Carbon Nanotube/Alumina/Polyethersulfone Hybrid Hollow Fiber Membranes with Enhanced Mechanical and Anti-Fouling Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphology

2.2. Porosity and Pore Size Distribution
| Sample | Pressure When the First Bubble Appeared (kPa) * | Maximum Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| Pristine | 200 | 178 |
| 0.2 wt % CNTs | 205 | 174 |
| 0.5 wt % CNTs | 240 | 148 |
| 1.0 wt % CNTs | 245 | 145 |


2.3. Mechanical Properties


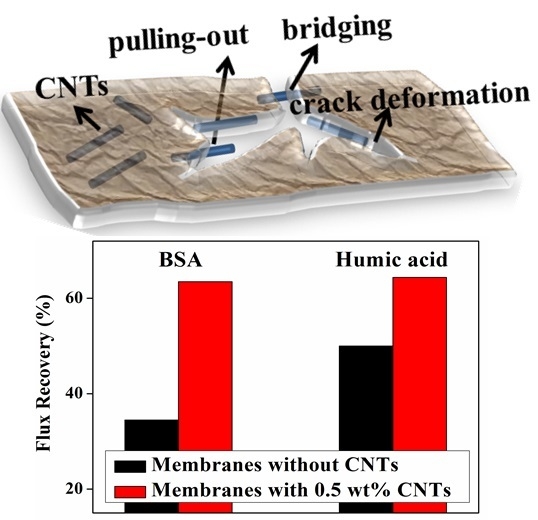
2.4. Flux, Rejection and Antifouling Properties


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Characterizations
3.3.1. Morphology and Surface Hydrophilicity
3.3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3.3. Flux, Rejection and Antifouling
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuura, T. Progress in membrane science and technology for seawater desalination—A review. Desalination 2001, 134, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C.; van Gestel, T.; Doyen, W.; Leysen, R. A review of pressure-driven membrane processes in wastewater treatment and drinking water production. Environ. Prog. 2003, 22, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, M.M.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnologies. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1946–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.M.; Dumee, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.D.; Duke, M.; Gomez, J.; Gray, S. Advances in membrane distillation for water desalination and purification applications. Water 2013, 5, 94–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intelligence, A.M. Market Report: Global Membrane Technology Market; Acmite Market Intelligence: Ratingen, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L. Biofouling of water treatment membranes: A review of the underlying causes, monitoring techniques and control measures. Membranes 2012, 2, 804–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, S. Comparison study of the effect of PVP and PANI nanofibers additives on membrane formation mechanism, structure and performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 385, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, S. Performance improvement of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane using well-dispersed polyaniline-poly(vinylpyrrolidone) nanocomposite as the additive. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 4661–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Chou, S.; Qiu, C.; Fane, A.G. Characterization of novel forward osmosis hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 355, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, S.H.; Idris, M.I.; Abdullah, H.Z.; Ismail, A.F. Short Review of Ultrafiltration of Polymer Membrane As a Self-Cleaning and Antifouling in the Wastewater System. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Materials, Penang, Malaysia, 26–27 March 2013.
- Goh, P.S.; Ng, B.C.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. Inorganic nanomaterials in polymeric ultrafiltration membranes for water treatment. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2015, 44, 216–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Ng, J.; Sun, D.D. High-performance multifunctional TiO2 nanowire ultrafiltration membrane with a hierarchical layer structure for water treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3731–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaysom, C.; Moon, S.H.; Ladewig, B.P.; Lu, G.Q.M.; Wang, L.Z. The influence of inorganic filler particle size on composite ion-exchange membranes for desalination. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 15124–15132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Preparation and characterization of poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) based ultrafiltration membranes using nano gamma-Al2O3. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Shen, H.-M.; Yang, H. Preparation and characterization of PVDF-SiO2 composite hollow fiber UF membrane by sol-gel method. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Peng, C.W.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yeh, J.M.; Wan, H.P.; Hung, W.C. Preparation and comparative properties of membranes based on PANI and three inorganic fillers. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, Y.S.; Xiang, C.B. Preparation of poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) ultrafiltration membrane modified by nano-sized alumina (Al2O3) and its antifouling research. Polymer 2005, 46, 7701–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. The effects of mechanical and chemical modification of TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface chemistry, structure and fouling performance of PES ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Abdulkarim, A.A.; Ooi, B.S.; Ismail, S. Recent development in additives modifications of polyethersulfone membrane for flux enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 246–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Z. Reinforcement and quantitative description of inorganic particulate-filled polymer composites. Compos. B 2013, 51, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Fan, Z.; Meng, Q.; Shen, C.; Gao, C. Stiff metal-organic framework-polyacrylonitrile hollow fiber composite membranes with high gas permeability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.H.; Pereira, T.; Choi, O.; Wang, Y.; Hahn, H.T. Surface functionalized alumina nanoparticle filled polymeric nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, D.X.; Wang, X.D. Experimental study of adhesion properties between membrane surface and humic acid during microfiltration. Eur. PubMed Cent. 2014, 35, 3007–3011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.W.; Zhou, L.K.; Li, H.X.; Wang, H.F.; Lang, J.-P. One-pot growth of free-standing CNTs/TiO2 nanofiber membrane for enhanced photocatalysis. Mater. Lett. 2013, 95, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesabi, Z.R.; Allam, N.K.; Dahmen, K.; Garmestani, H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Self-standing crystalline TiO2 nanotubes/CNTs heterojunction membrane: Synthesis and characterization. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2011, 3, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acrokiasamy, D.L.; Alam, J.; Alhoshan, M. Carbon nanotubes-blended poly (phenylene sulfone) membranes for ultrafiltration applications. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 3, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Yokwana, K.; Gumbi, N.; Adams, F.; Mhlanga, S.; Nxumalo, E.; Mamba, B. Development of functionalized doped carbon nanotube/polysulfone nanofiltration membranes for fouling control. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41835–41845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.Z.L.; Wang, Z.M.; Gao, C.J. Fabrication and characterization of polyethersulfone/carbon nanotubes (PES/CNTs) based mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) for nanofiltration application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 330, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltsios, K.; Athanasiou, E.; Aidinis, C.; Kanellopoulos, N. Microstructure formation phenomena in phase inversion membranes. J. Macromol. Sci. Phys. 1999, 38, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.H.; Chen, L.W. Pore formation mechanism of membranes from phase inversion process. Desalination 1995, 103, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrparvar, A.; Rahimpour, A.; Jahanshahi, M. Modified ultrafiltration membranes for humic acid removal. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuyavan, Y.L.; Anantharaman, N.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Ismail, A.F. Adsorptive removal of humic acid by zirconia embedded in a poly (ether sulfone) membrane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 11355–11364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lang, W.-Z.; Xu, H.-P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.-J. Improved poly (vinyl butyral) hollow fiber membranes by embedding multi-walled carbon nanotube for the ultrafiltrations of bovine serum albumin and humic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Kocic, A.; Zydney, A.L. Analysis of humic acid fouling during microfiltration using a pore blockage-cake filtration model. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 198, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and characterization of membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, H.; He, L.; Sridhar, T.; Suresh, A.K.; Bellare, J.; Wang, H. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-grafted BPPO ultrafiltration composite membranes with enhanced antifouling and antibacterial properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 14974–14981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Wang, K.; Davies, C.H.J.; Wang, H. Carbon Nanotube/Alumina/Polyethersulfone Hybrid Hollow Fiber Membranes with Enhanced Mechanical and Anti-Fouling Properties. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1366-1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031366
Feng Y, Wang K, Davies CHJ, Wang H. Carbon Nanotube/Alumina/Polyethersulfone Hybrid Hollow Fiber Membranes with Enhanced Mechanical and Anti-Fouling Properties. Nanomaterials. 2015; 5(3):1366-1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031366
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yi, Kun Wang, Chris H. J. Davies, and Huanting Wang. 2015. "Carbon Nanotube/Alumina/Polyethersulfone Hybrid Hollow Fiber Membranes with Enhanced Mechanical and Anti-Fouling Properties" Nanomaterials 5, no. 3: 1366-1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031366
APA StyleFeng, Y., Wang, K., Davies, C. H. J., & Wang, H. (2015). Carbon Nanotube/Alumina/Polyethersulfone Hybrid Hollow Fiber Membranes with Enhanced Mechanical and Anti-Fouling Properties. Nanomaterials, 5(3), 1366-1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031366