Aluminizing via Ionic Liquid Electrodeposition and Pack Cementation: A Comparative Study with Inconel 738 and a CoNiCrAlY
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- “IL aluminizing”: IN738 + Al by Ionic Liquids + Heat treatment (1100 °C in vacuum).
- “IL over-aluminizing”: IN738 + CoNiCrAlY + Al by Ionic Liquids + Heat treatment (1100 °C in vacuum).
- “Pack aluminizing”: IN738 + pack cementation process (1000 °C) + Heat treatment (1100 °C in vacuum).
- “Pack over-aluminizing”: IN738 + CoNiCrAlY + pack cementation process (1000 °C) + Heat treatment (1100 °C in vacuum).
- “Reference coating”: IN738 + CoNiCrAlY + Heat treatment (1100 °C in vacuum).
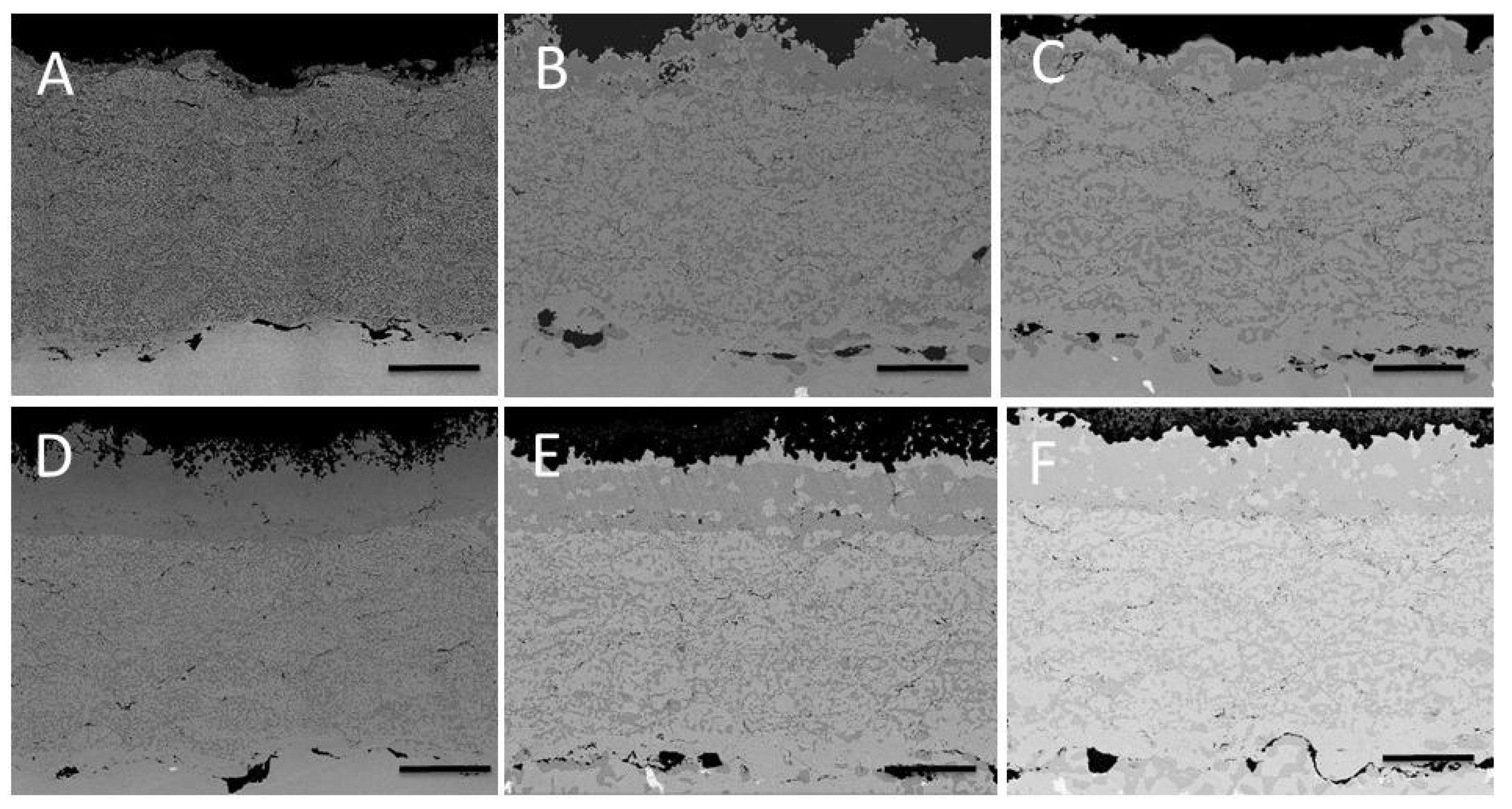
3. Results
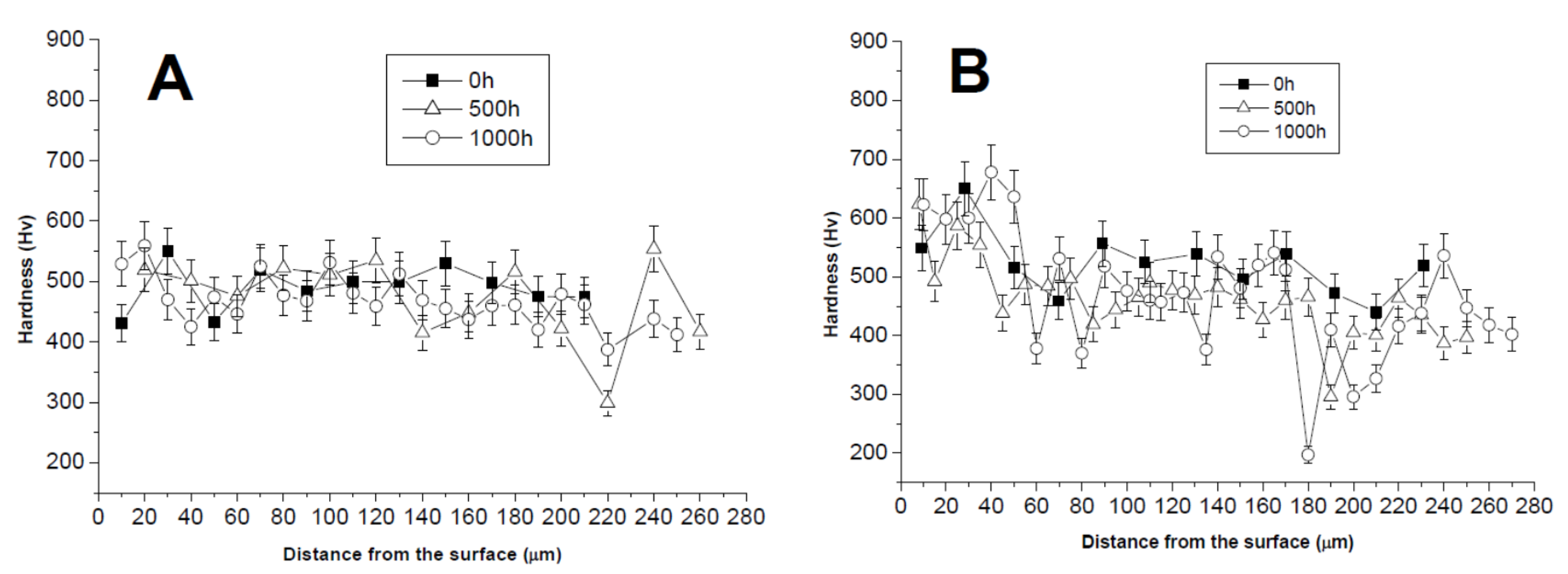
3.1. Comparison between Pack Aluminizing and IL Aluminizing over IN738
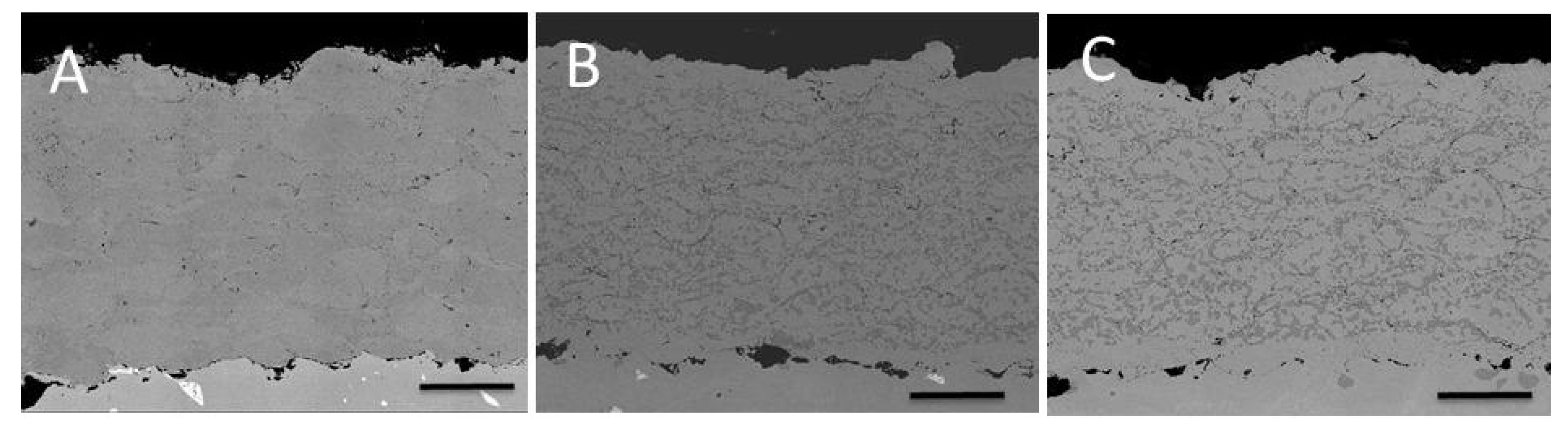
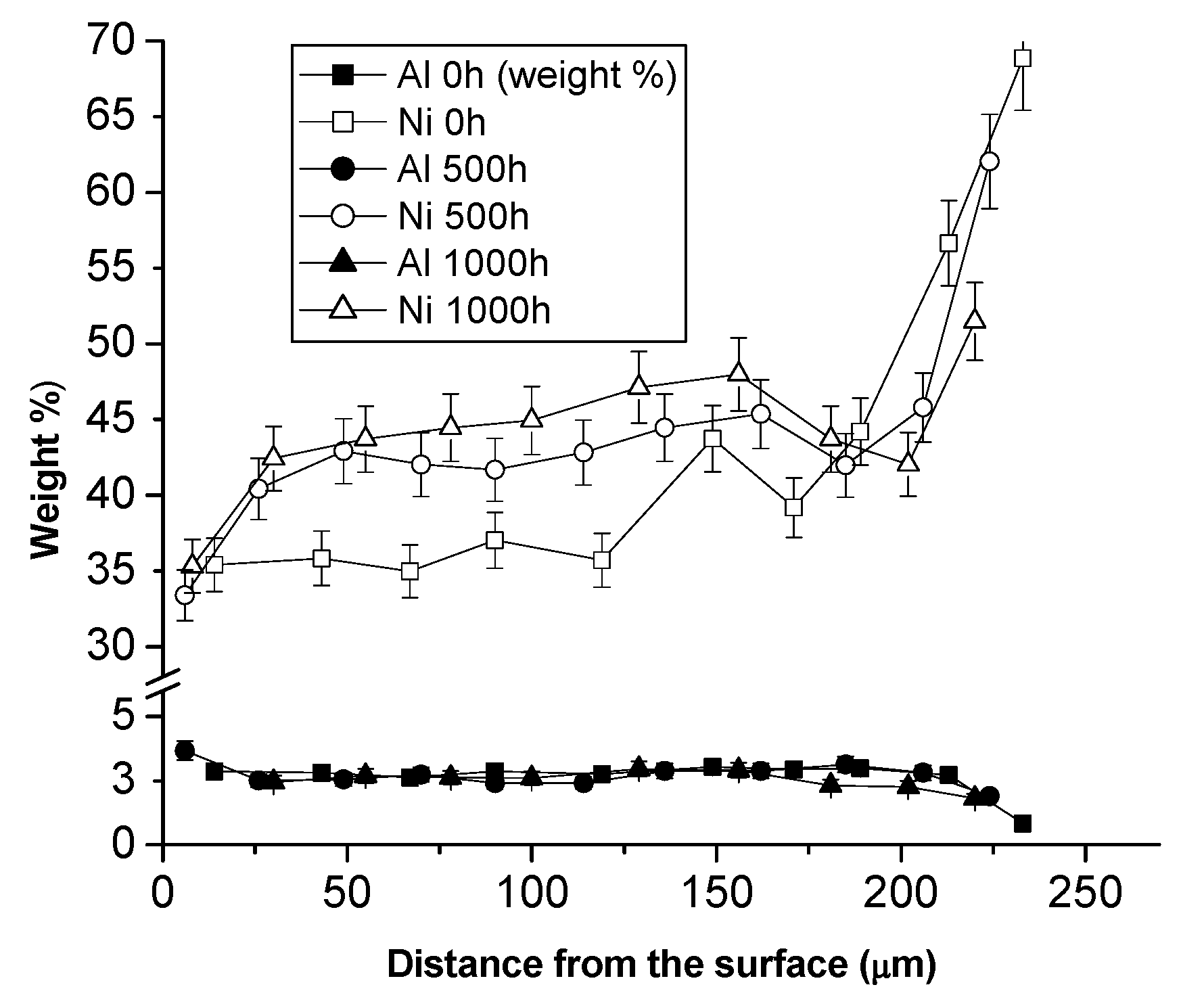
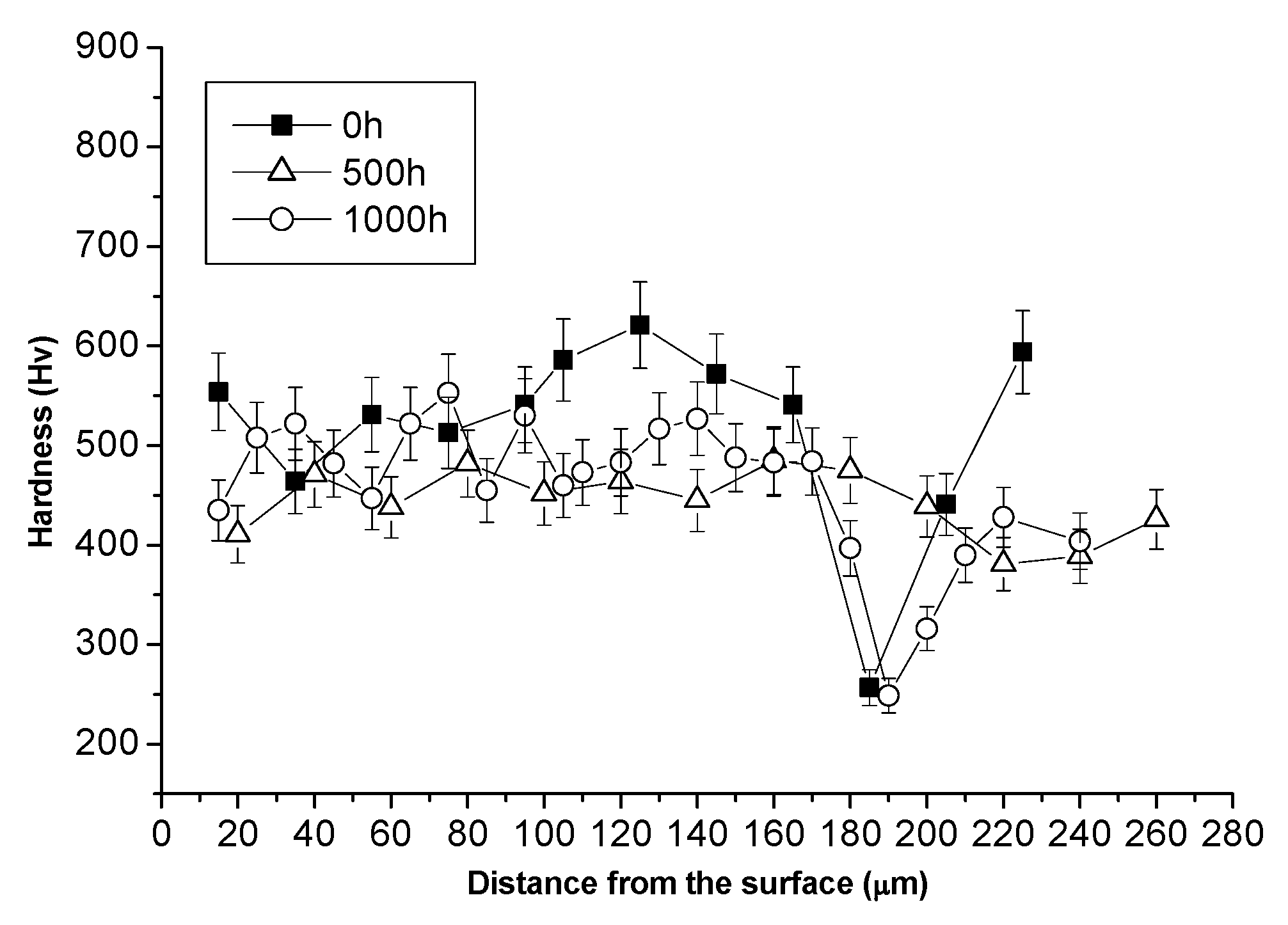
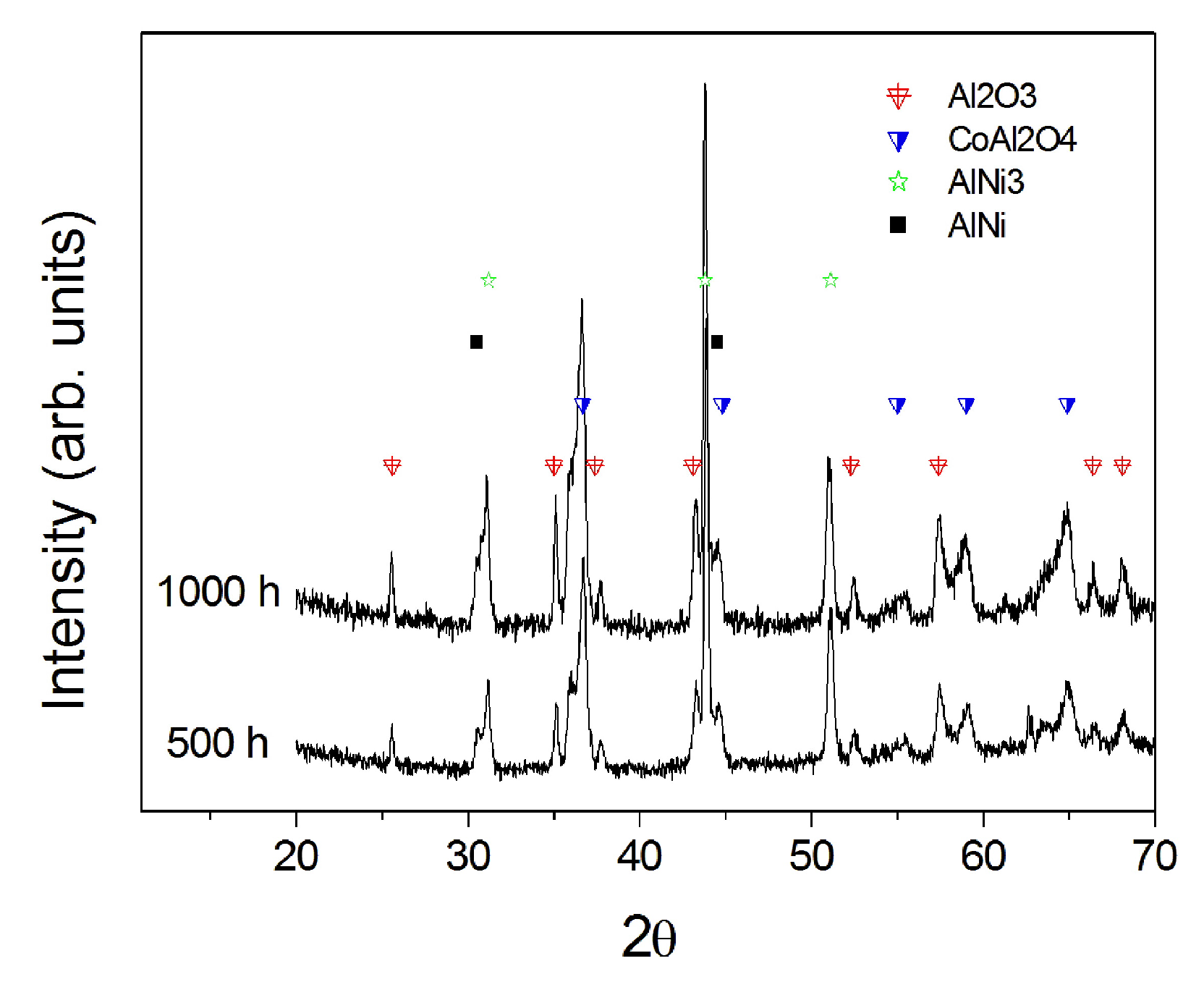
3.2. Tests on the Reference Coating: HVOF Sprayed CoNiCrAlY on IN738 with No Aluminizing Process + Heat Treatment (1100 °C in Vacuum).
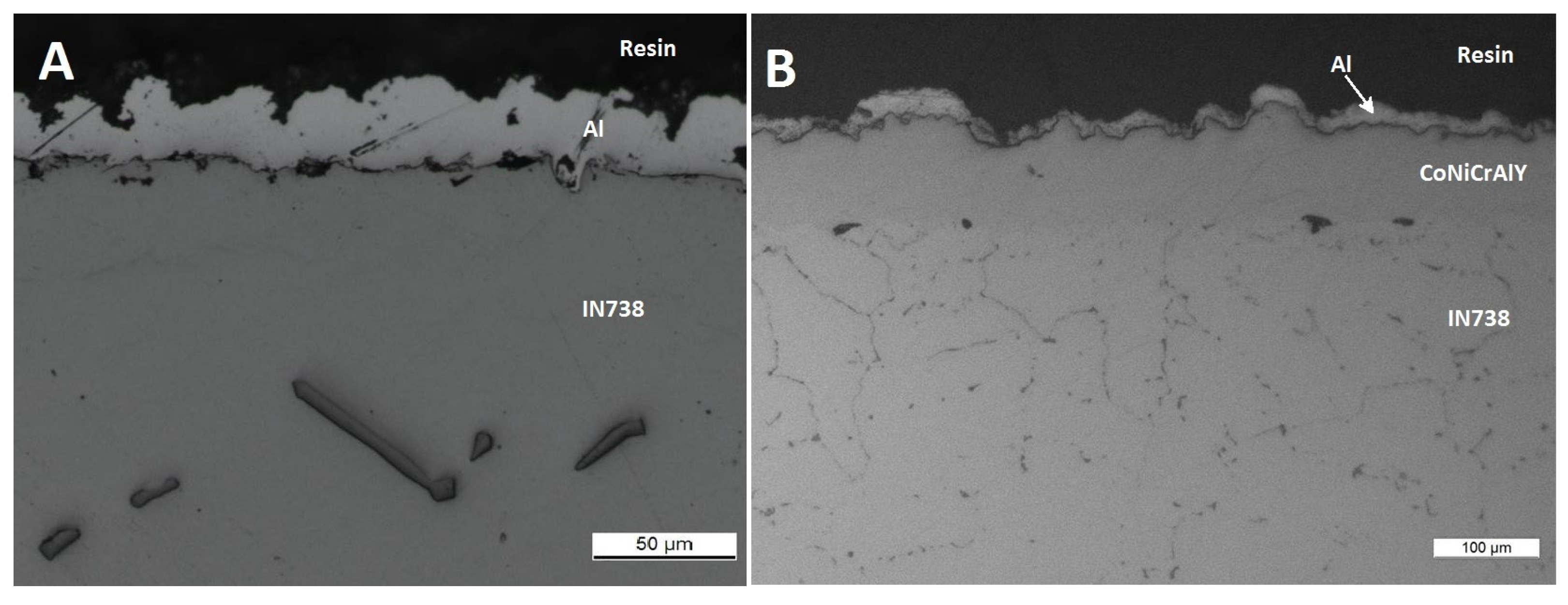
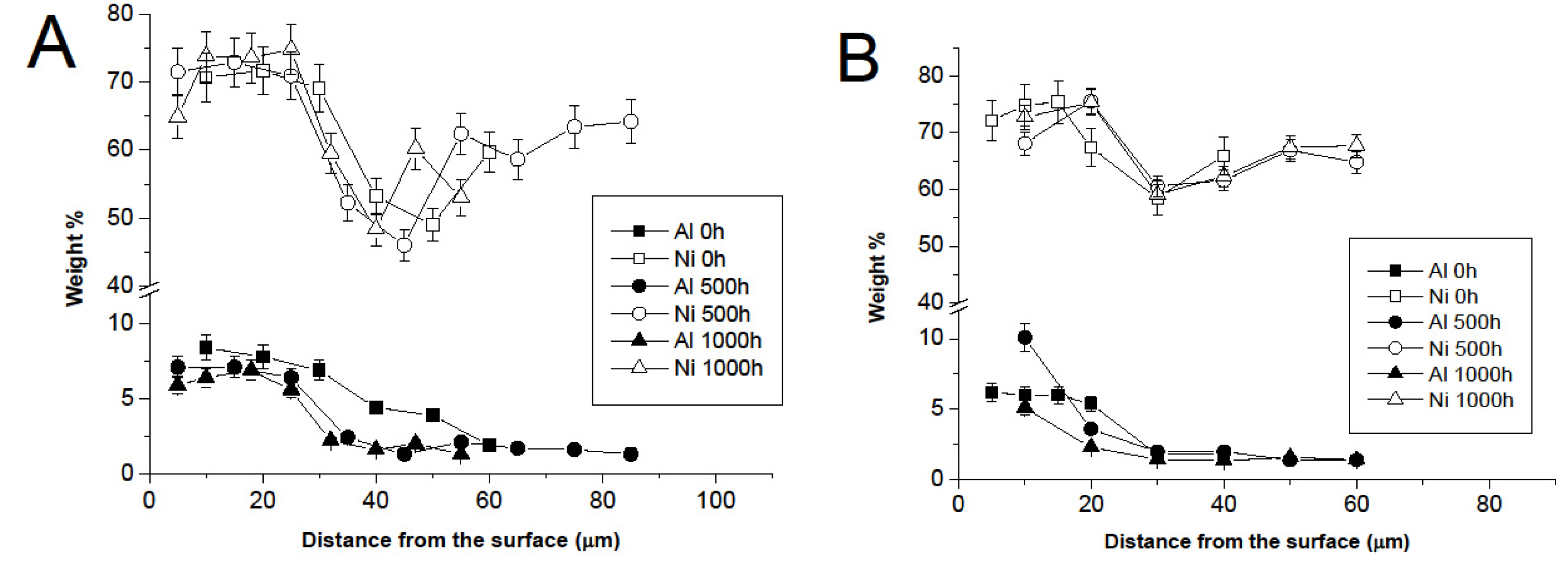
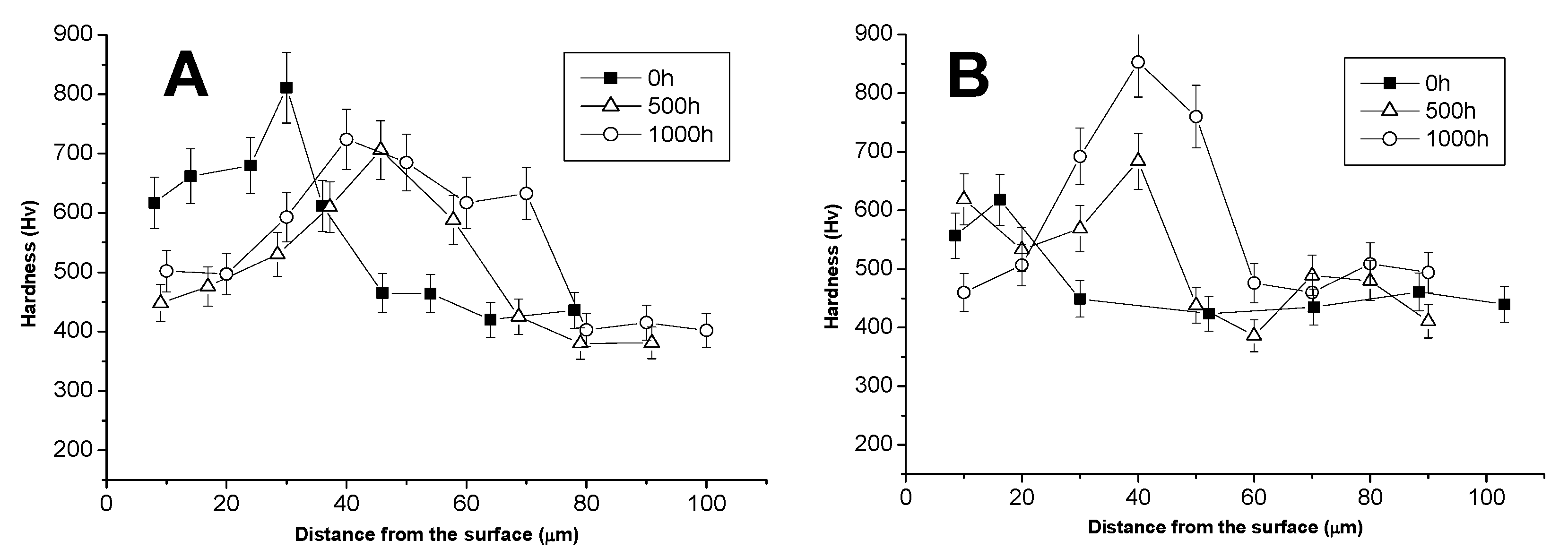
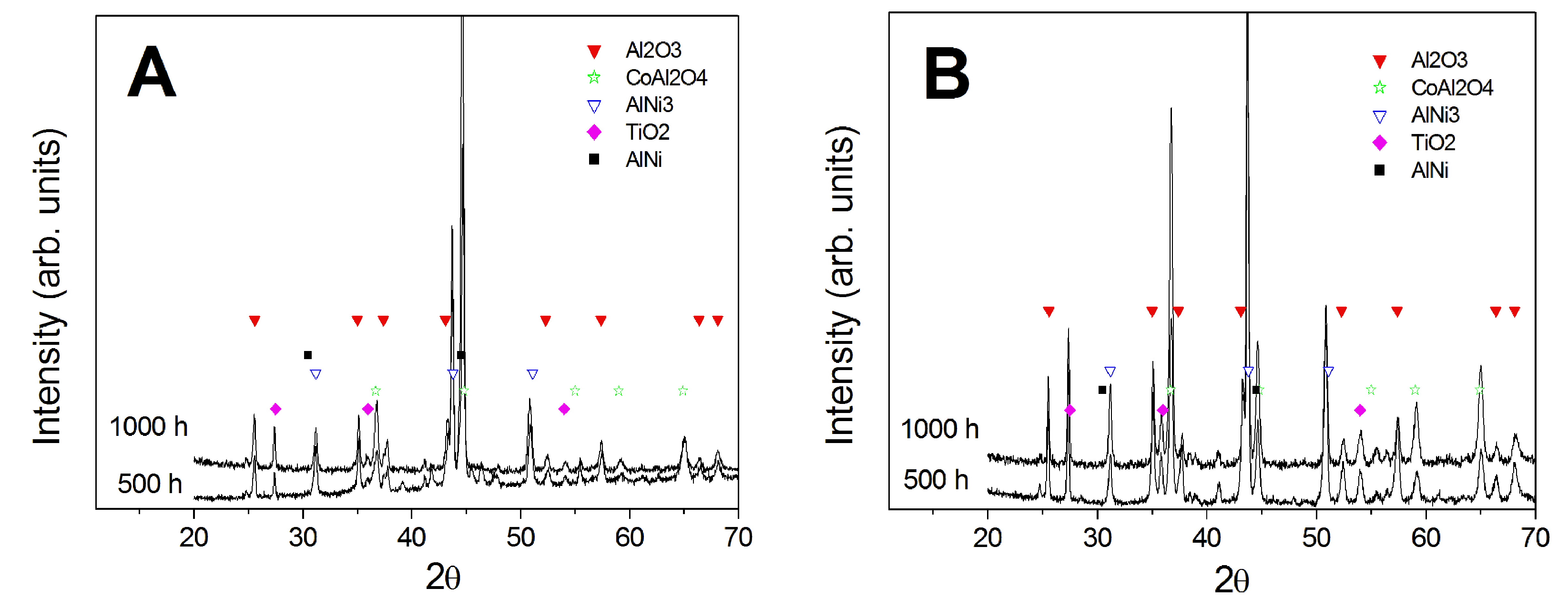
3.3. Comparison between Pack- and IL Over-Aluminizing
4. Conclusions
- Apparently, the two-step aluminizing process by Al-electrodeposition and consequent diffusion heat treatment (IL aluminizing) is not suitable for the direct application over IN738. Al inward diffusion seems to be inhibited by the possible formation of carbides or nitrides. These precipitates were observed after the diffusion post treatment, and they could result from the reaction of traces of ionic liquid entrapped in the growing Al layer with the base material. A further cleaning process could be attempted after the electroplating step in order to avoid the presence of IL residuals.
- Over-aluminizing of CoNiCrAlY is beneficial in order to create a viable anti-corrosion coating. This is due to the high Ni interdiffusion from the base material to the coating. This behavior causes the transformation of the β NiAl into γ Ni3Al, which is less protective under oxidative and corrosive environment. For this reason, a further aluminizing step (over-aluminizing) is required for these types of metallic coatings in order to enhance the oxidation resistance at high temperatures.
- Being virtually free of W, Ta, Ti, there is no formation of carbides in the CoNiCrAlY coat; therefore, IL over-aluminizing on CoNiCrAlY allows a better and deeper diffusion of the Al toward the coating with respect to the pack over-aluminizing process.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozza, F.; Bolelli, G.; Giolli, C.; Giorgetti, A.; Lusvarghi, L.; Sassatelli, P.; Scrivani, A.; Candeli, A.; Thoma, M. Diffusion mechanisms and microstructure development in pack aluminizing of Ni-based alloys. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2014, 239, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.D.; Burnell-Gray, J.S.; Datta, P.K. Aluminide coating formation on nickel-base superalloys by pack cementation process. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 5673–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Sah, I.; Lee, H.J.; Hong, S.; Jang, C. Development of an aluminide coating layer on Alloy 617 by Al sputtering and inter-diffusion heat treatments. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 244, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, L. Micro-indentation and erosion properties of thermal sprayed NiAl intermetallic-based alloy coatings. Wear 2003, 254, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, W. Effect of ceria on the erosion resistance of HVOF thermal sprayed NiAl intermetallic coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2003, 22, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevi, S.C.; Sikka, V.K.; Liu, C.T. Processing, properties, and applications of nickel and iron aluminides. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1997, 42, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lih, W.; Chang, E.; Wu, B.C.; Chao, C.H. The effect of pack-aluminisation on the microstructure of MCrA1Y and the performance of thermal barrier coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1992, 50, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.F.; Chao, C.H.; Wu, B.C.; Leu, R.Q.; Chang, E. Zirconia/pack-aluminized Co-29Cr-6AI-1Y thermal barrier coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1991, 9, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Dengzun, Y.; Chungen, Z. Low-temperature formation of aluminide coatings on Ni-base superalloys by pack cementation process. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2010, 23, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, H.; Angenete, J.; Stiller, K. Microstructure of oxide scales on aluminide diffusion coatings after short time oxidation at 1050 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 177–178, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, A.; Ferdinando, M.; Lavacchi, A.; Scrivani, A.; Giolli, C.; Bardi, U. Improvement of the oxidation resistance of CoNiCrAlY bond coats sprayed by high velocity oxygen-fuel onto nickel superalloy substrate. Coatings 2011, 1, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.L. Chemical vapour deposition of coatings. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2003, 48, 57–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, M.; Scrivani, A.; Giolli, C.; Giorgetti, A. Aluminizing turbine parts—Processes and coatings. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2011, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–10 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mishin, Y. Atomistic modeling of the γ and γ′-phases of the Ni–Al system. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chang, Y.A.; Wang, Y. Simulating interdiffusion microstructures in Ni–Al–Cr diffusion couples: A phase field approach coupled with CALPHAD database. Scripta Mater. 2004, 50, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardi, U.; Caporali, S.; Craig, M.; Lavacchi, A.; Nicholls, J. A Method for Making a Protective Coating on a Metal Substrate. European Patent No 2330233 A1, 1 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; Harris, R.C.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Ryder, K.S.; Wen-Sun, I. Aluminium electrodeposition under ambient conditions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 14675–14681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Yoshii, K.; Jiang, X.; Sun, X.G.; Tsuda, T.; Mehio, N.; Dai, S. An AlCl3 based ionic liquid with a neutral substituted pyridine ligand for electrochemical deposition of aluminum. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 160, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Aluminium deposition from lewis acidic 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloroaluminate ionic liquid ([Bmim]Cl/AlCl3) modified with methyl nicotinate. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 1794–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Electrodeposition of bright Al coatings from 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloroaluminate ionic liquids with specific additives. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, D320–D324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, L. Low-temperature electrodeposition of aluminium from lewis acidic 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloroaluminate ionic liquids. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berretti, E.; Giaccherini, A.; Martinuzzi, S.M.; Innocenti, M.; Schubert, T.J.S.; Stiemke, F.M.; Caporali, S. Aluminium Electrodeposition from Ionic Liquid: Effect of Deposition Temperature and Sonication. Materials 2016, 9, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Project Scail-Up. Scaling-Up of the Aluminium Plating Process from Ionic Liquid. Available online: http://scailup.eu (accessed on 25 February 2017).
- Caporali, S.; Martinuzzi, S.M.; von Czarnecki, P.; Schubert, T.J.S.; Bardi, U. Effects of metal ions on the aluminum electrodeposition from ionic liquids. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
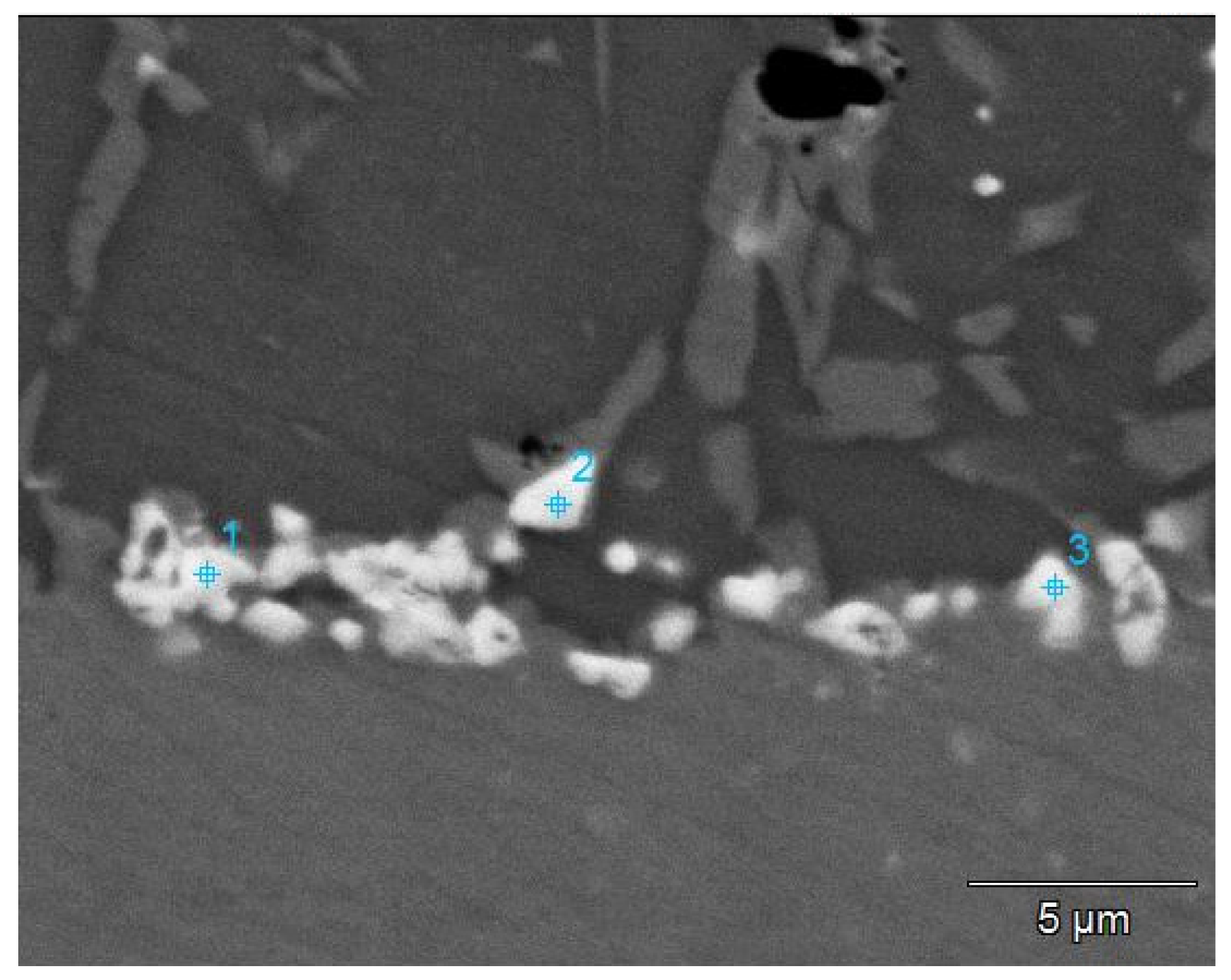



| Element | Point 1 | Point 2 | Point 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Ti | 3.7 | 1.7 | 15.5 |
| Cr | 50.4 | 45.9 | 3.3 |
| Co | 2.1 | 3.8 | 2.5 |
| Ni | 13.2 | 25.3 | 20.7 |
| Mo | 12.0 | 9.3 | – |
| W | 18.4 | 13.6 | – |
| Nb | – | – | 4.7 |
| Ta | – | – | 53.0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tagliaferri, L.; Berretti, E.; Giaccherini, A.; Martinuzzi, S.M.; Bozza, F.; Thoma, M.; Bardi, U.; Caporali, S. Aluminizing via Ionic Liquid Electrodeposition and Pack Cementation: A Comparative Study with Inconel 738 and a CoNiCrAlY. Coatings 2017, 7, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7060083
Tagliaferri L, Berretti E, Giaccherini A, Martinuzzi SM, Bozza F, Thoma M, Bardi U, Caporali S. Aluminizing via Ionic Liquid Electrodeposition and Pack Cementation: A Comparative Study with Inconel 738 and a CoNiCrAlY. Coatings. 2017; 7(6):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7060083
Chicago/Turabian StyleTagliaferri, Luca, Enrico Berretti, Andrea Giaccherini, Stefano M. Martinuzzi, Francesco Bozza, Martin Thoma, Ugo Bardi, and Stefano Caporali. 2017. "Aluminizing via Ionic Liquid Electrodeposition and Pack Cementation: A Comparative Study with Inconel 738 and a CoNiCrAlY" Coatings 7, no. 6: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7060083
APA StyleTagliaferri, L., Berretti, E., Giaccherini, A., Martinuzzi, S. M., Bozza, F., Thoma, M., Bardi, U., & Caporali, S. (2017). Aluminizing via Ionic Liquid Electrodeposition and Pack Cementation: A Comparative Study with Inconel 738 and a CoNiCrAlY. Coatings, 7(6), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7060083







