Hydration-Induced Phase Separation in Amphiphilic Polymer Matrices and its Influence on Voclosporin Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nomenclature for Tyrosine-derived Polymer Matrices
2.2. Voclosporin Release is Dependent on Matrix Composition

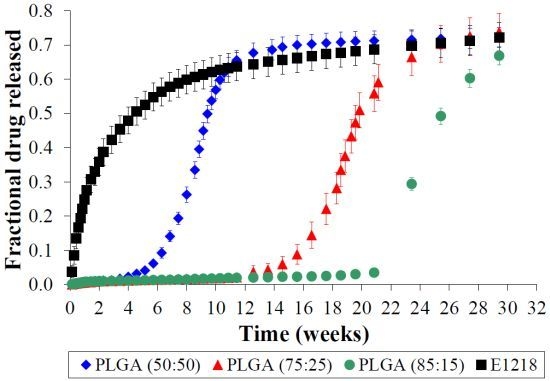
2.3. PLGA is Unsuitable for Controlled Voclosporin Release
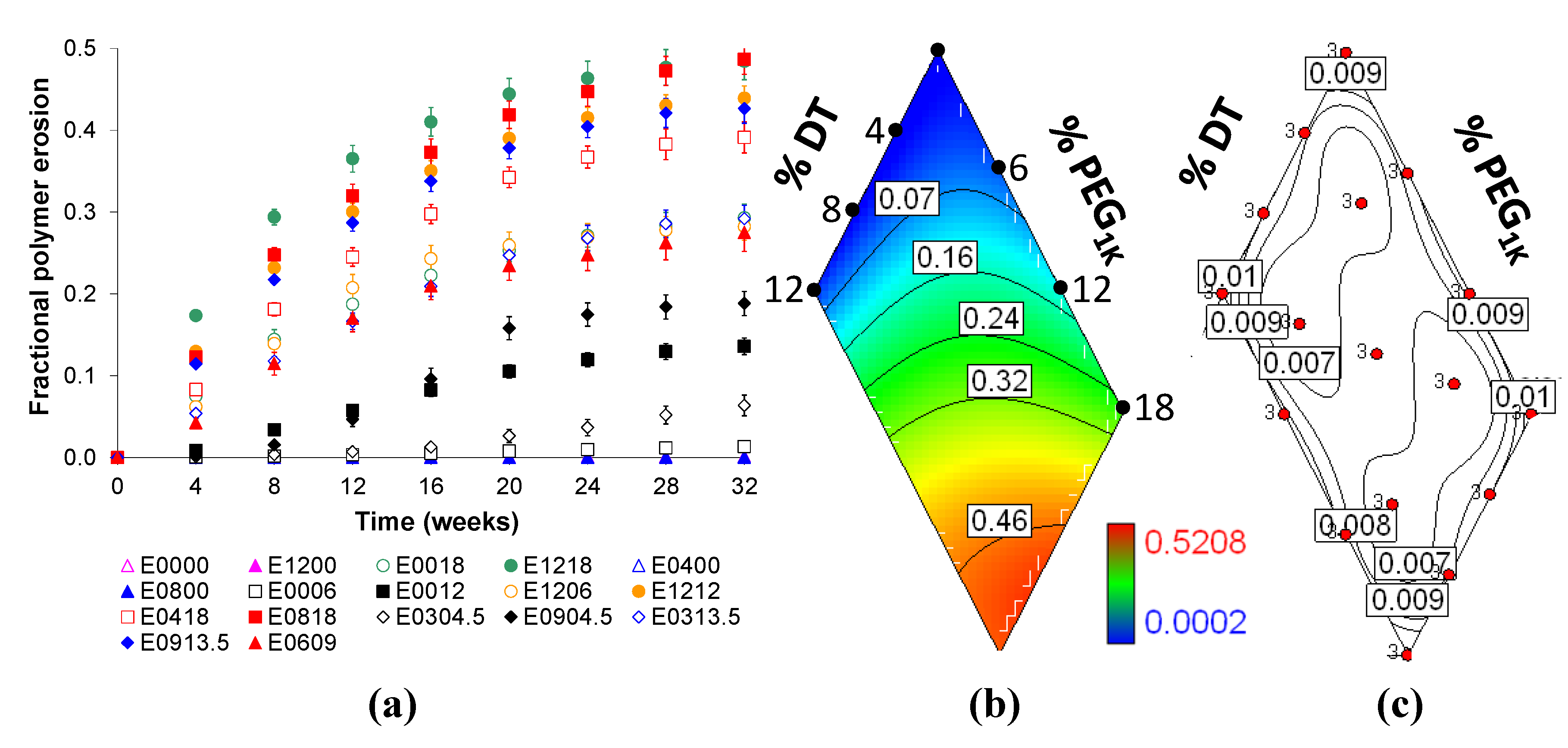
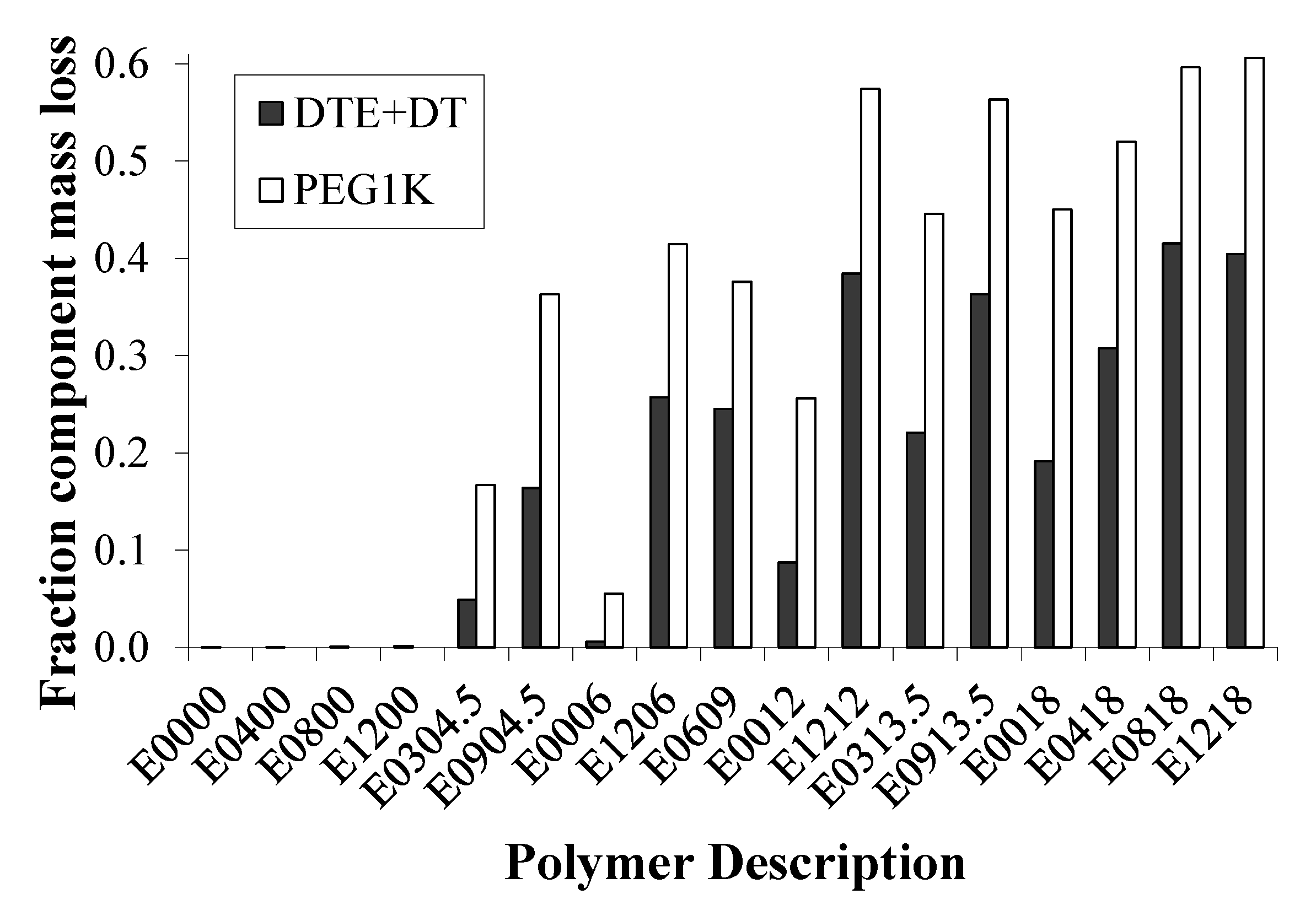
2.4. Bulk Polymer Resorption is Dependent on Matrix Composition

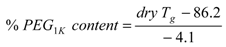
2.5. State of Voclosporin in Polymer Matrices
2.6. Water Domains are Formed in Eyyzz Copolymers
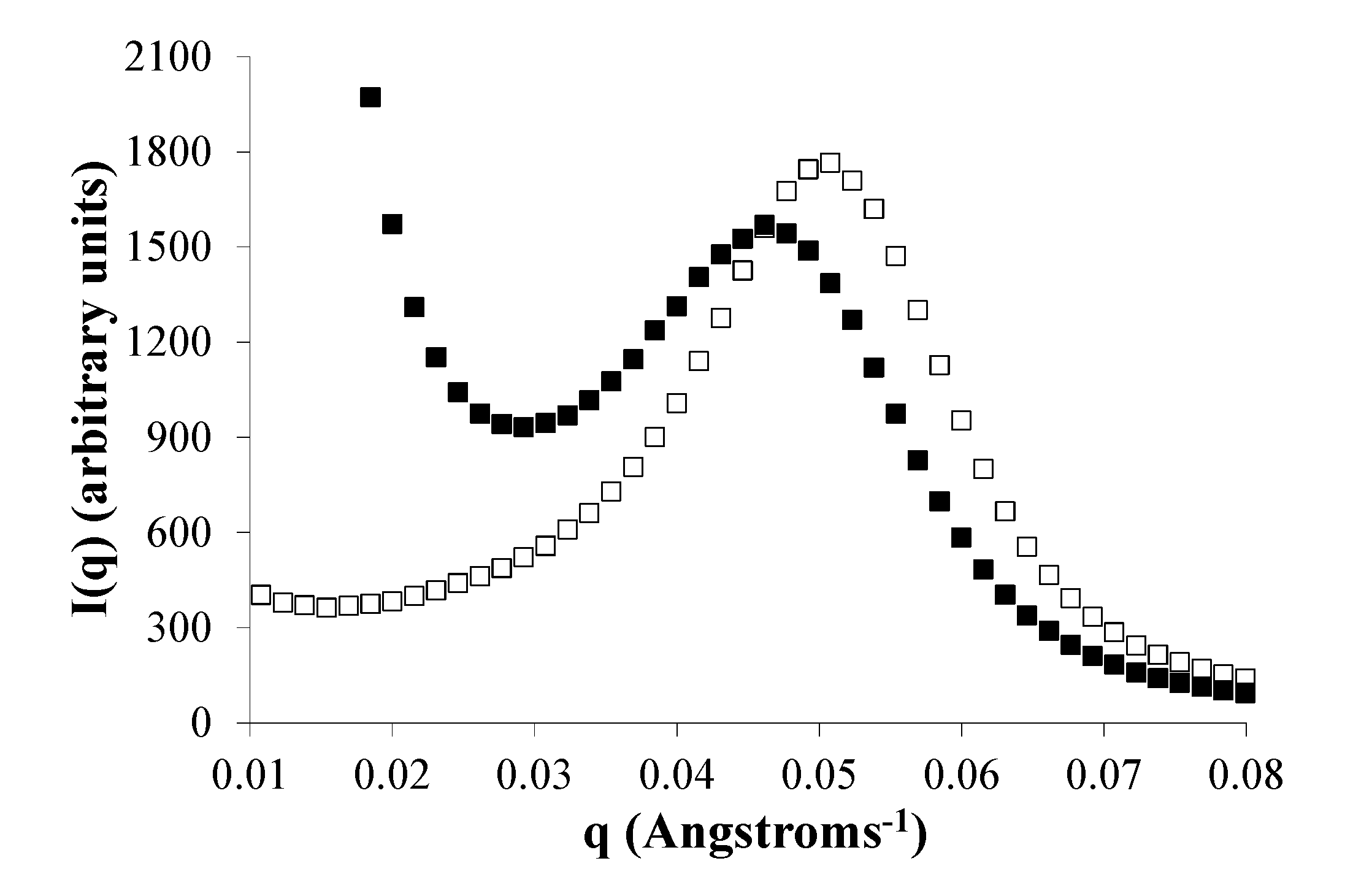
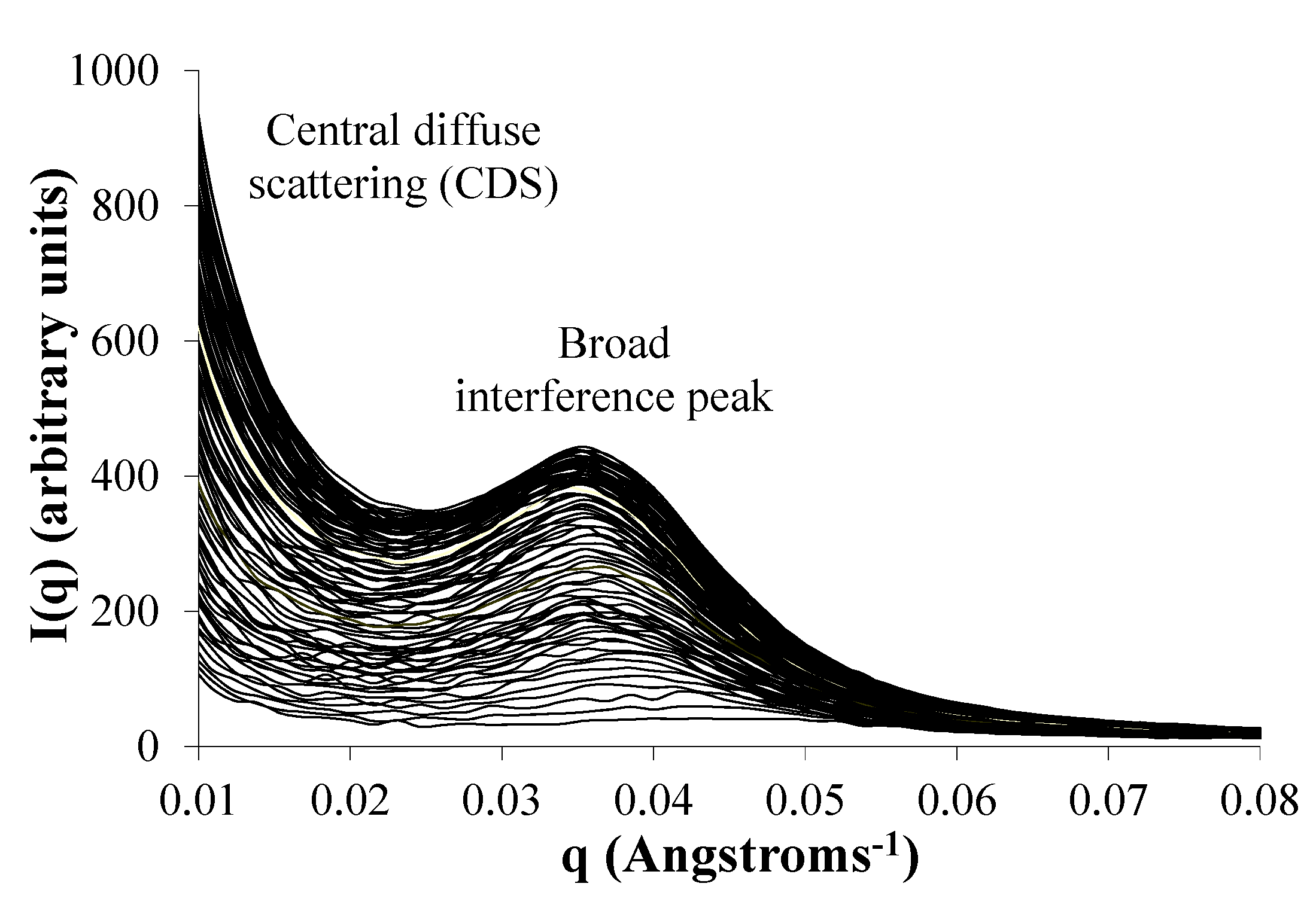
2.7. Phase Separation of PEG Segments Occur in Hydrated Eyyzz Copolymers
| Polymer composition | dPEG (Å), for polymer + VCS | DPEG (Å), for polymer + VCS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dry | 1 wk | 4 wk | 7 wk | Dry | 1 wk | 4 wk | 7 wk | |
| E0000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| E0400 | 247 | 283 | 425 | 291 | 204 | 183 | 234 | 229 |
| E0800 | 291 | 440 | - | 331 | 234 | 224 | 229 | |
| E1200 | 274 | 446 | 464 | 414 | 234 | 302 | 276 | 280 |
| E0304.5 | - | - | 323(b) | - | - | - | 159(b) | - |
| E0904.5 | - | - | 321(b) | - | - | - | 220(b) | - |
| E0006 | - | 212 | 213 | 264 | - | 132 | 172 | 234 |
| E1206 | - | 137(a) | 244 | - | 132(a) | 203 | - | |
| E0609 | - | 166 | 214 | 304 | - | 125 | 166 | 264 |
| E0012 | - | 194 | 246 | 333 | - | 137 | 159 | 222 |
| E1212 | - | 133 | 157 | 297 | - | 124 | 183 | 305 |
| E0313.5 | - | 149(a) | 180 | 266 | - | 156(a) | 178 | 253 |
| E0913.5 | - | 138 | 148 | 256 | - | 118 | 159 | 258 |
| E0018 | - | 133 | 154 | 228 | - | 163 | 176 | 225 |
| E0418 | - | 137 | 143 | 210 | - | 128 | 156 | 213 |
| E0818 | - | 121 | 135 | 201 | - | 124 | 145 | 209 |
| E1218 | - | 101 | 132 | 204 | - | 121 | 159 | 213 |
| E1818 | - | (c) | (c) | 192 | - | (c) | (c) | 197 |
| E1420 | - | 99 | (c) | 179 | - | 93 | (c) | 178 |
| E1224 | - | 93 | (c) | 175 | - | 105 | (c) | 179 |
| E1230 | - | 81 | (c) | 133 | - | 80 | (c) | 134 |
| DT homopolymer | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PEG homopolymer | 126 | (c) | (c) | (c) | 146 | (c) | (c) | (c) |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
3.2. Synthesis of Tyrosine-Derived Polymer Matrices
3.3. Poly(DL-Lactide-co-Glycolide), PLGA
3.4. Sample Preparation
3.5. In Vitro Kinetic Drug Release (KDR) Study
3.6. In Vitro Polymer Erosion Study
3.7. In Vitro Experimental Mixture Design for KDR and Polymer Erosion Studies

3.8. Measurement of Changes in Tg During Polymer Erosion
3.9. SANS Measurements
3.10. SAXS and WAXS Measurements
3.11. Analysis of Small Angle Scattering Data

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Hurrell, S.; Cameron, R.E. Polyglycolide: Degradation and drug release. Part I: Changes in morphology during degradation. J. Mat. Sci. Mat. Med. 2001, 12, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, S.; Cameron, R.E. The effect of initial polymer morphology on the degradation and drug release from polyglycolide. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, A.S. The origins and evolution of “controlled” drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Favre, E.; Ping, Z.H.; Neel, J. Clustering of solvents in membranes and its influence on membrane transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 113, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, D.; Hotovely-Salomon, A. Biodegradable multiblock PEO/PLA thermoplastic elastomers: Molecular design and properties. Polymer 2005, 46, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, T.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Li, S.M.; Vert, M. Synthesis and characterization of poly(oxyethylene)-poly(caprolactone) multiblock copolymers. Polym. Int. 1998, 45, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, M.M.; Kuptsov, S.A.; Shandryuk, G.A.; Plate, N.A.; Chalykh, A.E. Coherence of thermal transitions in poly(N-vunyl pyrrolidone)-poly(ethylene glycol) compatible blends 3. Impact of sorbed water upon phase behavior. Polymer 2000, 41, 5349–5359. [Google Scholar]
- Hammouda, B. Solvation characteristics of a model water-soluble polymer. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 3195–3199. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, M.; Sugiura, R.; Sakai, W.; Tsutsumi, N. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable network poly(ethylene glycol) films with elastic properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 2885–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, A.; Fornasiero, F.; Rodriguez, O.; Radke, C.J.; Prausnitz, J.M. Sorption and transport of water vapor in thin polymer films at 35 °C. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Siparsky, G.L.; Voorhees, K.J.; Dorgan, J.R.; Schilling, K. Water transport in polylactic acid (PLA), PLA/polycaprolactone copolymers, and PLA/polyethylene glycol blends. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1997, 5, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Starkweather, H.W. Clustering of water in polymers. Polym. Lett. 1963, 1, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.L.; Hopfenberg, H.B.; Stannett, V. Water transport and clustering in poly(vinyl chloride), poly(oxymethylene), and other polymers. J. Macromol. Sci. Phys. 1969, B3, 711–725. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Bae, Y.H. Hydrogels based on poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(tetramethylene oxide) or poly(dimethyl siloxane). II. Physical properties and bacterial adhesion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, S.L.; Kohn, J. Polymers derived from the amino acid L-tyrosine: Polycarbonates, polyarylates and copolymers with poly(ethylene glycol). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 447–466. [Google Scholar]
- Lewitus, D.; Smith, K.L.; Shain, W.; Kohn, J. Ultrafast resorbing polymers for use as carriers for cortical neural probes. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magno, M.H.R.; Kim, J.; Srinivasan, A.; McBride, S.; Bolikal, D.; Darr, A.; Hollinger, J.O.; Kohn, J. Synthesis, degradation and biocompatibility of tyrosine-derived polycarbonate scaffolds. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8885–8893. [Google Scholar]
- Anglade, E.; Yatscoff, R.; Foster, R.; Grau, U. Next-generation calcineurin inhibitors for ophthalmic indications. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1525–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnichenko, Y.B.; Wignall, G.D. Small-angle neutron scattering in materials science: Recent practical applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Challa, P.; Epstein, D.L.; Yuan, F. Controlled release of ethacrynic acid from poly(lactide-co-glycolide) films for glaucoma treatment. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4279–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.K.; Sanabria-DeLong, N.; Jemian, P.R.; Tew, G.N.; Bhatia, S.R. Micro- to Nanoscale Structure of Biocompatible PLA-PEO-PLA Hydrogels. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5039–5044. [Google Scholar]
- Abetz, V.; Simon, P.F.W. Phase behaviour and morphologies of block copolymers. In Advances in Polymer Science-Block Copolymers I; Abetz, V., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; Volume 189, pp. 125–212. [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps, A.A.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. Phase separation and physical properties of PEO-containing poly(ether ester amide)s. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Seery, T.A.P.; Weiss, R. Physically cross-linked alkylacrylamide hydrogels: Phase behavior and microstructure. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9994–10000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, P.R.; Murthy, N.S.; Weigand, S.; Breitenkamp, K.; Kade, M.; Emrick, T. Microphase separated structures in the solid and molten states of double-crystal graft copolymers of polyethylene and poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer 2008, 49, 3116–3124. [Google Scholar]
- Luk, A.; Murthy, N.S.; Wang, W.; Rojas, R.; Kohn, J. Study of nanoscale structures in hydrated biomaterials using small-angle neutronscattering. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.M; Wang, W; Kohn, J. Microphase separation in copolymers of hydrophilic PEG blocks and hydrophobic tyrosine-derived segments using simultaneous SAXS/WAXS/DSC. Polymer 2010, 51, 3978–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, J.A. Experiments with Mixtures : Designs, Models, and the Analysis Of Mixture Data, 3rd ed; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hammersley, A.P. FIT2D V9.129 Reference Manual V3.1; ESRF Internal Report, ESRF98HA01T; ESRF: Grenoble, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Laity, P.R.; Taylor, J.E.; Wong, S.S.; Khunkamchoo, P.; Norris, K.; Cable, M.; Andrews, G.T.; Johnson, A.F.; Cameron, R.E. A review of small-angle scattering models for random segmented poly(ether-urethane) copolymers. Polymer 2004, 45, 7273–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, N.S.; Akkapeddi, M.K.; Orts, W.J. Analysis of lamellar structure in semicrystalline polymers by studying the absorption of water and ethylene glycol in nylons using small-angle neutron scattering. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, I.J.; Murthy, N.S.; Kohn, J. Hydration-Induced Phase Separation in Amphiphilic Polymer Matrices and its Influence on Voclosporin Release. J. Funct. Biomater. 2012, 3, 745-759. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb3040745
Khan IJ, Murthy NS, Kohn J. Hydration-Induced Phase Separation in Amphiphilic Polymer Matrices and its Influence on Voclosporin Release. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2012; 3(4):745-759. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb3040745
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, I. John, N. Sanjeeva Murthy, and Joachim Kohn. 2012. "Hydration-Induced Phase Separation in Amphiphilic Polymer Matrices and its Influence on Voclosporin Release" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 3, no. 4: 745-759. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb3040745
APA StyleKhan, I. J., Murthy, N. S., & Kohn, J. (2012). Hydration-Induced Phase Separation in Amphiphilic Polymer Matrices and its Influence on Voclosporin Release. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 3(4), 745-759. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb3040745