Ethnic Similarities and Differences in the Relationship between Beta Cell Mass and Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Beta Cell Mass and Function in the Face of Obesity and Diabetes
2.1. Change in Beta Cell Function and Beta Cell Mass in T2DM
2.2. Change in Beta Cell Mass with Obesity
2.3. Association between Beta Cell Mass and Beta Cell Function
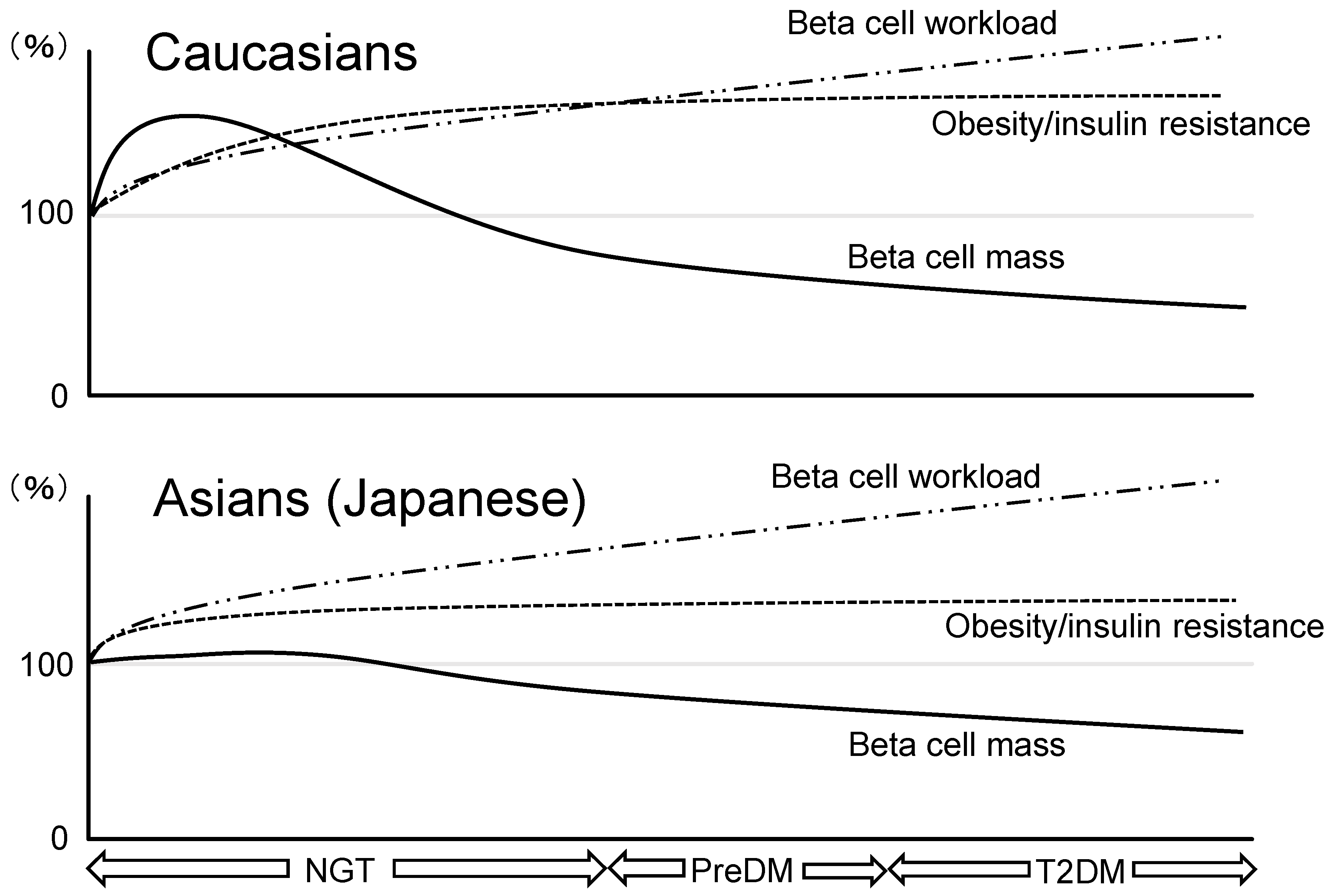
3. Similarities and Differences in Beta Cell Mass between Ethnicities
3.1. Ethnic Difference in Pathophysiological Features of T2DM
3.2. Beta Cell Mass in Asian Population
4. Treatment Strategy for T2DM in Asian Population
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abate, N.; Chandalia, M. The impact of ethnicity on type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2003, 17, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Peeters, A.; de Courten, M.; Stoelwinder, J. The magnitude of association between overweight and obesity and the risk of diabetes: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 89, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, S.; Vazquez, G.; Baker, W.L.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. The Collaborative Study of Obesity and Diabetes in Adults (CODA) project: Meta-analysis design and description of participating studies. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saisho, Y. β-cell dysfunction: Its critical role in prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobelli, C.; Toffolo, G.M.; Dalla Man, C.; Campioni, M.; Denti, P.; Caumo, A.; Butler, P.; Rizza, R. Assessment of beta-cell function in humans, simultaneously with insulin sensitivity and hepatic extraction, from intravenous and oral glucose tests. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1–E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Eldor, R.; Abdul-Ghani, M. Pathophysiologic approach to therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, S127–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defronzo, R.A. Banting Lecture. From the triumvirate to the ominous octet: A new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2009, 58, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.C.; Cnop, M.; Hull, R.L.; Fujimoto, W.Y.; Kahn, S.E. Beta-cell function is a major contributor to oral glucose tolerance in high-risk relatives of four ethnic groups in the U.S. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2170–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.E.; Janson, J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Ritzel, R.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.H.; Ko, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Ahn, Y.B.; Song, K.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Kang, M.I.; Cha, B.Y.; Lee, K.W.; et al. Selective beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahier, J.; Guiot, Y.; Goebbels, R.M.; Sempoux, C.; Henquin, J.C. Pancreatic beta-cell mass in European subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukami, H.; Takahashi, K.; Inaba, W.; Tsuboi, K.; Osonoi, S.; Yoshida, T.; Yagihashi, S. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced DNA damage, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy deficits in the decline of beta-cell mass in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poitout, V.; Robertson, R.P. Glucolipotoxicity: Fuel excess and beta-cell dysfunction. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.P. Antioxidant drugs for treating beta-cell oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes: Glucose-centric versus insulin-centric therapy. Discov. Med. 2010, 9, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Cardozo, A.K.; Cnop, M. The role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Donath, M.Y.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Role of IL-1beta in type 2 diabetes. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2010, 17, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haataja, L.; Gurlo, T.; Huang, C.J.; Butler, P.C. Islet amyloid in type 2 diabetes, and the toxic oligomer hypothesis. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talchai, C.; Xuan, S.; Lin, H.V.; Sussel, L.; Accili, D. Pancreatic β cell dedifferentiation as a mechanism of diabetic beta cell failure. Cell 2012, 150, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henquin, J.; Rahier, J. Pancreatic alpha cell mass in European subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Saisho, Y.; Inaishi, J.; Kou, K.; Murakami, R.; Yamada, T.; Itoh, H. Effects of glucocorticoid treatment on β- and α-cell mass in Japanese adults with and without diabetes. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2915–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, F.; Bouchi, R.; Kim-Muller, J.Y.; Ohmura, Y.; Sandoval, P.R.; Masini, M.; Marselli, L.; Suleiman, M.; Ratner, L.E.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Evidence of β-cell dedifferentiation in human type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.E.; Dhawan, S.; Hoang, J.; Cory, M.; Zeng, K.; Fritsch, H.; Meier, J.J.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. β-cell deficit in obese type 2 diabetes, a minor role of β-cell dedifferentiation and degranulation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonsky, K.S.; Given, B.D.; Van Cauter, E. Twenty-four-hour profiles and pulsatile patterns of insulin secretion in normal and obese subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saisho, Y.; Butler, A.E.; Manesso, E.; Elashoff, D.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. β-cell mass and turnover in humans: Effects of obesity and aging. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J.; Breuer, T.G.; Bonadonna, R.C.; Tannapfel, A.; Uhl, W.; Schmidt, W.E.; Schrader, H.; Menge, B.A. Pancreatic diabetes manifests when beta cell area declines by approximately 65% in humans. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaishi, J.; Saisho, Y.; Sato, S.; Kou, K.; Murakami, R.; Watanabe, Y.; Kitago, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Yamada, T.; Itoh, H. Effects of obesity and diabetes on α- and β-cell mass in surgically resected human pancreas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2874–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J.; Menge, B.A.; Breuer, T.G.; Muller, C.A.; Tannapfel, A.; Uhl, W.; Schmidt, W.E.; Schrader, H. Functional assessment of pancreatic beta-cell area in humans. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laedtke, T.; Kjems, L.; Porksen, N.; Schmitz, O.; Veldhuis, J.; Kao, P.C.; Butler, P.C. Overnight inhibition of insulin secretion restores pulsatility and proinsulin/insulin ratio in type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 279, E520–E528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, M.; Yoshiike, N.; Osaka, T.; Numba, Y.; Zimmet, P.; Inoue, S. Criteria and classification of obesity in Japan and Asia-Oceania. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2005, 94, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kodama, K.; Tojjar, D.; Yamada, S.; Toda, K.; Patel, C.J.; Butte, A.J. Ethnic differences in the relationship between insulin sensitivity and insulin response: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsumi, Y.; Morimoto, A.; Miyamatsu, N.; Noda, M.; Ohno, Y.; Deura, K. Effect of body mass index on insulin secretion or sensitivity and diabetes. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 48, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukami, H.; Takahashi, K.; Inaba, W.; Osonoi, S.; Kamata, K.; Tsuboi, K.; Yagihashi, S. Age-associated changes of islet endocrine cells and the effects of body mass index in Japanese. J. Diabetes Investig. 2014, 5, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, K.; Saisho, Y.; Satoh, S.; Yamada, T.; Itoh, H. Change in β-cell mass in Japanese nondiabetic obese individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 3724–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, D.S.; Larrivee, S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Johnson, W.D. Impact of lowering BMI cut points as recommended in the Revised American Diabetes Association’s Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2015 on diabetes screening in Asian Americans. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2166–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; McCarthy, M.I. The genetics of type 2 diabetes and its clinical relevance. Clin. Genet. 2013, 83, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, R.A.; Hartil, K.; Vaitheesvaran, B.; Arrieta-Cruz, I.; Knight, C.M.; Cook, J.R.; Kammoun, H.L.; Febbraio, M.A.; Gutierrez-Juarez, R.; Kurland, I.J.; et al. Integrated control of hepatic lipogenesis versus glucose production requires FoxO transcription factors. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T. The role of FOXO1 in β-cell failure and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Abdul-Ghani, M.A. Preservation of β-cell function: The key to diabetes prevention. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowler, W.C.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Christophi, C.A.; Hoffman, H.J.; Brenneman, A.T.; Brown-Friday, J.O.; Goldberg, R.; Venditti, E.; Nathan, D.M. 10-year follow-up of diabetes incidence and weight loss in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Lancet 2009, 374, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tripathy, D.; Schwenke, D.C.; Banerji, M.; Bray, G.A.; Buchanan, T.A.; Clement, S.C.; Henry, R.R.; Hodis, H.N.; Kitabchi, A.E.; et al. Pioglitazone for diabetes prevention in impaired glucose tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.R.; Haffner, S.M.; McMurray, J.J.; Bethel, M.A.; Holzhauer, B.; Hua, T.A.; Belenkov, Y.; Boolell, M.; Buse, J.B.; Buckley, B.M.; et al. Effect of nateglinide on the incidence of diabetes and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Han, K.A.; Oh, H.J.; Tan, K.E.; Sothiratnam, R.; Tjokroprawiro, A.; Klein, M. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of metformin extended-release oral antidiabetic therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: An observational trial in Asia. J. Diabetes 2012, 4, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunck, M.C.; Corner, A.; Eliasson, B.; Heine, R.J.; Shaginian, R.M.; Taskinen, M.R.; Smith, U.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Diamant, M. Effects of exenatide on measures of beta-cell function after 3 years in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowler, W.C.; Hamman, R.F.; Edelstein, S.L.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Ehrmann, D.A.; Walker, E.A.; Fowler, S.E.; Nathan, D.M.; Kahn, S.E. Prevention of type 2 diabetes with troglitazone in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saisho, Y. Importance of beta cell function for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2014, 3, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Glucose Clamp-Based Indices | |
| Acute insulin response (AIR) | Area under the curve (AUC) of plasma insulin during first 10 min of hyperglycemic clamp (200 mg/dL) |
| AIRmax | AIR with arginine stimulation |
| Reflects maximal insulin secretion | |
| Disposition index (DI) | Insulin secretion (AIR) adjusted for insulin sensitivity (M value) |
| Indices Based on 75 g Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) | |
| Insulinogenic index (II) | Increment of insulin divided by increment of glucose during first 30 min of 75 g OGTT |
| AUCinsulin/AUCglucose | AUC of insulin divided by AUC of glucose |
| Oral DI | Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) or Matsuda index is used as insulin sensitivity index; i.e., oral DI is calculated as II/HOMA-IR |
| Indices Based on Single Blood Sample | |
| HOMA-beta | 360 × fasting insulin (mU/L)/(fasting glucose (mg/dL) − 63) |
| C-peptide to glucose ratio (CPRI) | C-peptide (ng/mL)/glucose (mg/dL) (× 100) |
| Assessed in fasting and postprandial states | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inaishi, J.; Saisho, Y. Ethnic Similarities and Differences in the Relationship between Beta Cell Mass and Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6120113
Inaishi J, Saisho Y. Ethnic Similarities and Differences in the Relationship between Beta Cell Mass and Diabetes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2017; 6(12):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6120113
Chicago/Turabian StyleInaishi, Jun, and Yoshifumi Saisho. 2017. "Ethnic Similarities and Differences in the Relationship between Beta Cell Mass and Diabetes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 6, no. 12: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6120113
APA StyleInaishi, J., & Saisho, Y. (2017). Ethnic Similarities and Differences in the Relationship between Beta Cell Mass and Diabetes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 6(12), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6120113





