Regulating Al2O3/PAN/PEG Nanofiber Membranes with Suitable Phase Change Thermoregulation Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Compounding of PEG
2.3. Preparation of Shell-Spinning Solution
2.4. Preparation of Al2O3/PAN/PEG Nanofiber Membranes
2.5. Characterization of Al2O3/PAN/PEG Nanofiber Membranes
3. Results and Discussion
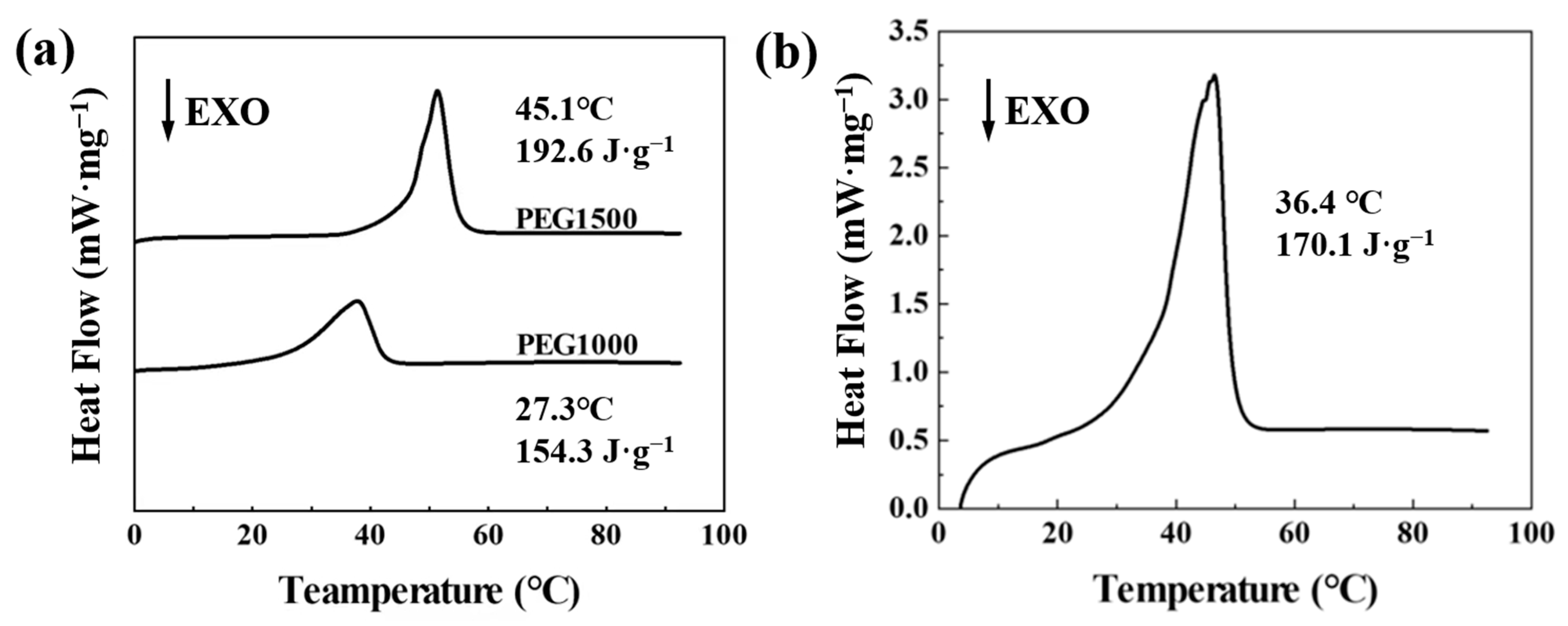
3.1. Ratio of Complex PEG
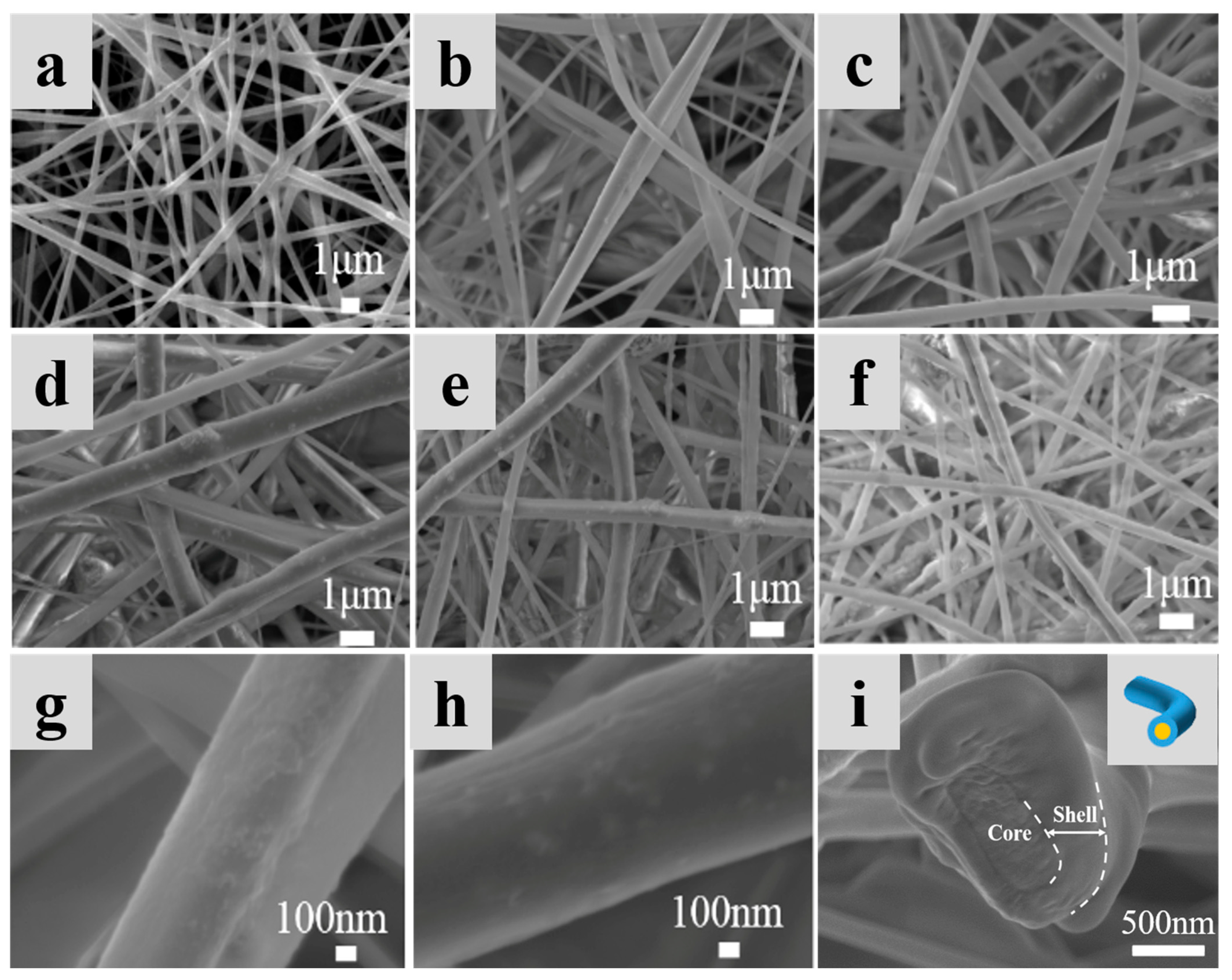
3.2. The Structure and Morphology of Al2O3/PAN/PEG
3.3. Thermal Stability Analysis
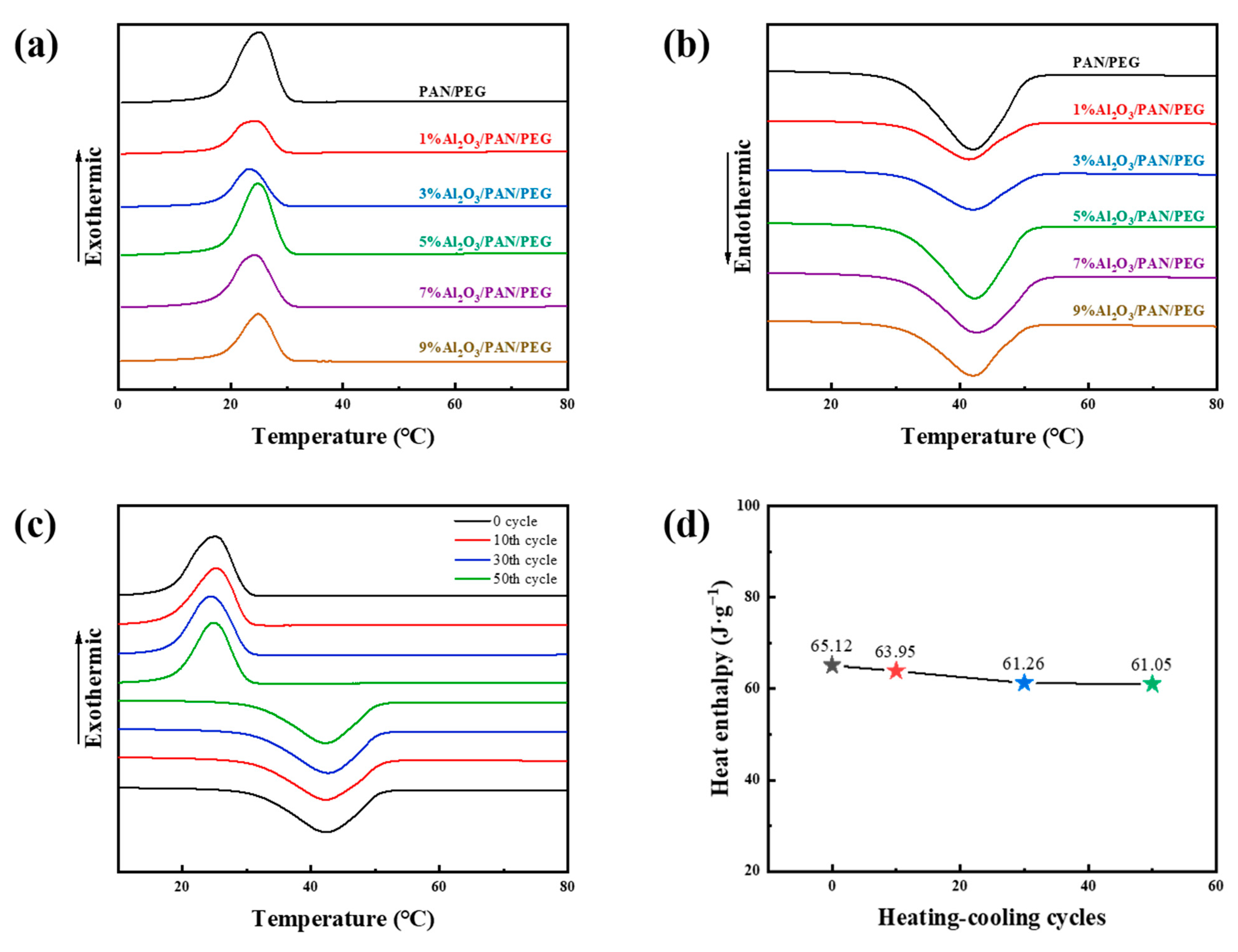
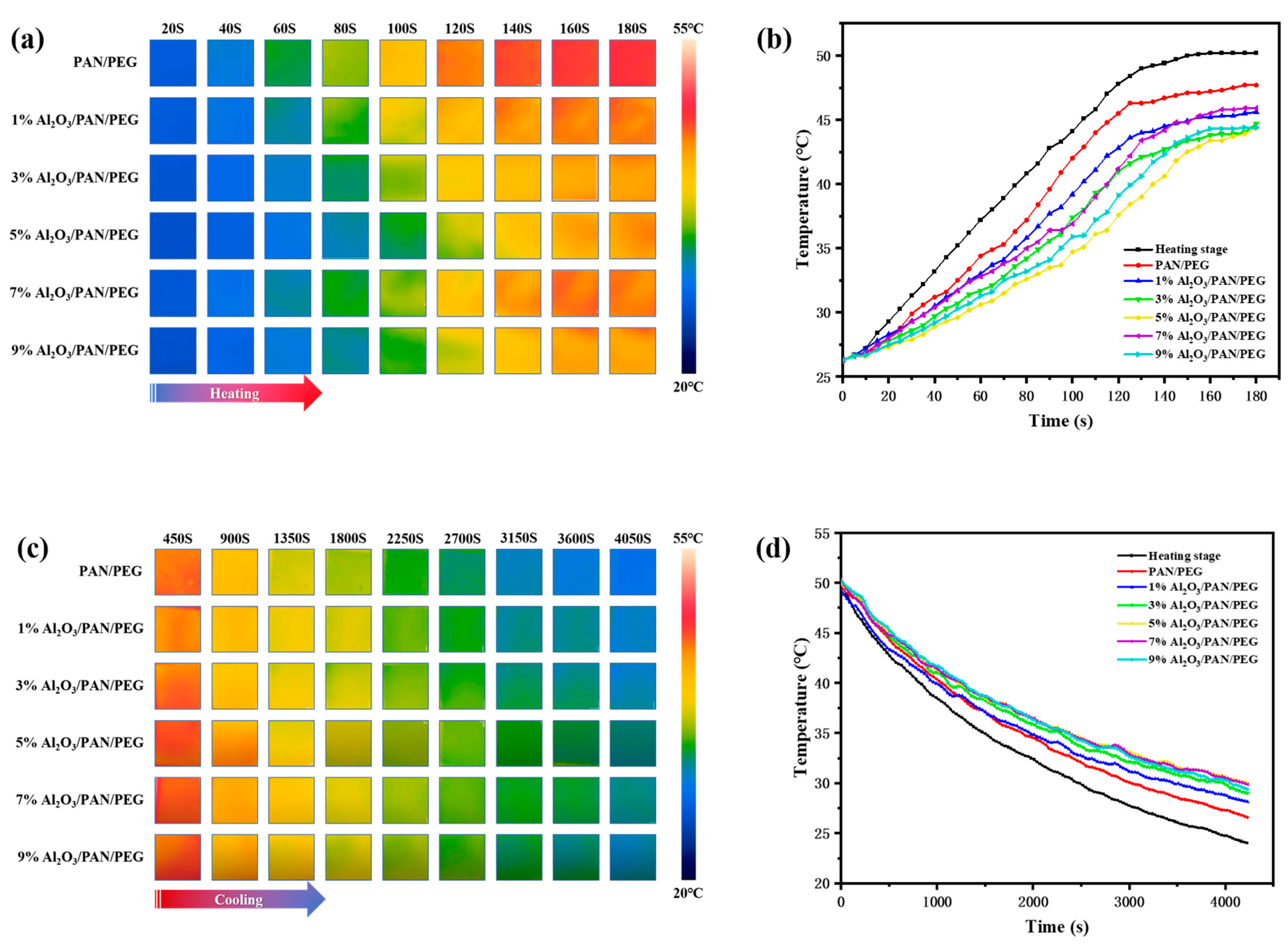
3.4. Analysis of Thermal Conductivity and Storage Performance
3.5. Analysis of Breathability and Moisture Permeability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. A review on membrane engineering for innovation in wearable fabrics and protective textiles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 350–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, G.R. Breathable polyurethane membranes for textile and related industries. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 1727, 2775–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Cui, Y. Advanced textiles for personal thermal management and energy. Joule 2020, 44, 724–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tat, T.; Chen, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Smart textiles for healthcare and sustainability. ACS Nano 2022, 169, 13301–13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. Full-wood photoluminescent and photothermic materials for thermal energy storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Liu, Y.; Shin, S.; Huang, S.; Ren, X.; Shu, W.; Cheng, J.; Tao, G.; Xu, W.; Chen, R.; et al. Emerging materials and strategies for personal thermal management. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 17, 1903921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Si, Y.; Ren, J.; Ding, B.; Li, B. Designing heat transfer pathways for advanced thermoregulatory textiles. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 17, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdel, E.; Naebe, M.; Sun, L.; Wang, X. Advanced functional fibrous materials for enhanced thermoregulating performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 1114, 13039–13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Pian, S.; Su, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. Hierarchical-morphology metafabric for scalable passive daytime radiative cooling. Science 2021, 373, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Fang, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Synthesis and thermosensitive behavior of polyacrylamide copolymers and their applications in smart textiles. Polymers 2015, 75, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Gong, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Bai, H. A thermally insulating textile inspired by polar bear hair. Adv. Mater. 2018, 3014, 1706807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, D.G.; Kandasubramanian, B. A review on polymeric-based phase change material for thermo-regulating fabric application. Polym. Rev. 2019, 603, 389–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.J.S. Coupling of interface kinetics and transformation-induced strain during pressure-induced solid–solid phase changes. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2002, 50, 1363–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z.; Ge, F. High-performance laminated fabric with enhanced photothermal conversion and joule heating effect for personal thermal management. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 137, 8851–8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jin, X.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W. Air-permeable, multifunctional, dual-energy-driven MXene-decorated polymeric textile-based wearable heaters with exceptional electrothermal and photothermal conversion performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 825, 12526–12537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, L.; Si, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight and superelastic fibrous sponges with effective heat preservation and photo-thermal conversion for personal cold protection. Compos. Commun. 2021, 25, 100766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Shi, J.; Aftab, W.; Qin, M.; Usman, A.; Zhou, F.; Lv, Y.; Gao, S.; Zou, R. Engineering the thermal conductivity of functional phase-change materials for heat energy conversion, storage, and utilization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 308, 1904228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Fu, J.; Huan, C.; Qi, S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, G. Novel smart textile with phase change materials encapsulated core-sheath structure fabricated by coaxial electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wen, X.; Yin, H.; Liu, J. A novel CNT encapsulated phase change material with enhanced thermal conductivity and photo-thermal conversion performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 184, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Sun, D. Development of thermo-regulating polypropylene fibre containing microencapsulated phase change materials. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabha, D.K.; Muthukumar, P. Performance studies on a forced convection solar dryer integrated with a paraffin wax–based latent heat storage system. Sol. Energy 2017, 149, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Sheng, X.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Qu, J. Melamine foam/polyethylene glycol composite phase change material synergistically modified by polydopamine/MXene with enhanced solar-to-thermal conversion. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.; Halcovitch, N.R.; Griffin, J.M. Long-Term Solar Energy Storage under Ambient Conditions in a MOF-Based Solid–Solid Phase-Change Material. Chem. Mater. 2020, 3223, 9925–9936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, W.; Huang, X.; Wu, W.; Liang, Z.; Mahmood, A.; Zou, R. Nanoconfined phase change materials for thermal energy applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 116, 1392–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, M.; Xing, L.; Dong, W.; Li, A.; Zheng, H.; Wang, G. Smart integration of carbon quantum dots in metal-organic frameworks for fluorescence-functionalized phase change materials. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 18, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chao, W.; Di, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, T.; Yu, Q.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Wang, C. Multifunctional wood based composite phase change materials for magnetic-thermal and solar-thermal energy conversion and storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 200, 112029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Rao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Huo, Y.; Li, Y. Review on nanoencapsulated phase change materials: Preparation, characterization and heat transfer enhancement. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhan, Y.; Huan, C.; Qi, S.; Cheng, H.; Xu, G. Core-Sheath Paraffin-Wax-Loaded Nanofibers by Electrospinning for Heat Storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 1015, 12759–12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Yuan, W. Smart nanocomposite nonwoven wearable fabrics embedding phase change materials for highly efficient energy conversion-storage and use as a stretchable conductor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 133, 4508–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W. Electrospun polyethylene glycol/cellulose acetate phase change fibers with core–sheath structure for thermal energy storage. Renew. Energy 2013, 60, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-X.; Xie, R.; Wang, X.-X.; Wen, G.-Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Ju, X.-J.; Chu, L.-Y. Fabrication of nanofibers with phase-change core and hydrophobic shell, via coaxial electrospinning using nontoxic solvent. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 5017, 5729–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Shao, Z.-q.; Wang, J.-q.; Gu, M.-j. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles decorated cellulose triacetate nanofibers for protein adsorption by coaxial electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, C.; Jia, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L. Review on electrospun ultrafine phase change fibers (PCFs) for thermal energy storage. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, M.; Williams, G.R. High-quality janus nanofibers prepared using three-fluid electrospinning. Chem. Commun. 2017, 5333, 4542–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, G.-Q.; Yang, J.; Bao, R.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yang, W.; Xie, B.-H.; Yang, M.-B. Enhanced comprehensive performance of polyethylene glycol based phase change material with hybrid graphene nanomaterials for thermal energy storage. Carbon 2015, 88, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, L.F.; Castell, A.; Barreneche, C.; de Gracia, A.; Fernández, A.I. Materials used as PCM in thermal energy storage in buildings: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 153, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.-Q.; Tseng, Y.-L.; Shih, Y.-F.; Lian, H.-Y.; Yu, Y.-H. Synthesis of novel phase change material microcapsule and its application. Polymer 2017, 133, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Correia, I.J. Electrospun polycaprolactone/aloe vera_chitosan nanofibrous asymmetric membranes aimed for wound healing applications. Polymers 2017, 95, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 1198, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Zhang, D.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, W. Preparation of Ag doped keratin/PA6 nanofiber membrane with enhanced air filtration and antimicrobial properties. Polymers 2019, 119, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

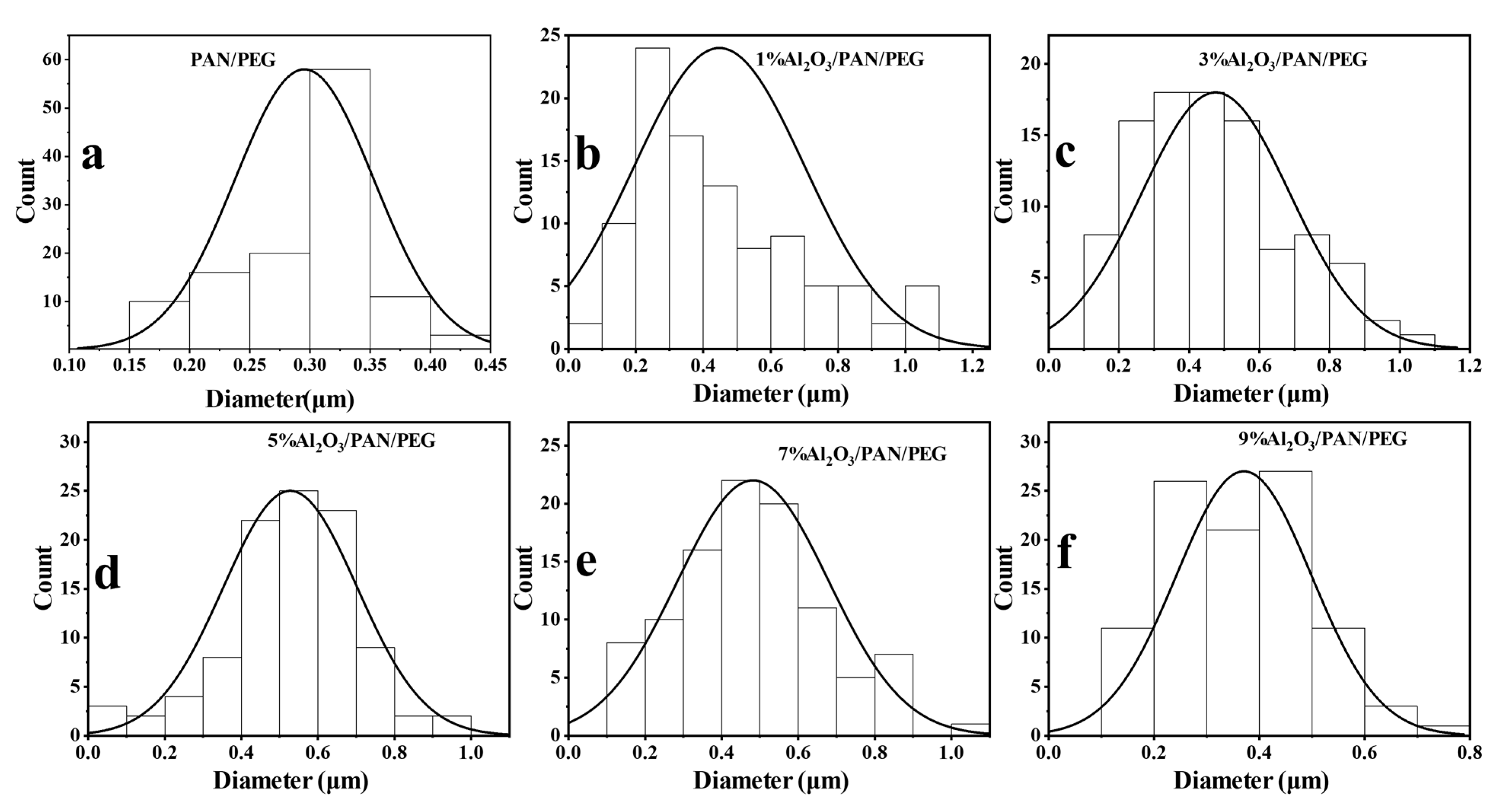


| Sample | Average Diameter/nm | Standard Deviation/nm |
|---|---|---|
| PAN/PEG | 300 | 150 |
| 1%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 448 | 253 |
| 3%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 476 | 211 |
| 5%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 528 | 175 |
| 7%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 482 | 197 |
| 9%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 371 | 128 |
| Sample | Melting | Cooling | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmo/°C | Tmp/°C | ∆Hm/J·g−1 | Tco/°C | Tcp/°C | ∆Hc/J·g−1 | |
| PAN/PEG | 31.8 | 42.3 | 70.38 | 18.4 | 25.1 | −69.12 |
| 1%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 31.5 | 41.4 | 30.48 | 18.0 | 24.6 | −27.64 |
| 3%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 31.6 | 41.3 | 32.62 | 18.2 | 23.3 | −30.36 |
| 5%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 31.9 | 41.1 | 60.05 | 19.1 | 24.8 | −54.78 |
| 7%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 32.3 | 41.2 | 52.01 | 18.0 | 24.3 | −47.06 |
| 9%Al2O3/PAN/PEG | 32.2 | 41.6 | 41.34 | 19.2 | 25.0 | −36.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y. Regulating Al2O3/PAN/PEG Nanofiber Membranes with Suitable Phase Change Thermoregulation Features. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162313
Huang L, Chen Y, Xu Z, He C, Li Y, Zhao J, Tang Y. Regulating Al2O3/PAN/PEG Nanofiber Membranes with Suitable Phase Change Thermoregulation Features. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(16):2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162313
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Leping, Ying Chen, Zhaobao Xu, Cui He, Youmu Li, Jinchao Zhao, and Youhong Tang. 2023. "Regulating Al2O3/PAN/PEG Nanofiber Membranes with Suitable Phase Change Thermoregulation Features" Nanomaterials 13, no. 16: 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162313
APA StyleHuang, L., Chen, Y., Xu, Z., He, C., Li, Y., Zhao, J., & Tang, Y. (2023). Regulating Al2O3/PAN/PEG Nanofiber Membranes with Suitable Phase Change Thermoregulation Features. Nanomaterials, 13(16), 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162313







