Eco-Friendly Capsaicin-Containing Water-Based Antifouling Coatings for Marine Aquaculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Formulation and Preparation of Coatings
2.3. Characterization of Coatings
2.4. Antibacterial Activity
2.5. Leaching of Biocides
3. Results and Discussion
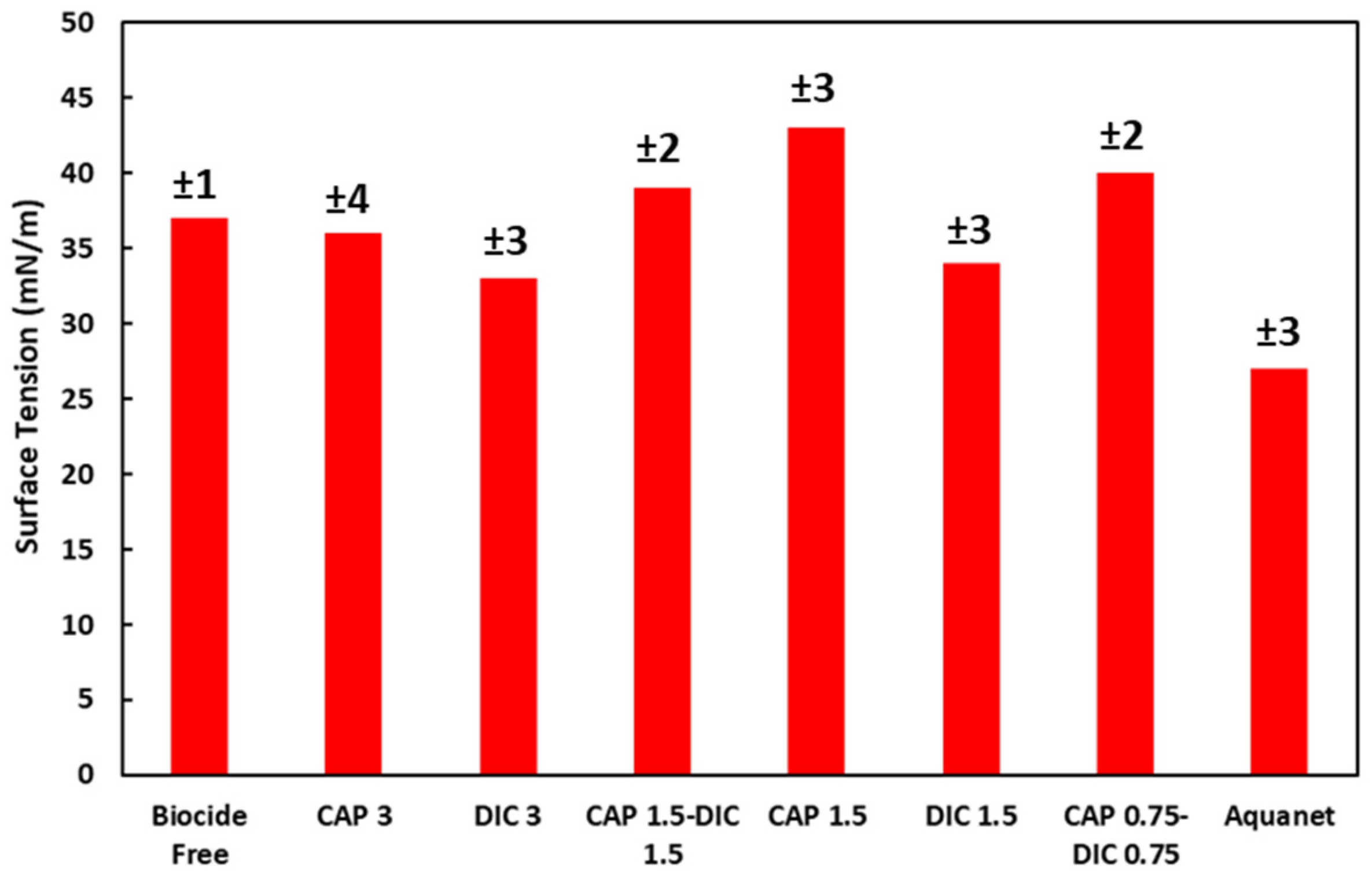
3.1. Formulation and Preparation of Coatings
3.2. Antibacterial Activity of Coatings
3.3. Leaching of Biocides
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling Technology—Past, Present and Future Steps towards Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Antifouling Coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Duan, Y.; Cui, M.; Huang, R.; Su, R.; Qi, W.; He, Z. Biomimetic Surface Coatings for Marine Antifouling: Natural Antifoulants, Synthetic Polymers and Surface Microtopography. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Pan, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G. Dynamic Surface Antifouling: Mechanism and Systems. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1087–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.P. Effects of Coating Roughness and Biofouling on Ship Resistance and Powering. Biofouling 2007, 23, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloecher, N.; Floerl, O. Efficacy Testing of Novel Antifouling Coatings for Pen Nets in Aquaculture: How Good Are Alternatives to Traditional Copper Coatings? Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; Erdogan, U.H.; Cavas, L. Prevention of Biofouling on Aquaculture Nets with Eco-friendly Antifouling Paint Formulation. Color. Technol. 2020, 136, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omae, I. Organotin Antifouling Paints and Their Alternatives. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2003, 17, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonak, S.; Pangam, P.; Giriyan, A.; Hawaldar, K. Implications of the Ban on Organotins for Protection of Global Coastal and Marine Ecology. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, S96–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytreberg, E.; Karlsson, J.; Eklund, B. Comparison of Toxicity and Release Rates of Cu and Zn from Anti-Fouling Paints Leached in Natural and Artificial Brackish Seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.H.; Tatara, C.P.; Scholz, N.L. Copper-Induced Olfactory Toxicity in Salmon and Steelhead: Extrapolation across Species and Rearing Environments. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, L.; Weis, J.S.; Cabello, F.; Pizarro, J.; Bostick, K. Chemical Use in Salmon Aquaculture: A Review of Current Practices and Possible Environmental Effects. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.V.; Brooks, S. The Environmental Fate and Effects of Antifouling Paint Biocides. Biofouling 2010, 26, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.R.G.; Readman, J.W. 12 Booster Biocide Antifoulants: Is History Repeating Itself? In Late Lessons from Early Warnings: Science, Precaution, Innovation; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Floerl, O.; Sunde, L.; Bloecher, N. Potential Environmental Risks Associated with Biofouling Management in Salmon Aquaculture. Aquacult. Environ. Interact. 2016, 8, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloecher, N.; Floerl, O. Towards Cost-effective Biofouling Management in Salmon Aquaculture: A Strategic Outlook. Rev. Aquacult. 2021, 13, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASC Salmon Standard Operational Review-Version; Aquaculture Stewardship Council: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2016.
- Oliveira, I.B.; Beiras, R.; Thomas, K.V.; Suter, M.J.-F.; Barroso, C.M. Acute Toxicity of Tralopyril, Capsaicin and Triphenylborane Pyridine to Marine Invertebrates. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Barrios, C.A.; Cutright, T.; Zhang Newby, B. Evaluation of Toxicity of Capsaicin and Zosteric Acid and Their Potential Application as Antifoulants. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, M.; Ginestra, G.; Youcefi, F.; Filocamo, A.; Bisignano, C.; Riazi, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Selected Polyphenols and Capsaicinoids Identified in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) and Their Possible Mode of Interaction. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Wang, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, F.; Ji, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lin, T.; Zhang, X. Studies on the Synthesis, Pungency and Anti-Biofouling Performance of Capsaicin Analogues. Sci. China Chem. 2012, 55, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hao, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C.; Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Shao, Q.; Guo, Z. PH-Responsive Capsaicin@chitosan Nanocapsules for Antibiofouling in Marine Applications. Polymer 2018, 158, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, X.; Huang, J.; Li, H. Flame Sprayed Environmentally Friendly High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)–Capsaicin Composite Coatings for Marine Antifouling Applications. Mater. Lett. 2019, 238, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Juhani, A.A.; Newby, B.-M.Z. Assessments of Capsaicin Incorporated Silicone Rubber as Antifouling Coatings. J. Rubber Res. 2014, 17, 173–186. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Chen, S.; Qin, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Fan, J.; Wang, C.; Dong, M.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, F.; et al. Antifouling and Antibacterial Behaviors of Capsaicin-Based PH Responsive Smart Coatings in Marine Environments. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X. Synthesis and Fouling Resistance of Capsaicin Derivatives Containing Amide Groups. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jasensky, J.; Ulrich, N.W.; Cheng, J.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z.; He, C. Capsaicin-Inspired Thiol–Ene Terpolymer Networks Designed for Antibiofouling Coatings. Langmuir 2017, 33, 13689–13698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, C.K.; Turner, A.; Readman, J.; Frickers, T. Environmental Risks Associated with Booster Biocides Leaching from Spent Anti-Fouling Paint Particles in Coastal Environments. Water Environ. Res. 2014, 86, 2330–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrebii, M.; Ben Mabrouk, A.; Boufi, S. Synthesis and Properties of Hybrid Alkyd–Acrylic Dispersions and Their Use in VOC-Free Waterborne Coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, M.; Gherardelli, V.; Heisinger, A.; Fernández, J.; Olmos, P.; Ovalle, L.; Ilardi, P.; Avendaño-Herrera, R. First Description of Atypical Furunculosis in Freshwater Farmed Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L., in Chile. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 22196; Measurement of Antibacterial Activity on Plastics and Other Non-Porous Surfaces. International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- ASTM 3359; Standard Test Methods for Rating Adhesion By Tape Test. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
- ISO 15181-2; Paints and Varnishes—Determination of Release Rate of Biocides from Antifouling Paints. International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Eguía, E.; Trueba, A. Application of Marine Biotechnology in the Production of Natural Biocides for Testing on Environmentally Innocuous Antifouling Coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2007, 4, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressy, C.; Briand, J.-F.; Lafond, S.; Davy, R.; Mazeas, F.; Tanguy, B.; Martin, C.; Horatius, L.; Anton, C.; Quiniou, F.; et al. What Governs Marine Fouling Assemblages on Chemically Active Antifouling Coatings? Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 164, 106701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, J.T.; Bollmann, U.E.; Bester, K. The Occurrence of Modern Organic Antifouling Biocides in Danish Marinas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | Biocide Free | CAP 3 | DIC 3 | CAP 1.5-DIC 1.5 | CAP 1.5 | DIC 1.5 | CAP 0.75-DIC 0.75 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 16.07 | 15.59 | 15.59 | 15.35 | 15.79 | 15.79 | 15.79 |
| Disperbyk 2080 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 2.09 | 1.85 | 1.85 | 1.85 |
| AMP | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| BYK 24 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| Capsaicin | - | 3.00 | _ | 1.50 | 1.50 | _ | 0.75 |
| Dichlofluanid | - | _ | 3.00 | 1.50 | _ | 1.50 | 0.75 |
| Kronos 2360 (TiO2) | 19.69 | 19.10 | 19.10 | 19.10 | 19.17 | 19.17 | 19.17 |
| Alberdingk® AC 2403 | 60.00 | 58.19 | 58.19 | 57.27 | 58.41 | 58.41 | 58.41 |
| BYK 24 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 |
| BYK 349 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| Dowanol DPM | 1.66 | 1.61 | 1.61 | 1.58 | 1.62 | 1.62 | 1.62 |
| BYK 7420 ES | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| Total (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Efficacy of Antibacterial Property | Antimicrobial Value (R) | % cfu Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Zero | 0.5 < R | <68% |
| Low | 0.5 < R < 1 | 68% to 90% |
| Medium | 1 < R < 2 | 90% to 99% |
| Significant | 2 < R < 3 | 99% to 99.9% |
| Strong | R > 3 | >99.9% |
| Coating | Adhesion Classification | Roughness |
|---|---|---|
| Biocide Free | 5B | 0.5 ± 0.2 |
| CAP 3 | 5B | 1.7 ± 0.5 |
| DIC 3 | 5B | 1.3 ± 0.6 |
| CAP 1.5-DIC 1.5 | 5B | 1.6 ± 0.5 |
| CAP 1.5 | 5B | 1.2 ± 0.6 |
| DIC 1.5 | 5B | 1.3 ± 0.3 |
| CAP 0.75-DIC 0.75 | 5B | 1.3 ± 0.3 |
| Aquanet | 5B | 1.1 ± 0.4 |
| Coating | Antimicrobial Value (R) | % cfu Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Biocide Free | 0.64 | 68–90 |
| CAP 3 | >3.34 | >99.9 |
| DIC 3 | 2.22 | 99.0–99.9 |
| CAP 1.5-DIC 1.5 | >3.34 | >99.9 |
| CAP 1.5 | 1.05 | 90–99 |
| DIC 1.5 | 1.38 | 90–99 |
| CAP 0.75-DIC 0.75 | 3.46 | >99.9 |
| Aquanet | 2.66 | 99.0–99.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beyazkilic, Z.; Faccini, M.; Escobar, A.M.; Bautista, L. Eco-Friendly Capsaicin-Containing Water-Based Antifouling Coatings for Marine Aquaculture. Coatings 2023, 13, 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091616
Beyazkilic Z, Faccini M, Escobar AM, Bautista L. Eco-Friendly Capsaicin-Containing Water-Based Antifouling Coatings for Marine Aquaculture. Coatings. 2023; 13(9):1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091616
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeyazkilic, Zeynep, Mirko Faccini, Ana Maria Escobar, and Lorenzo Bautista. 2023. "Eco-Friendly Capsaicin-Containing Water-Based Antifouling Coatings for Marine Aquaculture" Coatings 13, no. 9: 1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091616







