Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Magnetic Nanoparticles Design
2.1. From Physics and Chemistry to Nanomedicine
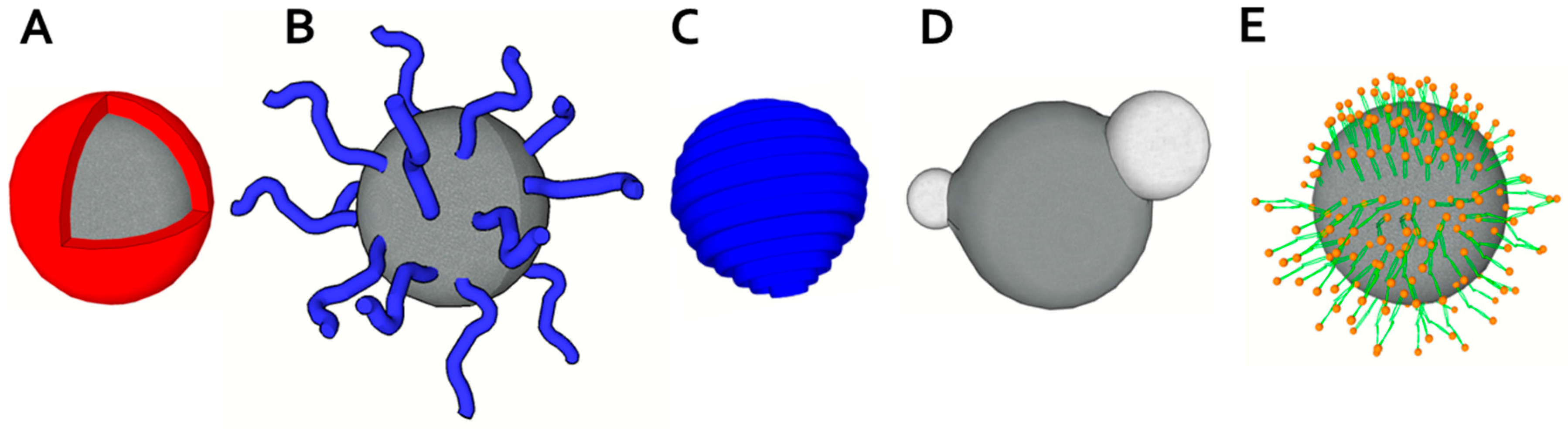
2.2. Physical Design
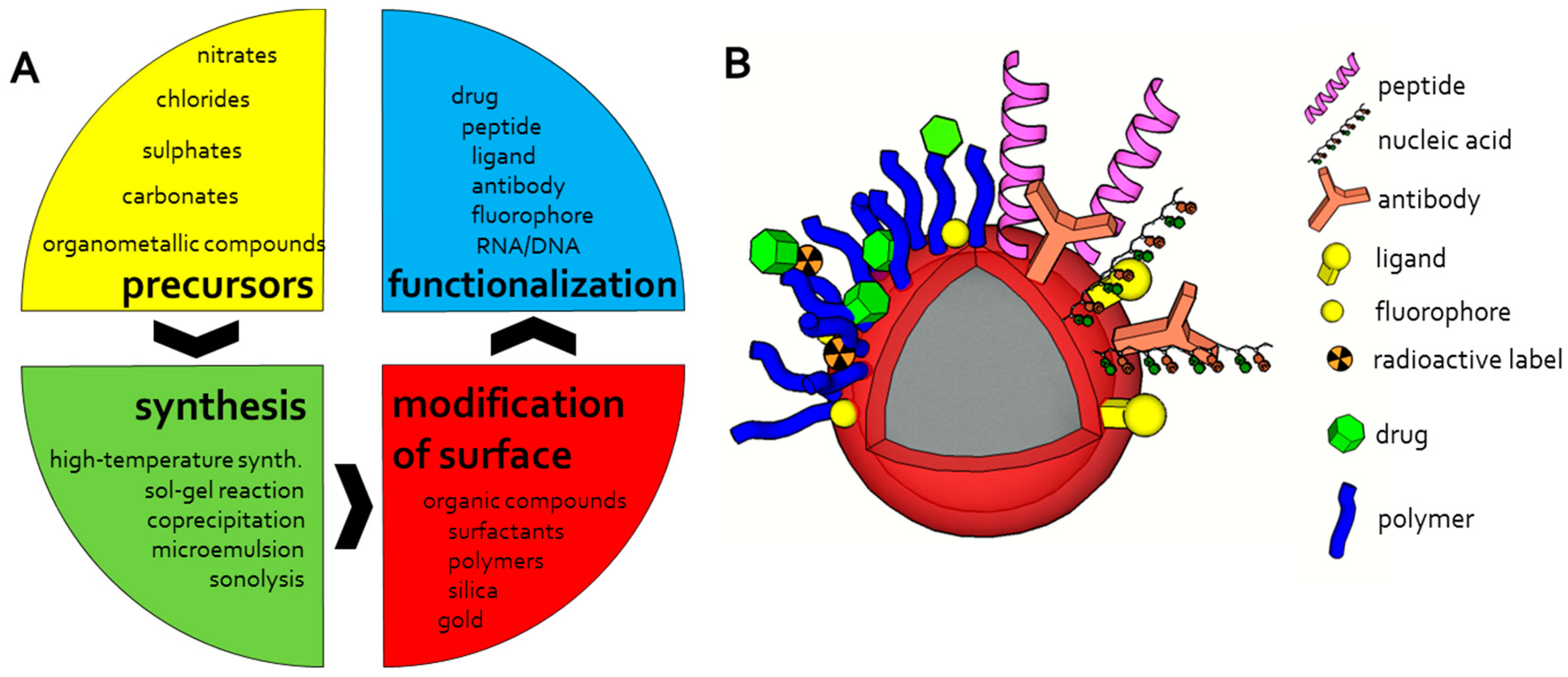
2.3. Chemical Design
3. Magnetic Nanoparticles Synthesis
3.1. Iron-Based Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.2. Cobalt Based Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.3. Other Magnetic Nanoparticles
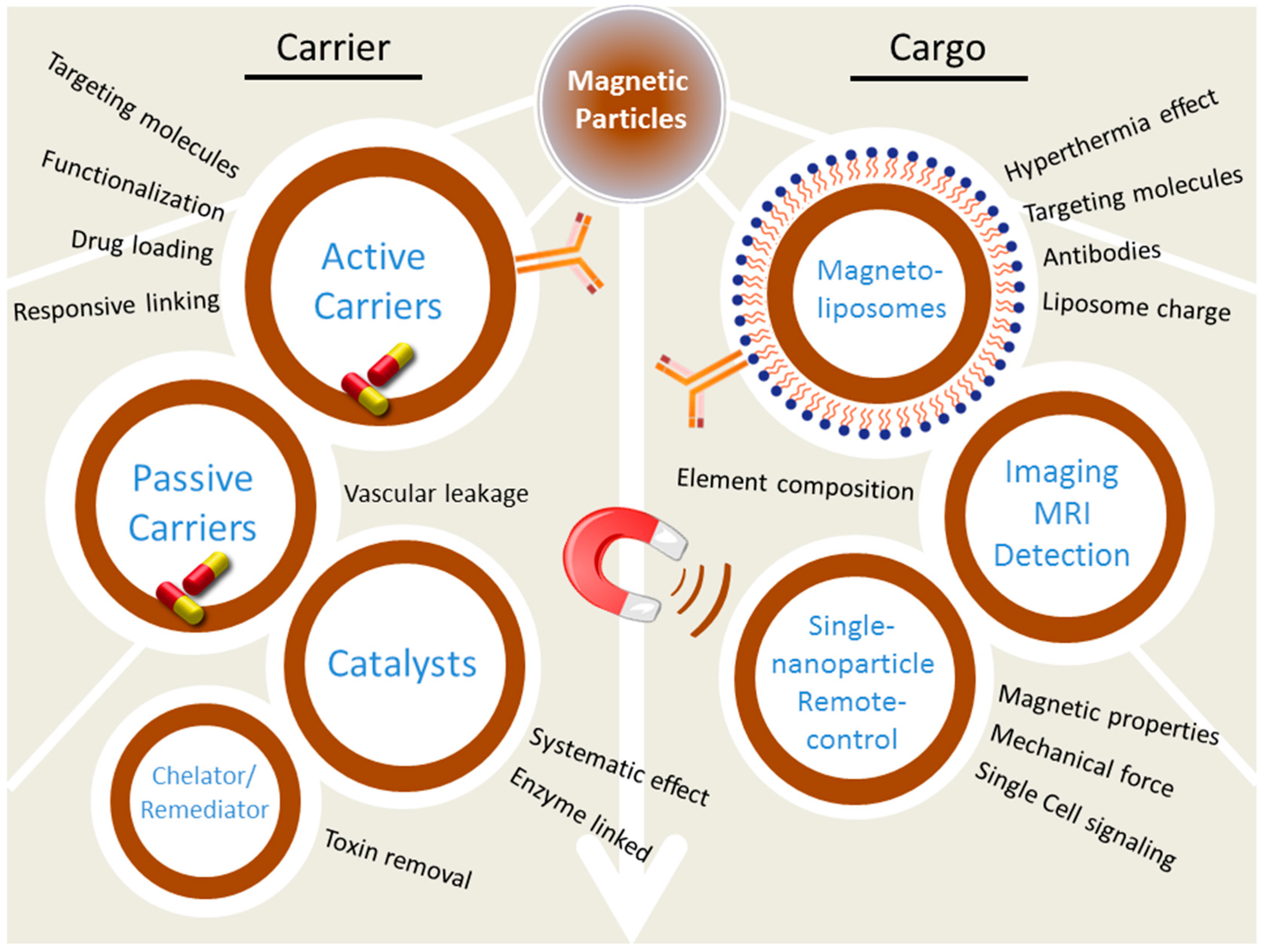
4. Magnetic Nanoparticles in the Real World
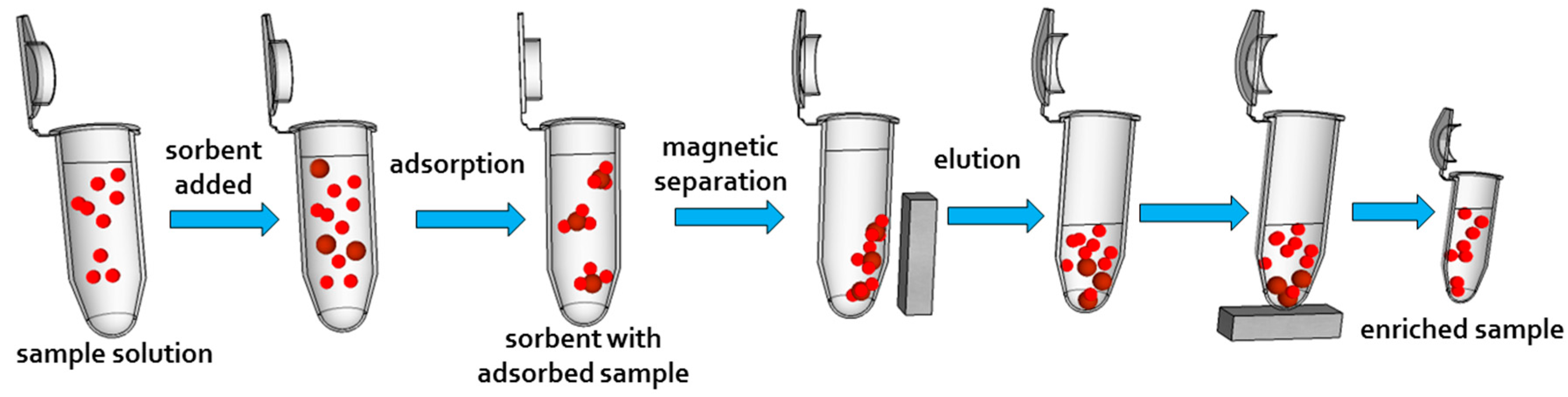
4.1. Analytical Chemistry—The On-Table Approaches
4.2. Preconcentration of Ions
4.3. Organic Compounds
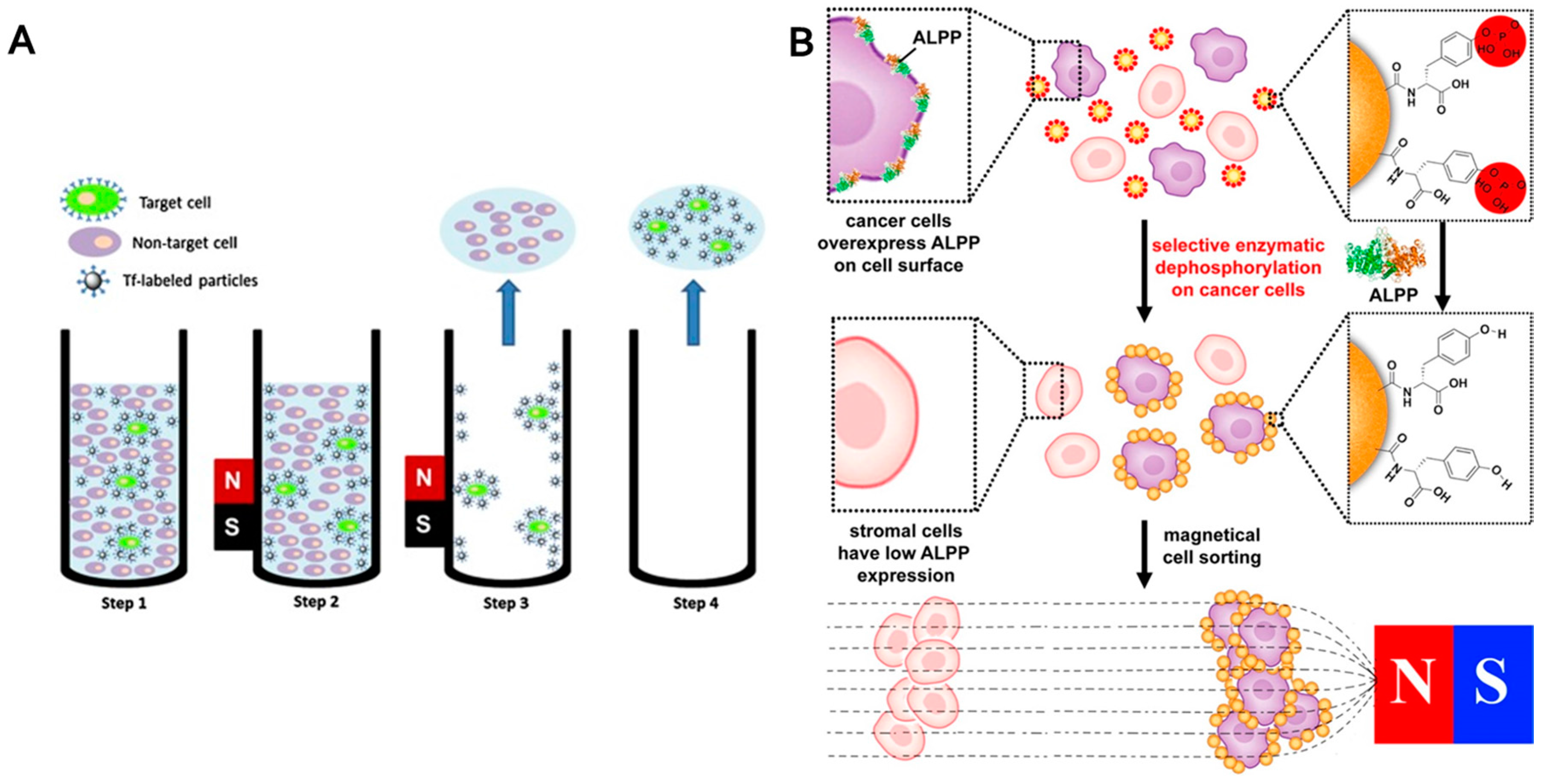
4.4. Cells and Biomolecules
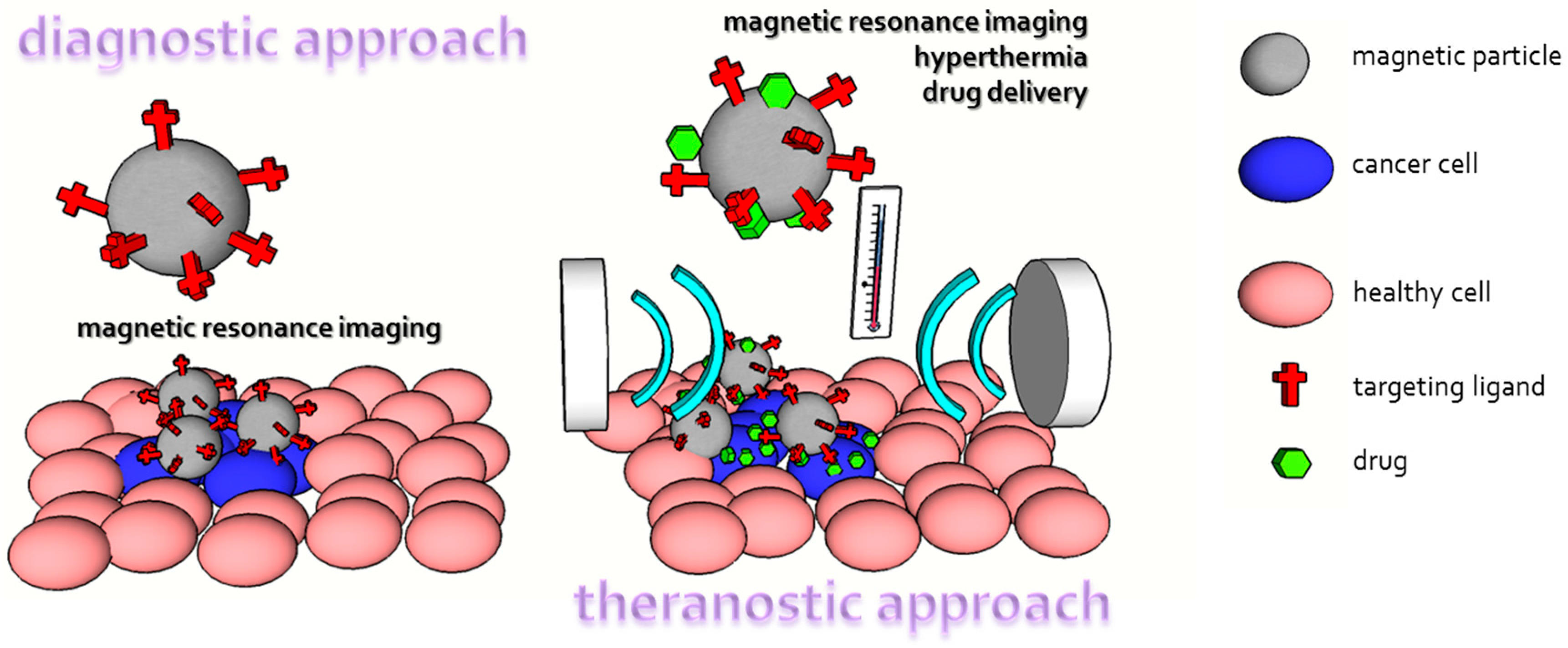
4.5. Therapy
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; Willner, I. Integrated nanoparticle-biomolecule hybrid systems: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6042–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigger, I.; Dubernet, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruthers, S.D.; Wickline, S.A.; Lanza, G.M. Nanotechnological applications in medicine. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessalova, V.; Perov, N.; Rodionova, V. New approaches in the design of magnetic tweezers-current magnetic tweezers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 415, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Loo, S.C.J. Application-driven multi-layered particles—The role of polymers in the architectural design of particles. Polymer 2015, 71, A1–A11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, F.X.; Chan, J.M.; Wang, A.Z.; Langer, R.S.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanoparticles in medicine: Therapeutic applications and developments. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F.; Feron, O.; Preat, V. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Passive and active tumor targeting of nanocarriers for anti-cancer drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazkova, I.; Nguyen, H.V.; Dostalova, S.; Kopel, P.; Stanisavljevic, M.; Vaculovicova, M.; Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. Apoferritin modified magnetic particles as doxorubicin carriers for anticancer drug delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13391–13402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasongkla, N.; Bey, E.; Ren, J.M.; Ai, H.; Khemtong, C.; Guthi, J.S.; Chin, S.F.; Sherry, A.D.; Boothman, D.A.; Gao, J.M. Multifunctional polymeric micelles as cancer-targeted, MRI-ultrasensitive drug delivery systems. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubayev, V.I.; Pisanic, T.R.; Jin, S.H. Magnetic nanoparticles for theragnostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalickova, S.; Nejdl, L.; Kudr, J.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Jimenez, A.M.J.; Kopel, P.; Kremplova, M.; Masarik, M.; Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; et al. Fluorescence characterization of gold modified liposomes with antisense N-myc DNA bound to the magnetisable particles with encapsulated anticancer drugs (doxorubicin, ellipticine and etoposide). Sensors 2016, 16, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitka, O.; Cernei, N.; Heger, Z.; Matousek, M.; Kopel, P.; Kynicky, J.; Masarik, M.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. Microfluidic chip coupled with modified paramagnetic particles for sarcosine isolation in urine. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heger, Z.; Zitka, J.; Cernei, N.; Krizkova, S.; Sztalmachova, M.; Kopel, P.; Masarik, M.; Hodek, P.; Zitka, O.; Adam, V.; et al. 3D-printed biosensor with poly(dimethylsiloxane) reservoir for magnetic separation and quantum dots-based immunolabeling of metallothionein. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitka, O.; Krizkova, S.; Krejcova, L.; Hynek, D.; Gumulec, J.; Masarik, M.; Sochor, J.; Adam, V.; Hubalek, J.; Trnkova, L.; et al. Microfluidic tool based on the antibody-modified paramagnetic particles for detection of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in urine of prostate cancer patients. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 3207–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlos Rodrigo, M.A.; Krejcova, L.; Kudr, J.; Cernei, N.; Kopel, P.; Richtera, L.; Moulick, A.; Hynek, D.; Adam, V.; Stiborova, M.; et al. Fully automated two-step assay for detection of metallothionein through magnetic isolation using functionalized γ-Fe2O3 particles. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1039, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, A.M.J.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Milosavljevic, V.; Krizkova, S.; Kopel, P.; Heger, Z.; Adam, V. Gold nanoparticles-modified nanomaghemite and quantum dots-based hybridization assay for detection of HPV. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, P.; Dostalova, S.; Buchtelova, H.; Cernei, N.; Krejcova, L.; Hynek, D.; Milosavljevic, V.; Jimenez, A.M.J.; Kopel, P.; Heger, Z.; et al. A two-step protocol for isolation of influenza a (H7N7) virions and their RNA for PCRdiagnostics based on modified paramagnetic particles. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cihalova, K.; Hegerova, D.; Jimenez, A.M.; Milosavljevic, V.; Kudr, J.; Skalickova, S.; Hynek, D.; Kopel, P.; Vaculovicova, M.; Adam, V. Antibody-free detection of infectious bacteria using quantum dots-based barcode assay. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 134, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cihalova, K.; Hegerova, D.; Dostalova, S.; Jelinkova, P.; Krejcova, L.; Milosavljevic, V.; Krizkova, S.; Kopel, P.; Adam, V. Particle-based immunochemical separation of methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus with indirect electrochemical detection of labeling oligonucleotides. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5123–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jang, J.T.; Choi, J.S.; Moon, S.H.; Noh, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, I.S.; Park, K.I.; Cheon, J. Exchange-coupled magnetic nanoparticles for efficient heat induction. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, D.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, T.H.; Cheon, J. Theranostic magnetic nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.H.; Zeng, H. Size-controlled synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8204–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.H.; Zeng, H.; Robinson, D.B.; Raoux, S.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; Li, G.X. Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baaziz, W.; Pichon, B.P.; Fleutot, S.; Liu, Y.; Lefevre, C.; Greneche, J.M.; Toumi, M.; Mhiri, T.; Begin-Colin, S. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Reproducible tuning of the size and nanosized-dependent composition, defects, and spin canting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 3795–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Sun, X.L.; Sun, S.H. Monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.H.; Gu, H.W.; Xu, B. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: Design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutz, S.; Hergt, R. Magnetic particle hyperthermia—A promising tumour therapy? Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Shinkai, M.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, T. Medical application of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbrich, K.; Hola, K.; Subr, V.; Bakandritsos, A.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Targeted drug delivery with polymers and magnetic nanoparticles: Covalent and noncovalent approaches, release control, and clinical studies. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5338–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, N.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.Q. Methotrexate-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles and their intracellular uptake into human cancer cells. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8858–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Guyen, T.T.T.; Duong, H.T.T.; Basuki, J.; Montembault, V.; Pascual, S.; Guibert, C.; Fresnais, J.; Boyer, C.; Whittaker, M.R.; Davis, T.P.; et al. Functional iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles with hyperthermia-induced drug release ability by using a combination of orthogonal click reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 14152–14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwu, J.R.; Lin, Y.S.; Josephrajan, T.; Hsu, M.H.; Cheng, F.Y.; Yeh, C.S.; Su, W.C.; Shieh, D.B. Targeted paclitaxel by conjugation to iron oxide and gold nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietze, R.; Lyer, S.; Duerr, S.; Struffert, T.; Engelhorn, T.; Schwarz, M.; Eckert, E.; Goeen, T.; Vasylyev, S.; Peukert, W.; et al. Efficient drug-delivery using magnetic nanoparticles—Biodistribution and therapeutic effects in tumour bearing rabbits. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.K.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Park, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.W.; Min, J.J.; Kim, K.; Jon, S. Drug-loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for combined cancer imaging and therapy in vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5362–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, J.; Allard-Vannier, E.; Burlaud-Gaillard, J.; Domenech, J.; Chourpa, I. Efficacy and hemotoxicity of stealth doxorubicin-loaded magnetic nanovectors on breast cancer xenografts. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, Y.; Xhaxhiu, K.; Kopel, P.; Hynek, D.; Zitka, O.; Adam, V. The isolation of DNA by polycharged magnetic particles: An analysis of the interaction by zeta potential and particle size. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Sant, S.; Wang, B.; Laurent, S.; Sen, T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): Development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Lee, J.S.H.; Zhang, M. Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiseh, O.; Gunn, J.W.; Zhang, M. Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomoucka, J.; Drbohlavova, J.; Huska, D.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Hubalek, J. Magnetic nanoparticles and targeted drug delivering. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaConte, L.; Nitin, N.; Bao, G. Magnetic nanoparticle probes. Mater. Today 2005, 8, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, M. Functional magnetic particles for medical application. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2002, 94, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Progress in applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 224001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, J.; Park, H.; Park, T.G. Bioinspired synthesis and characterization of gadolinium-labeled magnetite nanoparticles for dual contrast T1- and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.L.; Zhang, Z.D.; Xiao, Q.F.; Zhao, X.G.; Chuang, Y.C.; Jin, S.R.; Sun, W.M.; Li, Z.J.; Zheng, Z.X.; Yang, H. Characterization of ultrafine γ-Fe(C), α-Fe(C) and Fe3C particles synthesized by arc-discharge in methane. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkova, A.V.; Sorokina, O.N.; Rosenfeld, M.A.; Kovarski, A.L. Multifunctional biocompatible coatings on magnetic nanoparticles. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2012, 81, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.C. Progress in functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 224003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Huang, D.Y.; Muhammad, Z.Y.; Hou, Y.L.; Gao, S. Magnetic nanoparticle-based cancer therapy. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 027506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.C.; Adam, S.G.C. Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, E.Y.; Josephson, L.; Weissleder, R. “Clickable” nanoparticles for targeted imaging. Mol. Imaging 2006, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandivada, H.; Jiang, X.; Lahann, J. Click chemistry: Versatility and control in the hands of materials scientists. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouassi, G.K.; Irudayaraj, J. Magnetic and gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as a DNA sensor. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3234–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, I.; Tung, L.D.; Maenosono, S.; Walti, C.; Thanh, N.T.K. Synthesis of core-shell gold coated magnetic nanoparticles and their interaction with thiolated DNA. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Yang, M.; Zhang, R.; Qin, C.; Su, X.; Cheng, Z. Hybrid nanotrimers for dual T1 and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9884–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasset, F.; Mornet, S.; Demourgues, A.; Portier, J.; Bonnet, J.; Vekris, A.; Duguet, E. Synthesis, magnetic properties, surface modification and cytotoxicity evaluation of Y3Fe5−xAlxO12 (0 ≤ x ≤ 2) garnet submicron particles for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 234, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketomi, S.; Ozaki, Y.; Kawasaki, K.; Yuasa, S.; Miyajima, H. Transparent magnetic fluid: Preparation of YIG ultrafine particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1993, 122, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosseau, P.; Bachiorrini, A.; Guilhot, B. Elaboration de poudres de yig par coprecipitation. J. Therm. Anal. 1996, 46, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaqueiro, P.; Lopez-Quintela, M.A.; Rivas, J. Synthesis of yttrium iron garnet nanoparticlesvia coprecipitation in microemulsion. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Nishikawa, T.; Inui, T. Glycothermal synthesis of rare earth iron garnets. J. Mater. Res. 1998, 13, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, D.; Sharma, B.; Chakravorty, D. Preparation of glass-ceramics containing YIG. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1982, 1, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaqueiro, P.; Arturo Lopez-quintela, M. Synthesis of yttrium aluminium garnet by the citrate gel process. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaqueiro, P.; López-Quintela, M.A. Influence of complexing agents and pH on yttrium-iron garnet synthesized by the sol-Gel method. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2836–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaqueiro, P.; López-Quintela, M.A.; Rivas, J.; Greneche, J.M. Annealing dependence of magnetic properties in nanostructured particles of yttrium iron garnet prepared by citrate gel process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1997, 169, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Patil, K.C. Combustion synthesis and properties of Ln3Fe5O12 and yttrium aluminium garnets. J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 209, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubin, S.P.; Koksharov, Y.A.; Khomutov, G.B.; Yurkov, G.Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation methods, structure and properties. Usp. Khim. 2005, 74, 539–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanicki, D.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N.; Laurent, S. Synthesis and processing of magnetic nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2015, 8, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Yamini, Y.; Rezaee, M. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Nakanishi, T.; Arakaki, A.; Niwa, D.; Iida, H. Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles and their application to bioassays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, R.; Xing, R.; Xu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Gao, S.; Sun, S. Synthesis, functionalization, and biomedical applications of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2729–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boal, A.K. Synthesis and applications of magnetic nanoparticles. In Nanoparticles: Building Blocks for Nanotechnology; Rotello, V., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Samiei, M.; Davaran, S. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, M.A.; Kurihara, L.K.; Carpenter, E.E.; Calvin, S.; Harris, V.G. Chemically prepared magnetic nanoparticles. Int. Mater. Rev. 2004, 49, 125–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.G.; Noh, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, N.M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3995–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Vander Elst, L.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem.Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wu, Z.H.; Yu, T.; Jiang, C.Z.; Kim, W.S. Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, M.; Biswas, K.; Sundaresan, A.; Rao, C.N.R. MnO and NiO nanoparticles: Synthesis and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cao, Z.; Sajja, H.K.; Mao, H.; Wang, L.; Geng, H.; Xu, H.; Jiang, T.; Wood, W.C.; Nie, S.; et al. Development of receptor targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient drug delivery and tumor imaging. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2008, 4, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Hyeon, T. Designed synthesis of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2575–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbab, A.S.; Bashaw, L.A.; Miller, B.R.; Jordan, E.K.; Lewis, B.K.; Kalish, H.; Frank, J.A. Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging. Radiology 2003, 229, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankhurst, Q.; Jones, S.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine: The story so far. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 501002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Wells, S. Surface-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: Preparation, characterization, and cytotoxicity studies. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2004, 3, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, S.W. Magnetic fluids (ferrofluids) A2. In Magnetic Properties of Fine Particles; Dormann, J.L., Fiorani, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Curtis, A.S.G. Lactoferrin and ceruloplasmin derivatized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for targeting cell surface receptors. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimers, G.W.; Khalafalla, S.E. Preparing Magnetic Fluids by a Peptizing Method; U.S. Deparment of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; p. 13.
- Sjøgren, C.E.; Briley-Sæbø, K.; Hanson, M.; Johansson, C. Magnetic characterization of iron oxides for magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1994, 31, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, T.K.; Richey, J.; Strand, M.; Leslie-Pelecky, D.L.; Flask, C.A.; Labhasetwar, V. Magnetic nanoparticles with dual functional properties: Drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4012–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolnik, S.; Illum, L.; Davis, S.S. Long circulating microparticulate drug carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995, 16, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, A.; Kodas, T.; Pluym, T.; Xiong, Y. Aerosol processing of materials. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1993, 19, 411–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Lee, H.; Westervelt, R.M. Microelectromagnets for the control of magnetic nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 3308–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishton, S.A.; Lu, Y.; Altman, R.A.; Marley, A.C.; Bian, X.P.; Jahnes, C.; Viswanathan, R.; Xiao, G.; Gallagher, W.J.; Parkin, S.S.P. Magnetic tunnel junctions fabricated at tenth-micron dimensions by electron beam lithography. Microelectron. Eng. 1997, 35, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Leveneur, J.; Williams, G.V.M.; Mitchell, D.R.G.; Markwitz, A. Fabrication of surface magnetic nanoclusters using low energy ion implantation and electron beam annealing. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 115602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leveneur, J.; Kennedy, J.; Williams, G.V.M.; Metson, J.; Markwitz, A. Large room temperature magnetoresistance in ion beam synthesized surface fe nanoclusters on SiO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, T.; María del Puerto, M.; Sabino, V.V.; Teresita, G.C.; Carlos, J.S. The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R182. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.R.; Weissleder, R. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted imaging and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mornet, S.; Vasseur, S.; Grasset, F.; Veverka, P.; Goglio, G.; Demourgues, A.; Portier, J.; Pollert, E.; Duguet, E. Magnetic nanoparticle design for medical applications. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2006, 34, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, A.; Zhai, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Volinsky, A.A. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesis from tailings by ultrasonic chemical co-precipitation. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1882–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.Y.; Pan, T.T.; Li, H.Z. Microwave synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles used as a precursor of nanocomposites and ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 303, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Moon, J.Y.; Chang, Y.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, G.H. Poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and in vivo study as mri contrast agent. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 313–314, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zou, F.; Liu, L.; Tang, L.; Yu, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Tang, J.B.; Wu, L.X. Preparation and characterization of PEG-PEI/Fe3O4 nano-magnetic fluid by co-precipitation method. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Huh, Y.M.; Jun, Y.W.; Seo, J.W.; Jang, J.T.; Song, H.T.; Kim, S.; Cho, E.J.; Yoon, H.G.; Suh, J.S.; et al. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyeon, T.; Chung, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Park, B.H. Synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 6831–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.S.; Zhang, D.S.; Cong, X.M.; Wan, M.L.; Jin, L.Q. Using thermal energy produced by irradiation of Mn–Zn ferrite magnetic nanoparticles (MZF-NPS) for heat-inducible gene expression. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2673–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanini, A.; Lartigue, L.; Gavard, J.; Kacem, K.; Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F.; Chau, F.; Ammar, S. Zinc substituted ferrite nanoparticles with Zn0.9Fe2.1O4 formula used as heating agents for in vitro hyperthermia assay on glioma cells. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 416, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Kundu, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Panigrahi, S.; Sau, T.K.; Yusuf, S.M.; Pal, T. Magnetite nanoparticles with tunable gold or silver shell. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, D.L. Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 2005, 1, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Sun, S. Synthesis and stabilization of monodisperse fe nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10676–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, Y.; Antony, J.; Sharma, A.; Nutting, J.; Sikes, D.; Meyer, D. Iron/iron oxide core-shell nanoclusters for biomedical applications. J. Nanopart. Res. 2006, 8, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S. Recent advances in chemical synthesis, self-assembly, and applications of FePt nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Murray, C.B.; Weller, D.; Folks, L.; Moser, A. Monodisperse fept nanoparticles and ferromagnetic FePt nanocrystal superlattices. Science 2000, 287, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.; Fischer, N.O.; Emrick, T.; Rotello, V.M. Surface pegylation and ligand exchange chemistry of FePt nanoparticles for biological applications. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4617–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, B. Fluorescent magnetic nanocrystals by sequential addition of reagents in a one-pot reaction: A simple preparation for multifunctional nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11928–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Liang, G.; Zhang, B.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, B. FePt@CoS2 yolk–shell nanocrystals as a potent agent to kill HeLa cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Presa, P.; Multigner, M.; Morales, M.P.; Rueda, T.; Fernández-Pinel, E.; Hernando, A. Synthesis and characterization of FePt/Au core-shell nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 316, 753–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, G.; Hutten, A. Magnetic nanoparticles: Applications beyond data storage. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Wang, J.P. High-magnetic-moment core-shell-type FeCo–Au/Ag nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 152502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Sun, X.; Suzuki, Y.; Mann, D.; Liu, Z.; Terashima, M.; Yang, P.C.; McConnell, M.V.; Nishimura, D.G.; et al. FeCo/graphitic-shell nanocrystals as advanced magnetic-resonance-imaging and near-infrared agents. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.K.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Aerosol synthesis of gadolinium iron-garnet particles. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, Q.M.; Fernandes, S.; Eichenseer, C.M.; Besostri, F.; Korner, H.; Muller, R.; Reiser, O. Synthesis of functionalized, dispersible carbon-coated cobalt nanoparticles for potential biomedical applications. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 175, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, J.P.; Rutnakornpituk, M.; Vadala, M.; Esker, A.R.; Charles, S.W.; Wells, S.; Dailey, J.P.; Riffle, J.S. Magnetic cobalt dispersions in poly(dimethylsiloxane) fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 225, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Cantillo, C.; Santiago-Miranda, A.N.; Perales-Perez, O.; Xin, Y. Size- and phase-controlled synthesis of cobalt nanoparticles for potential biomedical applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, J.; St Pierre, T.; Rutnakornpituk, M.; Riffle, J. Silica coating of cobal nanoparticles increases their magnetic and chemical stability for biomedical applications. Eur. Cells Mater. 2002, 3, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dailey, J.P.; Phillips, J.P.; Li, C.; Riffle, J.S. Synthesis of silicone magnetic fluid for use in eye surgery. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 194, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutnakornpituk, M.; Baranauskas, V.; Riffle, J.; Connolly, J.; St Pierre, T.; Dailey, J. Polysiloxane fluid dispersions of cobalt nanoparticles in silica spheres for use in ophthalmic applications. Eur. Cells Mater. 2002, 3, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Vaucher, S.; Fielden, J.; Li, M.; Dujardin, E.; Mann, S. Molecule-based magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis of cobalt hexacyanoferrate, cobalt pentacyanonitrosylferrate, and chromium hexacyanochromate coordination polymers in water-in-oil microemulsions. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.H.; Murray, C.B. Synthesis of monodisperse cobalt nanocrystals and their assembly into magnetic superlattices (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 4325–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, J.C. Magnetic micro composites as vectors for bioactive agents: The state of art. Multilingue 1997, 93, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.C.; Dong, X.L. Magnetic properties and microstructure of carbon encapsulated Ni nanoparticles and pure Ni nanoparticles coated with NiO layer. Mater. Res. Bull. 2002, 37, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zheng, K.; He, L.; Wang, R.M.; Guo, L.; Chen, C.P.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z. Ni/Ni3C core-shell nanochains and its magnetic properties: One-step synthesis at low temperature. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi-Montes, N.; Gorria, P.; Martinez-Blanco, D.; Amghouz, Z.; Fuertes, A.B.; Barquin, L.F.; De Pedro, I.; Olivi, L.; Blanco, J.A. Unravelling the onset of the exchange bias effect in Ni(core)@NiO(shell) nanoparticles embedded in a mesoporous carbon matrix. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5674–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Wu, C.Y.; Han, X.Z. Preparation of nanoscale nio powders by polymer-network gel process. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 19, 624–626. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.C.; Anderson, M.A. Porous nickel oxide/nickel films for electrochemical capacitors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deki, S.; Yanagimoto, H.; Hiraoka, S.; Akamatsu, K.; Gotoh, K. NH2-terminated poly(ethylene oxide) containing nanosized NiO particles: Synthesis, characterization, and structural considerations. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4916–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Deng, X.Y.; Jin, Y. Experimental study on synthesis of NiO nano-particles. Scr. Mater. 2002, 47, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, H.T.; Awad, R.; Abdel-Gaber, A.M.; Bakeer, D.E.S. Synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of pure and EDTA-capped NiO nanosized particles. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Aliahmad, M.; Azizi, Y. NiO nanoparticles: Synthesis and characterization. J. Nanostruct. 2015, 5, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Safarikova, M.; Safarik, I. Magnetic solid-phase extraction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 194, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towler, P.H.; Smith, J.D.; Dixon, D.R. Magnetic recovery of radium, lead and polonium from seawater samples after preconcentration on a magnetic adsorbent of manganese dioxide coated magnetite. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 328, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondracek, M.H.P.; Jorgetto, A.O.; Silva, A.C.P.; Ivassechen, J.D.; Schneider, J.F.; Saeki, M.J.; Pedrosa, V.A.; Yoshito, W.K.; Colauto, F.; Ortiz, W.A.; et al. Synthesis of mesoporous silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles modified with 4-amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole and its application as Cu(II) adsorbent from aqueous samples. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 367, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.L.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, J.; Shao, D.D.; Wang, X.K. Synthesis of water-dispersible Fe3O4@β-cyclodextrin by plasma-induced grafting technique for pollutant treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, P.F.; Gou, J.Y. Rapid and economical synthesis of magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube/iron oxide composite and its application in preconcentration of U(VI). J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 195, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatabi, M.P.; Moghaddam, H.M.; Ghorbani, M. Efficient removal of cadmium using magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube nanoadsorbents: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, Z.L.; Ma, J.; Yang, M.X.; Hong, J.; Hu, X.H.; Qiu, Y.L.; Chen, J.H. One-pot, solid-phase synthesis of magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube/iron oxide composites and their application in arsenic removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 434, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, A.A.; Al Ghannam, S.M. Impregnated multiwalled carbon nanotubes as efficient sorbent for the solid phase extraction of trace amounts of heavy metal ions in food and water samples. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Determination of trace amounts of Cd(II), Cu(II), and Ni(II) in food samples using a novel functionalized magnetic nanosorbent. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylak, M.; Topalak, Z. Multiwalled carbon nanotube impregnated with tartrazine: Solid phase extractant for Cd(II) and Pb(II). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbia, M.; Kargosha, K.; Khoshbooei, S. Heavy metal ions removal from aqueous media by modified magnetic mesoporous silica MCM-48. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 93, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.H.; Lien, H.L.; Chung, J.S.; Yeh, H.D. Adsorption of precious metals in water by dendrimer modified magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.M.; Lien, H.L. Dendrimer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for removal of zinc (II) from aqueous solutions. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Alam, M.M.; Naushad, M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Kumar, M.; Ahamad, T. Sol-gel assisted synthesis of porous nano-crystalline CoFe2O4 composite and its application in the removal of brilliant blue-R from aqueous phase: An ecofriendly and economical approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramandi, N.F.; Shemirani, F. Surfacted ferrofluid based dispersive solid phase extraction; a novel approach to preconcentration of cationic dye in shrimp and water samples. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahri, F.B.; Niazi, A. Synthesis of modified maghemite nanoparticles and its application for removal of acridine orange from aqueous solutions by using Box-Behnken design. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 396, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.L.; Li, J.; Chen, C.L. Hierarchical MWCNTs/Fe3O4/PANI magnetic composite as adsorbent for methyl orange removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmacheva, V.V.; Apyari, V.V.; Furletov, A.A.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Zolotov, Y.A. Facile synthesis of magnetic hypercrosslinked polystyrene and its application in the magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonamides from water and milk samples before their HPLC determination. Talanta 2016, 152, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukchuay, T.; Kanatharana, P.; Wannapob, R.; Thavarungkul, P.; Bunkoed, O. Polypyrrole/silica/magnetite nanoparticles as a sorbent for the extraction of sulfonamides from water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3921–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmacheva, V.V.; Apyari, V.V.; Ibragimova, B.N.; Kochuk, E.V.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Zolotov, Y.A. A polymeric magnetic adsorbent based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles and hypercrosslinked polystyrene for the preconcentration of tetracycline antibiotics. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.C.; Chuong, P.H.; He, H. Core-shell nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted polymers: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2677–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.L.; Li, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.K. Development of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers with double templates for the rapid and selective determination of amphenicol antibiotics in water, blood, and egg samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1473, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.X.; Cui, X.H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, D.C.; Tang, Y.H. A highly-efficient imprinted magnetic nanoparticle for selective separation and detection of 17 β-estradiol in milk. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.D.; Zhou, Z.P.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wei, X.; Dai, X.H.; Gao, L.; Cao, Z.J.; Yan, Y.S. Versatile method to obtain homogeneous imprinted polymer thin film at surface of superparamagnetic nanoparticles for tetracycline binding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 7157–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.Y.; Li, Z.M.; Yang, Y.L. Magnetic nanoparticles based dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction as a novel technique for the determination of estrogens in pork samples. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdarian, M.; Ramezani, Z.; Ghadiri, A.A. Facile synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer: Perphenazine template and its application in urine and plasma analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1455, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Pan, X.Y.; Wang, S.C. Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer strategy and its application in the sudan dyes residue analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1405, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.H.; Xu, M.Z.; Wu, X.J.; Luo, J.H. Synergetic recognition and separation of kelthane and pyridaben base on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4019–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning, 4th ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.X.; Gu, H.C. Adsorption and desorption behaviors of DNA with magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6099–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandeventer, P.E.; Lin, J.S.; Zwang, T.J.; Nadim, A.; Johal, M.S.; Niemz, A. Multiphasic DNA adsorption to silica surfaces under varying buffer, pH, and ionic strength conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 5661–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Wei, W.; Li, J.J.; Qi, X.L.; Zuo, G.C.; Chen, Q.; Pan, X.H.; Dong, W. Amine-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for DNA separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.L.; Cui, Y.; Paoli, G.C.; Shi, C.L.; Wang, D.P.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, L.D.; Shi, X.M. Synthesis of amino-rich silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles for the efficient capture of DNA for PCR. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Hwang, N.R.; Hwang, S.H.; Cho, Y. Magnetic nanowires for rapid and ultrasensitive isolation of DNA from cervical specimens for the detection of multiple human papillomaviruses genotypes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudr, J.; Nejdl, L.; Skalickova, S.; Zurek, M.; Milosavljevic, V.; Kensova, R.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Kopel, P.; Hynek, D.; Novotna, M.; et al. Use of nucleic acids anchor system to reveal apoferritin modification by cadmium telluride nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.L.; Wu, S.J.; Duan, N.; Wang, Z.P. A near-infrared magnetic aptasensor for ochratoxin a based on near-infrared upconversion nanoparticles and magnetic nanoparticles. Talanta 2016, 158, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, N.M.; Bordelon, H.; Wang, K.K.A.; Albert, L.E.; Wright, D.W.; Haselton, F.R. Comparison of three magnetic bead surface functionalities for RNA extraction and detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6062–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarigh, G.D.; Shemirani, F. Simultaneous in situ derivatization and ultrasound-assisted dispersive magnetic solid phase extraction for thiamine determination by spectrofluorimetry. Talanta 2014, 123, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.M.; Deng, C.H.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yang, P.Y.; Zhang, X.M. A facile synthesis approach to C-8-functionalized magnetic carbonaceous polysaccharide microspheres for the highly efficient and rapid enrichment of peptides and direct maldi-tof-ms analysis. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2200–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, M.H.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Bruschweiler, R. Nanoparticle-assisted removal of protein in human serum for metabolomics studies. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Zhou, M.D.; Zheng, S.Y. Facile synthesis of magnetic mesoporous hollow carbon microspheres for rapid capture of low-concentration peptides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12719–12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, D.; Hlidkova, H.; Hiraoui, M.; Taverna, M.; Proks, V.; Mazl Chanova, E.; Smadja, C.; Kucerova, Z. Monodisperse carboxyl-functionalized poly(ethylene glycol)-coated magnetic poly(glycidyl methacrylate) microspheres: Application to the immunocapture of β-amyloid peptides. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.T.; Sun, L.Q.; Luo, A.Q. Preparation and evaluation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles incorporated molecularly imprinted polymers for protein separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.D.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H.W. NiCoMnO4: A bifunctional affinity probe for his-tagged protein purification and phosphorylation sites recognition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 18675–18683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, Z.; Naeimi, H.; Zarnani, A.H.; Nazari, M.; Nejadmoghaddam, M.R.; Ghahremanzadeh, R. Fast and highly efficient purification of 6×histidine-tagged recombinant proteins by Ni-decorated MnFe2O4@SiO2@NH2@2AB as novel and efficient affinity adsorbent magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36840–36848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisenbichler, C.; Rauch, J.S.; Guzel, Y.; Wernig, E.M.; Schemeth, D.; Tribus, M.; Tessadri, R.; Rainer, M. Development of magnetic ytterbium oxide core-shell particles for selectively trapping phosphopeptides. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.D.; Ding, C.; Yao, X.; Jia, L. Ethylene glycol assisted preparation of Ti4+-modified polydopamine coated magnetic particles with rough surface for capture of phosphorylated proteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 929, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.X.; Yang, K.G.; Shao, W.Y.; Qu, Y.Y.; Li, S.W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhang, Y.K. Boronic acid-functionalized particles with flexible three-dimensional polymer branch for highly specific recognition of glycoproteins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 9552–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caragata, M.; Shah, A.K.; Schulz, B.L.; Hill, M.M.; Punyadeera, C. Enrichment and identification of glycoproteins in human saliva using lectin magnetic bead arrays. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 497, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.N.; Wang, F.J.; Wan, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Cheng, K.; Zou, H.F. Magnetic nanoparticles coated with maltose-functionalized polyethyleneimine for highly efficient enrichment of N-glycopeptides. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1425, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.C.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Jiang, B.W.; Zhang, E.L.; Ye, J. Isolating sperm from cell mixtures using magnetic beads coupled with an anti-pH-20 antibody for forensic DNA analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.D.; Qiao, L.; Prudent, M.; Bondarenko, A.; Gasilova, N.; Moller, S.B.; Lion, N.; Pick, H.; Gong, T.Q.; Chen, Z.X.; et al. Sensitive and fast identification of bacteria in blood samples by immunoaffinity mass spectrometry for quick BSI diagnosis. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2987–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanduri, V.; Sorokulova, I.B.; Samoylov, A.M.; Simonian, A.L.; Petrenko, V.A.; Vodyanoy, V. Phage as a molecular recognition element in biosensors immobilized by physical adsorption. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Duncan, B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, L.S.; Rotello, V.M.; Nugen, S.R. Bacteriophage-based nanoprobes for rapid bacteria separation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16230–16236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Y.; Tsai, K.T.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Chao, Y.C.; Chang, H.H.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Y.L. Functionalized arrays of raman-enhancing nanoparticles for capture and culture-free analysis of bacteria in human blood. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Guo, Z.X.; Wu, H.F. Large protein analysis of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry using amoxicillin functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6269–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreira, S.C.; Spencer, J.; Schwarzacher, W.; Seddon, A.M. Cationized magnetoferritin enables rapid labeling and concentration of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria in magnetic cell separation columns. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3599–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.W.; Zhou, J.; Wu, L.H.; Sun, S.H.; Xu, B. Enzymatic transformation of phosphate decorated magnetic nanoparticles for selectively sorting and inhibiting cancer cells. Bioconjugate Chem. 2014, 25, 2129–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millan, J.L.; Fishman, W.H. Biology of human alkaline-phosphatases with special reference ts cancer. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1995, 32, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashevsky, B.E.; Zholud, A.M.; Kashevsky, S.B. Hydrodynamic instability in a magnetically driven suspension of paramagnetic red blood cells. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 6547–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajer-Mohammad-Ghazvini, P.; Kasra-Kermanshahi, R.; Nozad-Golikand, A.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Ghorbanzadeh-Mashkani, S.; Dabbagh, R. Cobalt separation by alphaproteobacterium MTB-KTN90: Magnetotactic bacteria in bioremediation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Li, Y.C.; MacDonald, T.; Wu, H.; Provenzale, J.; Peng, X.G.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, A.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; et al. Improving sensitivity and specificity of capturing and detecting targeted cancer cells with anti-biofouling polymer coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 150, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Sensors and biosensors based on magnetic nanoparticles. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 62, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, I.M.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, W.T. Micro- and nano-magnetic particles for applications in biosensing. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrittwieser, S.; Pelaz, B.; Parak, W.J.; Lentijo-Mozo, S.; Soulantica, K.; Dieckhoff, J.; Ludwig, F.; Guenther, A.; Tschope, A.; Schotter, J. Homogeneous biosensing based on magnetic particle labels. Sensors 2016, 16, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancar, H.D.; Soylemez, S.; Akpinar, Y.; Kesik, M.; Goker, S.; Gunbas, G.; Volkan, M.; Toppare, L. A novel acetylcholinesterase biosensor: Core-shell magnetic nanoparticles incorporating a conjugated polymer for the detection of organophosphorus pesticides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8058–8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvesh, S.; Darvesh, K.V.; McDonald, R.S.; Mataija, D.; Walsh, R.; Mothana, S.; Lockridge, O.; Martin, E. Carbamates with differential mechanism of inhibition toward acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4200–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, Q.L.; Han, L.; Hou, C.T.; Wang, F.; Liu, A.H. A sensitive acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on gold nanorods modified electrode for detection of organophosphate pesticide. Talanta 2016, 156, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, T.; Rawat, K.; Bohidar, H.B.; Solanki, P.R. Electrochemical immunosensor based on PEG capped iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 783, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, S.; Campas, M. Electrochemical enzyme sensor arrays for the detection of the biogenic amines histamine, putrescine and cadaverine using magnetic beads as immobilisation supports. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carinelli, S.; Ballesteros, C.X.; Marti, M.; Alegret, S.; Pividori, M.I. Electrochemical magneto-actuated biosensor for CD4 count in aids diagnosis and monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
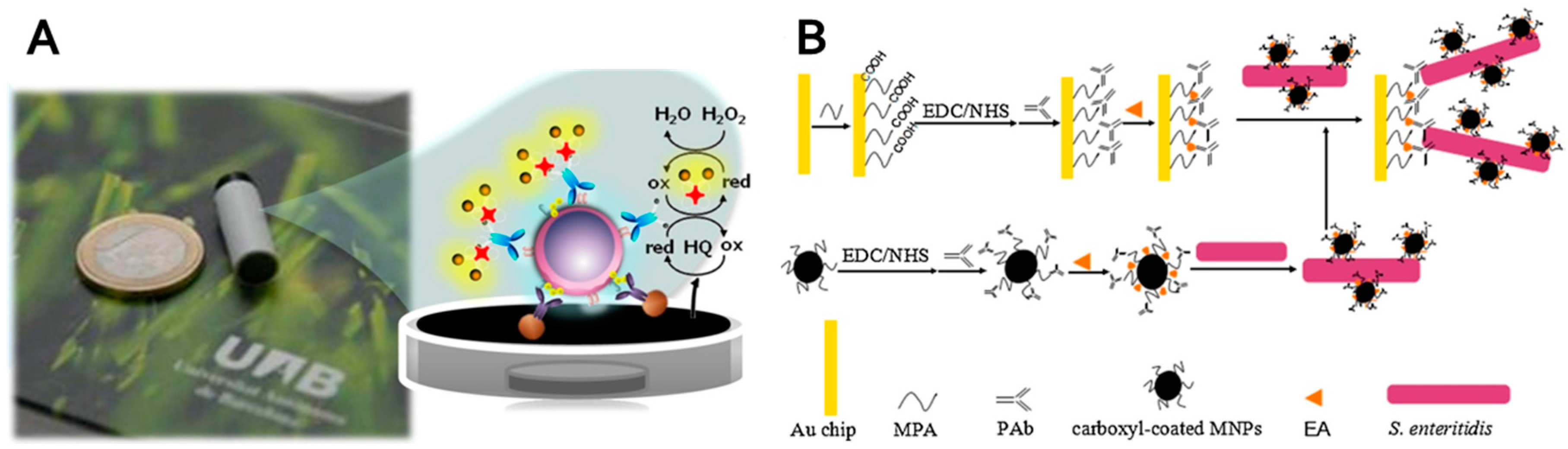
- Liu, X.; Hu, Y.X.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for fast, highly sensitive, and in situ detection of the magnetic nanoparticles-enriched salmonella enteritidis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, B.A.; Krause, C.E.; Jones, A.L.; Kremer, R.B.; Rusling, J.F. Cancer diagnostics via ultrasensitive multiplexed detection of parathyroid hormone-related peptides with a microfluidic immunoarray. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9269–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranifam, M. Analytical applications of chemiluminescence-detection systems assisted by magnetic microparticles and nanoparticles. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.X.; Wang, L. Detection of human leptin in serum using chemiluminescence immunosensor: Signal amplification by hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzymes and protein carriers by Fe3O4/polydopamine/Au nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.; Huke, B.; Lucke, M.; Hempelmann, R. Brownian relaxation of magnetic colloids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 289, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, J.; Parmvi, M.; Stromberg, M.; Svedlindh, P.; Donolato, M.; Hansen, M.F. Comparison of optomagnetic and AC susceptibility readouts in a magnetic nanoparticle agglutination assay for detection of C-reactive protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.Z.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.H.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.L.; Perrett, S.; et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetics and their applications in H2O2 and glucose detection. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2250–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinkova, P.; Opatrilova, R.; Kruzliak, P.; Styriak, I.; Pohanka, M. Colorimetric glucose assay based on magnetic particles having pseudo-peroxidase activity and immobilized glucose oxidase. Mol. Biotechnol. 2016, 58, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khun, K.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Lu, J.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Atif, M.; Ansari, A.A.; Willander, M. Potentiometric glucose sensor based on the glucose oxidase immobilized iron ferrite magnetic particle/chitosan composite modified gold coated glass electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, B.; Obaidat, I.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wust, P.; Hildebrandt, B.; Sreenivasa, G.; Rau, B.; Gellermann, J.; Riess, H.; Felix, R.; Schlag, P.M. Hyperthermia in combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milleron, R.S.; Bratton, S.B. “Heated” debates in apoptosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2329–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, T.B.; Tong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hansen, M.N.; Cheng, J.X.; Wei, A. Hyperthermic effects of gold nanorods on tumor cells. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larumbe, S.; Gomez-Polo, C.; Perez-Landazabal, J.I.; Pastor, J.M. Effect of a SiO2 coating on the magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condes. Matter 2012, 24, 266007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeonidis, K.; Morales, M.P.; Marciello, M.; Angelakeris, M.; De La Presa, P.; Lazaro-Carrillo, A.; Tabero, A.; Villanueva, A.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Serantes, D. In-situ particles reorientation during magnetic hyperthermia application: Shape matters twice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, B.; Calatayud, M.P.; Torres, T.E.; Fanarraga, M.L.; Ibarra, M.R.; Goya, G.F. Magnetic hyperthermia enhances cell toxicity with respect to exogenous heating. Biomaterials 2017, 114, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Rinaldi-Montes, N.; Alonso, J.; Amghouz, Z.; Garaio, E.; Garcia, J.A.; Gorria, P.; Blanco, J.A.; Phan, M.H.; Srikanth, H. Boosted hyperthermia therapy by combined AC magnetic and photothermal exposures in Ag/Fe3O4 nanoflowers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25162–25169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.J.; Lai, W.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Chiang, C.L. Multifunctional magnetic plasmonic nanoparticles for applications of magnetic/photo-thermal hyperthermia and surface enhanced raman spectroscopy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 331, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Girija, A.R.; Nagaoka, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Iwai, S.; Kizhikkilot, V.; Kato, K.; Maekawa, T.; Nair, S.D. An “all in one” approach for simultaneous chemotherapeutic, photothermal and magnetic hyperthermia mediated by hybrid magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25066–25078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstappen, C.C.P.; Heimans, J.J.; Hoekman, K.; Postma, T.J. Neurotoxic complications of chemotherapy in patients with cancer: Clinical signs and optimal management. Drugs 2003, 63, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pino, P.; Pelaz, B.; Zhang, Q.; Maffre, P.; Nienhaus, G.U.; Parak, W.J. Protein corona formation around nanoparticles—From the past to the future. Mater. Horiz. 2014, 1, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissinen, T.; Nakki, S.; Laakso, H.; Kuciauskas, D.; Kaupinis, A.; Kettunen, M.I.; Liimatainen, T.; Hyvonen, M.; Valius, M.; Grohn, O.; et al. Tailored dual pegylation of inorganic porous nanocarriers for extremely long blood circulation in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32723–32731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, Z.; Karimi, L.; Shokrollahi, H. Nano-magnetic particles used in biomedicine: Core and coating materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBain, S.C.; Griesenbach, U.; Xenariou, S.; Keramane, A.; Batich, C.D.; Alton, E.; Dobson, J. Magnetic nanoparticles as gene delivery agents: Enhanced transfection in the presence of oscillating magnet arrays. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 405102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, R.M.; Shete, P.B.; Thorat, N.D.; Otari, S.V.; Barick, K.C.; Prasad, A.; Ningthoujam, R.S.; Tiwale, B.M.; Pawar, S.H. Superparamagnetic iron oxide/chitosan core/shells for hyperthermia application: Improved colloidal stability and biocompatibility. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 355, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattarahmady, N.; Azarpira, N.; Hosseinpour, A.; Heli, H.; Zare, T. Albumin coated arginine-capped magnetite nanoparticles as a paclitaxel vehicle: Physicochemical characterizations and in vitro evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.P.; Mao, K.L.; Zhang, B.L.; Zhao, Y.Z. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with folic acid for dual target-specific drug delivery and mri in cancer theranostics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 70, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.P.; Whittaker, A.K. Functional magnetic porous silica for T1-T2 dual-modal magnetic resonance imaging and pH-responsive drug delivery of basic drugs. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 485702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.T.; Shah, B.P.; Lee, K.B. Combined magnetic nanoparticle-based microrna and hyperthermia therapy to enhance apoptosis in brain cancer cells. Small 2014, 10, 4106–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa, T.; Saito, H.; Minamiya, Y.; Mitobe, K.; Takashima, S.; Takahashi, N.; Ito, A.; Imai, K.; Motoyama, S.; Ogawa, J. Inhibition of Hsp90 and 70 sensitizes melanoma cells to hyperthermia using ferromagnetic particles with a low curie temperature. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 19, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Gu, H.C.; Zhang, D.S.Z.; Li, F.; Liu, T.Y.; Xia, W.L. Highly effective inhibition of lung cancer growth and metastasis by systemic delivery of siRNA via multimodal mesoporous silica-based nanocarrier. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 10058–10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arami, H.; Khandhar, A.; Liggitt, D.; Krishnan, K.M. In vivo delivery, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8576–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iatridi, Z.; Vamvakidis, K.; Tsougos, I.; Vassiou, K.; Dendrinou-Samara, C.; Bokias, G. Multifunctional polymeric platform of magnetic ferrite colloidal superparticles for luminescence, imaging, and hyperthermia applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 35059–35070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Q.F.; Peng, J.R.; Su, J.; Lu, X.L.; Zhao, Y.X.; Qian, Z.Y. Doxorubicin-conjugated heparin-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for combined anticancer drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 1963–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kudr, J.; Haddad, Y.; Richtera, L.; Heger, Z.; Cernak, M.; Adam, V.; Zitka, O. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090243
Kudr J, Haddad Y, Richtera L, Heger Z, Cernak M, Adam V, Zitka O. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(9):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090243
Chicago/Turabian StyleKudr, Jiri, Yazan Haddad, Lukas Richtera, Zbynek Heger, Mirko Cernak, Vojtech Adam, and Ondrej Zitka. 2017. "Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications" Nanomaterials 7, no. 9: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090243
APA StyleKudr, J., Haddad, Y., Richtera, L., Heger, Z., Cernak, M., Adam, V., & Zitka, O. (2017). Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications. Nanomaterials, 7(9), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090243