokyo, Japan, 3–6 March 2013; pp. 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, M.; Aliyu, S.; Deriche, M. Arabic sign language recognition using the leap motion controller. IEEE Int. Symp. Ind. Electron. 2014, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonse, M.; Ali, A.; Elons, A.S.; Badr, N.L.; Aboul-Ela, M. Arabic sign language benchmark database for different heterogeneous sensors. In Proceedings of the 2015 5th International Conference on Information & Communication Technology and Accessibility (ICTA), Marrakech, Morocco, 21–23 December 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, P.; Ghorpade, T.; Padiya, P. Indian sign language to forecast text using leap motion sensor and RF classifier. In Proceedings of the 2016 Symposium on Colossal Data Analysis and Networking (CDAN), Indore, India, 18–19 March 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglot, D.; Kulkarni, M. ANN based indian sign language numerals recognition using the leap motion controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies, ICICT 2016, Coimbatore, India, 26–27 August 2016; Volume 2, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircioǧlu, B.; Bülbül, G.; Köse, H. Turkish sign language recognition with leap motion. In Proceedings of the 2016 24th Signal Processing and Communication Application Conference (SIU), Zonguldak, Turkey, 16–19 May 2016; pp. 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simos, M.; Nikolaidis, N. Greek sign language alphabet recognition using the leap motion device. In Proceedings of the 9th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Thessaloniki, Greece, 18–20 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumsri, J.; Kimpan, W. Thai sign language translation using leap motion controller. In Proceedings of the International Multi Conference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, Hong Kong, China, 15–17 March 2017; Volume 2227, pp. 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, A.; Basuki, A.; Sigit, R.; Rahagiyanto, A.; Zikky, M. Feature extraction for indonesian sign language (SIBI) using leap motion controller. In Proceedings of the 2017 21st International Computer Science and Engineering Conference (ICSEC), Bangkok, Thailand, 15–18 November 2017; pp. 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, C.; Regina, E.; Guardino, C. American sign language recognition using leap motion sensor. In Proceedings of the 2014 13th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Detroit, MI, USA, 3–6 December 2014; pp. 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapari, R.B.; Kharat, G. American static signs recognition using leap motion sensor. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Competitive Strategies, Udaipur, India, 4–5 March 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, T.; Lee, B. American sign language recognition using leap motion controller with machine learning approach. Sensors 2018, 18, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avola, D.; Bernardi, M.; Cinque, L.; Foresti, G.L.; Massaroni, C. Exploiting recurrent neural networks and leap motion controller for the recognition of sign language and semaphoric hand gestures. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, S.; Khalifa, A.B.; Bouhlel, M.S. A comprehensive leap motion database for hand gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th International Conference on Sciences of Electronics, Technologies of Information and Telecommunications (SETIT), Hammamet, Tunisia, 18–20 December 2016; pp. 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, K.; Ganganath, N.; Cheng, C.; Tse, C.K. A real-time ASL recognition system using leap motion sensors. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Cyber-Enabled Distributed Computing and Knowledge Discovery, Xi’an, China, 17–19 September 2015; pp. 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisham, B.; Hamouda, A. Arabic static and dynamic gestures recognition using leap motion. J. Comput. Sci. 2017, 13, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tong, Z.; Chu, J. Dynamic hand gesture recognition with leap motion controller. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Grover, A.; Saini, P.; Singh, M. Contact dynamics emulation using leap motion controller. In International Conference on Advances in Computing and Data Sciences; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 721, pp. 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, S.; Boletsis, C. Augmented Reality & Gesture-based Architecture in Games for the Elderly. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2013, 189, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sourial, M.; Elnaggar, A.; Reichardt, D. Development of a virtual coach scenario for hand therapy using LEAP motion. In Proceedings of the 2016 Future Technologies Conference (FTC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–7 December 2017; pp. 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, P.P.; Pezzuti, E. Accuracy in fingertip tracking using leap motion controller for interactive virtual applications. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2017, 11, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.; Jahan, F.; Fruitwala, P. Proposed system on gesture controlled holographic projection using leap motion. In International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Intelligent Systems (ICTIS 2017); Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.G.; Schulze, J.P. Continuous-Motion Text Input in Virtual Reality. Electron. Imaging 2018, 450-1–450-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, K.; Nakajima, T. A Japanese input method using leap motion in virtual reality. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Mobile Computing and Ubiquitous Network (ICMU), Toyama, Japan, 3–5 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xiao, Z.G.; Menon, C. Virtual grasps recognition using fusion of Leap Motion and force myography. Virtual Real. 2018, 22, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Bong-Soo Sohn, B.S. Immersive Gesture Interfaces for Navigation of 3D Maps in HMD-Based Mobile Virtual Environments. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2018, 2585797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Yoon, H.; Soh, J.; Yang, Y.; Ejima, T. Hand gesture recognition using hidden markov models. IEEE Int. Conf. Syst. Man Cybern. 1997, 5, 4232–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautasso, C. Microservices in Practice, Part 1: Reality Check and Service Design. IEEE Softw. 2017, 34, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preventis, A.; Stravoskoufos, K.; Sotiriadis, S.; Petrakis, E.G.M. Interact: Gesture Recognition in the Cloud. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 7th International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, London, UK, 8–11 December 2014; pp. 501–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, G.; Dominio, F.; Zanuttigh, P. Hand gesture recognition with jointly calibrated leap motion and depth sensor. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 14991–15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’touq, J.; Hu, T.; Haddadin, S. Sub-millimetre accurate human hand kinematics: From surface to skeleton. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 21, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, G.-A. Markov Models for Pattern Recognition, 2nd ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2008; pp. 71–106. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, L.R. A tutorial on Hidden Markov Models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. Eee 1989, 77, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddell, S.K. Grammar, Gesture, and Meaning in American Sign Language; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 1–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobosz, K.; Buchczyk, K. One-Handed Braille in the Air. In International Conference on Computers Helping People with Special Needs ICCHP 2018, Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A Systematic Analysis of Performance Measures for Classification Tasks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukoreff, R.W.; MacKenzie, I.S. Metrics for text entry research: An evaluation of MSD and KSPC, and a new unified error metric. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Ft. Lauderdale, FL, USA, 5–10 April 2003; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walde, A.S.; Shiurkar, U.D. Sign Language Recognition Systems: A Review. Int. J. Recent Res. Asp. 2017, 4, 451–456. [Google Scholar]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaitkevičius, A.; Taroza, M.; Blažauskas, T.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Woźniak, M. Recognition of American Sign Language Gestures in a Virtual Reality Using Leap Motion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030445
Vaitkevičius A, Taroza M, Blažauskas T, Damaševičius R, Maskeliūnas R, Woźniak M. Recognition of American Sign Language Gestures in a Virtual Reality Using Leap Motion. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(3):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030445
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaitkevičius, Aurelijus, Mantas Taroza, Tomas Blažauskas, Robertas Damaševičius, Rytis Maskeliūnas, and Marcin Woźniak. 2019. "Recognition of American Sign Language Gestures in a Virtual Reality Using Leap Motion" Applied Sciences 9, no. 3: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030445





