Cell Imaging Using Two-Photon Excited CdS Fluorescent Quantum Dots Working within the Biological Window
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of CdS QDs
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3. Optical Characterization
2.4. Cell Viability and Cellular Uptake of CdS QDs
2.5. Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.6. Numerical Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. First Principle Calculations Based on Density Functional Theory
3.2. Morphological and Structural Characterization
3.3. Optical Properties
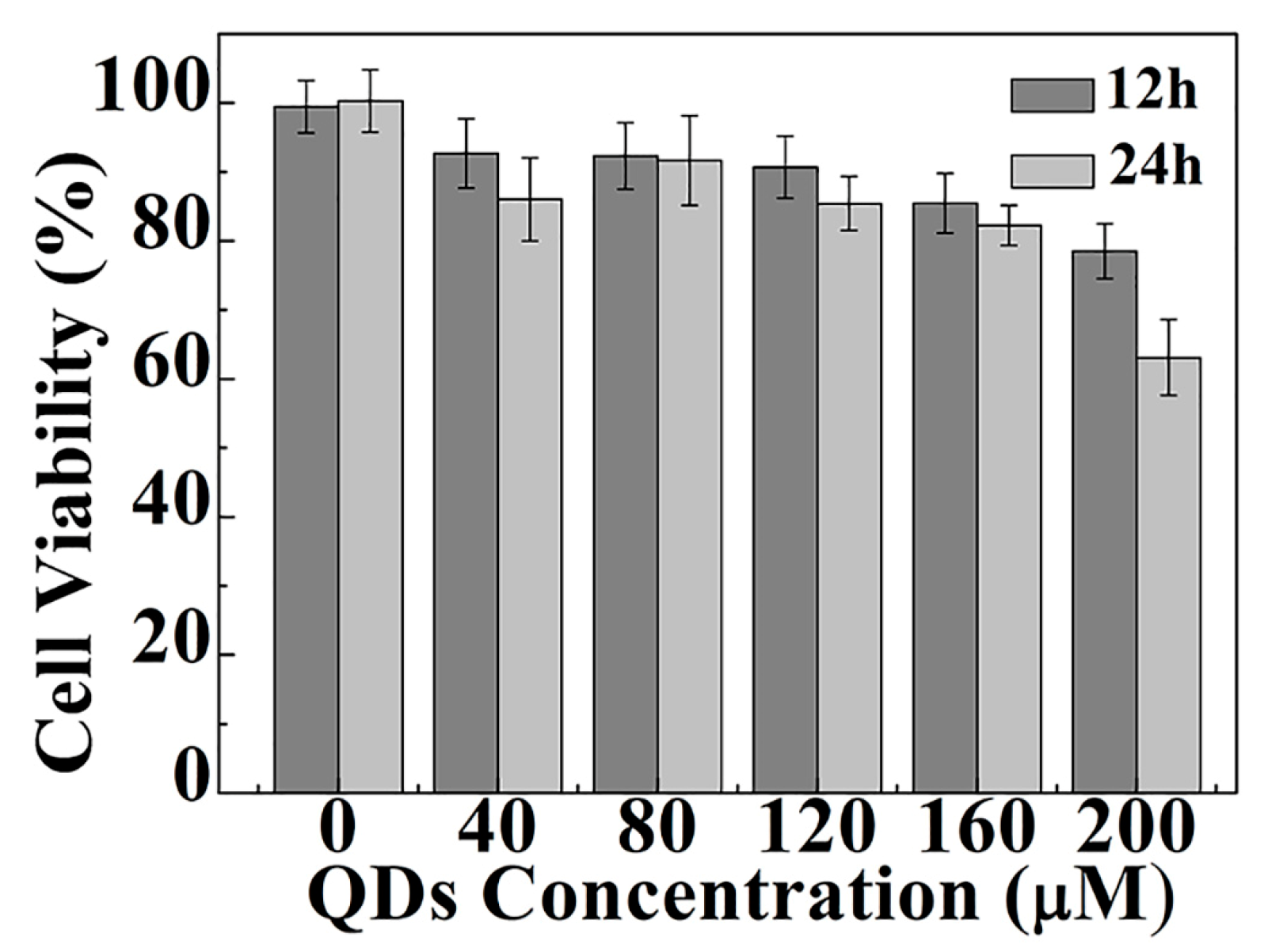
3.4. Cellular Toxicity of CdS QDs in HepG2 Cells
3.5. Interaction between the CdS QDs and HepG2 Cells
3.6. Two-Photon Excitation Bioimaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dehghani, A.; Ardekani, S.M.; Hassan, M.; Gomes, V.G. Collagen derived carbon quantum dots for cell imaging in 3D scaffolds via two-photon spectroscopy. Carbon 2018, 131, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Lamon, S. Nanomaterials for optical data storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltaev, G.S.; Fu, D.J.; Sobirov, B.R.; Smirnov, M.S.; Ovchinnikov, O.V.; Zvyagin, A.I.; Ganeev, R.A. Optical limiting, nonlinear refraction and nonlinear absorption of the associates of Cd0.5Zn0.5S quantum dots and dyes. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 13865–13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Yeh, T.F.; Teng, H.; Chen, S.J. Three-dimensional patterned graphene oxide-quantum dot microstructures via two-photon crosslinking. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4970–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestro, L.; Ramirez-Hernandez, J.; Bogdan, N.; Capobianco, J.; Vetrone, F.; Solé, J.G.; Jaque, D. Deep tissue bio-imaging using two-photon excited CdTe fluorescent quantum dots working within the biological window. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Singhal, A.; Kim, B.Y.; Zheng, J.; Rutka, J.T.; Chan, W.C.W. Assessing near-infrared quantum dots for deep tissue, organ, and animal imaging applications. J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2008, 13, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.C.W.; Nie, S.M. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 1998, 281, 2016–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalet, X.; Pinaud, F.F.; Bentolila, L.A.; Tsay, J.M.; Doose, S.; Li, J.J.; Sundaresan, G.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Weiss, S. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 2005, 307, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, K.T.; Law, W.C.; Roy, I.; Jing, Z.; Huang, H.; Swihart, M.T.; Prasad, P.N. Aqueous phase synthesis of CdTe quantum dots for biophotonics. J. Biophotonics 2011, 4, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Califano, M.; Franceschetti, A.; Zunger, A. Temperature dependence of excitonic radiative decay in CdSe quantum dots: The role of surface hole traps. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veamatahau, A.; Jiang, B.; Seifert, T.; Makuta, S.; Latham, K.; Kanehara, M.; Teranishi, T.; Tachibana, Y. Origin of surface trap states in CdS quantum dots: Relationship between size dependent photoluminescence and sulfur vacancy trap states. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 2850–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, B.D.; Rao, Z.Y.; Zhang, B.H.; Gong, J.R. Strong Two-Photon-Induced Fluorescence from Photostable, Biocompatible Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Cellular and Deep-Tissue Imaging. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yao, Y.; Chen, Y.S. Imaging and Quantifying the Morphology and Nanoelectrical Properties of Quantum Dot Nanoparticles Interacting with DNA. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummen, G.P.C. Quantum Dots-From Synthesis to Applications in Biomedicine and Life Sciences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.H.Y.; Evans, C.M.; Swartz, B.D.; Neukirch, A.J.; Young, J.; Prezhdo, O.V.; Krauss, T.D. Colloidal Semiconductor Quantum Dots with Tunable Surface Composition. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4465–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruchez, M.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss, S.; Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.W.; Hildebrandt, N. Semiconductor quantum dots for in vitro diagnostics and cellular imaging. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Shuhendler, A.; Ye, D.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Two-photon excitation nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6725–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.Y.; Hu, M.; Fan, C.H.; He, Y.; Li, Q.N.; Li, W.X.; Wang, L.H.; Shen, P.P.; Huang, Q. The cytotoxicity of CdTe quantum dots and the relative contributions from released cadmium ions and nanoparticle properties. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4829–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Li, S. Size, dimensionality, and constituent stoichiometry dependence of bandgap energies in semiconductor quantum dots and wires. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 2851–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Xia, W.X.; Zhou, L.Y.; Gong, F.Z.; Wu, L.L. Novel quantum dots: Water-based CdTeSe/ZnS and YAG hybrid phosphor for white light-emitting diodes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Song, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhong, L.; Liu, J.; Qi, Y. Greener synthesis and optimization of highly photoluminescence Mn2+-doped ZnS quantum dots. J. Lumin. 2015, 158, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.H.; Le, Q.; Lan, S.; Liang, J.X.; Tie, S.L.; Xu, J.L. Modifying the mechanical properties of gold nanorods by copper doping and triggering their cytotoxicity with ultrasonic wave. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 163, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, J. Ab initio modeling of quantum transport properties of molecular electronic devices. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 245407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiri, L.; Patla, I.; Acharya, S.; Golan, Y.; Efrima, S. Raman spectroscopy of ultranarrow CdS nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11843–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckel, J.S.; Zimmer, J.P.; Coe-Sullivan, S.; Stott, N.E.; Bulovic, V.; Bawendi, M.G. Blue luminescence from (CdS)ZnS core-shell nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2154–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanhel, L.; Haase, M.; Weller, H.; Henglein, A. Photochemistry of colloidal semiconductors. Part 20. Surface modification and stability of strong luminescing CdS particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 5649–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Feng, G.Y.; Dai, S.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.H. Femtosecond pulsed laser ablation in microfluidics for synthesis of photoluminescent ZnSe quantum dots. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Qu, L.H.; Guo, W.Z.; Peng, X.G. Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2854–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.H.; Djouahra, S.; Tilley, R.D. Controlled formation of 3D CdS nanocrystal superlattices in solution. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3035–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, U.; Eich, D.; Chen, Z.H.; Fink, R.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Umbach, E. Thermal behaviour of CdS nanoparticles investigated by high resolution photoelectron spectroscopy. Phys. Status Solidi A 1999, 173, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasieniak, J.; Mulvaney, P. From Cd-rich to Se-rich-the manipulation of CdSe nanocrystal surface stoichiometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, J.; Kuruvilla, B.A.; Sarma, D.D. Photoelectron spectroscopic study of CdS nanocrystallites. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 7473–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, U.; Eich, D.; Chen, Z.; Fink, R.; Kulkarni, S.; Umbach, E. Detailed investigation of CdS nanoparticle surfaces by high-resolution photoelectron spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 306, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasieniak, J.; Califano, M.; Watkins, S.E. Size-Dependent Valence and Conduction Band-Edge Energies of Semiconductor Nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5888–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chestnoy, N.; Harris, T.D.; Hull, R.; Brus, L.E. Luminescence and photophysics of cadmium sulfide semiconductor clusters: The nature of the emitting electronic state. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 3393–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.F.; Xu, C.X.; Dai, J.; Li, J.T.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, P.L. Improved UV photoresponse of ZnO nanorod arrays by resonant coupling with surface plasmons of Al nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3396–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.Y.; Ripmeester, J.A.; Wu, X.H.; Kingston, D.; Yu, K.; Joly, A.G.; Chen, W. Upconversion luminescence of colloidal CdS and ZnCdS semiconductor quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 16261–16266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, V.; Chibli, H.; Fiammengo, R.; Galeone, A.; Malvindi, M.A.; Vecchio, G.; Cingolani, R.; Nadeau, J.L.; Pompa, P.P. InP/ZnS as a safer alternative to CdSe/ZnS core/shell quantum dots: In vitro and in vivo toxicity assessment. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Roy, I.; Yong, K.T.; Pudavar, H.E.; Prasad, P.N. High-resolution light microscopy using luminescent nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 2, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


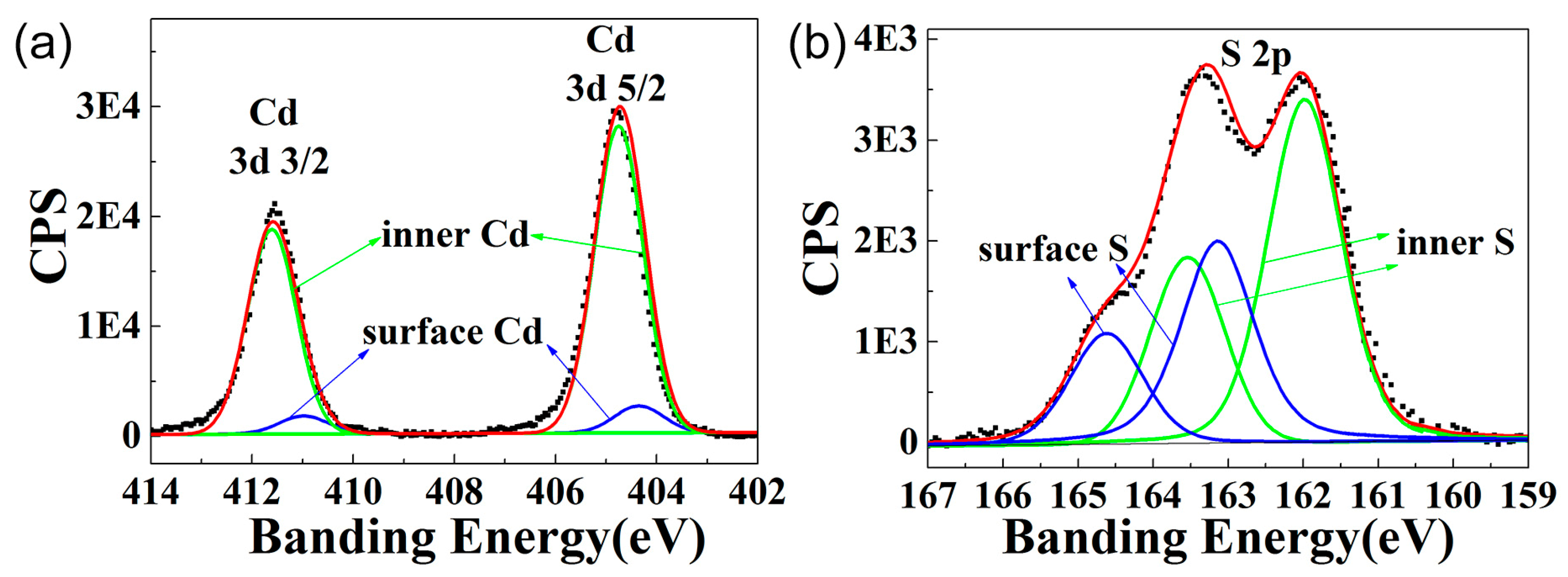



| QDs | C1s% | Cd3d% | S2p% | Cd/S Ratio | Cds/Cdi | Ss/Si | Cds/Ss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdS | 85.61 | 6.50 | 7.89 | 0.83 | 0.086 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Sample | (nm) | (nm) | (nm) | Φ (%) | UCL Γ (ns) | σ2 (GM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R6G | 425 | 800 | 553 | 95 | - | 39.90 |
| CdS | 425 | 800 | 640 | 8.14 | 1.68 | 54.33 |
| Sample | (b) | (f) | (c) | (g) | (d) | (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (cell) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Intensity (min) | 11 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 11 | 96 |
| Intensity (max) | 110 | 99 | 3 | 89 | 110 | 179 |
| Intensity (mean) | 37.7 | 31.2 | 1.0 | 38.2 | 37.7 | 133.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Wei, Z.; Liu, H.; Peng, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Fan, H. Cell Imaging Using Two-Photon Excited CdS Fluorescent Quantum Dots Working within the Biological Window. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030369
Zhang N, Liu X, Wei Z, Liu H, Peng J, Zhou L, Li H, Fan H. Cell Imaging Using Two-Photon Excited CdS Fluorescent Quantum Dots Working within the Biological Window. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(3):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030369
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Nannan, Xiao Liu, Zhongchao Wei, Haiying Liu, Jie Peng, Liya Zhou, Hongmei Li, and Haihua Fan. 2019. "Cell Imaging Using Two-Photon Excited CdS Fluorescent Quantum Dots Working within the Biological Window" Nanomaterials 9, no. 3: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030369
APA StyleZhang, N., Liu, X., Wei, Z., Liu, H., Peng, J., Zhou, L., Li, H., & Fan, H. (2019). Cell Imaging Using Two-Photon Excited CdS Fluorescent Quantum Dots Working within the Biological Window. Nanomaterials, 9(3), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030369






