One-Step Electrochemical Fabrication of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticles Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine, Ascorbic Acid, and Uric Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
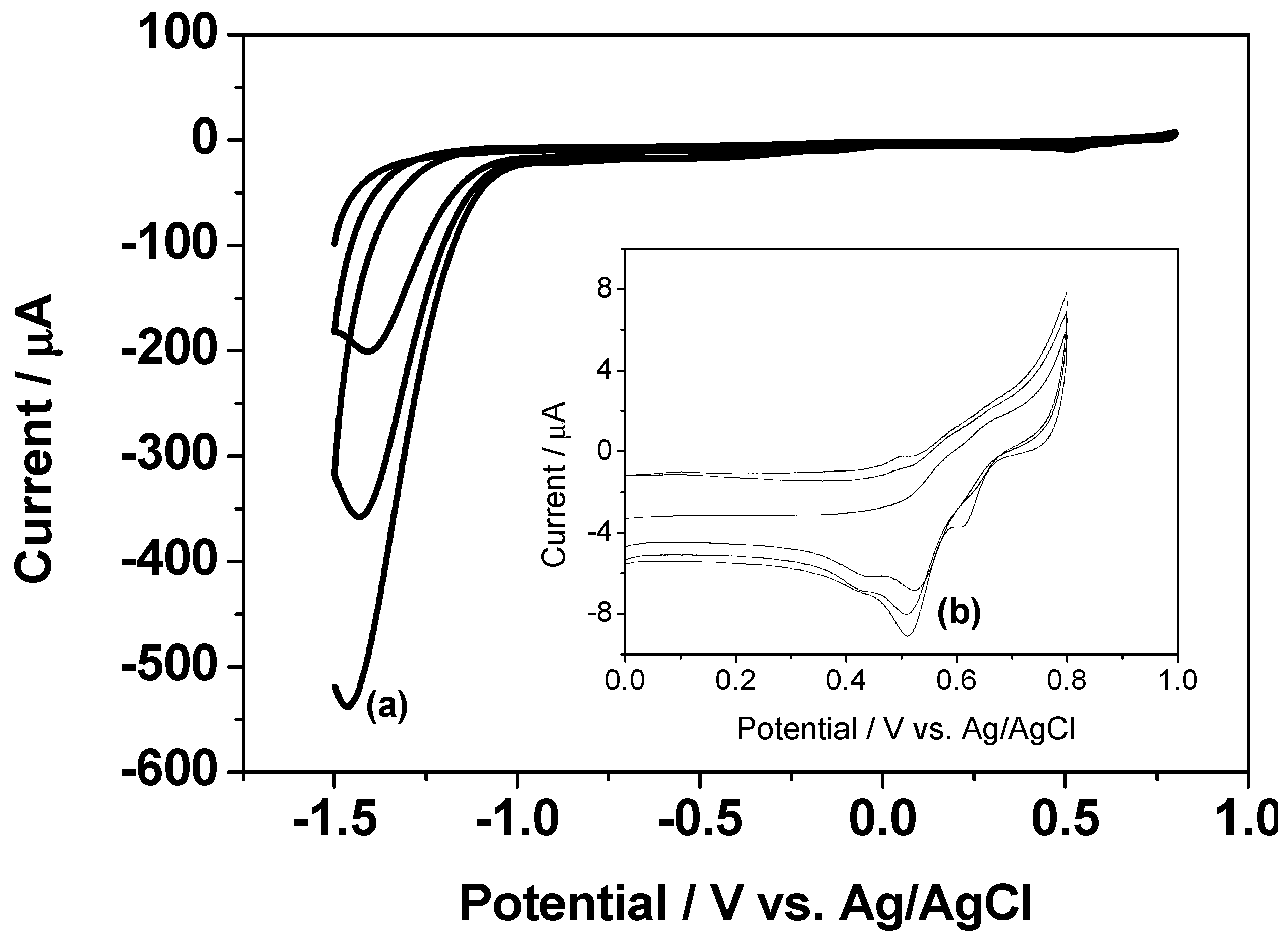
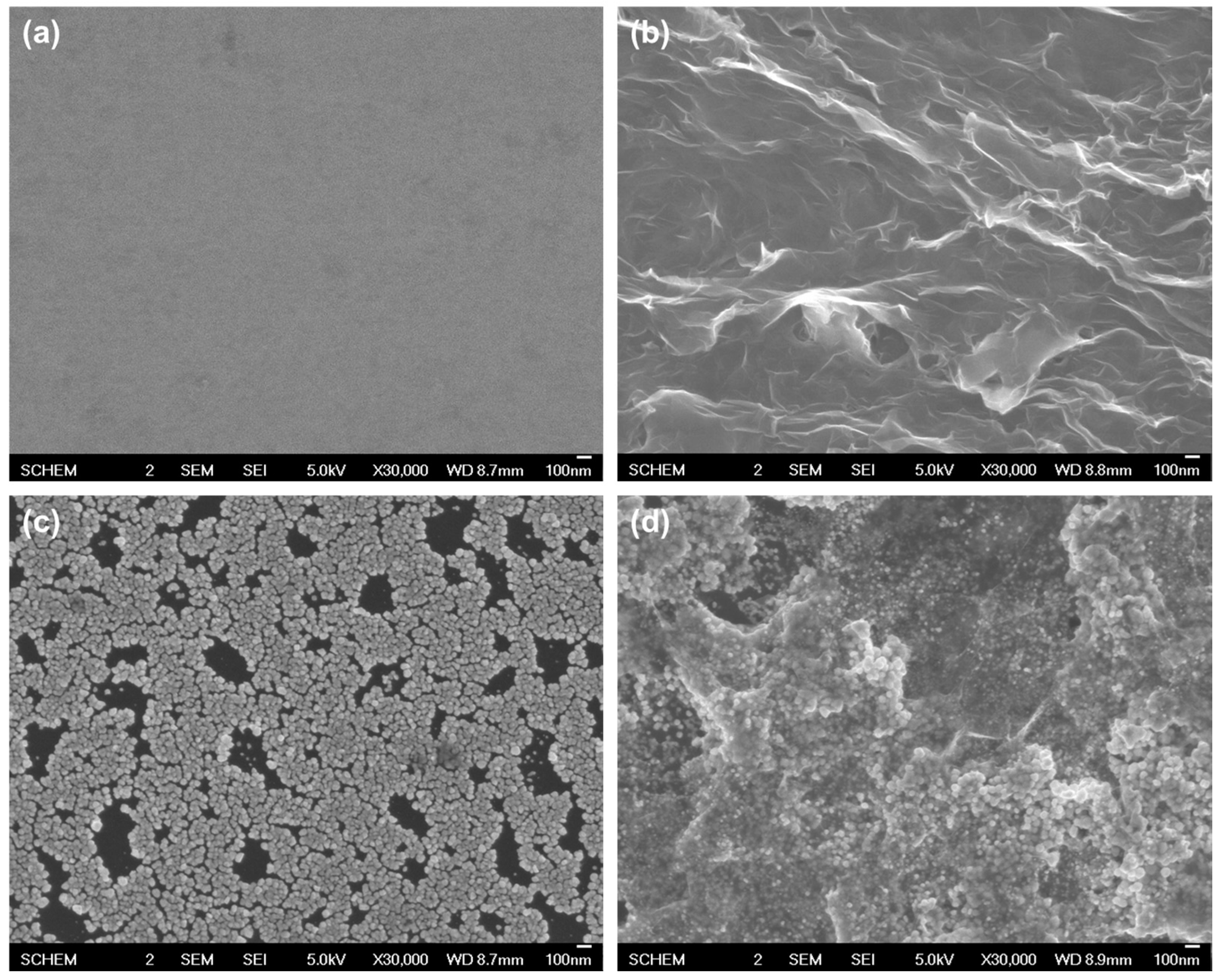
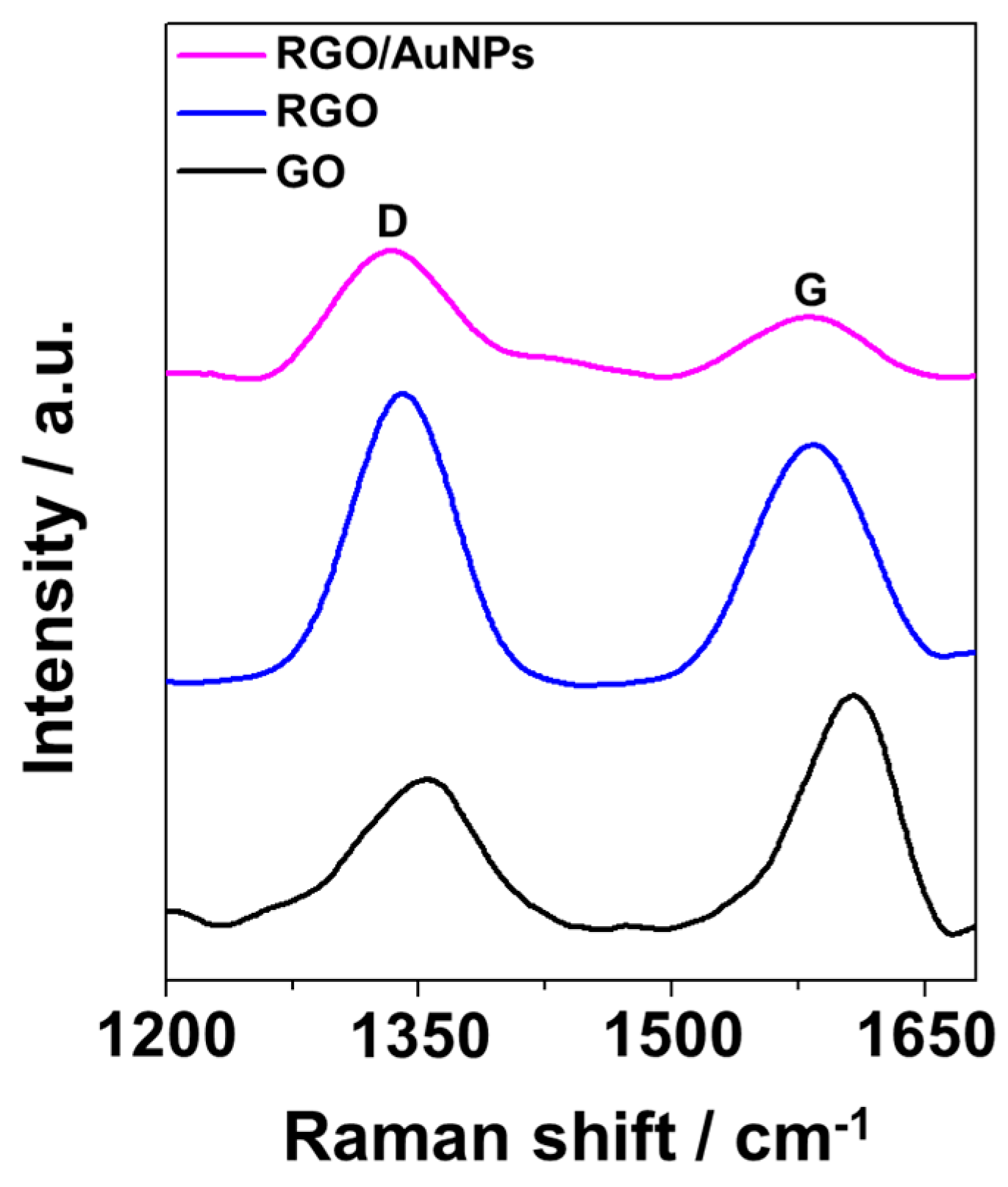
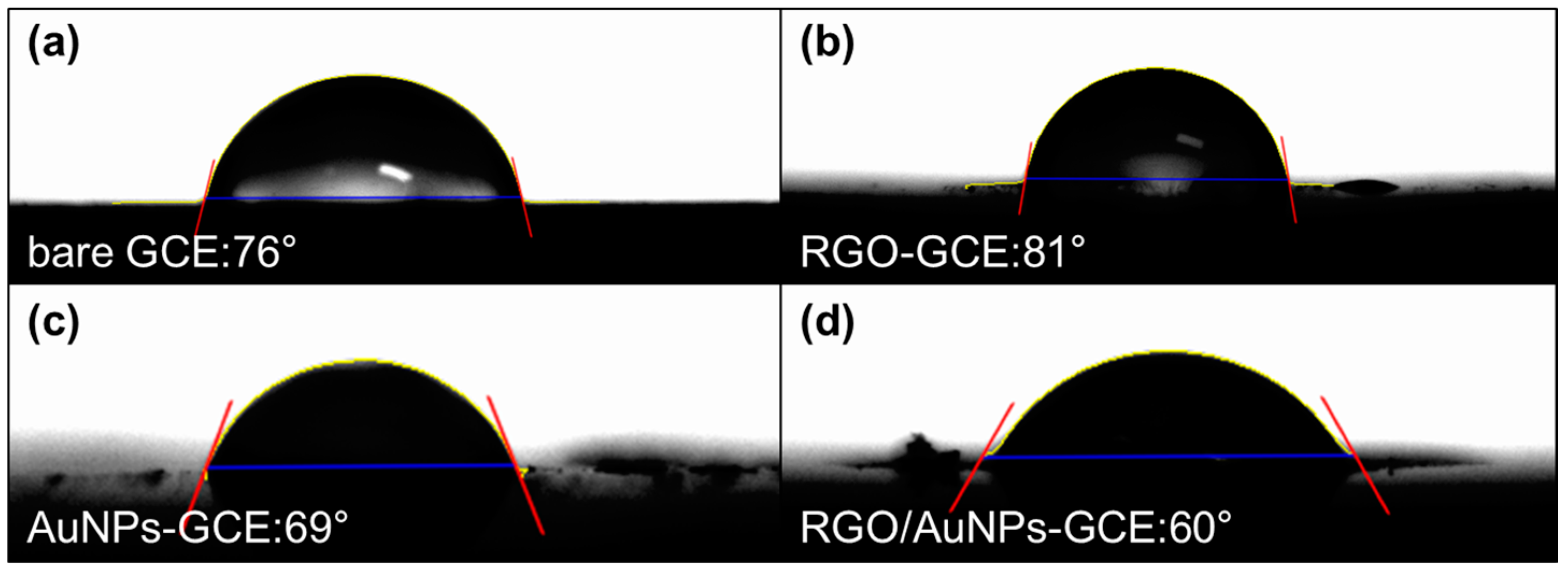
2.1. Preparation and Structure Characterization of RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode
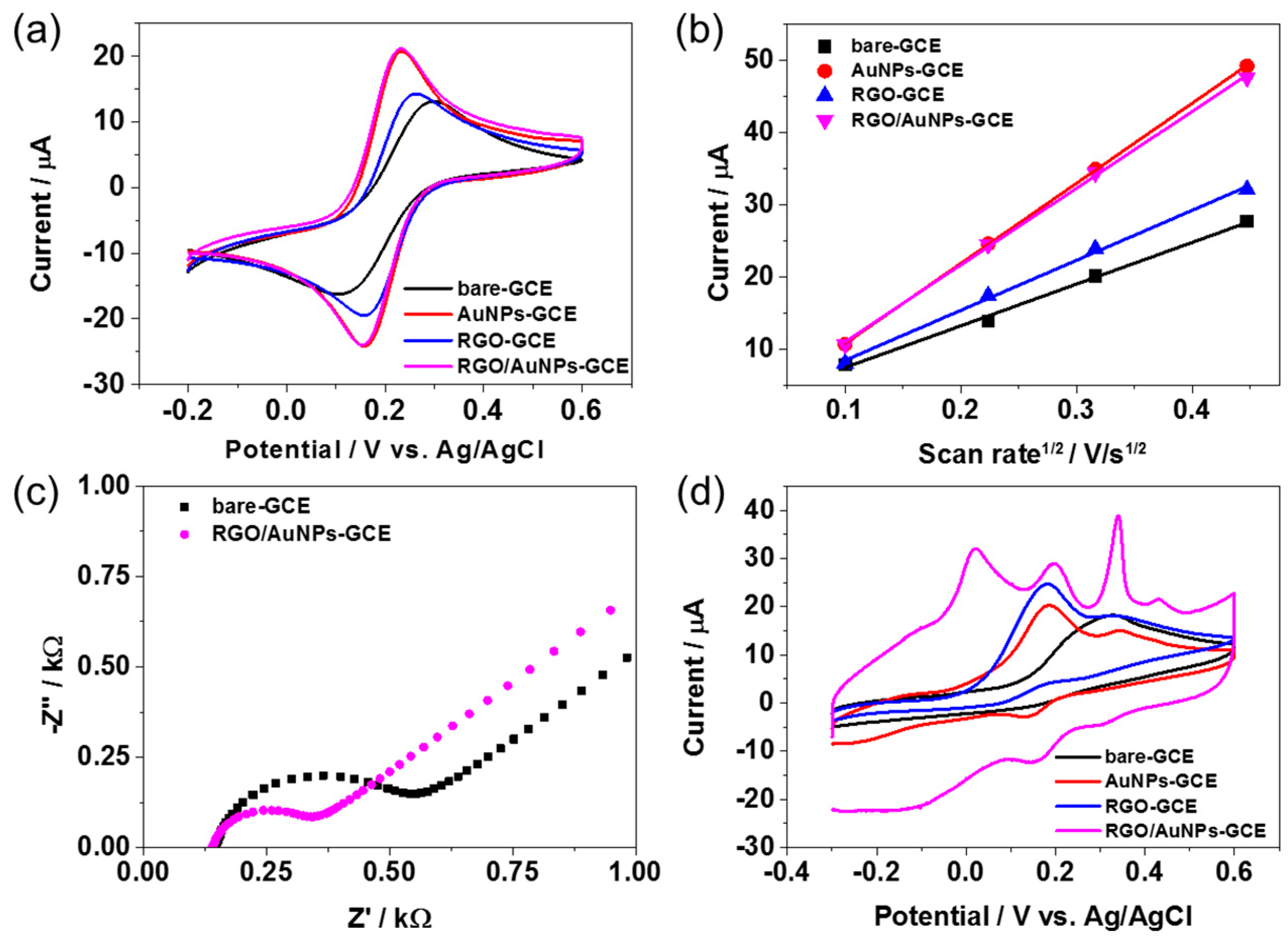
2.2. Electrochemical Properties of RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode
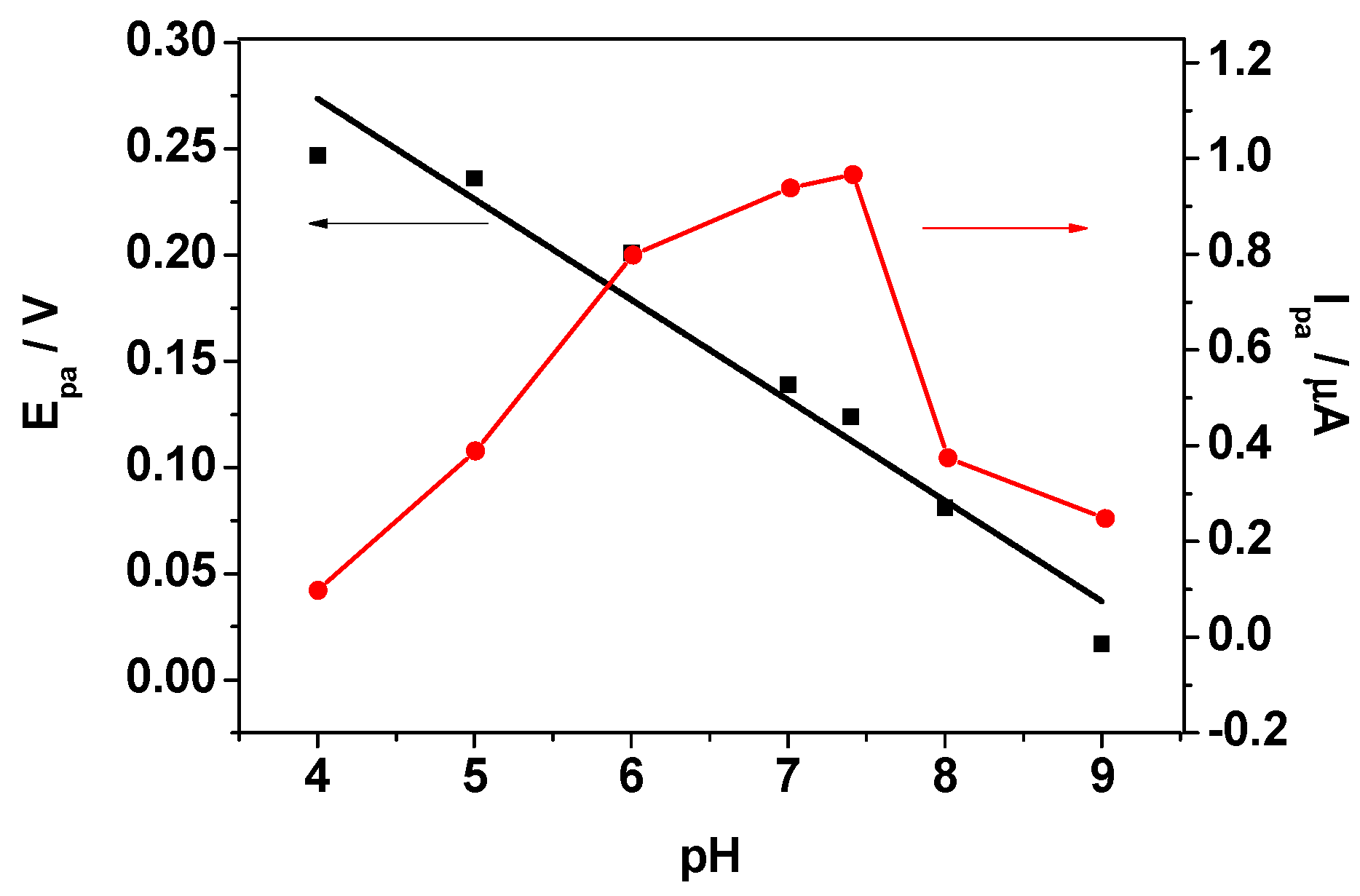
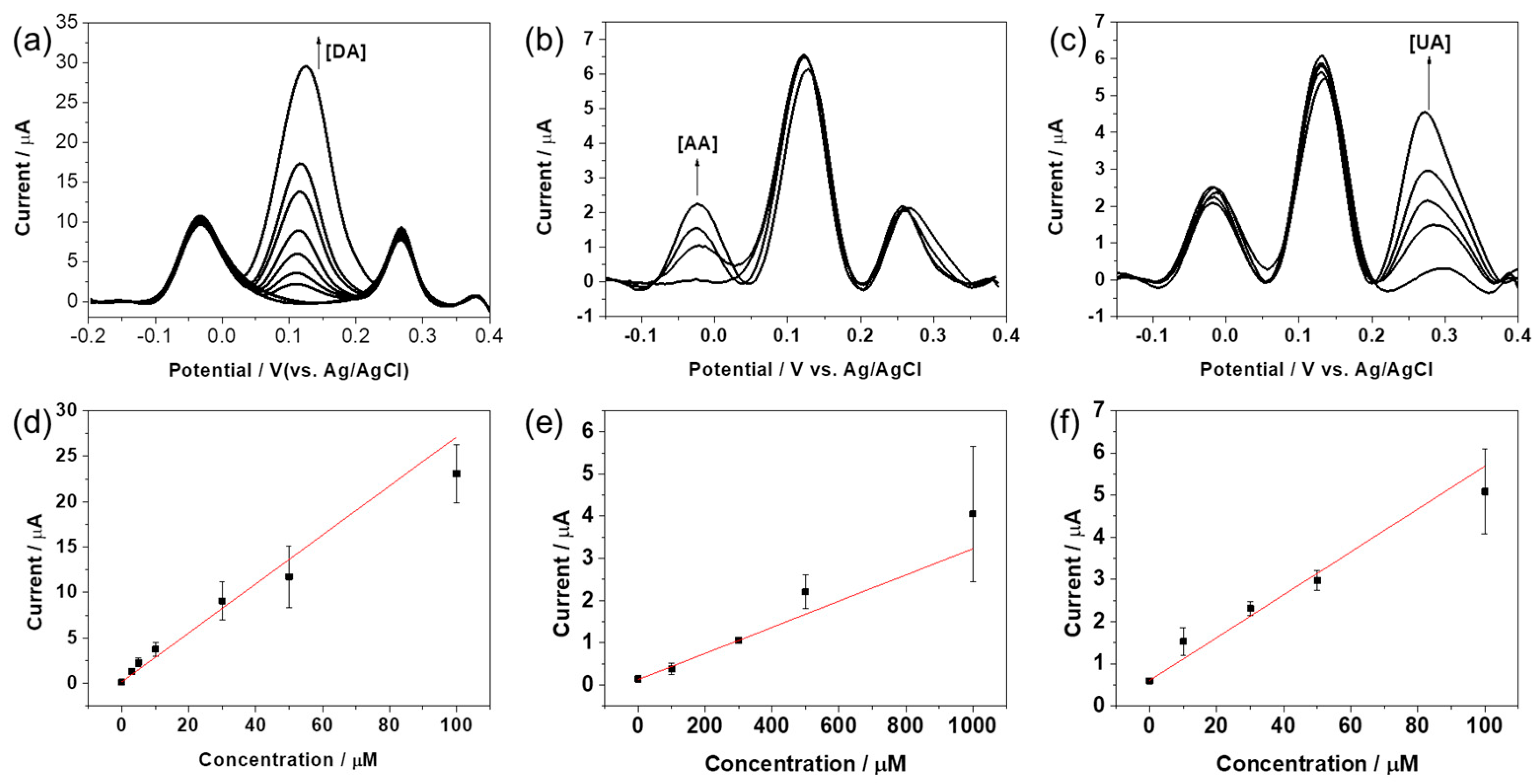
2.3. Selective Determination of DA, AA, and UA
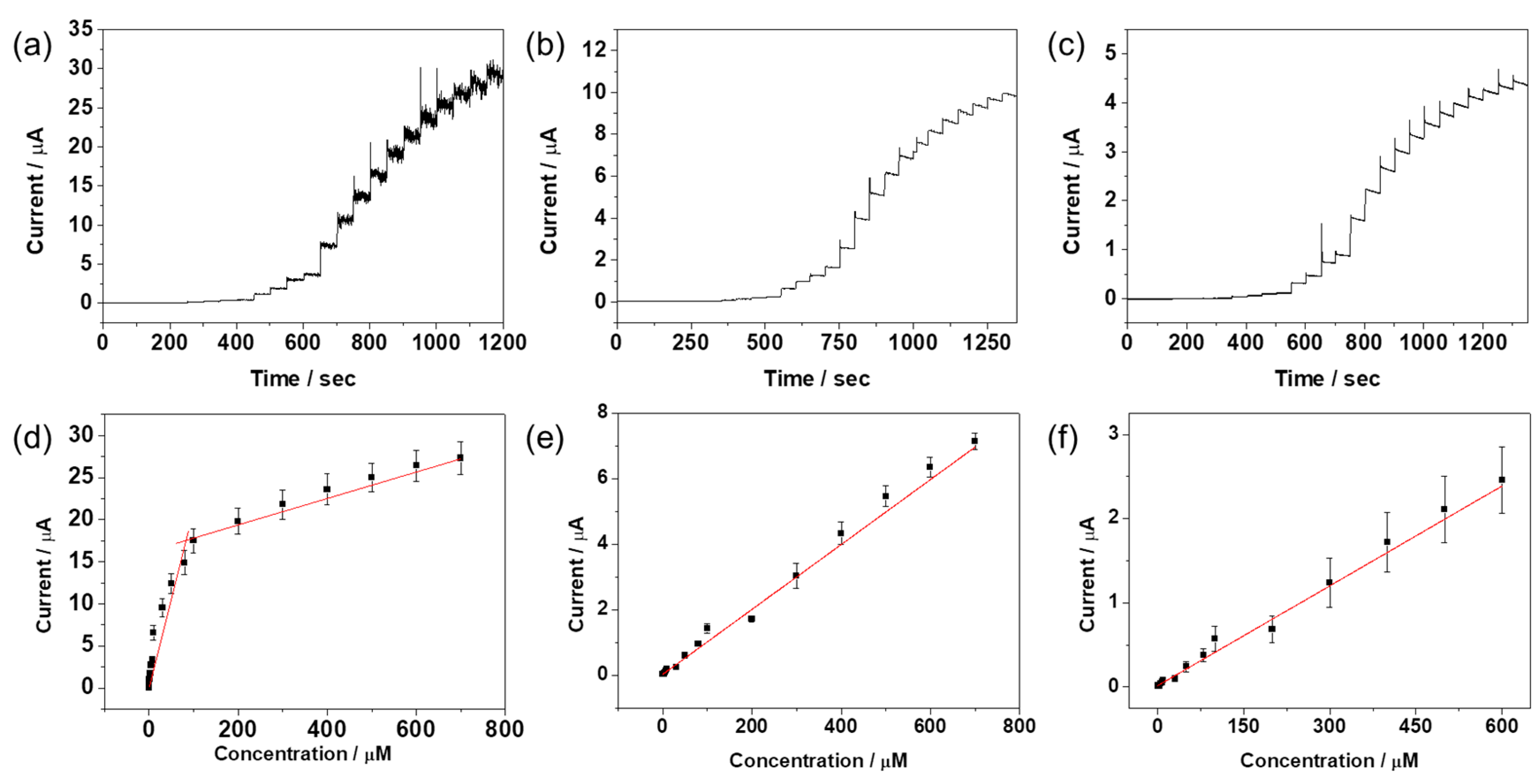
2.4. Amperometric Responses of DA, AA, and UA
2.5. Interference Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Preparation of RGO/AuNPs Nanocomposite Electrode
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Björklund, A.; Dunnett, S.B. Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: An update. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.L.; Kahn, R.S.; Ko, G.; Davidson, M. Dopamine in schizophrenia: A review and reconceptualization. Am. J. Psychiatry 1991, 148, 1474–1486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freed, C.R.; Greene, P.E.; Breeze, R.E.; Tsai, W.-Y.; DuMouchel, W.; Kao, R.; Dillon, S.; Winfield, H.; Culver, S.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Transplantation of embryonic dopamine neurons for severe Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeer, P.L.; Itagaki, S.; Boyes, B.E.; McGeer, E.G. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 1988, 38, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.; Dragunow, M.; Faull, R.L.M. The pattern of neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease: A comparative study of cannabinoid, dopamine, adenosine and GABA(A) receptor alterations in the human basal ganglia in Huntington’s disease. Neuroscience 2000, 97, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Jia, X.; Li, J.; Wang, E. Ratiometric fluorescence detection of tyrosinase activity and dopamine using thiolate-protected gold nanoclusters. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4897–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, V.S.-Y.; Lai, C.-Y.; Huang, J.; Song, S.-A.; Xu, S. Molecular recognition inside of multifunctionalized mesoporous silicas: Toward selective fluorescence detection of dopamine and glucosamine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11510–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Li, S.; Han, F.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Ma, W.; Kuang, H.; Li, A.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. SERS-active Au@Ag nanorod dimers for ultrasensitive dopamine detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotopoulou, M.A.; Ioannou, P.C. Post-column terbium complexation and sensitized fluorescence detection for the determination of norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine using high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 462, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, M.; Ferrario, C.R.; Schultz, K.N.; Robinson, T.E.; Kennedy, R.T. Monitoring Dopamine In Vivo by Microdialysis Sampling and On-Line CE-Laser-Induced Fluorescence. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6717–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.I.; Galpern, W.R.; Brownell, A.-L.; Matthews, R.T.; Bogdanov, M.; Isacson, O.; Keltner, J.R.; Beal, M.F.; Rosen, B.R.; Jenkins, B.G. Detection of dopaminergic neurotransmitter activity using pharmacologic MRI: Correlation with PET, microdialysis, and behavioral data. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 38, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.-W.; Yoon, Y.W.; Heo, J.; Yu, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.H. Electrochemical detection of nanomolar dopamine in the presence of neurophysiological concentration of ascorbic acid and uric acid using charge-coated carbon nanotubes via facile and green preparation. Talanta 2016, 147, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Meng, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, C. Microwave-assisted preparation of N-doped carbon dots as a biosensor for electrochemical dopamine detection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 452, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Ni, B.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Finely Composition-Tunable Synthesis of Ultrafine Wavy PtRu Nanowires as Effective Electrochemical Sensors for Dopamine Detection. Langmuir 2017, 33, 8070–8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.L.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Cui, X.T. A graphene oxide/conducting polymer nanocomposite for electrochemical dopamine detection: Origin of improved sensitivity and specificity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5209–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruneanu, S.; Biris, A.R.; Pogacean, F.; Socaci, C.; Coros, M.; Rosu, M.C.; Watanabe, F.; Biris, A.S. The influence of uric and ascorbic acid on the electrochemical detection of dopamine using graphene-modified electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 154, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathi, C.; Venkateswara Raju, C.; Muthukumaran, P.; Wilson, J.; Ravi, G. Au-Pd bimetallic nanoparticles anchored on α-Fe2O3 nonenzymatic hybrid nanoelectrocatalyst for simultaneous electrochemical detection of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. Ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of hydroquinone, catechol and resorcinol based on the electrochemical co-reduction prepared Au-Pd nanoflower/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 231, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Bhat, S.A.; Pandit, S.A.; Rather, G.M.; Khan, K.Z.; Bhat, M.A. Imidazolium Based Surface Active Ionic Liquids as Novel Micellar Media for Simultaneous and Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, L.; David, V.; David, I.G.; Lazăr, P.; Mihailciuc, C.; Stamatin, I.; Ciobanu, A.; Ştefănescu, C.D.; Nagy, L.; Nagy, G.; et al. Electropolymerized molecular imprinting on glassy carbon electrode for voltammetric detection of dopamine in biological samples. Talanta 2016, 160, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Ma, Z. A glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, X. Three-dimensional nitrogen-doped graphene as an ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for the detection of dopamine. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, L.; Lu, J.; Li, J. Application of graphene-modified electrode for selective detection of dopamine. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, H.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Xu, S.; Li, C.; Guo, W.; Qu, C.; Yang, B. MgO nanobelt-modified graphene-tantalum wire electrode for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 168, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xie, L.; Li, H. Electrochemical biosensor based on reduced graphene oxide and Au nanoparticles entrapped in chitosan/silica sol–gel hybrid membranes for determination of dopamine and uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 682, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Pandiyan, T.; Satpati, B.; Srivastava, R. Simultaneous and sensitive determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid, and tryptophan with silver nanoparticles-decorated reduced graphene oxide modified electrode. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Zheng, J.-N.; Lv, Z.-Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, A.-J.; Feng, J.-J. Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid using Pt nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Du, J.; Wang, H.; Zou, C.; Jiang, F.; Yang, P.; Du, Y. A facile electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide and Au nanoplates modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; You, T. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid at electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Fu, Y.; Yang, P.; Du, Y. Direct electrodeposition of reduced graphene oxide on carbon fiber electrode for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 456, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Morrin, A.; Killard, A.J.; Smyth, M.R. Application of Nanoparticles in Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhai, Y.; Dong, S. Electrochemical Sensing and Biosensing Platform Based on Chemically Reduced Graphene Oxide. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5603–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, V.; Periasamy, A.P.; Chen, S.-M. Highly selective amperometric nitrite sensor based on chemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 17, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, E. Synthesis and electrochemical applications of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 598, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahshid, S.; Li, C.; Mahshid, S.S.; Askari, M.; Dolati, A.; Yang, L.; Luo, S.; Cai, Q. Sensitive determination of dopamine in the presence of uric acid and ascorbic acid using TiO2 nanotubes modified with Pd, Pt and Au nanoparticles. Analyst 2011, 136, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.-L.; Wang, X.-F.; Qian, Q.-Y.; Wang, F.-B.; Xia, X.-H. A Green Approach to the Synthesis of Graphene Nanosheets. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Luo, S.; Tang, Y.; Chen, L. Direct Electrodeposition of Graphene Enabling the One-Step Synthesis of Graphene-Metal Nanocomposite Films. Small 2011, 7, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Laborda, E.; Crossley, A.; Compton, R.G. Surface oxidation of gold nanoparticles supported on a glassy carbon electrode in sulphuric acid medium: Contrasts with the behaviour of “macro” gold. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-471-04372-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.-L.; Chang, K.-H.; Hu, C.-C.; Cheng, W.-L.; Zen, J.-M. Improved voltammetric peak separation and sensitivity of uric acid and ascorbic acid at nanoplatelets of graphitic oxide. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Lopa, N.S.; Ju, M.J.; Lee, J.-J. Highly sensitive and simultaneous detection of dopamine and uric acid at graphene nanoplatelet-modified fluorine-doped tin oxide electrode in the presence of ascorbic acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 792, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, M.D.; Tatawawadi, S.V.; Piekarski, S.; Adams, R.N. Electrochemical studies of the oxidation pathways of catecholamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, G.C.; Craig, E.B. Understanding Voltammetry; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-84816-586-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Gong, K.; Zhang, H.; Mao, L. Layer-by-layer assembled carbon nanotubes for selective determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, S.; Zou, W.; Zhou, T. N-Doped carbon nanorods as ultrasensitive electrochemical sensors for the determination of dopamine. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8157–8163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovtyukhova, N.I.; Ollivier, P.J.; Martin, B.R.; Mallouk, T.E.; Chizhik, S.A.; Buzaneva, E.V.; Gorchinskiy, A.D. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Ultrathin Composite Films from Micron-Sized Graphite Oxide Sheets and Polycations. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S., Jr.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Targets | DA | AA | UA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amperometry | Linear regression equation | ip (μA) = 7.6 × 10−8 + 0.43C (μM) R2 = 0.954 (0.14–100 μM), ip (μA) = 1.4 × 10−8 + 0.023C (μM) R2 = 0.968 (100–700 μM) | ip (μA) = 4.8 × 10−8 + 0.0081 C (μM) R2 = 0.988 | ip (μA) = 2.1 × 10−8 + 0.0035 C (μM) R2 = 0.979 |
| LOD (μM) | 0.14 | 9.5 | 25 | |
| Sensitivity (μA·μM−1) | 0.43 | 8.1 × 10−3 | 3.5 × 10−3 | |
| DPV | Linear regression equation | ip (μA) = 1.8 × 10−7 + 0.27 C (μM) R2 = 0.935 | ip (μA) = 1.2 × 10−7 + 0.0031 C (μM) R2 = 0.989 | ip (μA) = 6.0 × 10−7 + 0.051 C (μM) R2 = 0.977 |
| LOD (μM) | 0.69 | 5.7 | 2.2 | |
| Sensitivity (μA·μM−1) | 0.27 | 3.1 × 10−3 | 0.051 | |
| Electrode Material | LOD (μM) | Sensitivity (μA/μM) | Range (μM) | Remarks | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGO/Au nanoplate | 1.4 | 1.0 | 6.8–41 | Multi-step, ERGO, Drop-casting | [28] |
| RGO-AuNPs-CSHMs | 0.3 | 0.048 | 1–200 | Multi-step, CRGO, Drop-casting | [25] |
| AgNPs/rGO | 5.4 | 0.39 | 10–800 | Multi-step, CRGO, Drop-casting | [26] |
| ERGO | 0.5 | 0.482 | 0.5–60 | Two-step, ERGO, Drop-casting | [29] |
| Pt/RGO | 0.45 | 0.0391 | 10–170 | Two-step, CRGO, Drop-casting | [27] |
| MgO/Gr/Ta | 0.15 | 1.191 | 0.1–7 | Multi-step, CVD-Graphene | [24] |
| ERGO/CFE | 0.77 | 0.1024 | 1.5–224.82 | One-step, ERGO | [30] |
| RGO/AuNPs | 0.137 | 0.43 | 0.14–700 | One-step, ERGO | This work |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-S.; Yu, S.H.; Kim, T.H. One-Step Electrochemical Fabrication of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticles Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine, Ascorbic Acid, and Uric Acid. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010017
Lee C-S, Yu SH, Kim TH. One-Step Electrochemical Fabrication of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticles Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine, Ascorbic Acid, and Uric Acid. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chang-Seuk, Su Hwan Yu, and Tae Hyun Kim. 2018. "One-Step Electrochemical Fabrication of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticles Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine, Ascorbic Acid, and Uric Acid" Nanomaterials 8, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010017





