Effects of Carbon Source on TiC Particles’ Distribution, Tensile, and Abrasive Wear Properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu Nanocomposites Prepared in the Al-Ti-C System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
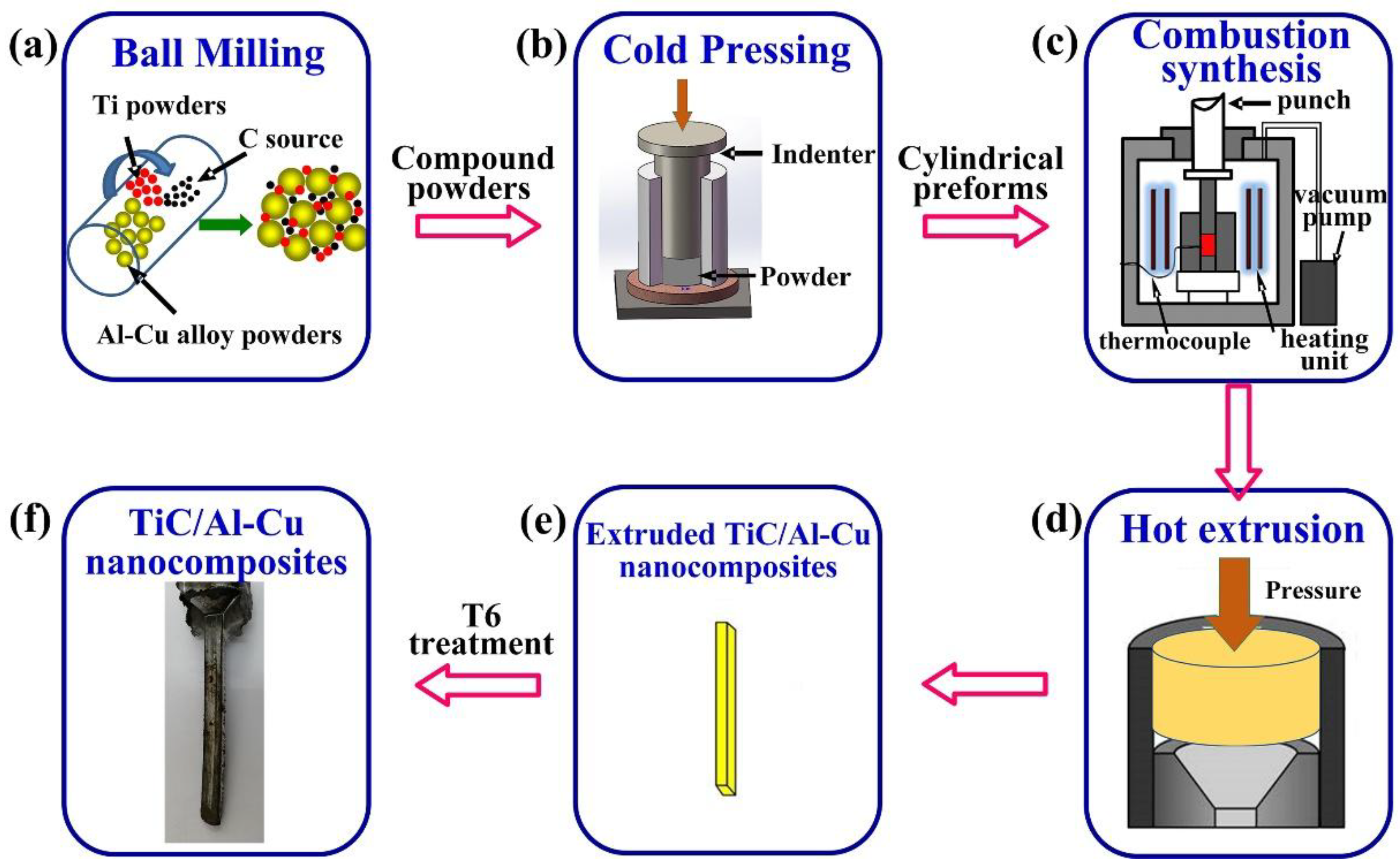
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
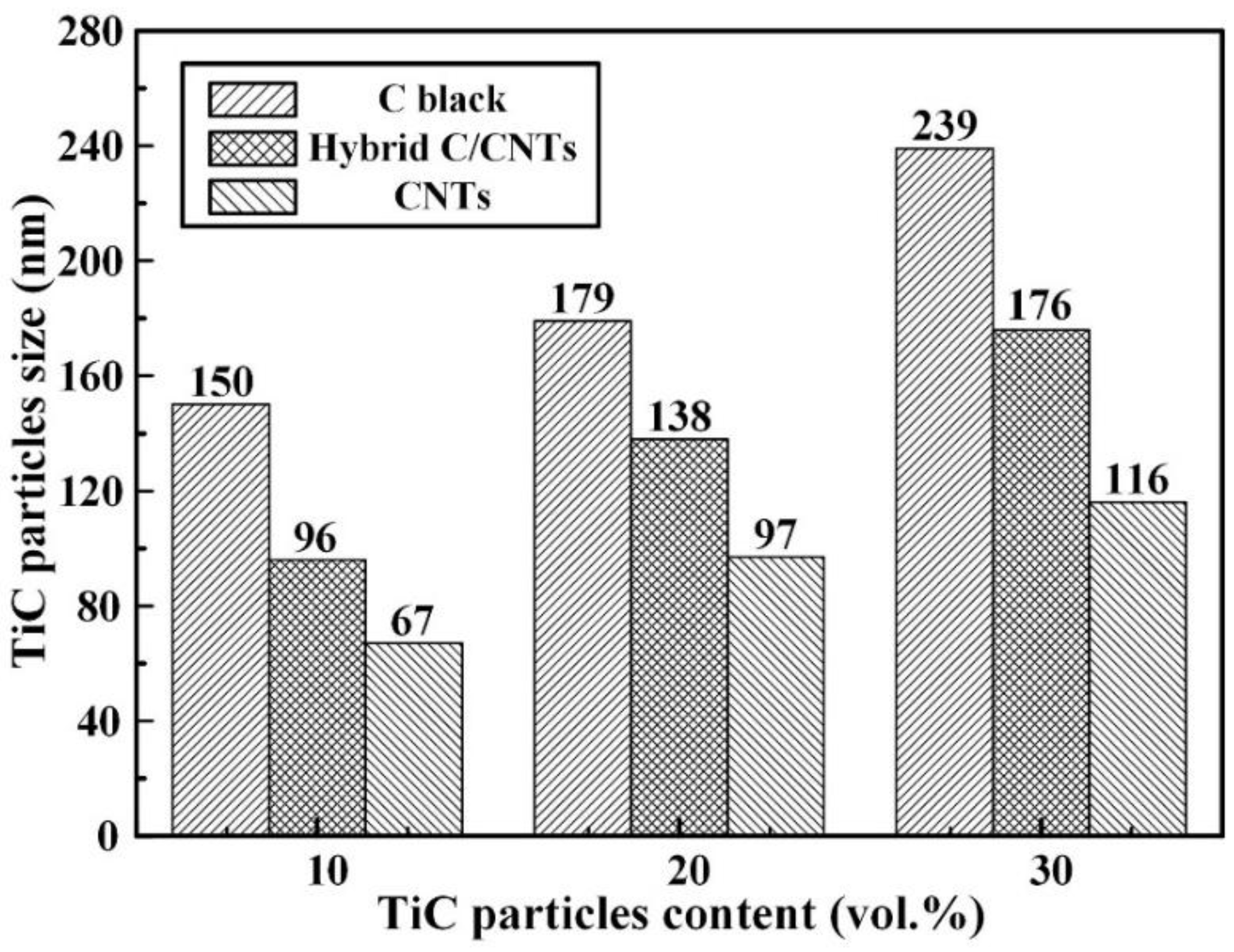
3.1. Microstructure and Mchanical Properties
3.2. Abrasive Wear Behaviors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toozandehjani, M.; Matori, K.A.; Ostovan, F.; Aziz, S.A.; Mamat, S.M. Effect of milling time on the microstructure, physical and mechanical properties of Al-Al2O3 nanocomposite synthesized by ball milling and powder metallurgy. Materials 2017, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Ma, X.; Chen, H.W.; Zhao, X.J.; Liu, X.F. Preferred orientation and interfacial structure in extruded nano-Al3BC/6061Al. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.; Mandal, A.; Deepak Kumar, S.; Bajpai, S.; Chakraborty, M.; West, G.D.; Srirangam, P. Effect of semi-solid forging on microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ cast Al-Cu-TiB2 composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, N.; Sivaraj, M.; Muthuraman, S. Microstructure characterization and thermal properties of Al-TiC sintered nano composites. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 107, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasali, E.; Fazili, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Ebadzadeh, T. Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-TiC metal matrix composite prepared by conventional, microwave and spark plasma sintering methods. Materials 2017, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozdniakov, A.V.; Lotfy, A.; Qadir, A.; Shalaby, E.; Khomutov, M.G.; Churyumov, A.Y.; Zolotorevskiy, V.S. Development of Al-5Cu/B4C composites with low coefficient of thermal expansion for automotive application. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.S.; Zhao, Q.L.; Zhao, C.J.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q.C. The dry sliding wear properties of nano-sized TiCp/Al-Cu composites at elevated temperatures. Materials 2017, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, I.; Afshar, A.; Ahmadi, S. Al2O3/Si3N4 nanocomposite coating on aluminum alloy by the anodizing route: Fabrication, characterization, mechanical properties and electrochemical behavior. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 12105–12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.S.; Yang, H.Y.; Tong, C.Z.; Qiu, F. Fabrication of TiCx-TiB2/Al composites for application as a heat sink. Materials 2016, 9, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, B.D.; Kim, Y.; Ahn, C.W.; Choi, J.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Yoon, W.H.; Park, D.S.; Yoon, S.Y.; Ma, B.J. Fabrication and characterization of aluminum nitride thick film coated on aluminum substrate for heat dissipation. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 18141–18147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, P.Y.; Hu, N.X.; Gong, Z.Z.; Ye, W.T.; Wei, Q.P.; Zhou, K.C.; Yu, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.F. A new design of composites for thermal management: Aluminium reinforced with continuous CVD diamond coated W spiral wires. Mater. Des. 2016, 101, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekner, B.; Myalski, J.; Pawlik, T.; Sopicka-Lizer, M. Effect of carbon in fabrication Al-SiC nanocomposites for tribological application. Materials 2017, 10, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.J.; Qiu, F.; Wang, J.G.; Wang, H.Y.; Jiang, Q.C. Microstructures and mechanical properties of the Al2014 composites reinforced with bimodal sized SiC particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 637, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, Y.; Kilicli, V. Abrasive wear behaviour of SiCp/Al alloy composite in comparison with ausferritic ductile iron. Wear 2011, 271, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, C.Y.; Chen, Z.; Ji, G.; Zhong, S.H.; Wu, Y.; Brisset, F.; Wang, H.W.; Ji, V. Microstructure study of cold rolling nanosized in-situ TiB2 particle reinforced Al composites. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkaya, S.; Canakci, A. Effect of the B4C content and the milling time on the synthesis, consolidation and mechanical properties of AlCuMg-B4C nanocomposites synthesized by mechanical milling. Powder Technol. 2016, 297, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wu, S.S.; Lü, S.L.; Duan, X.C.; Zhong, Z.Y. Preparation of in-situ TiB2 and Mg2Si hybrid particulates reinforced Al-matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 651, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaftelen, H.; Ünlü, N.; Göller, G.; Lütfi Öveçoglu, M.; Henein, H. Comparative processing-structure–property studies of Al-Cu matrix composites reinforced with TiC particulates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathula, S.; Anandani, R.C.; Dhar, A.; Srivastava, A.K. Microstructural features and mechanical properties of Al 5083/SiCp metal matrix nano- composites produced by high energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 545, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Dong, B.X.; Qiu, F.; Geng, R.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jiang, Q.C. The superior elevated-temperature mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Si composites reinforced with in situ hybrid-sized TiCx-TiB2 particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 728, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraj, M.; Selvakumar, N. Experimental analysis of Al–TiC sintered nanocomposite on EDM process parameters using ANOVA. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavros, H.; Karantzalis, A.E.; Lekatou, A. Solidification Observations and sliding wear behavior of cast TiC particulate-reinforced AlMgSi matrix composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, F.; Zhao, Q.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Jiang, Q.C. Simultaneously increasing the elevated-temperature tensile strength and plasticity of in situ nano-sized TiCp/Al-Cu-Mg composites. Mater. Charact. 2017, 125, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, R. Synthesis and tribological characterization of in situ cast Al-TiC composites. Wear 2005, 259, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, F.; Ouyang, L.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Zha, M.; Shu, S.L.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jiang, Q.C. A novel approach of using ground CNTs as the carbon source to fabricate uniformly distributed nano-sized TiCx/2009Al composites. Materials 2015, 8, 8839–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Qiu, F.; Shu, S.L.; Wang, L.; Chang, F.; Hu, W.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Q.C. Mechanical properties and abrasive wear behaviors of in situ nano-TiCx/Al–Zn–Mg–Cu composites fabricated by combustion synthesis and hot press consolidation. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.Y.; Huang, G.R.; Wang, K.K.; Chen, C.F.; Huang, J.C. High thermal dissipation of Al heat sink when inserting ceramic powders by ultrasonic mechanical coating and armoring. Materials 2017, 10, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.S.; Zhao, Q.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q.C. Enhanced strength and ductility at room and elevated temperatures of Al-Cu alloy matrix composites reinforced with bimodal-sized TiCp compared with monomodal–sized TiCp. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 724, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.S.; Zhao, Q.L.; Geng, R.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q.C. Improved creep resistance of Al-Cu alloy matrix composite reinforced with bimodal-sized TiCp. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 713, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.N.; Saha, S.C.; Datta, G.L.; Chakraborty, M. Studies on synthesis of in-situ Al-TiC metal matrix composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, N.; Khosroshahi, R.; Emamy, M.; Zolriasatein, A. Investigation of microstructure, hardness and wear properties of Al-4.5 wt.% Cu-TiC nanocomposites produced by mechanical milling. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3718–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.J.; Kandalova, E.G.; Nikitin, V.I. In situ synthesis of Al-TiC in aluminium melt. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2545–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.D.; Wang, H.Q.; Dai, D.H.; Chang, F. Densification behavior, microstructure evolution, and wear property of TiC nanoparticle reinforced AlSi10Mg bulk-form nanocomposites prepared by selective laser melting. J. Laser Appl. 2015, 27, S17003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.S.; Tang, J.; Qiu, F.; Wang, J.G.; Jiang, Q.C. Effects of nano-TiCp on the microstructures and tensile properties of TiCp/Al-Cu composites. Mater. Charact. 2014, 94, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazak, H.; Schoenstein, F.; Abdellaoui, M.; Jouini, N. Spark plasma sintering consolidation of nanostructured TiC prepared by mechanical alloying. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekatou, A.; Karantzalis, A.E.; Evangelou, A.; Gousia, V.; Kaptay, G.; Gácsi, Z.; Baumli, P.; Simon, A. Aluminium reinforced by WC and TiC nanoparticles (ex-situ) and aluminide particles (in-situ): Microstructure, wear and corrosion behaviour. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikici, B.; Gavgali, M.; Bedir, F. Synthesis of in situ TiC nanoparticles in liquid aluminum: The effect of sintering temperature. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, F.; Zhao, Q.L.; Zha, M.; Jiang, Q.C. Superior high creep resistance of in situ nano-sized TiCx/Al-Cu-Mg composite. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Li, S.F.; Imai, H.; Jia, L.; Umeda, J.; Takahashi, M.; Kondoh, K. An approach for homogeneous carbon nanotube dispersion in Al matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2015, 72, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najimi, A.A.; Shahverdi, H.R. Effect of milling methods on microstructures and mechanical properties of Al6061-CNT composite fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 702, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.B.; Shen, P.; Zhou, D.S.; Jiang, Q.C. Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of nano-TiCx particles with different shapes by using carbon nano-tube as C source. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Tong, H.T.; Gao, Y.Y.; Zou, Q.; Dong, B.X.; Li, Q.; Chu, J.G.; Chang, F.; Shu, S.L.; Jiang, Q.C. Microstructures and compressive properties of Al matrix composites reinforced with bimodal hybrid in-situ nano-/micro-sized TiC particles. Materials 2018, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindivan, H.; Kayali, E.S.; Cimenoglu, H. Tribological behavior of squeeze cast aluminum matrix composites. Wear 2008, 265, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisiol, C.; Jourani, A.; Bouvier, S. Effect of hardness, microstructure, normal load and abrasive size on friction and on wear behaviour of 35NCD16 steel. Wear 2017, 388–389, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Samples | Designed Composition | Actual TiC Content | Carbon Source | Used Powders (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10B | 10 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 8.9 vol.% | C black | 83.1% Al + 13.5% Ti + 3.4% C black |
| 10H | 10 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 9.0 vol.% | Hybrid C/CNTs | 83.1% Al + 13.5% Ti + 1.7% C black + 1.7% CNTs |
| 10C | 10 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 9.2 vol.% | CNTs | 83.1% Al + 13.5% Ti + 3.4% CNTs |
| 20B | 20 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 19.8 vol.% | C black | 68.7% Al + 25.0% Ti + 6.3% C black |
| 20H | 20 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 19.9 vol.% | Hybrid C/CNTs | 68.7% Al + 25.0% Ti + 3.15% C black + 3.15% CNTs |
| 20C | 20 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 19.9 vol.% | CNTs | 68.7% Al + 25.0% Ti + 6.3% CNTs |
| 30B | 30 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 29.8 vol.% | C black | 56.1% Al + 35.1% Ti + 8.8% C black |
| 30H | 30 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 29.9 vol.% | Hybrid C/CNTs | 56.1% Al + 35.1% Ti + 4.4% C black + 4.4% CNTs |
| 30C | 30 vol.% TiC/Al-Cu | 29.9 vol.% | CNTs | 56.1% Al + 35.1% Ti + 8.8% CNTs |
| Samples | σ0.2 (MPa) | σUTS (MPa) | εf (%) | Hardness (HV) | Actual Density (g/cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al alloy | 320 ± 6 | 468 ± 13 | 17.6 ± 2.8 | 135.7 ± 3 | 2.997 ± 0.001 |
| 10B | 394 ± 8 | 493 ± 12 | 2.5 ± 1.4 | 213.8 ± 5 | 2.814 ± 0.003 |
| 10H | 441 ± 6 | 570 ± 16 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 228.5 ± 8 | 3.249 ± 0.002 |
| 10C | 415 ± 7 | 553 ± 12 | 3.9 ± 2.0 | 199.3 ± 5 | 3.085 ± 0.002 |
| 20B | 426 ± 5 | 522 ± 10 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | 270.0 ± 4 | 3.293 ± 0.004 |
| 20H | 503 ± 8 | 636 ± 13 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 295.6 ± 9 | 3.575 ± 0.002 |
| 20C | 471 ± 9 | 591 ± 8 | 3.0 ± 1.3 | 269.9 ± 11 | 3.320 ± 0.003 |
| 30B | 470 ± 10 | 551 ± 9 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 303.3 ± 5 | 3.538 ± 0.004 |
| 30H | 531 ± 9 | 656 ± 12 | 3.0 ± 0.8 | 331.2 ± 5 | 3.555 ± 0.003 |
| 30C | 508 ± 7 | 616 ± 14 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 285.1 ± 6 | 3.599 ± 0.003 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.-Y.; Qiu, F.; Liu, T.-S.; Chu, J.-G.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Jiang, Q.-C. Effects of Carbon Source on TiC Particles’ Distribution, Tensile, and Abrasive Wear Properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu Nanocomposites Prepared in the Al-Ti-C System. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080610
Gao Y-Y, Qiu F, Liu T-S, Chu J-G, Zhao Q-L, Jiang Q-C. Effects of Carbon Source on TiC Particles’ Distribution, Tensile, and Abrasive Wear Properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu Nanocomposites Prepared in the Al-Ti-C System. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(8):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080610
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yu-Yang, Feng Qiu, Tian-Shu Liu, Jian-Ge Chu, Qing-Long Zhao, and Qi-Chuan Jiang. 2018. "Effects of Carbon Source on TiC Particles’ Distribution, Tensile, and Abrasive Wear Properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu Nanocomposites Prepared in the Al-Ti-C System" Nanomaterials 8, no. 8: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080610
APA StyleGao, Y.-Y., Qiu, F., Liu, T.-S., Chu, J.-G., Zhao, Q.-L., & Jiang, Q.-C. (2018). Effects of Carbon Source on TiC Particles’ Distribution, Tensile, and Abrasive Wear Properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu Nanocomposites Prepared in the Al-Ti-C System. Nanomaterials, 8(8), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080610






