Green Preparation of High Yield Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Coal-Tar-Pitch by Mild Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
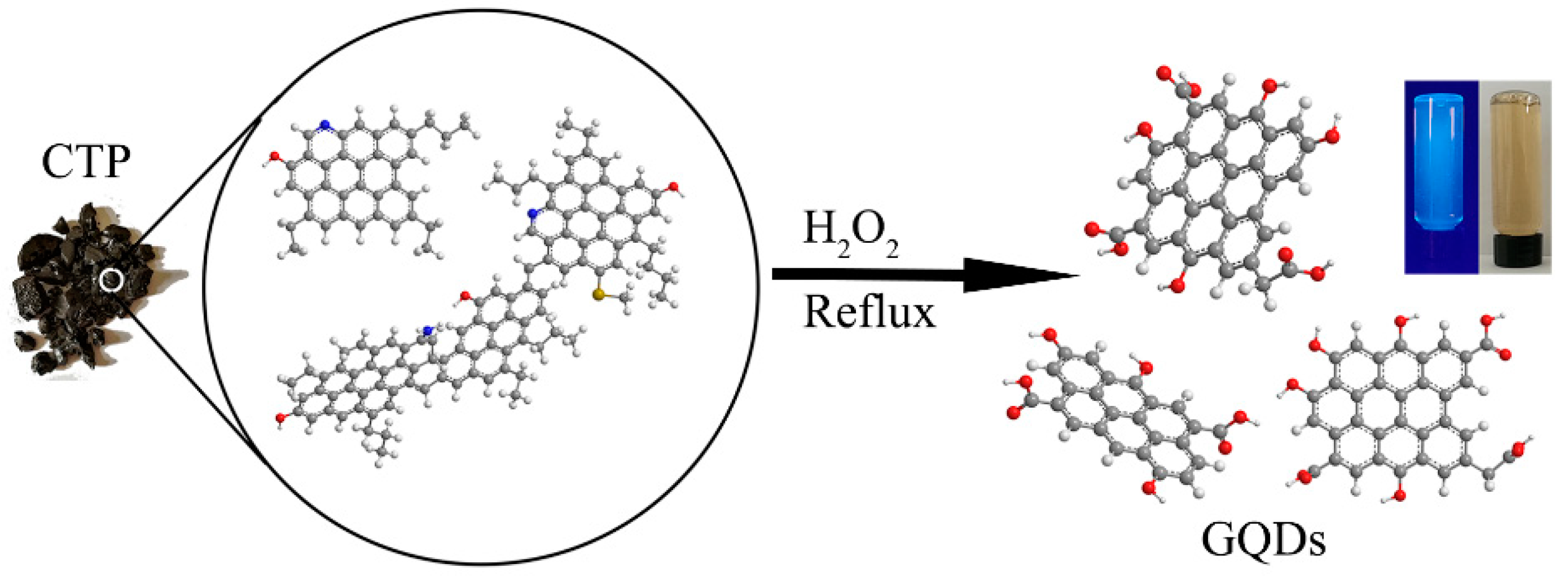
2.2. Preparation of GQDs
2.3. Characterization of GQDs
2.4. Product GQDs Yields Calculation
2.5. Relative QY Measurements
2.6. Energy Gap Calculation
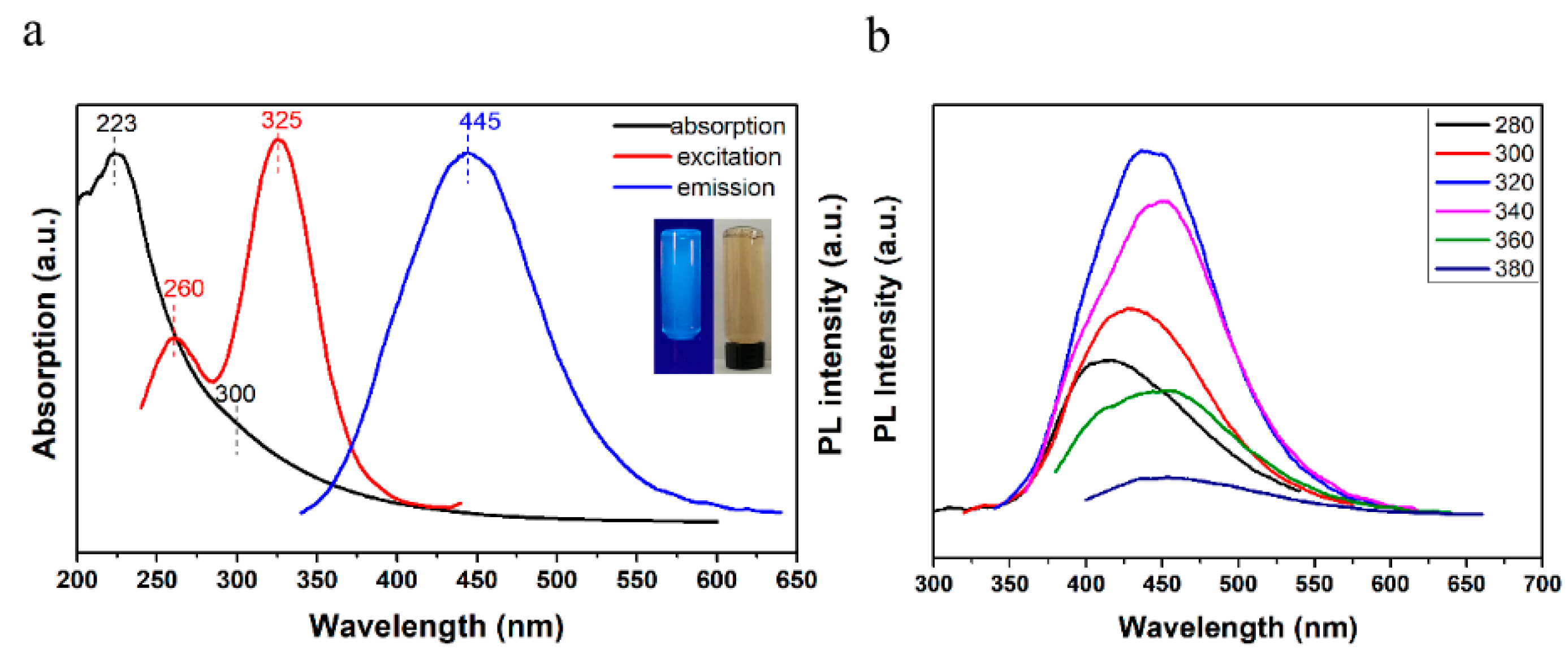
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geim, A.K. Graphene: Status and prospects. Science 2009, 324, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balandin, A.A. Thermal properties of graphene and nanostructured carbon materials. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castro Neto, A.H.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N.M.R.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 109–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soldano, C.; Mahmood, A.; Dujardin, E. Production, properties and potential of graphene. Carbon 2010, 48, 2127–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raccichini, R.; Varzi, A.; Passerini, S.; Scrosati, B. The role of graphene for electrochemical energy storage. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitounis, D.; Ali-Boucetta, H.; Hong, B.H.; Min, D.; Kostarelos, K. Prospects and Challenges of Graphene in Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Graphene and its derivatives for the development of solar cells, photoelectrochemical, and photocatalytic applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1362–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rui, M.; Song, J.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, H. Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots for Optoelectronic and Energy Devices: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Guo, S. Chemically doped fluorescent carbon and graphene quantum dots for bioimaging, sensor, catalytic and photoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Cui, W. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity toward Organic Pollutants Degradation and Mechanism Insight of Novel CQDs/Bi2O2CO3 Composite. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.T.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Luo, K.Q.; Chen, P. Glowing Graphene Quantum Dots and Carbon Dots: Properties, Syntheses, and Biological Applications. Small 2015, 11, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Smith, T.; Banaszak, A.; Boeckl, J. Graphene Quantum Dots Electrochemistry and Sensitive Electrocatalytic Glucose Sensor Development. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Hou, L.; Yuan, C. Green and Facile Synthesis of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots towards Fluorescent Ink and Sensing Applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Lv, G.; Hu, W.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Dai, Z. Synthesis and applications of graphene quantum dots: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018, 7, 157–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Ziccarelli, I.; Pistone, A. Graphene quantum dots: Multifunctional nanoplatforms for anticancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6471–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ji, R.; Cao, X.; Lin, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Teng, K.S.; Luk, C.M.; Zeng, S.; Hao, J.; et al. Deep Ultraviolet Photoluminescence of Water-Soluble Self-Passivated Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5102–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene Quantum Dots Derived from Carbon Fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, A.; Xu, Y.; Shan, F.; Li, A.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Barrow, C.; Liu, J. Graphene quantum dots directly generated from graphite via magnetron sputtering and the application in thin-film transistors. Carbon 2015, 88, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.; Hsu, C.L.; Chen, H.; Chang, C.; Kao, H.; Chou, L.C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Chang, W.; Tseng, S.; et al. Graphene quantum dots conjugated with polymers for two-photon properties under two-photon excitation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16874–16880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Xiang, C.; Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Huang, K.; Yan, Z.; Cook, N.P.; Samuel, E.L.G.; Hwang, C.; Ruan, G.; et al. Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumawat, M.K.; Thakur, M.; Gurung, R.B.; Srivastava, R. Graphene Quantum Dots from Mangifera indica: Application in Near-Infrared Bioimaging and Intracellular Nanothermometry. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 5, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, S.P.; Henry, L.; Yesilbag Tonga, G.; Huang, K.; Das, R.; Giroire, B.; Marre, S.; Rotello, V.M.; Penicaud, A.; Poulin, P.; et al. High Yield Synthesis of Aspect Ratio Controlled Graphenic Materials from Anthracite Coal in Supercritical Fluids. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5293–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal Route for Cutting Graphene Sheets into Blue-Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Fan, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, L.; Lv, Y.; Lin, J. One-step microwave synthesis of N-doped hydroxyl-functionalized carbon dots with ultra-high fluorescence quantum yields. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15281–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, P.; Liang, R.; Jabari, E.; Marzbanrad, E.; Toyserkani, E.; Zhou, Y.N. Single-step synthesis of graphene quantum dots by femtosecond laser ablation of graphene oxide dispersions. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8863–8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, S.; Palomares, E.; Martinez-Ferrero, E. Graphene and Carbon Quantum Dot-Based Materials in Photovoltaic Devices: From Synthesis to Applications. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Wei, M.; Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Xing, S. Tailoring Blue-Green Double Emissions in Carbon Quantum Dots via Co-Doping Engineering by Competition Mechanism between Chlorine-Related States and Conjugated π-Domains. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, D.B.; Pillai, V.K. Electrochemical Preparation of Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 12522–12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, J.; Yang, J.; Park, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, H. Mass Production of Graphene Quantum Dots by One-Pot Synthesis Directly from Graphite in High Yield. Small 2014, 10, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, M.; CoIlin, G. A review of the significance of polycyclic aromatic chemistry for pitch science. Fuel 1993, 72, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, Y.; Zhi, L.; Rouhanipour, A.; Andrienko, D.; Räder, H.J.; Müllen, K. Graphitic Nanoribbons with Dibenzo[e,l]pyrene Repeat Units: Synthesis and Self-Assembly. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 6878–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Chang, Q.; Xue, C.; Yang, J.; Hu, S. Full-colour carbon dots: From energy-efficient synthesis to concentration-dependent photoluminescence properties. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3074–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, A.M. Standards for photoluminescence quantum yield measurements in solution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 2213–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Rong, M.; Luo, F.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Luminescent graphene quantum dots as new fluorescent materials for environmental and biological applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 54, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.T.; Loo, A.H.; Sofer, Z.; Klímová, K.; Pumera, M. Coke-derived graphene quantum dots as fluorescence nanoquencher in DNA detection. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Somers, L.A.; Johnson, A.T.C. High Yield Preparation of Macroscopic Graphene Oxide Membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 898–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, X.; Li, J.; Wang, E. One-pot green synthesis of optically pH-sensitive carbon dots with upconversion luminescence. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5572–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, S.; Shao, M.; Lee, S. Upconversion and Downconversion Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots: Ultrasonic Preparation and Photocatalysis. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Shi, G.; Dai, L.; Qu, L. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Oxygen-Rich Functional Groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 134, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourissou, D.; Guerret, O.; Gabbaï, F.P.; Bertrand, G. Stable Carbenes. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 39–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, R. Trimethylene and the Addition of Methylene to Ethylene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 90, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Huang, G.; Xing, B.; Jia, J.; Zhang, C. Green Preparation of High Yield Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Coal-Tar-Pitch by Mild Oxidation. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100844
Liu Q, Zhang J, He H, Huang G, Xing B, Jia J, Zhang C. Green Preparation of High Yield Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Coal-Tar-Pitch by Mild Oxidation. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(10):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100844
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Quanrun, Jingjie Zhang, He He, Guangxu Huang, Baolin Xing, Jianbo Jia, and Chuanxiang Zhang. 2018. "Green Preparation of High Yield Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Coal-Tar-Pitch by Mild Oxidation" Nanomaterials 8, no. 10: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100844
APA StyleLiu, Q., Zhang, J., He, H., Huang, G., Xing, B., Jia, J., & Zhang, C. (2018). Green Preparation of High Yield Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Coal-Tar-Pitch by Mild Oxidation. Nanomaterials, 8(10), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100844





