Electrospun Fenoprofen/Polycaprolactone @ Tranexamic Acid/Hydroxyapatite Nanofibers as Orthopedic Hemostasis Dressings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
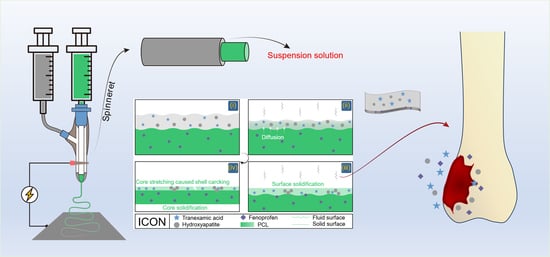
2.2. Conducting Modified Coaxial Electrospinning
2.3. Modified Coaxial Electrospinning Processes
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Morphologies and Inner Chambers
2.4.2. Physical State and Compatibility
2.4.3. Hydrophilic Properties
2.4.4. In Vitro Drug Release Profiles
2.4.5. In Vitro Hemostatic Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selections of Raw Components for Fabricating the Orthopedic Dressings
3.2. Reasonable Implementations of the Modified Coaxial Electrospinning
3.3. Morphology and Inner Structures of Nanofibers
3.4. Physical States and Compatibility
3.5. Wettability of Fibrous Membranes
3.6. In Vitro Release Profile of Fenoprofen
3.7. In Vitro Hemostatic Time Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gehrig, L.M.B. Orthopaedic Surgery. Am. J. Surg. 2011, 202, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanghe, K.K.; Chalmers, B.P.; Blevins, J.L.; Figgie, M.P.; Carli, A.V.; Agrusa, C.J.; Sculco, P.K.; Gausden, E.B. Hemostatic Agents in Orthopaedic Surgery. HSS J. 2023, 19, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Ge, J.; Bai, Y.; Liang, C.; Yang, L. Translation of Bone Wax and Its Substitutes: History, Clinical Status and Future Directions. J. Orthop. Transl. 2019, 17, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Gerhard, E.; Wang, Y.; Tran, R.T.; Xu, H.; Yan, S.; Rizk, E.B.; Armstrong, A.D.; Zhou, Y.; Du, J.; et al. Development of Biodegradable Osteopromotive Citrate-Based Bone Putty. Small 2022, 18, 2203003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Xie, J.; Jiang, J.; Shuler, F.D.; Bartlett, D.E. Rational Design of Nanofiber Scaffolds for Orthopaedic Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1459–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Chunta, S.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y. Enhanced Oral Bioavailability from Food Protein Nanoparticles: A Mini Review. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, W. Poly(Glutamic Acid)-Engineered Nanoplatforms for Enhanced Cancer Phototherapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubnov, A.A.; Belov, V.S.; Kargina, Y.V.; Tikhonowski, G.V.; Popov, A.A.; Kharin, A.Y.; Shestakov, M.V.; Perepukhov, A.M.; Syuy, A.V.; Volkov, V.S.; et al. Laser-Ablative Synthesis of Silicon–Iron Composite Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Chakraborty, D.; Cho, E.-B.; Seo, J.G. Recent Developments on the Catalytic and Biosensing Applications of Porous Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Pan, H.; Gong, W.; Yu, D.G.; Sun, Y. Electrosprayed Eudragit RL100 Nanoparticles with Janus Polyvinylpyrrolidone Patches for Multiphase Release of Paracetamol. Nanoscale 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; He, H.; Du, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, P. Electrosprayed Core (Cellulose Acetate)–Shell (Polyvinylpyrrolidone) Nanoparticles for Smart Acetaminophen Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhao, P.; Yu, D.G. Electrosprayed Stearic-Acid-Coated Ethylcellulose Microparticles for an Improved Sustained Release of Anticancer Drug. Gels 2023, 9, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, C.; Zhao, W. Fluorine Substitution Tunes the Nanofiber Chirality of Supramolecular Hydrogels to Promote Cell Adhesion and Proliferation. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2023, 5, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Kim, E.J.; Tang, Y.; Xu, H.; Yu, D.G.; Song, W.; Kim, B.J. Rational Design of Hyper-Crosslinked Polymers for Biomedical Applications. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 8, 1459–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Fu, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liang, W.; Shao, H. A Mini-Review on the Emerging Role of Nanotechnology in Revolutionizing Orthopaedic Surgery: Challenges and the Road Ahead. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1191509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Tang, Y.; Qian, C.; Kim, B.J.; Liao, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospinning Spinneret: A Bridge Between the Visible World and the Invisible Nanostructures. Innovation 2023, 4, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liang, Z.; Guo, J.; Chen, B.; Zhou, S.; Yu, D.-G. Application of Electrospun Drug-Loaded Nanofibers in Cancer Therapy. Polymers 2024, 16, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, B.; Duan, L.; Zhu, Z. Mucus-Penetrating Silk Fibroin-Based Nanotherapeutics for Efficient Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Zhao, P. The Key Elements for Biomolecules to Biomaterials and to Bioapplications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, H. The Applications of Ferulic-Acid-Loaded Fibrous Films for Fruit Preservation. Polymers 2022, 14, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, J.; Fang, B.; Ying, Y.; Yu, D.G.; He, H. Three EHDA Processes from a Detachable Spinneret for Fabricating Drug Fast Dissolution Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 310, 2300361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Huang, C. Electrospun Biomolecule-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, Y.; Wang, B.; Chang, M.-W.; Sun, R.; Zhang, L. Sandwich-structured electrospun pH-responsive dental pastes for anti-caries. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 668, 131399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bai, Y.; Shi, H.; Yue, B.; Shen, S.; Yu, D.G. Efficient Piezophotocatalysis of ZnO@PVDF Coaxial Nanofibers Modified with BiVO4 and Ag for the Simultaneous Generation of H2O2 and Removal of Pefloxacin and Cr(VI) in Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, D.G.; Lu, X. The Influence of the Ultrasonic Treatment of Working Fluids on Electrospun Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1184767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.G. Processes of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride-Based Nanofibers, Their Piezoelectric Properties, and Several Fantastic Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz Rocha, J.E.; Moreno Tovar, K.R.; Navarro Mendoza, R.; Gutiérrez Granados, S.; Cavaliere, S.; Giaume, D.; Barboux, P.; Jaime Ferrer, J.S. Critical Electrospinning Parameters for Synthesis Control of Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Kenawy, E.-R.; Wadoud, A.A.; Elhadary, M.I. Wearable Electrospun Piezoelectric Mats Based on a PVDF Nanofiber–ZnO@ZnS Core–Shell Nanoparticles Composite for Power Generation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Du, Q.; Wan, J.; Yu, D.-G.; Tan, F.; Yang, X. Improved Synergistic Anticancer Action of Quercetin and Tamoxifen Citrate Supported by An Electrospun Complex Nanostructure. Mater. Des. 2024, 238, 112657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Hou, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Williams, G.R. Energy-Saving Electrospinning with a Concentric Teflon-Core Rod Spinneret to Create Medicated Nanofibers. Polymers 2020, 12, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, W.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun Porous Nanofibers: Pore–forming Mechanisms and Applications for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Wastewater. Polymers 2022, 14, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Yu, D.G.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z. Electrospun Tri-Layer Nanodepots for Sustained Release of Acyclovir. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Xu, L. Impact Evaluations of Articles in Current Drug Delivery Based on Web of Science. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, S.; Wen, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. Chelating adsorption-engaged synthesis of ultrafine iridium nanoparticles anchored on N-doped carbon nanofibers toward highly efficient hydrogen evolution in both alkaline and acidic media. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2023, 641, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhang, C.; Han, J.; He, S.; Liu, K.; Jiang, S. Nanocellulose-Based Nanogenerators for Sensor Applications: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Chen, H.; Qi, C.; Lv, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. A Novel Electrospun Nanofiber System with PEGylated Paclitaxel Nanocrystals Enhancing the Transmucus Permeability and In Situ Retention for An Efficient Cervicovaginal Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 650, 123660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Yuan, D.; Ning, X. Efficient synthesis of PVDF/PI side-by-side bicomponent nanofiber membrane with enhanced mechanical strength and good thermal stability. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Ren, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. Confinement of prussian blue analogs boxes inside conducting polymer nanotubes enables significantly enhanced catalytic performance for water treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yue, G.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Hou, L.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; et al. Fabrication and applications of multi-fluidic electrospinning multi-structure hollow and core–shell nanofibers. Engineering 2022, 13, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mo, D.; Cui, Z.; Li, X.; Lian, H. Hybrid Electrospinning Printing for Nanofiber Self-Supporting 3D Microfluidic Devices. Fiber. Polym. 2024, 25, 201–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Zhou, J. Electrospun multi-chamber nanostructures: A powerful platform for sustainable biobased chemical nanofibers. Next Mater. 2024, 2, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Maciejewska, B.M.; Lißner, M.; Thomson, D.; Townsend, D.; Millar, R.; Petrinic, N.; Grobert, N. Unveiling the Mechanism of the in Situ Formation of 3D Fiber Macroassemblies with Controlled Properties. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 6800–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, S.A.R.; Kniep, J.; Barroca, N.; Almeida, J.C.; Fernandes, M.H.V. Nanofibrous Hybrid Scaffolds Based on PCL-Borosilicate System by a Green Sol-Gel Process. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 29, 101396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becelaere, J.; Frateur, O.; Schoolaert, E.; Vanhoorne, V.; D’hooge, D.R.; Vervaet, C.; Hoogenboom, R.; De Clerck, K. Solvent Electrospinning Amorphous Solid Dispersions with High Itraconazole, Celecoxib, Mebendazole and Fenofibrate Drug Loading and Release Potential. J. Control. Release 2023, 362, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, X.; Yan, J.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, P.; Yang, H. Electrospun Multi-Chamber Core–Shell Nanofibers and Their Controlled Release Behaviors: A Review. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 16, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, K.; Yu, D.-G. Enhancing diabetic wound healing: Advances in electrospun scaffolds from pathogenesis to therapeutic applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1354286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, L. Tri-Layer Core–Shell Fibers from Coaxial Electrospinning for a Modified Release of Metronidazole. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G.; Guo, Y.; Lian, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, L. Enhancing the Antibacterial Properties of Magnesium Alloys with Copper-Doped Anhydrous Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles Embedded into the Polycaprolactone Coating for Medical Implants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 18965–18976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, N.; Khodir, W.K.W.A.; Hamid, S.A.; Nasir, M.H.M.; Hamzah, A.S.; Cruz-Maya, I.; Guarino, V. PCL/Gelatin/Graphene Oxide Electrospun Nanofibers: Effect of Surface Functionalization on In Vitro and Antibacterial Response. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, C.J.; Paul, A.; Duruanyanwu, J.; Sackho, K.; Campagnolo, P.; Stolojan, V. The Manufacturing Conditions for the Direct and Reproducible Formation of Electrospun PCL/Gelatine 3D Structures for Tissue Regeneration. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yu, X.; Cui, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, B.; Mo, X. Development of Biodegradable Polymeric Stents for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou-Francis, A.; Piercey, M.; Al-Qatami, O.; Mazzanti, G.; Khattab, R.; Ghanem, A. Polycaprolactone Blends for Fracture Fixation in Low Load-Bearing Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangomannan, S.; Louis, K.; Dharmaraj, B.M.; Kandasamy, V.S.; Soundarapandian, K.; Gopi, D. Carbon Nanofiber/Polycaprolactone/Mineralized Hydroxyapatite Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Potential Orthopaedic Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6342–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P. Electrospun Core–Sheath Nanofibers with a Cellulose Acetate Coating for the Synergistic Release of Zinc Ion and Drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, P. A Combined Electrohydrodynamic Atomization Method for Preparing Nanofiber/Microparticle Hybrid Medicines. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1308004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenawy, E.-R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Mansfield, K.; Layman, J.; Simpson, D.G.; Sanders, E.H.; Wnek, G.E. Release of Tetracycline Hydrochloride from Electrospun Poly(Ethylene-Co-Vinylacetate), Poly(Lactic Acid), and a Blend. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratian, A.; Shelby, T.; Hasan, L.K.; Bolia, I.K.; Weber, A.E.; Petrigliano, F.A. Utilization of Tranexamic Acid in Surgical Orthopaedic Practice: Indications and Current Considerations. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2021, 13, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylis, J.R.; Lee, M.M.; St. John, A.E.; Wang, X.; Simonson, E.; Cau, M.; Kazerooni, A.; Gusti, V.; Statz, M.L.; Yoon, J.S.J.; et al. Topical Tranexamic Acid Inhibits Fibrinolysis More Effectively When Formulated with Self-propelling Particles. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarda, S.; Errassifi, F.; Marsan, O.; Geffre, A.; Trumel, C.; Drouet, C. Adsorption of Tranexamic Acid on Hydroxyapatite: Toward the Development of Biomaterials with Local Hemostatic Activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 66, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes, F.M.; Philippi, J.V.; Belle, F.; da Silva, F.S.; Morisso, F.D.P.; Volz, D.R.; Ziulkoski, A.L.; Bobinski, F.; Zepon, Κ.M. Iota-Carrageenan/Xyloglucan/Serine Powders Loaded with Tranexamic Acid for Simultaneously Hemostatic, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Performance. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 137, 212805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, C.B.; Singh, C.; Patil, P.; Manna, K.; Singh, S.; Varshney, R.; Mathur, R. Tranexamic Acid (Class I Drug) Reduced and Capped Gold Nanoparticles as a Potential Hemostatic Agent with Enhanced Performance. Nanotechnology 2023, 35, 095102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darakhshan, S.; Goudarzi, F.; Mirzaie, S.; Karami, A.; Kiani, A. Hemostatic Polyurethane Sponge Containing Kaolin, Tannic Acid, and Tranexamic Acid. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 3013–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nqoro, X.; Adeyemi, S.A.; Ubanako, P.; Ndinteh, D.T.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Aderibigbe, B.A. A Topical Alginate-Based Wound Gel Fixated with Metal-Based Nanoparticles and Tranexamic Acid as a Hemostatic Wound Healing System. BioNanoScience 2023, 13, 2400–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molapour Rashedi, S.; Khajavi, R.; Rashidi, A.; Rahimi, M.K.; Bahador, A. Novel PLA/ZnO Nanofibrous Nanocomposite Loaded with Tranexamic Acid as an Effective Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, P.; Datta, P. Tranexamic Acid-Loaded Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers as Drug Delivery System for Hemorrhage Control Applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrwa, R.; Otto, K.; Voigt, S.; Enkelmann, A.; Schnabelrauch, M.; Neubert, T.; Schneider, G. Electrospun Mucosal Wound Dressings Containing Styptics for Bleeding Control. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshosaz, J.; Choopannejad, Z.; Minaiyan, M.; Kharazi, A.Z. Rapid Hemostasis by Nanofibers of Polyhydroxyethyl Methacrylate/Polyglycerol Sebacic Acid: An in Vitro/in Vivo Study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartatiek; Yudyanto; Wuriantika, M.I.; Utomo, J.; Nurhuda, M.; Masruroh; Santjojo, D.J.D.H. Nanostructure, Porosity and Tensile Strength of PVA/Hydroxyapatite Composite Nanofiber for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 3203–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szcześ, A.; Hołysz, L.; Chibowski, E. Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P. Electrospun Core–Sheath PCL Nanofibers Loaded with NHA and Simvastatin and Their Potential Bone Regeneration Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1205252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Xiong, X.; Liu, H. Biomimetic Growth of Hydroxyapatite on Phosphorylated Electrospun Cellulose Nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Chae, W.-P.; Chang, K.-W.; Chun, S.; Kim, S.; Jeong, Y.; Kang, I.-K. Composite Nanofiber Mats Consisting of Hydroxyapatite and Titania for Biomedical Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94B, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmas, J.; Krukowski, S.; Laskus, A.; Jurkitewicz, M. Synthetic Hydroxyapatite in Pharmaceutical Applications. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 2472–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tang, Q.-L.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Wang, K.-W.; Zhang, M.-L.; Zhai, W.-Y.; Chang, J. Hydroxyapatite Nanorods/Poly(Vinyl Pyrolidone) Composite Nanofibers, Arrays and Three-Dimensional Fabrics: Electrospun Preparation and Transformation to Hydroxyapatite Nanostructures. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3013–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, L.M.; Thakur, A.; Jalili, N.A.; Detamore, M.; Gaharwar, A.K. Nanoengineered Biomaterials for Repair and Regeneration of Orthopaedic Tissue Interfaces. Acta Biomater. 2016, 42, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, N.; Sundaramurthy, A.; Chen, S.-M.; Sundramoorthy, A.K. Graphene Oxide/Oxidized Carbon Nanofiber/Mineralized Hydroxyapatite Based Hybrid Composite for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 124005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, F.A.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H. Fabrication of Titanium Dioxide Nanofibers Containing Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, H. Biomimetic Synthesis and Characterization of Carbon Nanofiber/Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffolds. Carbon 2013, 51, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ranjbar, A.; Semirumi, D.T. Enhanced Knee Joint Treatment Using a Hybrid Hyaluronic Acid-Alginate Filler Reinforced with Hydroxyapatite-Titanium Nanoparticles for Sports-Related Injuries. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, H. Mechanisms of Promoting the Differentiation and Bone Resorption Function of Osteoclasts by Staphylococcus Aureus Infection. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 312, 151568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, J.; Yedoti, P.; Dastidar, P. A Supramolecular Topical Gel Derived from a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug, Fenoprofen, Is Capable of Treating Skin Inflammation in Mice. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; He, L.; Musha, H.; Du, J.; Wang, B.; Han, P.; et al. Repurposed Fenoprofen Targeting Saer Attenuates Staphylococcus Aureus Virulence in Implant-Associated Infections. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 1354–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhou, K.; Xia, Y.; Qian, C.; Yu, D.-G.; Xie, Y.; Liao, Y. Electrospun Trilayer Eccentric Janus Nanofibers for A Combined Treatment of Periodontitis. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Dong, P.; Tian, F.; Li, F.; Meng, X. Electrospun Kaolin-Loaded Chitosan/PEO Nanofibers for Rapid Hemostasis and Accelerated Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, M.; Xie, Y.; Yu, D.G. Comparisons of Antibacterial Performances between Electrospun Polymer@drug Nanohybrids with Drug-Polymer Nanocomposites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Feng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhou, X.; He, C. Nanofibers for the Immunoregulation in Biomedical Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1334–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, Y.; Shi, J.; Yu, Q.; Liu, S.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, H. Advanced Postoperative Tissue Antiadhesive Membranes Enabled with Electrospun Nanofibers. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 17, 1643–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, Z.; Baddi, S.; Gao, F.L.; Feng, C.L. Gallic Acid-Doped Multifunctional Hybrid Hydrogel for Antioxidant and Antibacterial Studies. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 206, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, N.; Ren, Q.; Niu, S.; Zhu, L.; Hong, L.; Cui, K.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Wen, M.; et al. Janus Nanofiber Membranes with Photothermal-Enhanced Biofluid Drainage and Sterilization for Diabetic Wounds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2315020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yu, D.G.; Li, X. Biodegradable Flexible Conductive Film Based on Sliver Nanowires and PLA Electrospun Fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 142, e55433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, F.; Yang, Y.; He, H.; Qi, J.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y. Establishment of in vitro dissolution based on similarity with in vivo dissolution: A case study on aripiprazole. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Wu, M.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.; Ge, R.; Yu, D.-G. Engineered Spindles of Little Molecules Around Electrospun Nanofibers for Biphasic Drug Release. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 4, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H.O.; Makram, T.S.; Mosallam, S. Effect of Polymers on the Physicochemical Properties and Biological Performance of Fenoprofen Calcium Dihydrate-Triacetyl-β-Cyclodextrin Complex. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A. Analysis of Fickian and Non-Fickian Drug Release from Polymers. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1985, 60, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Structural and functional design of electrospun nanofibers for hemostasis and wound healing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1027–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Nanofibrous hemostatic materials: Structural design, fabrication methods, and hemostatic mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 2022, 154, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, L. Applications of injectable hemostatic materials in wound healing: Principles, strategies, performance requirements, and future perspectives. Theranostics 2023, 13, 4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Yu, X.; Shen, Y.; Sun, B.; Guo, W.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Shafiq, M.; et al. Electrospinning Inorganic Nanomaterials to Fabricate Bionanocomposites for Soft and Hard Tissue Repair. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, M.; Madheswaran, D.; Valtera, J.; Kostakova, E.K.; Lukas, D. Alternating Current Electrospinning: The Impacts of Various High-Voltage Signal Shapes and Frequencies on the Spinnability and Productivity of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers. Mater. Des. 2022, 213, 110308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, M.; Madheswaran, D.; Hauzerova, S.; Novotny, V.; Hedvicakova, V.; Jencova, V.; Kostakova, E.K.; Schindler, M.; Lukas, D. AC Electrospinning: Impact of High Voltage and Solvent on the Electrospinnability and Productivity of Polycaprolactone Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.-C.; Zhang, C.; Xing, Z.; Ahmad, Z.; Ding, Q.; Chang, M.-W. Controlled engineering of multifunctional porous structures using tri-needle co-axial electrohydrodynamic flow and sacrificial media. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Qian, Y.; Haghayegh, M.; Xia, Y.; Yang, S.; Gao, R.; Zhu, M. Electrospun Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Nanofibers for Accelerating Wound Healing: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 3171–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, N.O.; Gabut, S.; Maton, M.; Odou, P.; Vialette, M.; Pinon, A.; Neut, C.; Tabary, N.; Blanchemain, N.; Martel, B. Electrospun Filtering Membrane Designed as Component of Self-Decontaminating Protective Masks. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raje, K.; Ohashi, K.; Fujita, S. Three-Dimensional Printer-Assisted Electrospinning for Fabricating Intricate Biological Tissue Mimics. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Teng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y. Electrospun nanofiber materials for photothermal interfacial evaporation. Materials 2023, 16, 5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tören, E.; Buzgo, M.; Mazari, A.A.; Khan, M.Z. Recent Advances in Biopolymer Based Electrospun Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhang, S. Design of Novel PLK4 Inhibitors As TRIM37-Amplified Breast Cancer Drugs Using 3D-QSAR, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Methods. Mol. Simul. 2024, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| NO. | Electrospinning | Core (w/v) | Shell (w/v) | Flow Rate (mL/h) | Morphologies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core/Shell | |||||
| F1 | Uniaxial | Solution A | -- | 1.2/0 | Monoaxial fiber |
| F2 | Modified coaxial | Solution A | TFE | 1.2/0.3 | Monoaxial fiber |
| F3 | Modified coaxial | Solution A | Solution B | 1.2/0.3 | Core–shell nanofiber |
| F4 | Modified coaxial | Solution A | Solution B + 5% (w/v) PVP K30 | 1.2/0.3 | Core–shell nanofiber |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.; Wang, M.; Yu, S.; Yu, D.-G.; Bligh, S.W.A. Electrospun Fenoprofen/Polycaprolactone @ Tranexamic Acid/Hydroxyapatite Nanofibers as Orthopedic Hemostasis Dressings. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070646
Huang C, Wang M, Yu S, Yu D-G, Bligh SWA. Electrospun Fenoprofen/Polycaprolactone @ Tranexamic Acid/Hydroxyapatite Nanofibers as Orthopedic Hemostasis Dressings. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(7):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070646
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chang, Menglong Wang, Siyou Yu, Deng-Guang Yu, and Sim Wan Annie Bligh. 2024. "Electrospun Fenoprofen/Polycaprolactone @ Tranexamic Acid/Hydroxyapatite Nanofibers as Orthopedic Hemostasis Dressings" Nanomaterials 14, no. 7: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070646