Oxalic Acid-Induced Photodissolution of Ferrihydrite and the Fate of Loaded As(V): Kinetics and Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Fhy and Fhy*-As(V)
2.2. Photodissolution Kinetics
2.3. Solution Analysis and Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
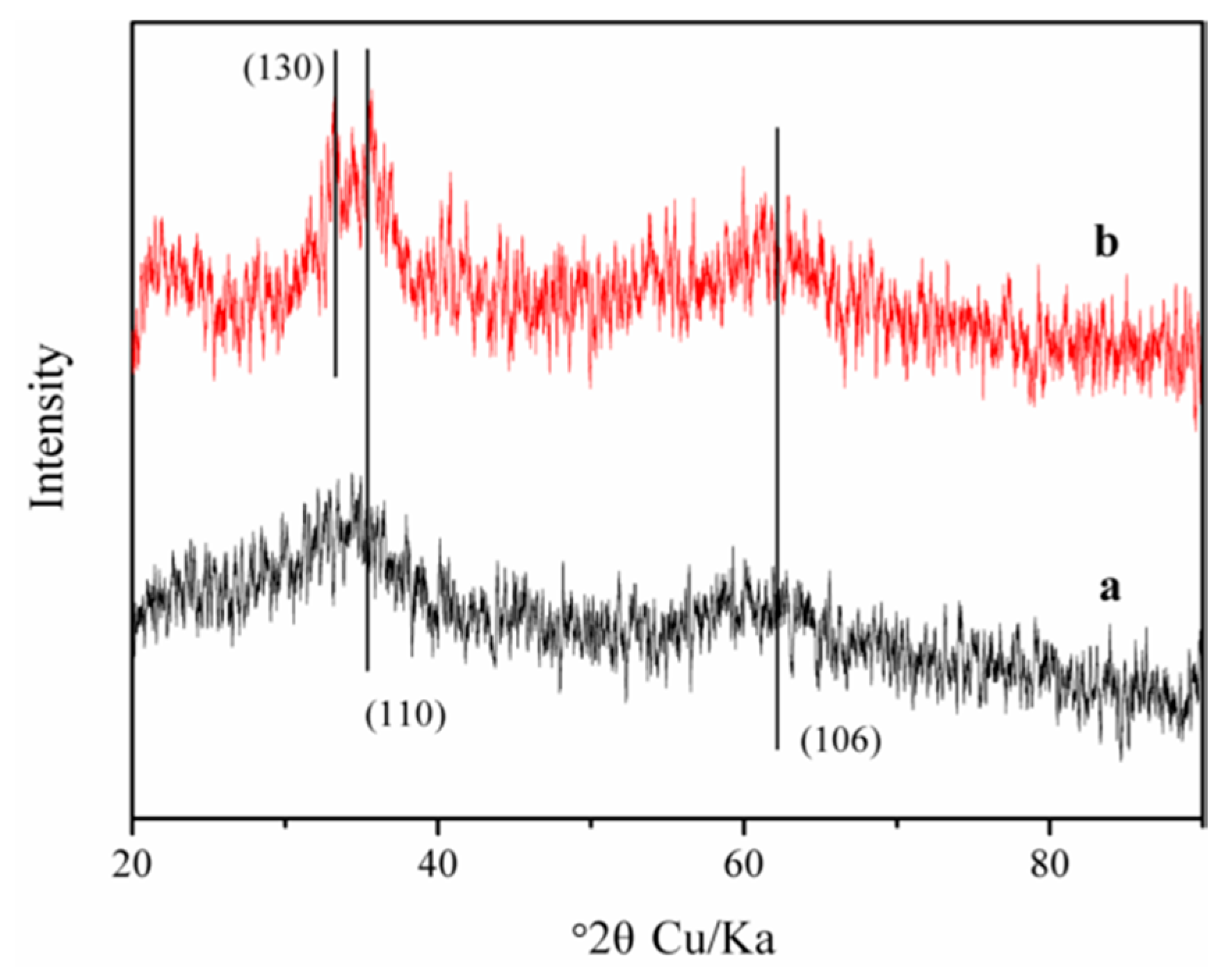
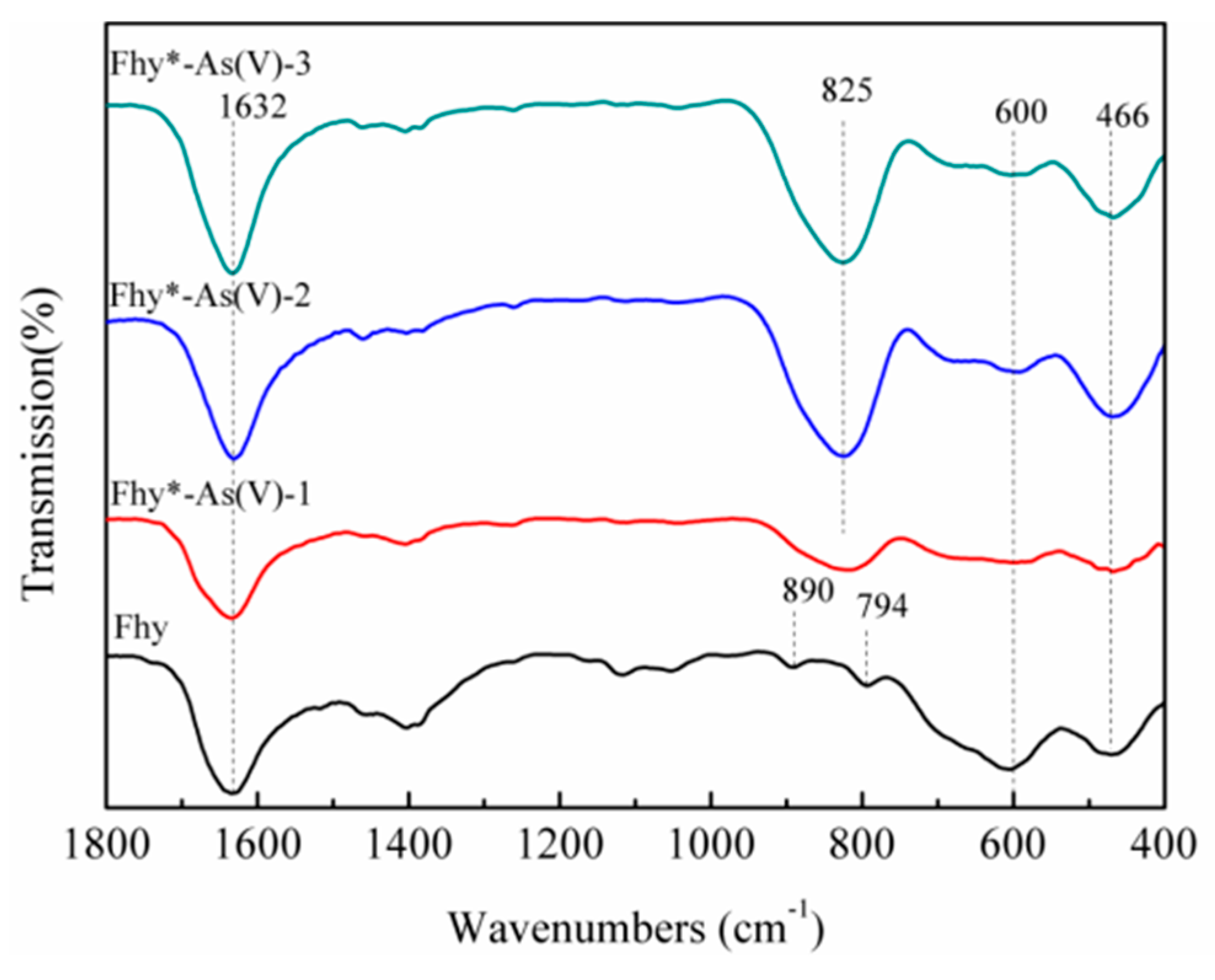
3.1. Characterization of Fhy and Fhy*-As(V)
3.2. Effect of Oxalic Acid on the Photodissolution of Fhy
3.3. Effect of UV/Oxalate on the Dissolution of Fhy*-As(V) and the Mobilization of As(V)
3.4. Mechanism of Photodissolution and As(V) Fate in the System of Fhy*-As(V)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ahsan, H. Cancer burden from asenic in drinking water in Banladesh. Am. J. Public Health 2004, 94, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duker, A.A.; Carranza, E.J.; Hale, M. Arsenic geochemistry and health. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents-A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, F.; Ueta, E.; Kawasaki, N. Characteristics of a novel adsorbent Fe–Mg-type hydrotalcite and its adsorption capability of As(III) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 59, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.I.; Naushad, M.; Chaudhry, S.A. Promising prospects of nanomaterials for arsenic water remediation: A comprehensive review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 60–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.T.; Ji, Z.Y.; Wu, S.H.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.M.; Jia, S.Y. Photoreductive dissolution of schwertmannite induced by oxalate and the mobilization of adsorbed As(V). Chemosphere 2018, 208, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.T.; Han, J.; Li, T.T.; Sun, F.; Lin, J.H.; Lou, C.W. Visible light-induced oxidation of aqueous arsenite using facile Ag2O/TiO2 composites: Performance and mechanism. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 377, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asere, T.G.; Stevens, C.V.; Laing, G.D. Use of (modified) natural adsorbents for arsenic remediation: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.L.; Liu, M.Z.; Wang, N.N.; Li, G.J. A critical review on arsenic removal from water using iron-based adsorbents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 39545–39560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, K.P.; Jain, A.; Loeppert, R.H. Arsenite and arsenate on ferrihdrite: Kinetics, equilibrium, and adsorption envelopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.R.; Zhang, L.M.; Wan, G.P.; Shan, X.; Deng, J.S.; Luo, Y.M. Adsorption performance and mechanism of As(V) uptake over mesoporous Y-Al binary oxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2016, 65, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbs, J.J.; Berqerquó, T.S.; Reinsch, B.C.; Lowry, G.V.; Banerjee, S.K.; Penn, R.L. Reductive dissolution of arssenic-bearing ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 3382–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendorf, S.; Michael, H.A.; Van Geen, A. Spatial and temporal variations of ground water arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science 2010, 328, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banwart, S.; Davies, S.; Stumm, W. The role of oxalic acid in accelerating the reductive dissolution of hematite (α-Fe2O3) by ascorbate. Colloids Surf. 1989, 39, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzberger, B.; Laubscher, H. Reactivity of various types of iron(III) (hydr)oxides towards light-induced dissolution. Mar. Chem. 1995, 50, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borer, P.M.; Sulzberger, B.; Reichard, P.; Kraemer, S.M. Effect of siderophores on the light-induced dissolution of colloidal iron (III)(hydr)oxides. Mar. Chem. 2005, 93, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borer, P.; Sulzberger, B.; Hug, S.J.; Kraemer, S.M.; Kretzschmar, R. Photoreductive dissolution of iron(III) (hydr)oxides in the absence and presence of organic ligands: Experimental studies and kinetic modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borer, P.; Kraemer, S.M.; Sulzberger, B.; Hug, S.J.; Kretzschmar, R. Photodissolution of lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH) in the presence of desferrioxamine B and aerobactin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4673–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, P.U.; Kretzschmar, R.; Kraemer, S.M. Dissolution mechanisms of goethite in the presence of siderophores and organic acids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 5635–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, M.E.; Sulzerger, B. Atrazine degradation in irradiated iron/oxalate systems: Effects of pH and oxalate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Liu, C.S.; Li, F.B.; Li, X.M.; Zhou, S.G.; Liu, T.X.; Gu, M.H.; Wu, Q.T. Photogradation of orange I in the heterogeneous iron oxide-oxalate complex system under UVA irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.B.; Li, X.Z.; Liu, C.S.; Li, X.M.; Liu, T.X. Effect of oxalate on photodegradation of Bisphenol A at the interface of different iron oxides. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, F.B.; Zeng, F.; Liu, C.S. Effect of pH on pentachlorophenol degradation in irradiation in irradiated iron/oxalate systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, P.; Lan, Y.; Zhou, L. Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in schwertmannite/oxalate suspension under UV irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Jia, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.H.; Han, X. Mobilization and re-adsorption of arsenate on ferrihydrite and hematite in the presence of oxalate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, R.K.; Zheng, Y.; Rubenstone, J.; van Geen, A. A rapid colorimetric method for measuring arsenic concentrations in groundwater. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 526, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, L.L. Ferrozine—A new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, E.D.; Bush, R.T.; Sullivan, L.A.; Mitchell, D.R.G. Schwertmannite transformation to goethite via the Fe(II) pathway: Reaction rates and implications for iron-sulfide formation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4551–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambier, P. Infrared study of goethites of varying crystallinity and particle size: I. Interpretation of OH and lattice vibration frequencies. Clay Miner. 1986, 21, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, N.; Hausner, D.B.; Kubicki, J.D.; Strongin, D.R. Photodissolution of ferrihydrite in the presence of oxalic acid: An in situ ATR-FTIR/DFT study. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16246–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eick, M.J.; Peak, J.D.; Brady, W.D. The effect of oxyanions on the oxalate-promoted dissolution of goethite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| No. | As(V) Loading (mg g−1) |
|---|---|
| Fhy*-As(V)-a | 99.9 |
| Fhy*-As(V)-b | 146.8 |
| Fhy*-As(V)-c | 196.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, H.-T.; Han, J.; Li, T.-T.; Lin, Q.; Lin, J.-H.; Lou, C.-W. Oxalic Acid-Induced Photodissolution of Ferrihydrite and the Fate of Loaded As(V): Kinetics and Mechanism. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081143
Ren H-T, Han J, Li T-T, Lin Q, Lin J-H, Lou C-W. Oxalic Acid-Induced Photodissolution of Ferrihydrite and the Fate of Loaded As(V): Kinetics and Mechanism. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(8):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081143
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Hai-Tao, Jing Han, Ting-Ting Li, Qi Lin, Jia-Horng Lin, and Ching-Wen Lou. 2019. "Oxalic Acid-Induced Photodissolution of Ferrihydrite and the Fate of Loaded As(V): Kinetics and Mechanism" Nanomaterials 9, no. 8: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081143
APA StyleRen, H.-T., Han, J., Li, T.-T., Lin, Q., Lin, J.-H., & Lou, C.-W. (2019). Oxalic Acid-Induced Photodissolution of Ferrihydrite and the Fate of Loaded As(V): Kinetics and Mechanism. Nanomaterials, 9(8), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081143







