Plant Mediated Green Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles: Comparison of Toxicity of Engineered and Plant Mediated CuO Nanoparticles towards Daphnia magna
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Plant CuO Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Ion Release Profile of CuO Nanoparticles
2.5. Acute Toxicity Experiments
2.5.1. Bioassay
2.5.2. Assessment of CuO Nanoparticles Accumulation in Daphnia
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
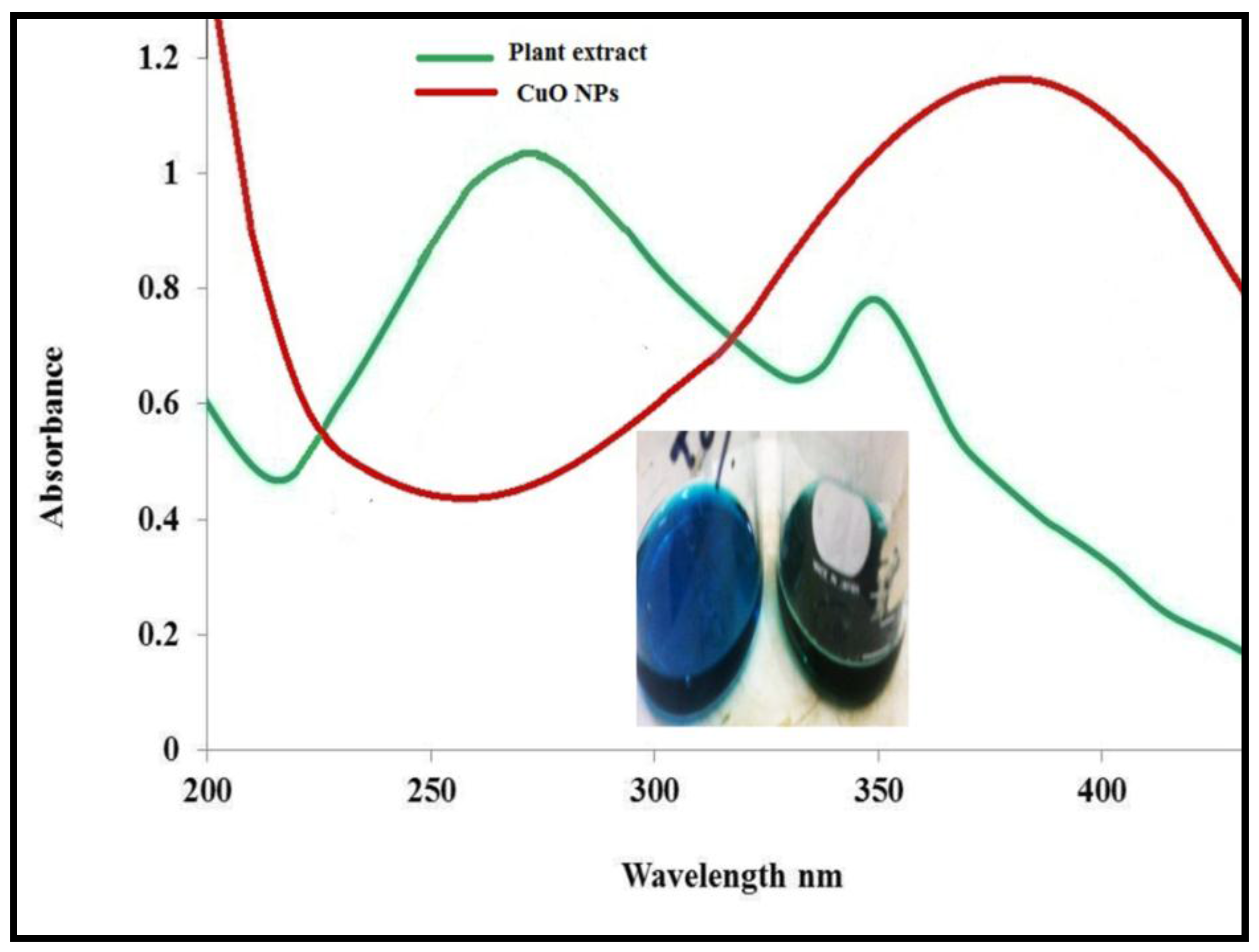
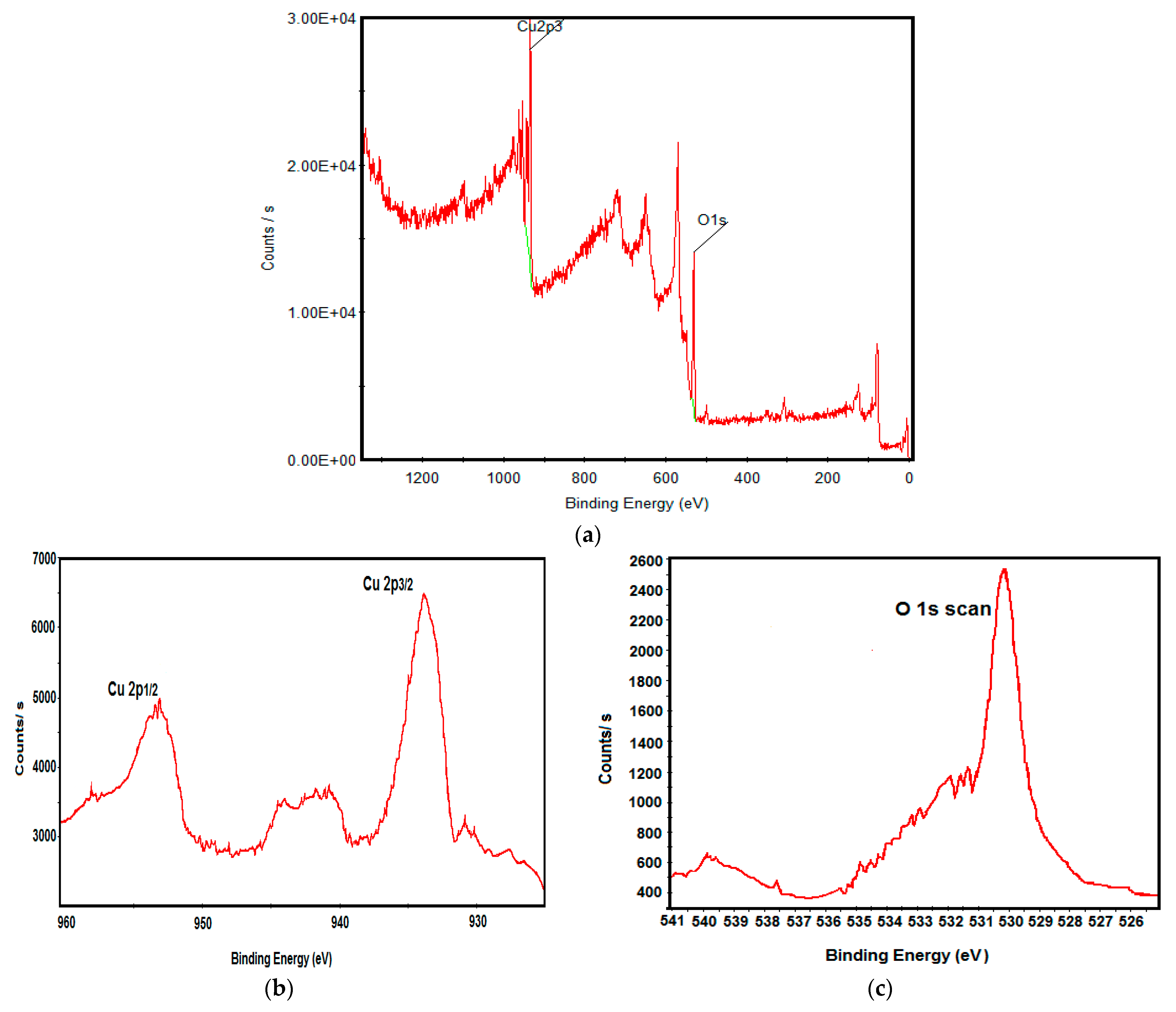
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of CuO Nanoparticles
3.2. Ion Release from CuO Nanoparticles
3.3. Toxicity Bioassay
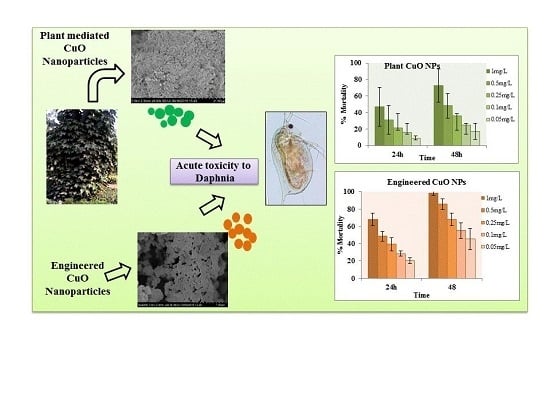
3.3.1. Forty-Eight Hour Acute Toxicity of CuO Nanoparticles
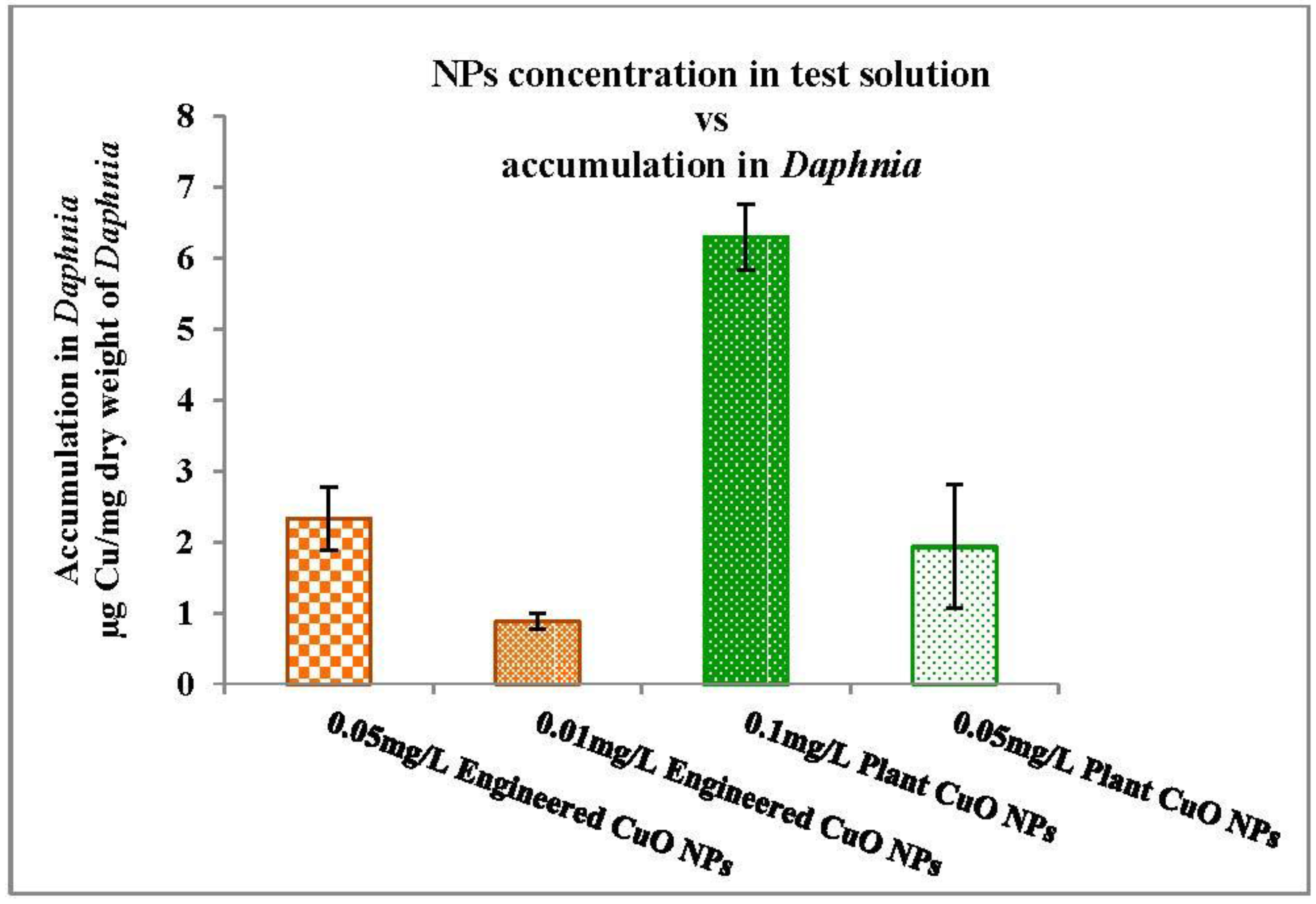
3.3.2. Nanoparticles Accumulation in Daphnia
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Pelaez, M.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Obare, S.O.; Falaras, P.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Anthony Byrne, J.; Choi, H.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chapter 5: The green synthesis and environmental applications of nanomaterials. In Sustainable Preparation of Metal Nanoparticles: Methods and Applications; Luque, R., Varma, R.S., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 106–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ershov, B.G.; Janata, E.; Michaelis, M.; Henglein, A. Reduction of aqueous copper (2+) by carbon dioxide (1−): First steps and the formation of colloidal copper. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 8996–8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhas, N.A.; Raj, C.P.; Gedanken, A. Synthesis, characterization, and properties of metallic copper nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, C.; Jungk, H.O. Polyol-mediated preparation of nanoscale oxide particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopić, S.; Dvorak, P.; Friedrich, B. Synthesis of spherical nanosized copper powder by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. World Metall. 2005, 58, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Q.; Wu, X. Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using L-ascorbic acid. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guajardo-Pacheco, M.J.; Morales-Sánchez, J.E.; González-Hernández, J.; Ruiz, F. Synthesis of copper nanoparticles using soybeans as a chelant agent. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thekkae Padil, V.V.; Černík, M. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using gum karaya as a biotemplate and their antibacterial application. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 889–898. [Google Scholar]
- Yallappa, S.; Manjanna, J.; Sindhe, M.A.; Satyanarayan, N.D.; Pramod, S.N.; Nagaraja, K. Microwave assisted rapid synthesis and biological evaluation of stable copper nanoparticles using T. arjuna bark extract. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 110, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angajala, G.; Pavan, P.; Subashini, R. One-step biofabrication of copper nanoparticles from aegle Marmelos correa aqueous leaf extract and evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and mosquito larvicidal efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 51459–51470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naika, H.R.; Lingaraju, K.; Manjunath, K.; Kumar, D.; Nagaraju, G.; Suresh, D.; Nagabhushana, H. Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. extract and their antibacterial activity. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, R.; Manikandan, P.; Malarvizhi, V.; Fathima, T.; Shivashangari, K.S.; Ravikumar, V. Green synthesis of colloidal copper oxide nanoparticles using Carica papaya and its application in photocatalytic dye degradation. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 121, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswadevarayalu, A.; Ramana, P.V.; Kumar, G.S.; Sumalatha, J.; Reddy, S.A. Fine ultrasmall copper nanoparticle (UCuNPs) synthesis by using Terminalia bellirica fruit extract and its antimicrobial activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2016, 27, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, P.; Saha, M.; Maiti, D. Microwave synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using tea leaf and coffee powder extracts and its antibacterial activity. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2014, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamuly, C.; Hazarika, M.; Das, J.; Bordoloi, M.; Borah, D.J.; Das, M.R. Bio-derived CuO nanoparticles for the photocatalytic treatment of dyes. Mater. Lett. 2014, 123, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.; Mohsenzadeh, S. Rapid, green, and eco-friendly biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles using flower extract of Aloe vera. Syn. React. Inorg. Met. 2015, 45, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thit, A.; Selck, H.; Bjerregaard, H.F. Toxicity of CuO nanoparticles and Cu ions to tight epithelial cells from Xenopus laevis (A6): Effects on proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell death. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, J.R.; Adeleye, A.S.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.; Keller, A.A. Aggregation, dissolution, and transformation of copper nanoparticles in natural waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2749–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rispoli, F.; Angelov, A.; Badia, D.; Kumar, A.; Seal, S.; Shah, V. Understanding the toxicity of aggregated zero valent copper nanoparticles against Escherichia coli. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasemets, K.; Ivask, A.; Dubourguier, H.C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanoparticles of ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Toxicol. In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2009, 23, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melegari, S.P.; Perreault, F.; Costa, R.H.; Popovic, R.; Matias, W.G. Evaluation of toxicity and oxidative stress induced by copper oxide nanoparticles in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142–143, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinlaan, M.; Ivask, A.; Blinova, I.; Dubourguier, H.C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golobic, M.; Jemec, A.; Drobne, D.; Romih, T.; Kasemets, K.; Kahru, A. Upon exposure to Cu nanoparticles, accumulation of copper in the isopod Porcellio scaber is due to the dissolved Cu ions inside the digestive tract. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12112–12119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-M.; An, Y.-J.; Yoon, H.; Kweon, H.-S. Toxicity and bioavailability of copper nanoparticles to the terrestrial plants mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) and wheat (Triticum aestivum): Plant agar test for water-insoluble nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Comparative toxicity of copper nanoparticles across three Lemnaceae species. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Weil, R.; Hyndman, K.A.; Denslow, N.D.; Powers, K.; Taylor, D.; Barber, D.S. Exposure to copper nanoparticles causes gill injury and acute lethality in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8178–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, H.L.; Cronholm, P.; Gustafsson, J.; Moller, L. Copper oxide nanoparticles are highly toxic: A comparison between metal oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.; Goddard, R.H.; Bielmyer-Fraser, G.K. Comparative effects of dissolved copper and copper oxide nanoparticle exposure to the sea anemone, Exaiptasia pallida. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 160, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.; Seena, S.; Pascoal, C.; Cassio, F. Copper oxide nanoparticles can induce toxicity to the freshwater shredder Allogamus ligonifer. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Culloty, S.; Darmody, G.; Lynch, S.; Davenport, J.; Ramirez-Garcia, S.; Dawson, K.A.; Lynch, I.; Blasco, J.; Sheehan, D. Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis: A redox proteomic investigation. Chemosphere 2014, 108, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, M.; Arslan, Z.; Demir, V.; Daniels, J.; Farah, I.O. Accumulation and toxicity of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles through waterborne and dietary exposure of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, A.M.; Limbach, L.K.; van Duc, L.; Krumeich, F.; Athanassiou, E.K.; Gerber, L.C.; Moch, H.; Stark, W.J. Nanoparticle cytotoxicity depends on intracellular solubility: Comparison of stabilized copper metal and degradable copper oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 197, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, E.R.; Inostroza-Blancheteau, C.; Obando, V.; Rubio, L.; Marcos, R. Genotoxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in Drosophila melanogaster. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2015, 791, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrocchi, U. CRC World Dictionary of Medicinal and Poisonous Plants: Common Names, Scientific Names, Eponyms, Synonyms, and Etymology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Oecd guidelines for the testing of chemicals. In Test No. 202: Daphnia sp., Acute Immobilization Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Udayabhanu; Nethravathi, P.C.; Kumar, M.A.P.; Suresh, D.; Lingaraju, K.; Rajanaika, H.; Nagabhushana, H.; Sharma, S.C. Tinospora cordifolia mediated facile green synthesis of cupric oxide nanoparticles and their photocatalytic, antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 33, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odzak, N.; Kistler, D.; Behra, R.; Sigg, L. Dissolution of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in aqueous media. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 191, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, N.; Leroux, F.; Knapen, D.; Bals, S.; Blust, R. The uptake of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles in the water-flea Daphnia magna under acute exposure scenarios. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, S.; Yoo, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, J.W.; Jung, J. Effect of salinity on acute copper and zinc toxicity to Tigriopus japonicus: The difference between metal ions and nanoparticles. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G. Assay Development: Fundamentals and Practices; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, K.P.; Caloto-Oliveira, Á.; Vicentini, D.S.; Melegari, S.P.; Matias, W.G.; Barbosa, S.; Kummrow, F. Acute toxicity of copper and chromium oxide nanoparticles to Daphnia similis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Contam. 2014, 9, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, N.; Vakurov, A.; Knapen, D.; Blust, R. The chronic toxicity of CuO nanoparticles and copper salt to Daphnia magna. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Vijver, M.G.; Chen, G.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Toxicity and accumulation of Cu and ZnO nanoparticles in Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4657–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinlaan, M.; Kahru, A.; Kasemets, K.; Arbeille, B.; Prensier, G.; Dubourguier, H.C. Changes in the Daphnia magna midgut upon ingestion of copper oxide nanoparticles: A transmission electron microscopy study. Water Res. 2011, 45, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, S.W. Acute toxicity of Ag and CuO nanoparticle suspensions against Daphnia magna: The importance of their dissolved fraction varying with preparation methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227–228, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Abid, A.D.; Kennedy, I.M.; Hristova, K.R.; Silk, W.K. To duckweeds (Landoltia punctata), nanoparticulate copper oxide is more inhibitory than the soluble copper in the bulk solution. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Becerra, R.; Rius, J.L.; Zorrilla, C. Tannin biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 100, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, Z.; Novak, P.; Kaslik, J.; Plachtova, P.; Brazdova, M.; Jancula, D.; Siskova, K.M.; Machala, L.; Marsalek, B.; Zboril, R.; et al. Iron(II,III)–polyphenol complex nanoparticles derived from green tea with remarkable ecotoxicological impact. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1674–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.U.; Rajasekharreddy, P. Green synthesis of silver-protein (core–shell) nanoparticles using Piper betle L. Leaf extract and its ecotoxicological studies on Daphnia magna. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 389, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Nanoparticle Type | Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| Engineered CuO NPs | −11.7 ± 2.52 | −2.10 ± 0.67 | 11.43 ± 1.62 | 18.13 ± 0.60 |
| Plant CuO NPs | −9.27 ± 1.10 | −3.76 ± 0.86 | 7.69 ± 0.35 | 16.25 ± 0.36 |
| Test Material | EC50 (mg/L) | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|
| Engineered CuO NPs | 0.102 ± 0.019 | 0.09–0.13 |
| Plant CuO NPs | 0.69 ± 0.226 | 0.38–0.9 |
| Actual Concentration | % Relative Contribution of Released Cu+ Ions to Accumulation | |
|---|---|---|
| NPs(particle) | NPs(ion) | |
| 0.05 mg/L Engineered CuO NPs | 74.0 ± 2.0 | 26.0 ± 2 |
| 0.01 mg/L Engineered CuO NPs | 83.7 ± 2.3 | 16.3 ± 2.3 |
| 0.1 mg/L Plant CuO NPs | 71.94 ± 3.30 | 28.06 ± 3.30 |
| 0.05 mg/L Plant CuO NPs | 82.87 ± 1.02 | 17.3 ± 1.02 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saif, S.; Tahir, A.; Asim, T.; Chen, Y. Plant Mediated Green Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles: Comparison of Toxicity of Engineered and Plant Mediated CuO Nanoparticles towards Daphnia magna. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110205
Saif S, Tahir A, Asim T, Chen Y. Plant Mediated Green Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles: Comparison of Toxicity of Engineered and Plant Mediated CuO Nanoparticles towards Daphnia magna. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(11):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110205
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaif, Sadia, Arifa Tahir, Tayyaba Asim, and Yongsheng Chen. 2016. "Plant Mediated Green Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles: Comparison of Toxicity of Engineered and Plant Mediated CuO Nanoparticles towards Daphnia magna" Nanomaterials 6, no. 11: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110205
APA StyleSaif, S., Tahir, A., Asim, T., & Chen, Y. (2016). Plant Mediated Green Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles: Comparison of Toxicity of Engineered and Plant Mediated CuO Nanoparticles towards Daphnia magna. Nanomaterials, 6(11), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110205