Detection and Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Abstract
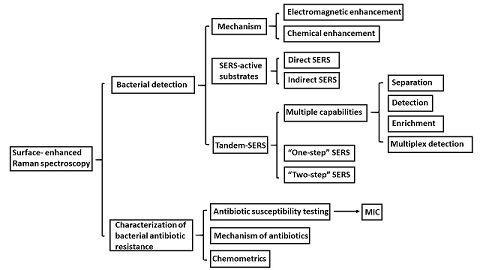
:1. Introduction
2. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) for Sensing Trace Level of Bacteria
2.1. Mechanism of SERS
2.2. SERS-Active Substrates for Bacterial Detection
2.2.1. Direct SERS
2.2.2. Indirect SERS
3. Tandem-SERS for Sensing Bacteria in a Sample Matrix
3.1. Tandem-SERS Methods
3.2. Tandem-SERS Integrated with Multiple Capabilities
3.3. “Two-Step” and “One-Step” SERS
4. Elucidating Antibiotic Resistant Mechanism of Bacteria Using SERS and Chemometrics
4.1. Characterization of Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria Using SERS
4.2. Chemometrics Used with SERS
5. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Law, J.W.-F.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Rapid methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens: Principles, applications, advantages and limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, G.; Murasova, P.; Hamiot, A.; Tsougeni, K.; Kaprou, G.; Eck, M.; Rabus, D.; Bilkova, Z.; Dupuy, B.; Jobst, G. Micro-nano-bio acoustic system for the detection of foodborne pathogens in real samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa, K.; Adley, C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, H.P.; Jaykus, L.-A. Detection of pathogens in foods: The current state-of-the-art and future directions. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 37, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracias, K.S.; McKillip, J.L. A review of conventional detection and enumeration methods for pathogenic bacteria in food. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, F.; López-Acedo, E.; Tabla, R.; Roa, I.; Gómez, A.; Rebollo, J.E. Improved detection of escherichia coli and coliform bacteria by multiplex pcr. BMC Biotechnol. 2015, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonnelle, E.; Mesquita, C.; Bille, E.; Day, N.; Dauphin, B.; Beretti, J.-L.; Ferroni, A.; Gutmann, L.; Nassif, X. Maldi-tof mass spectrometry tools for bacterial identification in clinical microbiology laboratory. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxatto, A.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G. Applications of maldi-tof mass spectrometry in clinical diagnostic microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 380–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabados, F.; Michels, M.; Kaase, M.; Gatermann, S. The sensitivity of direct identification from positive bact/alert™(biomérieux) blood culture bottles by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry is low. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Poulakou, G.; Ruppe, E.; Bouza, E.; Van Hal, S.J.; Brink, A. Antimicrobial resistance in the next 30 years, humankind, bugs and drugs: A visionary approach. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strommenger, B.; Kettlitz, C.; Werner, G.; Witte, W. Multiplex pcr assay for simultaneous detection of nine clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of resistant bacteria at very low antibiotic concentrations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, M.R.; García-Quintanilla, M.; Martín-Peña, R.; Cisneros, J.M.; McConnell, M.J. Progress on the development of rapid methods for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2710–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galvan, D.D.; Yu, Q. Surface-enhanced raman scattering for rapid detection and characterization of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 1701335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.Y.; White, I.M. A simple filter-based approach to surface enhanced raman spectroscopy for trace chemical detection. Analyst 2012, 137, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Kneipp, K.; Kneipp, H.; Bohr, H.G. Single-molecule SERS spectroscopy. In Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 261–277. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. SERS detection of small inorganic molecules and ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11214–11223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.-M.; Ma, W.-F.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.-C. Silver-coated magnetite–carbon core–shell microspheres as substrate-enhanced SERS probes for detection of trace persistent organic pollutants. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5210–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. SERS-based diagnosis and biodetection. Small 2010, 6, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneipp, J.; Kneipp, H.; Kneipp, K. SERS—A single-molecule and nanoscale tool for bioanalytics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneipp, K.; Kneipp, H.; Manoharan, R.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS)—A new tool for single molecule detection and identification. Bioimaging 1998, 6, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisanga, M.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Goodacre, R. Surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS) in microbiology: Illumination and enhancement of the microbial world. Appl. Spectrosc. 2018, 72, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNay, G.; Eustace, D.; Smith, W.E.; Faulds, K.; Graham, D. Surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS) and surface-enhanced resonance raman scattering (SERRS): A review of applications. Appl. Spectrosc. 2011, 65, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ru, E.; Blackie, E.; Meyer, M.; Etchegoin, P.G. Surface enhanced raman scattering enhancement factors: A comprehensive study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13794–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Seong, N.-H.; Dlott, D.D. Measurement of the distribution of site enhancements in surface-enhanced raman scattering. Science 2008, 321, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valley, N.; Greeneltch, N.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Schatz, G.C. A look at the origin and magnitude of the chemical contribution to the enhancement mechanism of surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS): Theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 2599–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, P.L.; Dieringer, J.A.; Shah, N.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008, 1, 601–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willets, K.A.; Van Duyne, R.P. Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.-I.; Ringe, E.; Van Duyne, R.P. SERS: Materials, applications, and the future. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziuk, D.; Moehwald, H. Prospects for plasmonic hot spots in single molecule SERS towards the chemical imaging of live cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 21072–21093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Z.; Yu, G.; Yang, D.; Zhao, J. Label and label-free based surface-enhanced raman scattering for pathogen bacteria detection: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, R.M.; Johnson, H.E.; Olembe, E.; Panneerselvam, A.; Malik, M.A.; Afzaal, M.; O’Brien, P.; Goodacre, R. Towards quantitatively reproducible substrates for SERS. Analyst 2008, 133, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, R.M.; Goodacre, R. Characterisation and identification of bacteria using SERS. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, R.M.; Goodacre, R. Discrimination of bacteria using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, R.M.; Brooker, A.; Goodacre, R. Surface-enhanced raman scattering for the rapid discrimination of bacteria. Faraday Discuss. 2006, 132, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. Recent advances in nanofabrication techniques for SERS substrates and their applications in food safety analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gates, B.D.; Xu, Q.; Stewart, M.; Ryan, D.; Willson, C.G.; Whitesides, G.M. New approaches to nanofabrication: Molding, printing, and other techniques. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1171–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Cardinal, M.F.; Kleinman, S.L.; Greeneltch, N.G.; Frontiera, R.R.; Blaber, M.G.; Schatz, G.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. High-performance SERS substrates: Advances and challenges. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Pang, S.; Chen, J.; McLandsborough, L.; Nugen, S.R.; Fan, M.; He, L. Label-free mapping of single bacterial cells using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2016, 141, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Ruan, W.; Yang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, B. Deposition of ag nanoparticles on porous anodic alumina for surface enhanced raman scattering substrate. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Ruan, W.; Wang, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, B. Fabrication of silver decorated anodic aluminum oxide substrate and its optical properties on surface-enhanced raman scattering and thin film interference. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11869–11873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.; Tsukruk, V.V. Nanoparticle-decorated nanocanals for surface-enhanced raman scattering. Small 2008, 4, 1980–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlow, S.; Meisel, S.; Cialla-May, D.; Weber, K.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. Isolation and identification of bacteria by means of raman spectroscopy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 89, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahraman, M.; Zamaleeva, A.I.; Fakhrullin, R.F.; Culha, M. Layer-by-layer coating of bacteria with noble metal nanoparticles for surface-enhanced raman scattering. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, D.; Ivleva, N.P.; Mircescu, N.E.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. SERS detection of bacteria in water by in situ coating with ag nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Mungroo, N.; Daikuara, L.; Neethirajan, S. Label-free NIR-SERS discrimination and detection of foodborne bacteria by in situ synthesis of ag colloids. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosier-Boss, P.; Sorensen, K.; George, R.; Obraztsova, A. SERS substrates fabricated using ceramic filters for the detection of bacteria. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2016, 153, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, H.; Xiao, W.; Sun, D.-W. SERS-microfluidic systems: A potential platform for rapid analysis of food contaminants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungroo, N.A.; Oliveira, G.; Neethirajan, S. SERS based point-of-care detection of food-borne pathogens. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.; März, A.; Schumacher, W.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. Towards a fast, high specific and reliable discrimination of bacteria on strain level by means of SERS in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, S.; Mao, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, C.; Cohick, Z.; Huang, P.-H.; Huang, T.J. In situ fabrication of 3D Ag@ Zno nanostructures for microfluidic surface-enhanced raman scattering systems. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12175–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.P.; Franca, A.S.; Irudayaraj, J. Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy applied to food safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Samuelson, D.R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Rasco, B.A.; Xu, J.; Konkel, M.E. Detecting and tracking nosocomial methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus using a microfluidic SERS biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2320–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlig, A.; Bocklitz, T.; Labugger, I.; Dees, S.; Henk, S.; Richter, E.; Andres, S.N.; Merker, M.; Stöckel, S.; Weber, K. Loc-SERS: A promising closed system for the identification of mycobacteria. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7998–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, H.; Choi, S.; Lee, H.J. Rapid label-free identification of klebsiella pneumoniae antibiotic resistant strains by the drop-coating deposition surface-enhanced raman scattering method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2017, 183, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiri, L.; Bronk, B.; Shabtai, Y.; Czege, J.; Efrima, S. Silver metal induced surface enhanced raman of bacteria. Colloids Surf. A 2002, 208, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, M.; Yazıcı, M.M.; Şahin, F.; Çulha, M. Convective assembly of bacteria for surface-enhanced raman scattering. Langmuir 2008, 24, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dina, N.; Zhou, H.; Colniţă, A.; Leopold, N.; Szoke-Nagy, T.; Coman, C.; Haisch, C. Rapid single-cell detection and identification of pathogens by using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2017, 142, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, K.; Irudayaraj, J. Silver nanosphere SERS probes for sensitive identification of pathogens. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16122–16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, Y.-W.; Park, B.; Tripp, R.A.; Zhao, Y. Differentiation and classification of bacteria using vancomycin functionalized silver nanorods array based surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy and chemometric analysis. Talanta 2015, 139, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamer, U.; Boyacı, İ.H.; Temur, E.; Zengin, A.; Dincer, I.; Elerman, Y. Fabrication of magnetic gold nanorod particles for immunomagnetic separation and SERS application. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Wang, C.; Yu, C. A self-referencing detection of microorganisms using surface enhanced raman scattering nanoprobes in a test-in-a-tube platform. Biosensors 2013, 3, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindranath, S.P.; Wang, Y.; Irudayaraj, J. SERS driven cross-platform based multiplex pathogen detection. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 152, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondera, T.J.; Hamme, A.T., II. A gold nanopopcorn attached single-walled carbon nanotube hybrid for rapid detection and killing of bacteria. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7534–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.; Sinha, S.S.; Pramanik, A.; Ray, P.C. Three-dimensional (3D) plasmonic hot spots for label-free sensing and effective photothermal killing of multiple drug resistant superbugs. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 18301–18308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madiyar, F.R.; Bhana, S.; Swisher, L.Z.; Culbertson, C.T.; Huang, X.; Li, J. Integration of a nanostructured dielectrophoretic device and a surface-enhanced raman probe for highly sensitive rapid bacteria detection. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3726–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakes, B.J.; Lipert, R.J.; Bannantine, J.P.; Porter, M.D. Detection of mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis by a sonicate immunoassay based on surface-enhanced raman scattering. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xu, C.; Tripp, R.A.; Huang, Y.-W.; Zhao, Y. Detection and differentiation of foodborne pathogenic bacteria in mung bean sprouts using field deployable label-free SERS devices. Analyst 2013, 138, 3005–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ravindranath, S.; Irudayaraj, J. Separation and detection of multiple pathogens in a food matrix by magnetic SERS nanoprobes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Knauer, M.; Ivleva, N.P.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. Synthesis of core-shell surface-enhanced raman tags for bioimaging. Anal. Chem. 2009, 82, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Singh, A.K.; Senapati, D.; Fan, Z.; Ray, P.C. Targeted highly sensitive detection of multi-drug resistant salmonella DT104 using gold nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9444–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, N.; Chang, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S. Salmonella typhimurium detection using a surface-enhanced raman scattering-based aptasensor. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 218, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, N.; Yan, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Vibrio parahaemolyticus detection aptasensor using surface-enhanced raman scattering. Food Control 2016, 63, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Cai, Q.; Lu, K.; Liao, F.; Shao, M. Bi-functional au/fes (Au/Co3O4) composite for in situ SERS monitoring and degradation of organic pollutants. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B. Gold nanoparticles enhanced SERS aptasensor for the simultaneous detection of salmonella typhimurium and staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, R.; Yang, L.; Yu, S.; Xu, S.; Xu, W. Fe3O4@ graphene oxide@ Ag particles for surface magnet solid-phase extraction surface-enhanced raman scattering (smspe-SERS): From sample pretreatment to detection all-in-one. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14160–14168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.J.; Tay, L.L.; Tanha, J.; Ryan, S.; Chau, L.K. Single-domain antibody-conjugated nanoaggregate-embedded beads for targeted detection of pathogenic bacteria. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 9330–9334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catala, C.; Mir-Simon, B.; Feng, X.; Cardozo, C.; Pazos-Perez, N.; Pazos, E.; Gómez-de Pedro, S.; Guerrini, L.; Soriano, A.; Vila, J. Online SERS quantification of staphylococcus aureus and the application to diagnostics in human fluids. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1600163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, P.; Jiang, P.-S.; Chang, H.-W.; Su, S.-C.; Tanha, J.; Tay, L.-L.; Chen, P.; Lin, Y.-J. Raman based detection of staphylococcus aureus utilizing single domain antibody coated nanoparticle labels and magnetic trapping. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4152–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, N.; Lemma, T.; Ge, H.; Toppari, J.J.; Hytönen, V.P.; Wang, J. Core–shell nanorod columnar array combined with gold nanoplate–nanosphere assemblies enable powerful in situ SERS detection of bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24394–24403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Kang, H.; Shao, L.; Hu, L.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S.; Gu, B. Label-free identification carbapenem-resistant escherichia coli based on surface-enhanced resonance raman scattering. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4761–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-Y.; Tsai, K.-T.; Wang, H.-H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chao, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Wang, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-L. Functionalized arrays of raman-enhancing nanoparticles for capture and culture-free analysis of bacteria in human blood. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Xu, K.; Xu, C.; Xu, B. Biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles for protein separation and pathogen detection. Chem. Commun. 2006, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Mi, L.; Gong, H.; Jiang, S.; Yu, Q. Multifunctional magnetic–plasmonic nanoparticles for fast concentration and sensitive detection of bacteria using SERS. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Qu, X.; Zhang, K.; Rong, Z.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. A rapid SERS method for label-free bacteria detection using polyethylenimine-modified au-coated magnetic microspheres and Au@ Ag nanoparticles. Analyst 2016, 141, 6226–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Rong, Z.; Ding, H.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Shao, N.; Dong, P.; Xiao, R. Facile synthesis of au-coated magnetic nanoparticles and their application in bacteria detection via a SERS method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19958–19967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearns, H.; Goodacre, R.; Jamieson, L.E.; Graham, D.; Faulds, K. SERS detection of multiple antimicrobial-resistant pathogens using nanosensors. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12666–12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temur, E.; Boyacı, İ.H.; Tamer, U.; Unsal, H.; Aydogan, N. A highly sensitive detection platform based on surface-enhanced raman scattering for escherichia coli enumeration. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Lu, X. Determination of chemical hazards in foods using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy coupled with advanced separation techniques. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hamme, A.T., II. Targeted highly sensitive detection/eradication of multi-drug resistant salmonella dt104 through gold nanoparticle–swcnt bioconjugated nanohybrids. Analyst 2014, 139, 3702–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L. A review of multifunctions of dielectrophoresis in biosensors and biochips for bacteria detection. Anal. Lett. 2012, 45, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Hsieh, W.H.; Liu, L.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chu, C.C.; Wang, S.T.; Kuo, I.T.; Chau, L.K.; Yang, C.Y. On-line SERS detection of single bacterium using novel SERS nanoprobes and a microfluidic dielectrophoresis device. Small 2014, 10, 4700–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjith Premasiri, W.; Lemler, P.; Chen, Y.; Gebregziabher, Y.; Ziegler, L.D. SERS analysis of bacteria, human blood, and cancer cells: A metabolomic and diagnostic tool. Front. Surf.-Enhanc. Raman Scatt. 2014, 257–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Do, J.; Premasiri, W.R.; Ziegler, L.D.; Klapperich, C.M. Rapid point-of-care concentration of bacteria in a disposable microfluidic device using meniscus dragging effect. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3265–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Maheshwari, S.; Chang, H.-C. Rapid bioparticle concentration and detection by combining a discharge driven vortex with surface enhanced raman scattering. Biomicrofluidics 2007, 1, 014106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, B.; Basaran-Akgul, N.; Temur, E.; Tamer, U.; Boyacı, İ.H. Sers-based sandwich immunoassay using antibody coated magnetic nanoparticles for escherichia coli enumeration. Analyst 2011, 136, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-M.; Liao, P.-H.; Chen, D.-W.; Lin, H.-P.; Chang, H.-C. A filter-like aunps@ ms SERS substrate for staphylococcus aureus detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamińska, A.; Witkowska, E.; Kowalska, A.; Skoczyńska, A.; Gawryszewska, I.; Guziewicz, E.; Snigurenko, D.; Waluk, J. Highly efficient SERS-based detection of cerebrospinal fluid neopterin as a diagnostic marker of bacterial infection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4319–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witkowska, E.; Szymborski, T.; Kamińska, A.; Waluk, J. Polymer mat prepared via forcespinning™ as a SERS platform for immobilization and detection of bacteria from blood plasma. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, J.H.; Schlotter, N.E.; Crawford, A.C.; Porter, M.D. Prospects for point-of-care pathogen diagnostics using surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3865–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naja, G.; Bouvrette, P.; Hrapovic, S.; Luong, J.H. Raman-based detection of bacteria using silver nanoparticles conjugated with antibodies. Analyst 2007, 132, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Dzink-Fox, J.L.; Chen, M.; Levy, S.B. Genetic characterization of highly fluoroquinolone-resistant clinical escherichia coli strains from china: Role ofacrr mutations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneiders, T.; Amyes, S.; Levy, S. Role of acrr and rama in fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from singapore. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2831–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liechti, G.; Kuru, E.; Hall, E.; Kalinda, A.; Brun, Y.; VanNieuwenhze, M.; Maurelli, A. A new metabolic cell-wall labelling method reveals peptidoglycan in chlamydia trachomatis. Nature 2014, 506, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, T.N.; Athamneh, A.I.; Senger, R.S. A study of the phenotypic responses of escherichia coli to multiple 4-carbon alcohols using raman spectroscopy. In Phenotypic And Metabolic Profiling Of Biological Samples In Near Real-Time Using Raman Spectroscopy; Virginia Tech: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2014; Volume 1001, p. 78. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.-T.; Lin, Y.-H.; Hung, C.-S.; Liu, T.-J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Wang, H.-H.; Wang, D.-W.; Wang, J.-K. A high speed detection platform based on surface-enhanced raman scattering for monitoring antibiotic-induced chemical changes in bacteria cell wall. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premasiri, W.; Chen, Y.; Williamson, P.; Bandarage, D.; Pyles, C.; Ziegler, L. Rapid urinary tract infection diagnostics by surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS): Identification and antibiotic susceptibilities. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3043–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Han, Y.-Y.; Shih, P.-H.; Lian, W.-N.; Wang, H.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Wang, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-L. Rapid bacterial antibiotic susceptibility test based on simple surface-enhanced raman spectroscopic biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Huang, W.E.; Zhang, B.-F.; Martin, F.L.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhang, K.-S.; Zhu, Y.-G. Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy for identification of heavy metal arsenic (v)-mediated enhancing effect on antibiotic resistance. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3164–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Pang, S.; Zhang, H.; Fan, M.; He, L. Characterization of lactococcus lactis response to ampicillin and ciprofloxacin using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, D.; Ivleva, N.P.; Mircescu, N.E.; Schubert, S.R.; Niessner, R.; Wieser, A.; Haisch, C. Label-free in situ discrimination of live and dead bacteria by surface-enhanced raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6553–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Al-Qadiri, H.M.; Lin, M.; Rasco, B.A. Application of mid-infrared and raman spectroscopy to the study of bacteria. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.I.; Goodacre, R. Metabolic fingerprinting in disease diagnosis: Biomedical applications of infrared and raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2006, 131, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodacre, R. Explanatory analysis of spectroscopic data using machine learning of simple, interpretable rules. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 32, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huang, Q.; Miller, W.G.; Aston, D.E.; Xu, J.; Xue, F.; Zhang, H.; Rasco, B.A.; Wang, S.; Konkel, M.E. Comprehensive detection and discrimination of campylobacter species by use of confocal micro-raman spectroscopy and multilocus sequence typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2932–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athamneh, A.; Alajlouni, R.; Wallace, R.; Seleem, M.; Senger, R. Phenotypic profiling of antibiotic response signatures in escherichia coli using raman spectroscopy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, N.; Chen, H.-C.; Gau, S.-L.; Lin, T.-H.; Lin, H.-S.; You, B.-J.; Tsai, P.-C.; Chen, I.-R.; Tsai, M.-F.; Wang, I.-K. Diagnosis of bacterial pathogens in the dialysate of peritoneal dialysis patients with peritonitis using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 461, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| SERS-Active Nanomaterial | Target Bacteria | LOD (CFU/mL) | LOQ (CFU/mL) | Sample Matrix | Detection Time | Chemometric Models | COMMENTS | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs | E. coli | 8.0 × 102 | N/A | N/A | 3.1 h | - | Direct, microfluidic | [51] |
| AgNPs | methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3.3 min | DFA, HCA | Direct, microfluidic concentration | [54] |
| AgNPs | M. tuberculosis | - | N/A | - | 1 h | PCA, LDA | Direct, microfluidic concentration | [55] |
| AuNP surface | K. pneumoniae | N/A | N/A | N/A | 30 min | PCA | Direct, fluoroquinolone-resistant | [56] |
| AgNPs | E. coli, A. calcoaceticus, B. megaterium, P. aeruginosa | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Direct | [57] |
| AgNPs | E. coli, S. cohnii | N/A | N/A | N/A | 10 s | N/A | Direct, convective assembly | [58] |
| AgNPs and AuNPs | E. coli, S. cohnii | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Direct, layer-by-layer deposition | [45] |
| AgNPs | E. coli, S. epidermidis | 2.5 × 102 | N/A | N/A | 10 min | HCA | Direct, in situ adsorption | [46] |
| AgNPs | E. coli, M. morganii, E. lactis, L. casei | NA | N/A | N/A | <5 min | PCA | Direct, in situ synthesis | [59] |
| Ag nanospheres | E. coli, S. typhimurium, S. aureus | 10 | N/A | N/A | N/A | CVA | Direct, self-assembly, Ag nanocrystals | [60] |
| Ag nanorods | A. baumannii, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | PCA, HCA, PLS-DA | Indirect, vancomycin-coated | [61] |
| Octupolar metastructures | Brucella | 104 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Indirect, bacteriophage, EBL fabrication | - |
| Au nanorods | E. coli | 3.5 × 101 | 3.5 × 102 | N/A | <2 h | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, biotin-avidin, magnetic core | [62] |
| Ag nanocubes | E. coli | 102 | N/A | N/A | - | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, polyclonal antibody | [63] |
| AgNPs, AuNPs, and Ag/Au core shell NP | E. coli O157:H7, S. Typhimurium, S. aureus | 102–103 | N/A | N/A | <30 min | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, aptamers, multiplex detection | [64] |
| Au “nanopopcorn” @ single wall carbon nanotubes | E. coli | 102 | 102 | N/A | - | N/A | Indirect, antibody, photothermal inactivation | [65] |
| AuNP @ graphene oxide | MRSA | 5 | N/A | N/A | - | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, photothermal inactivation | [66] |
| Au “nanoovals” | E. coli | 2.1×102 | N/A | Chicken broth, apple juice, soil solution | 50 s | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, antibody, DEP concentration | [67] |
| AuNPs | Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis | 5.0 × 102 | N/A | Milk | <24 h | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, antibody | [68] |
| Au “nanopopcorn” @ graphene oxide | MRSA | 10 | N/A | N/A | - | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, aptamer | - |
| Ag nanorod arrays | S. Enteritidis, S. enterica | 102 | N/A | Mung bean sprouts samples | - | PCA, PLS-DA | Indirect, vancomycin-coated surface | [69] |
| C | S. Typhimurium, S. aureus | 103 | N/A | Spinach | N/A | N/A | Indirect, antibody, Fe3O4/SiO2 secondary NPs | [70] |
| Ag/SiO2 core/shell NPs | S. Typhimurium | 108 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, antibody | [71] |
| Au “nanopopcorn” | S. Typhimurium DT 104 | 10 | N/A | Romaine lettuce | 5 min | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, monoclonal antibody | [72] |
| SiO2/Au and Au/Ag core/shell NPs | S. Typhimurium | 15 | 15 | Milk | N/A | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporters, aptamers | [73] |
| Au/Ag core–shell nanoparticles | V. parahaemolyticus | 10 | 10 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporters, aptamers | [74] |
| Au nanopopcorn | S. Typhimurium DT 104 | 10 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, antibody, photothermal inactivation | [75] |
| Fe3O4/Au core/shell NPs | S. Typhimurium, S. aureus | 15 | 102 | Pork sample | N/A | N/A | Indirect, aptamer, magnetic separation | [76] |
| MnFe2O4/Au core/shell | S. aureus | 10 | N/A | Apple, pear, and grapes peels | N/A | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, aptamer, magnetic separation | [77] |
| Au nanoaggregate-embedded beads | S. aureus | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter, antibody | [78] |
| AgNPs | S. aureus | 15 | 15 | Urine, blood, or pleural and ascites fluids | N/A | N/A | Direct, antibody, aptamer, Raman reporter | [79] |
| Fe3O4/Au core/shell NP | S. aureus | 1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Indirect, antibody, magnetic concentration/separation | [80] |
| Au/Ag core/shell nanorod arrays | S. xylosus, L. monocytogenes, E. faecium | 50 | N/A | N/A | PCA | N/A | Indirect, Raman reporter | [81] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Li, S.; Petersen, M.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. Detection and Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100762
Wang K, Li S, Petersen M, Wang S, Lu X. Detection and Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(10):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100762
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kaidi, Shenmiao Li, Marlen Petersen, Shuo Wang, and Xiaonan Lu. 2018. "Detection and Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy" Nanomaterials 8, no. 10: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100762
APA StyleWang, K., Li, S., Petersen, M., Wang, S., & Lu, X. (2018). Detection and Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials, 8(10), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100762