Hydrothermal Synthesis of Cellulose-Derived Carbon Nanospheres from Corn Straw as Anode Materials for Lithium ion Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Synthesis
2.2. Material Characterizations
2.3. Electrochemical Measurement
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of CCS
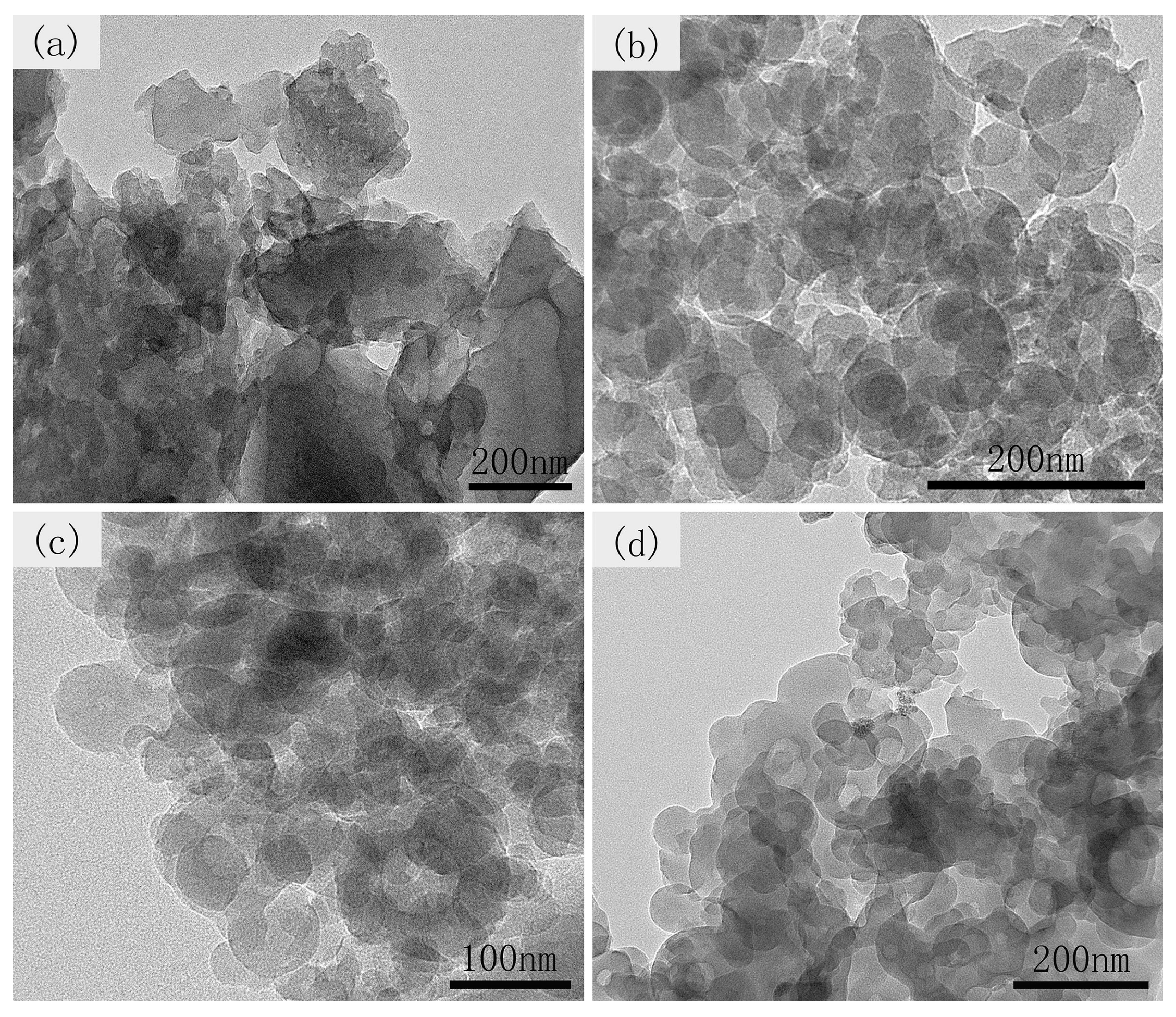
3.2. Characterization of CCS
3.3. Electrochemical Properties of CCS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.; Yang, J.; Bai, T.; Long, B.; Zhou, X. Biomass waste-derived honeycomb-like nitrogen and oxygen dual-doped porous carbon for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 192, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Hyeon, T. Recent progress in the synthesis of porous carbon materials. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2073–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, T.; Yang, H.; Wang, X. Characterization of products from hydrothermal liquefaction and carbonation of biomass model compounds and real biomass. J. Fuel Technol. 2011, 39, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Mokaya, R. Ordered mesoporous carbon hollow spheres nanocast using mesoporous silica via chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.J.F. New perspectives on the structure of graphitic carbons. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2005, 30, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Van, K.; Luong, T.T.T. Activated carbon derived from rice husk by NaOH activation and its application in supercapacitor. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2014, 24, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, J.Q.; Yuan, T.Q.; Sun, R.C. Preparation and characterization of lignocellulosic oil sorbent by hydrothermal treatment of populus fiber. Materials 2014, 7, 6733–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kothari, U.; Kong, L.; Lee, Y.Y.; Gupta, R.B. Hydrothermal pretreatment of switchgrass and corn stover for production of ethanol and carbon microspheres. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kim, S.; Heo, M.S.; Kim, J.E.; Suh, H.; Kim, I. Easy synthesis of hierarchical carbon spheres with superior capacitive performance in supercapacitors. Langmui 2013, 29, 12266–12274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J. Preparation and characterization of biobased graphene from kraft lignin. Bio Resour. 2017, 12, 6545–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yoshikawa, K.; Park, K.Y. Characteristics of biochar obtained by hydrothermal carbonization of cellulose for renewable energy. Energies 2015, 8, 14040–14048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Cui, W.J.; Jin, L.H.; Wang, C.X.; Xia, Y.Y. Preparation of three-dimensional ordered mesoporous carbon sphere arrays by a two-step templating route and their application for supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3661–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, G.A.; Fuertes, A.B.; Sevilla, M. N-doped microporous carbon microspheres for high volumetric performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 168, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Yushin, G. Review of nanostructured carbon materials for electrochemical capacitor applications: Advantages and limitations of activated carbon, carbide-derived carbon, zeolite-templated carbon, carbon aerogels, carbon nanotubes, onion-like carbon, and grapheme. WIREs Energy Environ. 2014, 3, 424–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.; Qi, H.; Yu, K.F.; Li, X. Formation mechanism and characterization of porous biomass carbon for excellent performance lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12666–12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B. The production of carbon materials by hydrothermal carbonization of cellulose. Carbon 2009, 47, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B.; Mokaya, R. High density hydrogen storage in superactivated carbons from hydrothermally carbonized renewable organic materials. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B. Graphitic carbon nanostructures from cellulose. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 490, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Maciá-Agulló, J.A.; Fuertes, A.B. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass as a route for the sequestration of CO2: Chemical and structural properties of the carbonized products. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3152–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, C.; Sieben, J.M.; Brun, N.; Sevilla, M.; van der Mauelen, T.; Morallón, E.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Titirici, M. Hydrothermal carbons from hemicellulose-derived aqueous hydrolysis products as electrode materials for supercapacitors. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Lee, S.W.; Liang, Z.; Lee, H.-W.; Yan, K.; Yao, H.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Chu, S.; Cui, Y. Interconnected hollow carbon nanospheres for stable lithium metal anodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, A.; Hernan, L.; Morales, J. Limitations of disordered carbons obtained from biomass as anodes for real lithium-ion batteries. Chemsuschem. 2011, 4, 658–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libra, J.A.; Ro, K.S.; Kammann, C.; Funke, A.; Berge, N.D.; Neubauer, Y.; Titirici, M.-M.; Fuhner, C.; Bens, O.; Kern, J.; et al. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass residuals: A comparative review of the chemistry, processes and applications of wet and dry pyrolysis. Biofuels 2011, 2, 71–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, S.; Song, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, W.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Aldhayan, D.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of hierarchically porous carbon spheres with yolk-shell structure for high performance supercapacitors. Catal. Today 2015, 243, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.P.; Liu, S.X. Carbon spheres obtained via citric acid catalysed hydrothermal carbonisation of cellulose. Mater. Res. 2013, 17, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.Q.; Cao, J.P.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhuang, Q.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Wei, X.Y. Preparation of porous carbon sphere from waste sugar solution for electric double-layer capacitor. J. Power Sources 2017, 361, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inada, M.; Enomoto, N.; Hojo, J.; Hayashi, K. Structural analysis and capacitive properties of carbon spheres prepared by hydrothermal carbonization. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Li, X.F.; Deng, J.; Gong, Y.T.; Wang, H.T.; Mao, S.J.; Wang, Y. Sustainable and scalable synthesis of monodisperse carbon nanospheres and their derived superstructures. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, Z.Z.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Rafique, R.F. Catalytic activation and application of micro-spherical carbon derived from hydrothermal carbonization of lignocellulosic biomass: Statistical analysis using box-behnken design. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102680–102694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y. Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2004, 43, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, R.; Dou, Y.; Wu, Z.; Huang, T.; Feng, D.; Yang, J.; Yu, A.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of mesoporous carbon spheres with a hierarchical pore structure for the electrochemical double-layer capacitor. Carbon 2011, 49, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Kang, Z.C. Graphitic structure and surface chemical activity of nanosize carbon spheres. Carbon 1997, 35, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.W.; Li, C.M.; Archer, L.A. Designed synthesis of coaxial SnO2@carbon hollow nanospheres for highly reversible lithium storage. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2536–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, G. Sustainable nitrogen-containing hierarchical porous carbon spheres derived from sodium lignosulfonate for high-performance supercapacitors. Carbon 2018, 132, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xia, H.; Zhou, J.; Xie, W. Nano-micro carbon spheres anchored on porous carbon derived from dual-biomass as high rate performance supercapacitor electrodes. J. Power Sources 2018, 381, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Preparation of mono-dispersed carbonaceous spheres via hydrothermal process. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2648–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, G. Porous nitrogen-doped carbon derived from peanut shell as anode material for lithium ion battery. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 9844–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.M.; Thomas, A.; Yu, S.H.; Müller, J.; Antonietti, M. A direct synthesis of mesoporous carbons with bi-continuous pore morphology from crude plant material by hydrothermal carbonization. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4205–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.M.; Antonietti, M.; Baccile, N. Hydrothermal carbon from biomass: A comparison of the local structure from poly-to monosaccharides and pentoses/hexoses. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Zhu, J.; Liao, L.; Scanlon, M.D.; Ge, P.; Ji, C.; Girault, H.H.; Liu, B. Nanocomposite of MoS2 on ordered mesoporous carbon nanospheres: A highly active catalyst for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 22, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Lama, F.; Puente-Santiago, A.R.; Caballero, A.; Balu, A.M.; Romero, A.A. Non-porous carbonaceous materials derived from coffee waste grounds as highly sustainable anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.L.; Zhang, K.Y.; Tian, N.; Qin, A.M.; Liao, L.; Du, R.; Wei, C. Biomass carbon derived from sisal fiber as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 2015, 142, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.M.; Buchholz, D.; Vaalma, C.; Giffin, G.A.; Passerini, S. Apple-biowaste-derived hard carbon as a powerful anode material for Na-ion batteries. Chem. Electr. Chem. 2016, 3, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrebola, J.C.; Caballero, A.; Hernan, L.; Morales, J.; Marin, M.O.; Serrano, V.G. Improving the performance of biomass-derived carbons in li-ion batteries by controlling the lithium insertion process. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A791–A797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, A.M.; Kumar, T.P.; Ramesh, R.; Thomas, S.; Jeong, S.K.; Nahm, K.S. Pyrolitic carbon from biomass precursors as anode materials for lithium batteries. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 430, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.F.; Li, J.; Qi, H.; Liang, C. Cellulose-derived hollow carbonaceous nanospheres from rice husks as anode for lithium-ion batteries with enhanced reversible capacity and cyclic performance. Chem. Select. 2017, 2, 3627–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.G.; Mao, C.P.; Wang, L.; Jia, M.; Sun, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M.W.; Lu, Z.S. Bio-inspired synthesis of carbon hollow microspheres from a spergillus flavus conidia for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 59655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Ye, J.C.; Fang, X.L.; Zhang, X.W.; Zheng, M.S.; Dong, Q.F. Hollow-in-hollow carbon spheres for lithium-ion batteries with superior capacity and cyclic performance. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 186, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.T.; Zhang, Z.F.; Wu, T.Y.; Xue, Y. Nanoporous carbon microspheres as anode material for enhanced capacity of lithium ion batteries. Ionics 2018, 24, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Material | C Rate | Specific Capacity/ mA h g−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porous carbon from peanut shell | 0.1 | 180 | [37] |
| Carbon particle from coffee waste | 0.27 | 285 | [41] |
| Honeycomb carbon from sisal fiber | 0.1 | 530 | [42] |
| Carbon particle from apple waste | 0.1 | 245 | [43] |
| Carbon from cherry stones | 5 | 200 | [44] |
| Carbon sheet from banana fiber | 0.1 | 310 | [45] |
| Carbon Nanospheres Type | Particle Size/nm | Specific Area/m2 g−1 | C Rate | Specific Capacity/mA h g−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hollow nanospheres | 50–150 | 369.44 | 0.2 | 489 | [46] |
| Hollow microspheres | 1000–3000 | 309.9 | 0.27 | 475 | [47] |
| Hollow-in-hollow | 350 | 1190.1 | 0.27 | 973 | [48] |
| Nanoporous microspheres | 700 | 2798.9 | 1.08 | 780 | [49] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, K.; Wang, J.; Song, K.; Wang, X.; Liang, C.; Dou, Y. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Cellulose-Derived Carbon Nanospheres from Corn Straw as Anode Materials for Lithium ion Batteries. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010093
Yu K, Wang J, Song K, Wang X, Liang C, Dou Y. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Cellulose-Derived Carbon Nanospheres from Corn Straw as Anode Materials for Lithium ion Batteries. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(1):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010093
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Kaifeng, Jingjing Wang, Kexian Song, Xiaofeng Wang, Ce Liang, and Yanli Dou. 2019. "Hydrothermal Synthesis of Cellulose-Derived Carbon Nanospheres from Corn Straw as Anode Materials for Lithium ion Batteries" Nanomaterials 9, no. 1: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010093
APA StyleYu, K., Wang, J., Song, K., Wang, X., Liang, C., & Dou, Y. (2019). Hydrothermal Synthesis of Cellulose-Derived Carbon Nanospheres from Corn Straw as Anode Materials for Lithium ion Batteries. Nanomaterials, 9(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010093






