Amperometric Self-Referencing Ceramic Based Microelectrode Arrays for D-Serine Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. MEA Preparation
2.3. Enzyme Preparation and Immobilization
2.4. Electropolymerization of Meta-Phenylenediamine (mPD)
2.5. In Vitro Calibration and Recording Parameters
2.6. Surgery and Freely Moving Test of the D-Serine MEAs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. In Vitro Calibration Results
3.2. Selectivity
3.3. Other D-Amino Acids
3.4. RgDAAO vs. pkDAAO
3.5. Freely Moving Measurement of D-Serine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashimoto, A.; Nishikawa, T.; Hayashi, T.; Fujii, N.; Harada, K.; Oka, T.; Takahashi, K. The presence of free d-serine in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1992, 296, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, A.; Nishikawa, T.; Oka, T.; Takahashi, K. Endogenous d-serine in rat brain: N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-related distribution and aging. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, M.J.; Molliver, M.E.; Snyder, S.H. d-D-serine, an endogenous synaptic modulator: Localization to astrocytes and glutamate-stimulated release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3948–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, M.J.; Brady, R.O.; Molliver, M.E.; Snyder, S.H. d-serine as a neuromodulator: Regional and developmental localizations in rat brain glia resemble nmda receptors. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balu, D.T.; Presti, K.T.; Huang, C.C.Y.; Muszynski, K.; Radzishevsky, I.; Wolosker, H.; Guffanti, G.; Ressler, K.J.; Coyle, J.T. Serine racemase and d-serine in the amygdala are dynamically involved in fear learning. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mothet, J.P.; Parent, A.T.; Wolosker, H.; Brady, R.O., Jr.; Linden, D.J.; Ferris, C.D.; Rogawski, M.A.; Snyder, S.H. d-serine is an endogenous ligand for the glycine site of the n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4926–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panatier, A.; Theodosis, D.T.; Mothet, J.P.; Touquet, B.; Pollegioni, L.; Poulain, D.A.; Oliet, S.H. Glia-derived d-serine controls nmda receptor activity and synaptic memory. Cell 2006, 125, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, M.; Baux, G.; Mothet, J.P. d-serine signalling in the brain: Friend and foe. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolosker, H.; Dumin, E.; Balan, L.; Foltyn, V.N. d-amino acids in the brain: d-serine in neurotransmission and neurodegeneration. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3514–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.C.; Tsai, G.E.; Ma, C.L.; Ehmsen, J.T.; Mustafa, A.K.; Han, L.; Jiang, Z.I.; Benneyworth, M.A.; Froimowitz, M.P.; Lange, N.; et al. Targeted disruption of serine racemase affects glutamatergic neurotransmission and behavior. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneberger, C.; Papouin, T.; Oliet, S.H.; Rusakov, D.A. Long-term potentiation depends on release of d-serine from astrocytes. Nature 2010, 463, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVito, L.M.; Balu, D.T.; Kanter, B.R.; Lykken, C.; Basu, A.C.; Coyle, J.T.; Eichenbaum, H. Serine racemase deletion disrupts memory for order and alters cortical dendritic morphology. Genes Brain Behav. 2011, 10, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossat, P.; Turpin, F.R.; Sacchi, S.; Dulong, J.; Shi, T.; Rivet, J.M.; Sweedler, J.V.; Pollegioni, L.; Millan, M.J.; Oliet, S.H.; et al. Glial d-serine gates nmda receptors at excitatory synapses in prefrontal cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneberger, C.; Bard, L.; Rusakov, D.A. d-serine: A key to synaptic plasticity? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, L.; Podda, M.V.; Leone, L.; Piacentini, R.; Mastrodonato, A.; Cappelletti, P.; Sacchi, S.; Pollegioni, L.; Grassi, C.; D’Ascenzo, M. Reduced d-serine levels in the nucleus accumbens of cocaine-treated rats hinder the induction of nmda receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity. Brain 2013, 136, 1216–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balu, D.T.; Takagi, S.; Puhl, M.D.; Benneyworth, M.A.; Coyle, J.T. d-serine and serine racemase are localized to neurons in the adult mouse and human forebrain. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, S.; Li, L.; Moss, J.; Petrelli, F.; Casse, F.; Gebara, E.; Lopatar, J.; Pfrieger, F.W.; Bezzi, P.; Bischofberger, J.; et al. Synaptic integration of adult-born hippocampal neurons is locally controlled by astrocytes. Neuron 2015, 88, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Crux, S.; Marinesco, S.; Montagna, E.; Sgobio, C.; Shi, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhu, K.; Dorostkar, M.M.; Muller, U.C.; et al. Amyloid precursor protein maintains constitutive and adaptive plasticity of dendritic spines in adult brain by regulating d-serine homeostasis. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, A.R.; Heresco-Levy, U. d-serine in neuropsychiatric disorders: New advances. Adv. Psychiatry 2014, 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, D.T.; Coyle, J.T. The nmda receptor ‘glycine modulatory site’ in schizophrenia: d-serine, glycine, and beyond. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 20, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, C.; Lourenco, M.V.; Vargas-Lopes, C.; Suemoto, C.K.; Brandao, C.O.; Reis, T.; Leite, R.E.; Laks, J.; Jacob-Filho, W.; Pasqualucci, C.A.; et al. d-serine levels in alzheimer’s disease: Implications for novel biomarker development. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolosker, H.; Balu, D.T.; Coyle, J.T. The rise and fall of the d-serine-mediated gliotransmission hypothesis. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollegioni, L.; Sacchi, S. Metabolism of the neuromodulator d-serine. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2387–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papouin, T.; Henneberger, C.; Rusakov, D.A.; Oliet, S.H.R. Astroglial versus neuronal d-serine: Fact checking. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolosker, H.; Balu, D.T.; Coyle, J.T. Astroglial versus neuronal d-serine: Check your controls! Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiacco, T.A.; McCarthy, K.D. Multiple lines of evidence indicate that gliotransmission does not occur under physiological conditions. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savtchouk, I.; Volterra, A. Gliotransmission: Beyond black-and-white. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernot, P.; Mothet, J.P.; Schuvailo, O.; Soldatkin, A.; Pollegioni, L.; Pilone, M.; Adeline, M.T.; Cespuglio, R.; Marinesco, S. Characterization of a yeast d-amino acid oxidase microbiosensor for d-serine detection in the central nervous system. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zain, Z.M.; O’Neill, R.D.; Lowry, J.P.; Pierce, K.W.; Tricklebank, M.; Dewa, A.; Ab Ghani, S. Development of an implantable d-serine biosensor for in vivo monitoring using mammalian d-amino acid oxidase on a poly (O-phenylenediamine) and nafion-modified platinum-iridium disk electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernot, P.; Maucler, C.; Tholance, Y.; Vasylieva, N.; Debilly, G.; Pollegioni, L.; Cespuglio, R.; Marinesco, S. d-serine diffusion through the blood-brain barrier: Effect on d-serine compartmentalization and storage. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigetomi, E.; Jackson-Weaver, O.; Huckstepp, R.T.; O’Dell, T.J.; Khakh, B.S. Trpa1 channels are regulators of astrocyte basal calcium levels and long-term potentiation via constitutive d-serine release. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10143–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papouin, T.; Dunphy, J.M.; Tolman, M.; Dineley, K.T.; Haydon, P.G. Septal cholinergic neuromodulation tunes the astrocyte-dependent gating of hippocampal nmda receptors to wakefulness. Neuron 2017, 94, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polcari, D.; Kwan, A.; Van Horn, M.R.; Danis, L.; Pollegioni, L.; Ruthazer, E.S.; Mauzeroll, J. Disk-shaped amperometric enzymatic biosensor for in vivo detection of d-serine. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3501–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polcari, D.; Perry, S.C.; Pollegioni, L.; Geissler, M.; Mauzeroll, J. Localized detection of d-serine by using an enzymatic amperometric biosensor and scanning electrochemical microscopy. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, A.; Oka, T.; Nishikawa, T. Extracellular concentration of endogenous free d-serine in the rat brain as revealed by in vivo microdialysis. Neuroscience 1995, 66, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Kawai, J.; Imai, K.; Toyo’oka, T. Simultaneous determination of d- and l-serine in rat brain microdialysis sample using a column-switching HPLC with fluorimetric detection. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004, 18, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onozato, M.; Nakazawa, H.; Ishimaru, K.; Nagashima, C.; Fukumoto, M.; Hakariya, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Ichiba, H.; Fukushima, T. Alteration in plasma and striatal levels of d-serine after d-serine administration with or without nicergoline: An in vivo microdialysis study. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umino, A.; Ishiwata, S.; Iwama, H.; Nishikawa, T. Evidence for tonic control by the gabaa receptor of extracellular d-serine concentrations in the medial prefrontal cortex of rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.L.; Wightman, R.M. Rapid dopamine release in freely moving rats. In Electrochemical Methods for Neuroscience; Michael, A.C., Borland, L.M., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Eschenko, O.; Sara, S.J. Learning-dependent, transient increase of activity in noradrenergic neurons of locus coeruleus during slow wave sleep in the rat: Brain stem-cortex interplay for memory consolidation? Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 2596–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hascup, K.N.; Hascup, E.R.; Stephens, M.L.; Glaser, P.E.; Yoshitake, T.; Mathe, A.A.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Kehr, J. Resting glutamate levels and rapid glutamate transients in the prefrontal cortex of the flinders sensitive line rat: A genetic rodent model of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, M.B.; Douglas, C.L.; Vyazovskiy, V.V.; Cirelli, C.; Tononi, G. Long-term homeostasis of extracellular glutamate in the rat cerebral cortex across sleep and waking states. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, J.J.; Gerhardt, G.A. Self-referencing ceramic-based multisite microelectrodes for the detection and elimination of interferences from the measurement of l-glutamate and other analytes. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hascup, K.N.; Rutherford, E.C.; Quintero, J.E.; Day, B.K.; Nickell, J.R.; Pomerleau, F.; Huettl, P.; Burmeister, J.J.; Gerhardt, G.A. Second-by-second measures of l-glutamate and other neurotransmitters using enzyme-based microelectrode arrays. In Electrochemical Methods for Neuroscience; Michael, A.C., Borland, L.M., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.; Harrison, N.R.; Gonzales, C.B.; Schilstrom, B.; Konradsson-Geuken, A. Effects of age and acute ethanol on glutamatergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex of freely moving rats using enzyme-based microelectrode amperometry. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.M.; Quintero, J.E.; Pomerleau, F.; Huettl, P.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Glaser, P.E. Simultaneous glutamate recordings in the frontal cortex network with multisite biomorphic microelectrodes: New tools for adhd research. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 252, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, J.J.; Pomerleau, F.; Huettl, P.; Gash, C.R.; Werner, C.E.; Bruno, J.P.; Gerhardt, G.A. Ceramic-based multisite microelectrode arrays for simultaneous measures of choline and acetylcholine in CNS. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, C.F.; Ledo, A.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Laranjinha, J.; Barbosa, R.M. Neurometabolic and electrophysiological changes during cortical spreading depolarization: Multimodal approach based on a lactate-glucose dual microbiosensor arrays. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, S.C.; Nicolelis, M.A. Acquiring local field potential information from amperometric neurochemical recordings. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 179, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledo, A.; Lourenco, C.F.; Laranjinha, J.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Barbosa, R.M. Combined in vivo amperometric oximetry and electrophysiology in a single sensor: A tool for epilepsy research. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12383–12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hascup, E.R.; af Bjerken, S.; Hascup, K.N.; Pomerleau, F.; Huettl, P.; Stromberg, I.; Gerhardt, G.A. Histological studies of the effects of chronic implantation of ceramic-based microelectrode arrays and microdialysis probes in rat prefrontal cortex. Brain Res. 2009, 1291, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantinato, S.; Pollegioni, L.; Pilone, M.S. Engineering, expression and purification of a his-tagged chimeric d-amino acid oxidase from rhodotorula gracilis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2001, 29, 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Konradsson-Geuken, A.; Gash, C.R.; Alexander, K.; Pomerleau, F.; Huettl, P.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Bruno, J.P. Second-by-second analysis of alpha 7 nicotine receptor regulation of glutamate release in the prefrontal cortex of awake rats. Synapse 2009, 63, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, J.J.; Pomerleau, F.; Palmer, M.; Day, B.K.; Huettl, P.; Gerhardt, G.A. Improved ceramic-based multisite microelectrode for rapid measurements of l-glutamate in the cns. J. Neurosci. Methods 2002, 119, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, B.K.; Pomerleau, F.; Burmeister, J.J.; Huettl, P.; Gerhardt, G.A. Microelectrode array studies of basal and potassium-evoked release of l-glutamate in the anesthetized rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, E.C.; Pomerleau, F.; Huettl, P.; Stromberg, I.; Gerhardt, G.A. Chronic second-by-second measures of l-glutamate in the central nervous system of freely moving rats. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press/Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hinzman, J.M.; Thomas, T.C.; Burmeister, J.J.; Quintero, J.E.; Huettl, P.; Pomerleau, F.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Lifshitz, J. Diffuse brain injury elevates tonic glutamate levels and potassium-evoked glutamate release in discrete brain regions at two days post-injury: An enzyme-based microelectrode array study. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortz, D.M.; Jorgensen, C.V.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Bruno, J.P. Transient inactivation of the ventral hippocampus in neonatal rats impairs the mesolimbic regulation of prefrontal glutamate release in adulthood. Neuropharmacology 2014, 84, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunewald, R.A. Ascorbic acid in the brain. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1993, 18, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, F.E.; May, J.M. Vitamin c function in the brain: Vital role of the ascorbate transporter SVCT2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundersen, V.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Bergersen, L.H. Neuroglial transmission. Phys. Rev. 2015, 95, 695–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, N.R.; Ledo, A.; Laranjinha, J.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Barbosa, R.M. Simultaneous measurements of ascorbate and glutamate in vivo in the rat brain using carbon fiber nanocomposite sensors and microbiosensor arrays. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 121, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamase, K.; Konno, R.; Morikawa, A.; Zaitsu, K. Sensitive determination of d-amino acids in mammals and the effect of d-amino-acid oxidase activity on their amounts. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollegioni, L.; Ghisla, S.; Pilone, M.S. Studies on the active centre of rhodotorula gracilis d-amino acid oxidase and comparison with pig kidney enzyme. Biochem. J. 1992, 286 Pt 2, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molla, G.; Vegezzi, C.; Pilone, M.S.; Pollegioni, L. Overexpression in escherichia coli of a recombinant chimeric rhodotorula gracilis d-amino acid oxidase. Protein Expr. Purif. 1998, 14, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
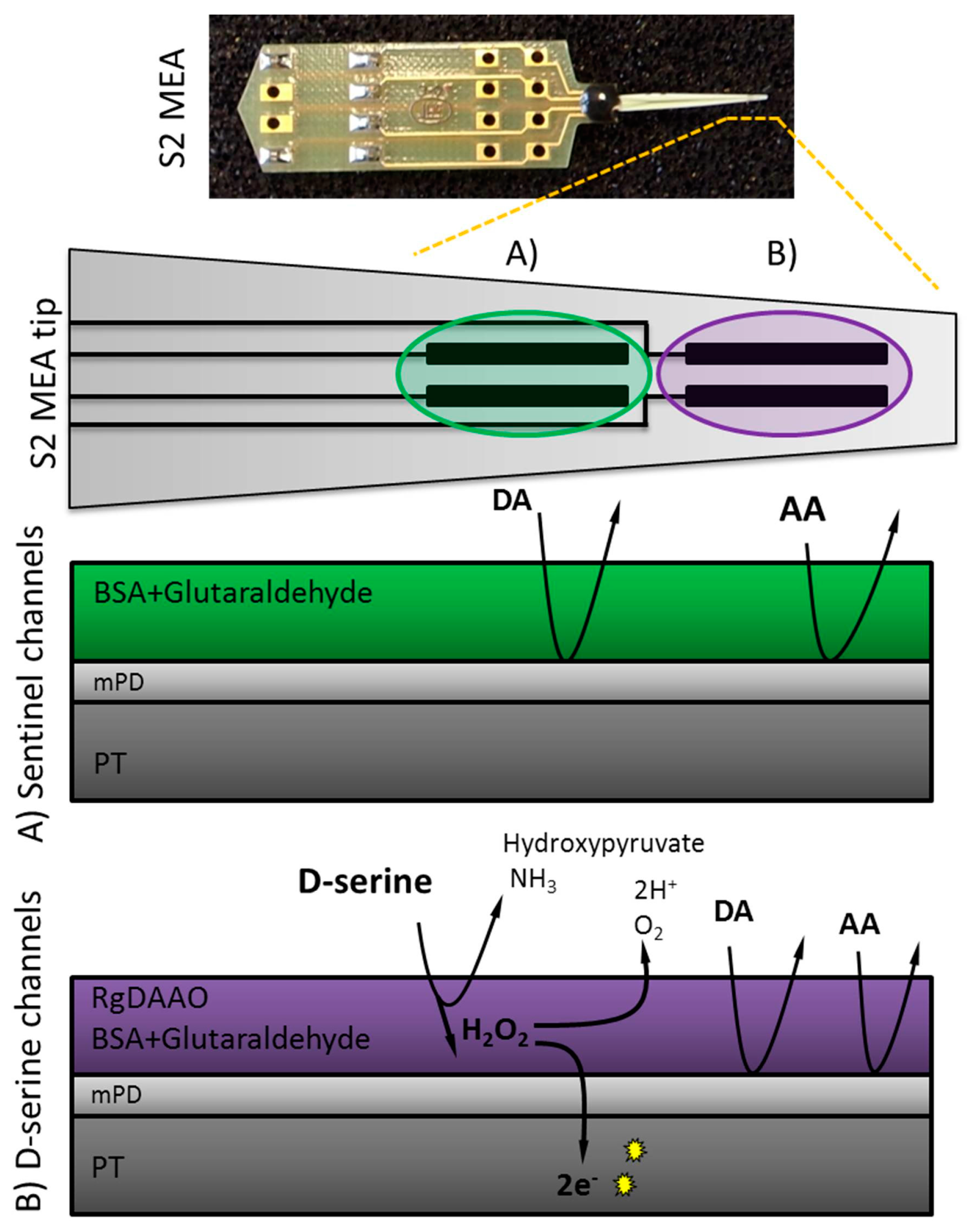

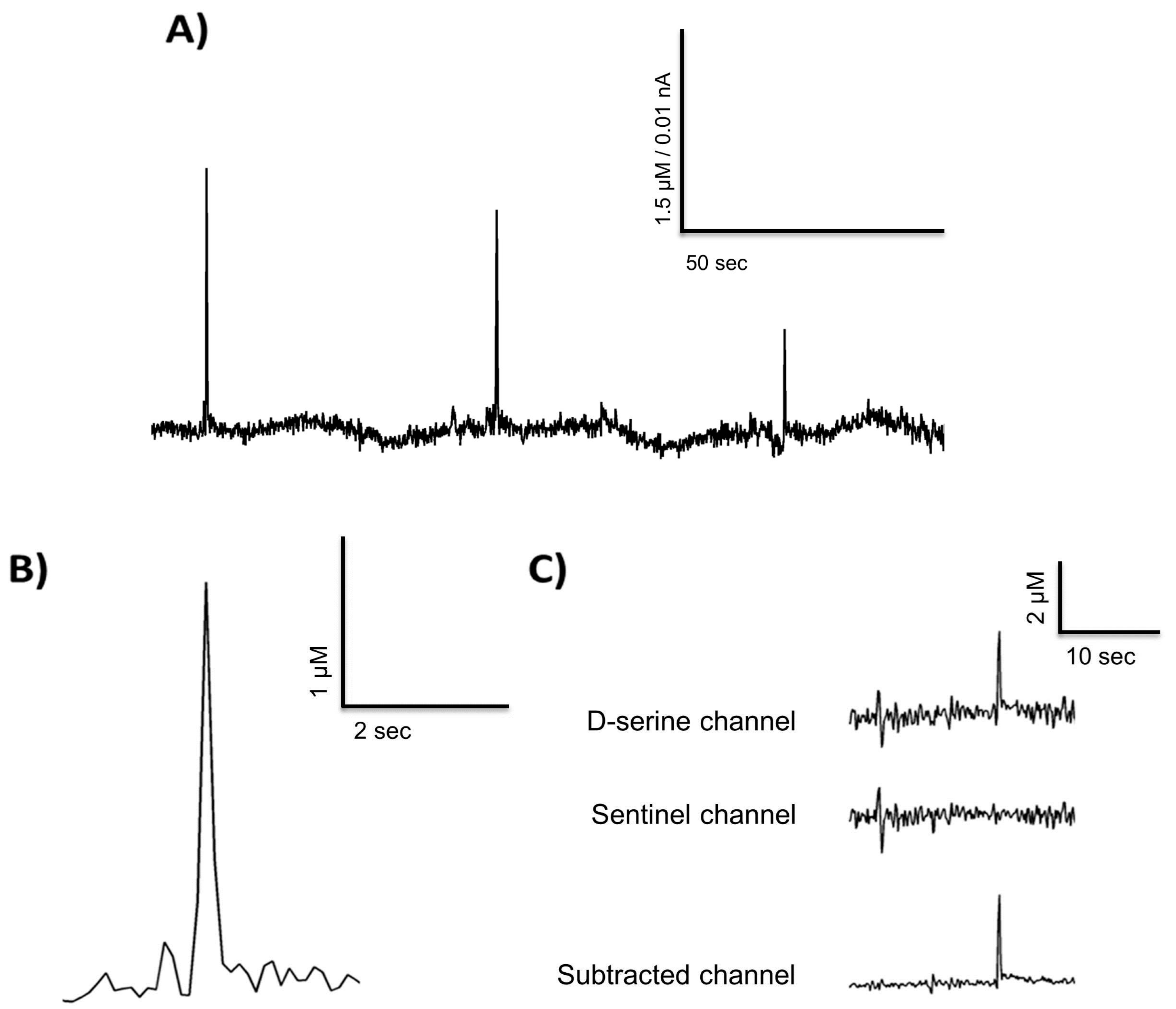
| Parameters | Sensitivity | LOD | Linearity (R2) | Selectivity Against AA | Selectivity Against L-Glutamate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold criteria | ≥2 pA/µM | ≤0.5 µM | 1 | ≥80 | ≥80 |
| Measurements | 8.61 ± 0.83 pA/µM | 0.17 ± 0.01 µM | 0.9986 ± 0.0005 | 191.75 ± 19.55 | 521.3 ± 112.23 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos-Beltrán, D.; Konradsson-Geuken, Å.; Quintero, J.E.; Marshall, L. Amperometric Self-Referencing Ceramic Based Microelectrode Arrays for D-Serine Detection. Biosensors 2018, 8, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010020
Campos-Beltrán D, Konradsson-Geuken Å, Quintero JE, Marshall L. Amperometric Self-Referencing Ceramic Based Microelectrode Arrays for D-Serine Detection. Biosensors. 2018; 8(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos-Beltrán, Diana, Åsa Konradsson-Geuken, Jorge E. Quintero, and Lisa Marshall. 2018. "Amperometric Self-Referencing Ceramic Based Microelectrode Arrays for D-Serine Detection" Biosensors 8, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010020
APA StyleCampos-Beltrán, D., Konradsson-Geuken, Å., Quintero, J. E., & Marshall, L. (2018). Amperometric Self-Referencing Ceramic Based Microelectrode Arrays for D-Serine Detection. Biosensors, 8(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010020





