Improving the Power Conversion Efficiency of Carbon Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells by Growing the Dots on a TiO2 Photoanode In Situ
Abstract
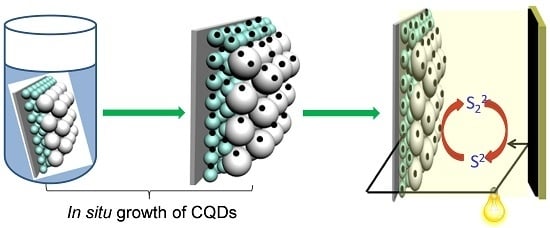
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of TiO2-Coated Photoanode
3.3. In Situ Growth of CQDs on TiO2 Surface
3.4. Construction of the Solar Cell
3.5. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bella, F.; Galliano, S.; Falco, M.; Viscardi, G.; Barolo, C.; Grätzel, M.; Gerbaldi, C. Unveiling iodine-based electrolytes chemistry in aqueous dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 4880–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliano, S.; Bella, F.; Gerbaldi, C.; Falco, M.; Viscardi, G.; Grätzel, M.; Barolo, C. Photoanode/Electrolyte Interface Stability in Aqueous Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Energy Technol. 2016, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, F.; Galliano, S.; Falco, M.; Viscardi, G.; Barolo, C.; Grätzel, M.; Gerbaldi, C. Approaching truly sustainable solar cells by the use of water and cellulose derivatives. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, G.Y.; Lin, B.; Qu, J.; Yuan, N.Y.; Ding, J.N.; Gu, Z. Performance enhancement of aqueous dye-sensitized solar cells via introduction of a quasi-solid-state electrolyte with an inverse opal structure. Sol. Energy 2016, 127, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zheng, D.; Wang, M.; Lin, C.; Lin, Z. High efficiency perovskite solar cells: From complex nanostructure to planar heterojunction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5994–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraghechi, P.; Labelle, A.J.; Kirmani, A.R.; Lan, X.; Adachi, M.M.; Thon, S.M.; Hoogland, S.; Lee, A.; Ning, Z.; Fischer, A. The Donor-Supply Electrode Enhances Performance in Colloidal Quantum Dot Solar Cells. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6111–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Pan, Z.; Morasero, I.; Canovas, E.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Gong, X.Q.; Wang, J.; Bonn, M.; Bisquert, J. Boosting Power Conversion Efficiencies of Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells Beyond 8% by Recombination Control. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5602–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Toward High-Efficient Red Emissive Carbon Dots: Facile Preparation, Unique Properties, and Applications as Multifunctional Theranostic Agents. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8659–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Carbon Dots Prepared by Hydrothermal Treatment of Dopamine as an Effective Fluorescent Sensing Platform for the Label-Free Detection of Iron(III) Ions and Dopamine. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 7243–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Bing, T.; Shangguan, D. Carbon dots based dual-emission silica nanoparticles as a ratiometric nanosensor for Cu2+. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, S. Amphiphilic Egg-Derived Carbon Dots: Rapid Plasma Fabrication, Pyrolysis Process, and Multicolor Printing Patterns. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9297–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. A Biocompatible Fluorescent Ink Based on Water-Soluble Luminescent Carbon Nanodots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12215–12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kalytchuk, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Kershaw, S.V.; Rogach, A.L. Thickness-dependent full-color emission tunability in a flexible carbon dot ionogel. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Rui, M.; Song, J.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, H. Carbon and graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic and energy devices: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Li, S.; Fan, Z.; Meng, X.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Shining carbon dots: Synthesis and biomedical and optoelectronic applications. Nano Today 2016, 11, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, S.; Palomares, E.; Martinez-Ferrero, E. Graphene and Carbon Quantum Dot-Based Materials in Photovoltaic Devices: From Synthesis to Applications. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, R.; Deepa, M.; Srivastava, A.K. Förster resonance energy transfer and carbon dots enhance light harvesting in a solid-state quantum dot solar cell. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3907–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Ming, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.; Lee, S.T. Bioinspired photoelectric conversion system based on carbon-quantum-dot-doped dye-semiconductor complex. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5080–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirtchev, P.; Henderson, E.J.; Soheilnia, N.; Yip, C.M.; Ozin, G.A. Solution phase synthesis of carbon quantum dots as sensitizers for nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Ma, D.K.; Zhang, Y.G.; Chen, W.; Huang, S.M. N-doped carbon quantum dots for TiO2-based photocatalysts and dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, J.; Marinovic, A.; Sevilla, M.; Dunn, S.; Titirici, M. Biomass-Derived Carbon Quantum Dot Sensitizers for Solid-State Nanostructured Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4463–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margraf, J.; Lodermeyer, F.; Strauss, V.; Haines, P.; Walter, J.; Peukert, W.; Costa, R.; Clark, T.; Guldi, D. Using carbon nanodots as inexpensive and environmentally friendly sensitizers in mesoscopic solar cells. Nanoscale Horiz. 2016, 1, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, P.; Cong, S.; Wu, J.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Dai, X.; Yi, Q.; Zou, G. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots for “green” quantum dot solar cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Cui, X.; Li, B.; Li, L.S. Large, solution-processable graphene quantum dots as light absorbers for photovoltaics. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Wu, R.; Adamska, L.; Velizhanin, K.A.; Doorn, S.K.; Sykora, M. In situ synthesis of graphene molecules on TiO2: Application in sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20473–20478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saud, P.S.; Pant, B.; Park, M.; Chae, S.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Mohamed, E.-N.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Kim, H.-Y. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of fly ash incorporated TiO2 nanofibers for effective removal of organic pollutants. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Zuo, S.; Li, B. Preparation and visible light photocatalytic activity of carbon quantum dots/TiO2 nanosheet composites. Carbon 2014, 68, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Li, H. CdS sensitized TiO2 photoanodes for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells by hydrothermal assisted chemical bath deposition and post-annealing treatment. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 107957–107963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Li, Q.; Li, H. Toward highly efficient CdS/CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells incorporating a fullerene hybrid-nanostructure counter electrode on transparent conductive substrates. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30617–30623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Yin, K.; Li, H. Improving the Power Conversion Efficiency of Carbon Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells by Growing the Dots on a TiO2 Photoanode In Situ. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060130
Zhang Q, Zhang G, Sun X, Yin K, Li H. Improving the Power Conversion Efficiency of Carbon Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells by Growing the Dots on a TiO2 Photoanode In Situ. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(6):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060130
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Quanxin, Geping Zhang, Xiaofeng Sun, Keyang Yin, and Hongguang Li. 2017. "Improving the Power Conversion Efficiency of Carbon Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells by Growing the Dots on a TiO2 Photoanode In Situ" Nanomaterials 7, no. 6: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060130
APA StyleZhang, Q., Zhang, G., Sun, X., Yin, K., & Li, H. (2017). Improving the Power Conversion Efficiency of Carbon Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells by Growing the Dots on a TiO2 Photoanode In Situ. Nanomaterials, 7(6), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060130