Role of Inelastic Transverse Compressive Behavior and Multiaxial Loading on the Transverse Impact of Kevlar KM2 Single Fiber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
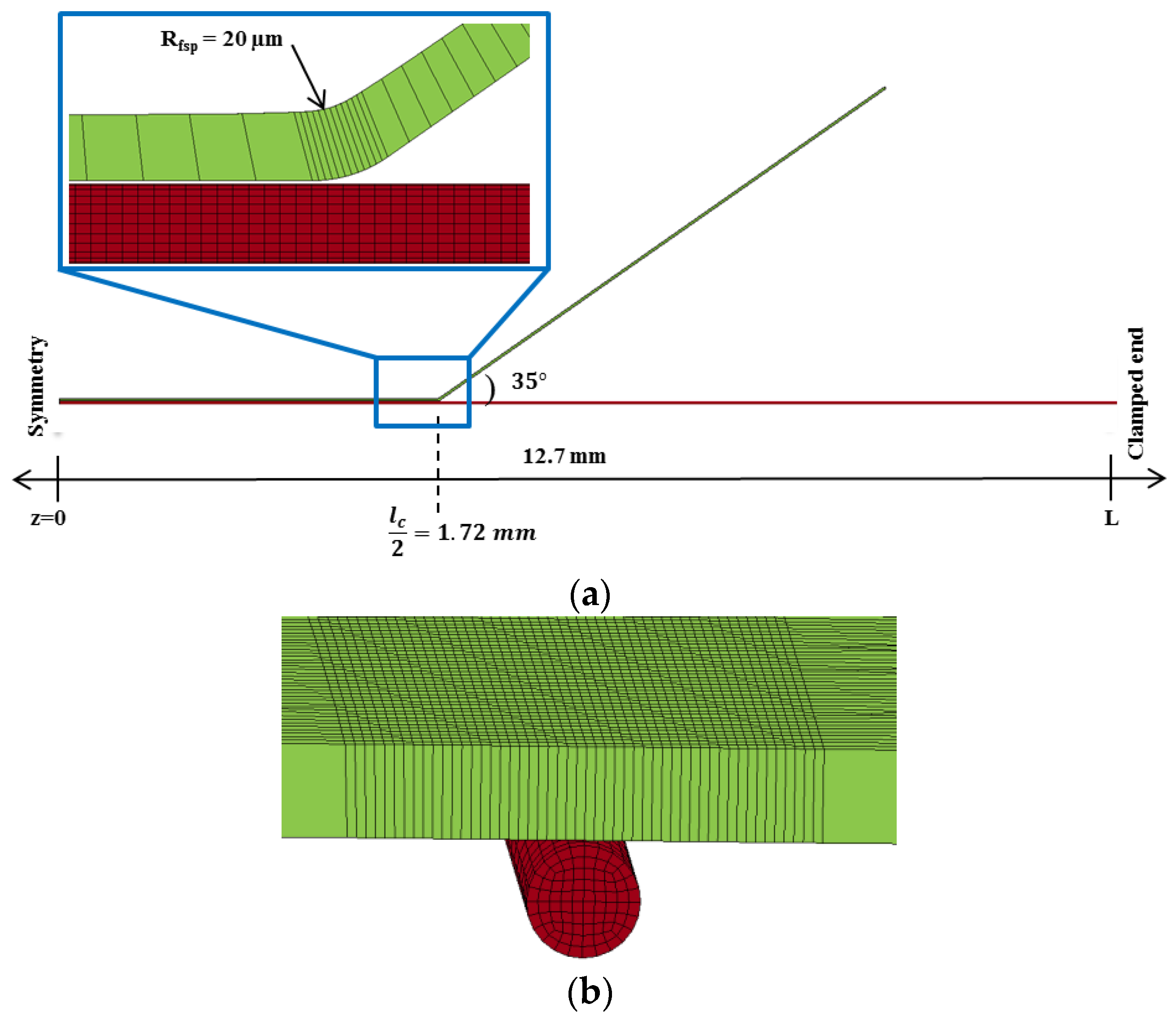
2. Single-Fiber Transverse Impact
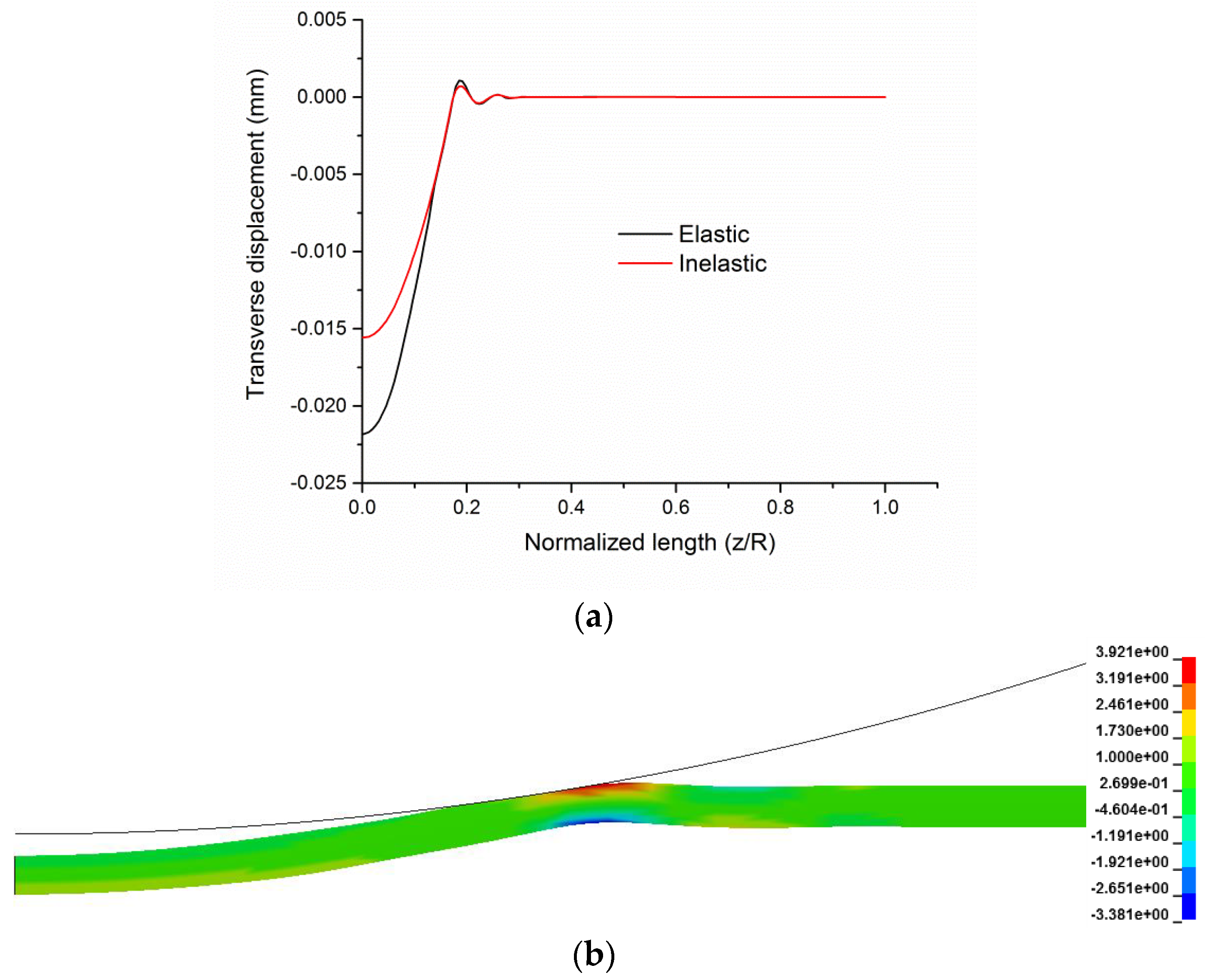
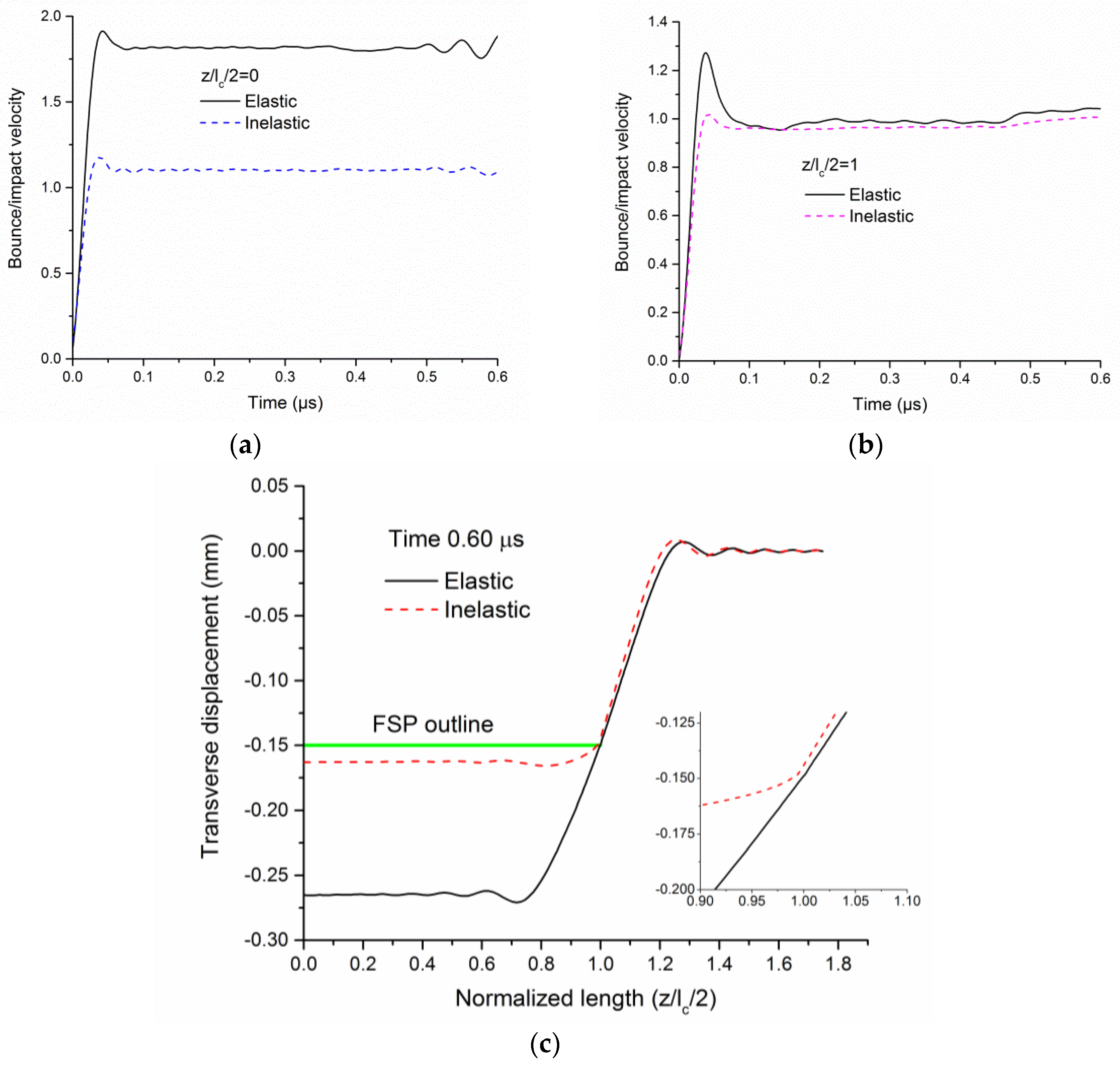
2.1. Cylindrical Projectile Impact
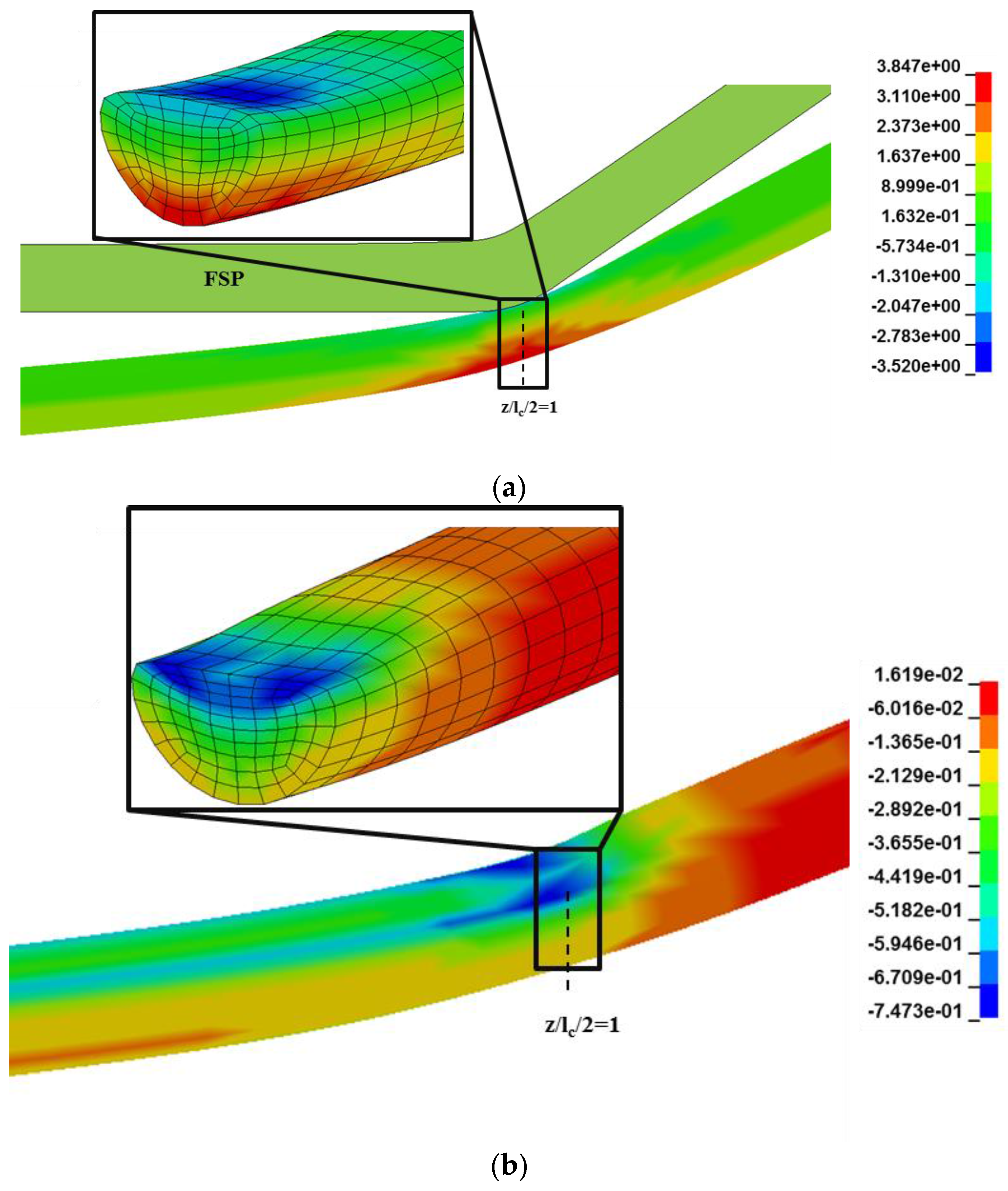
2.2. FSP Impact
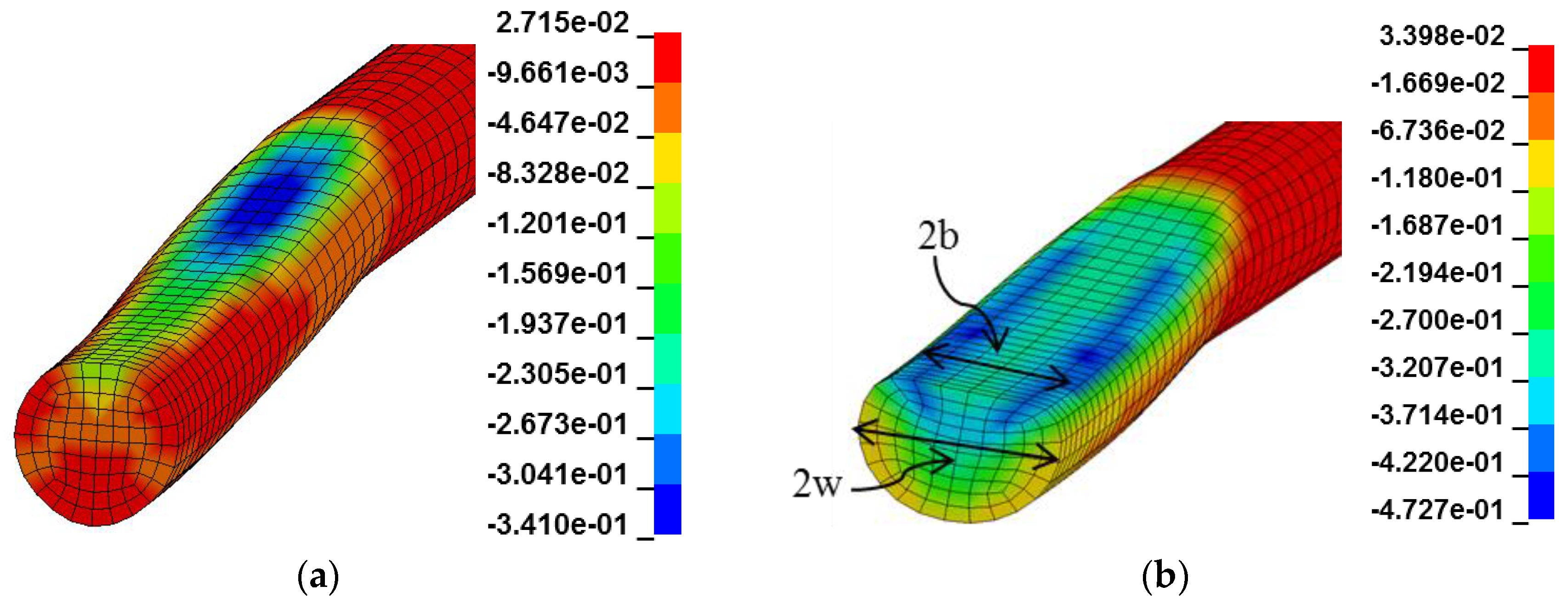
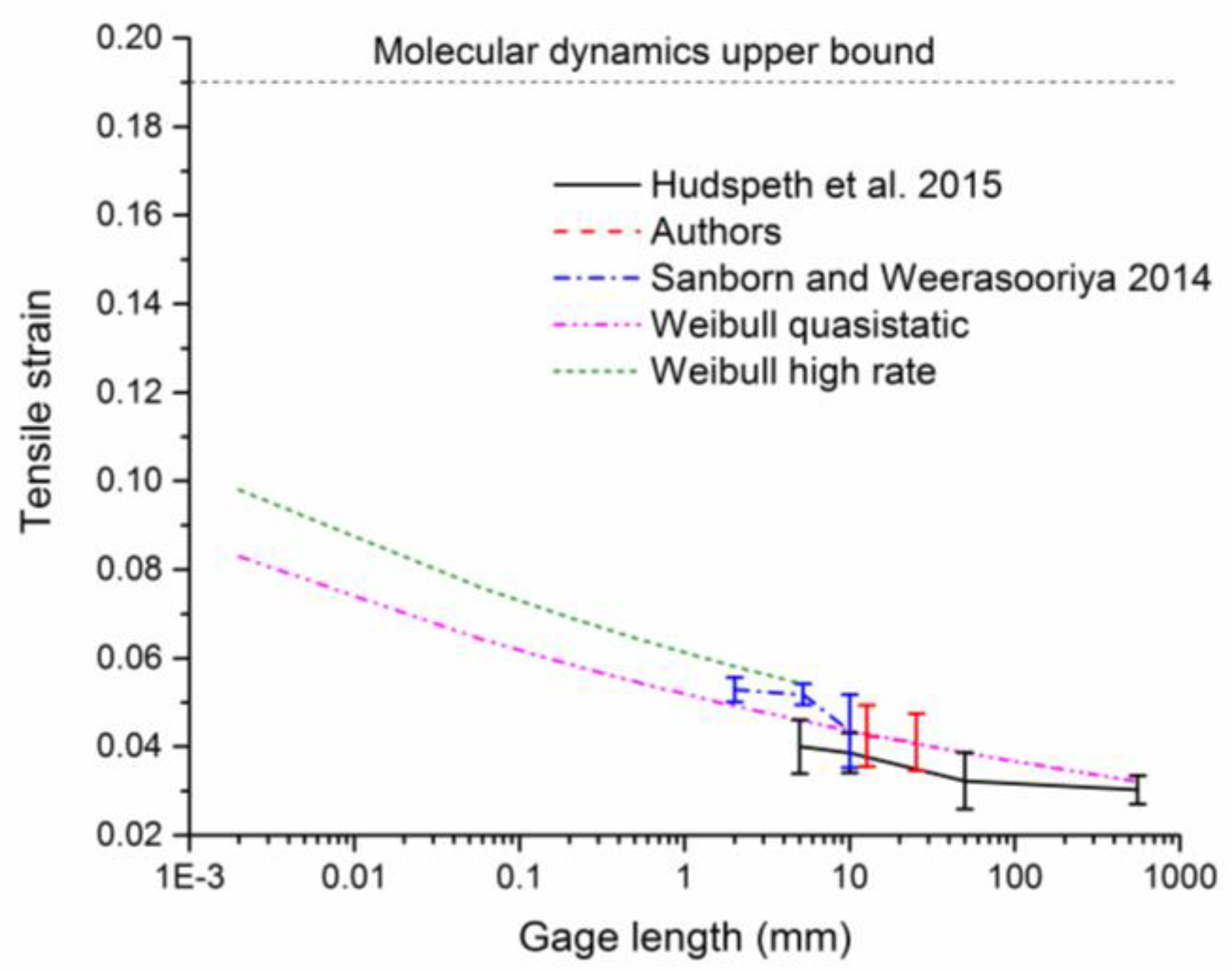
3. Multiaxial Loading and Failure
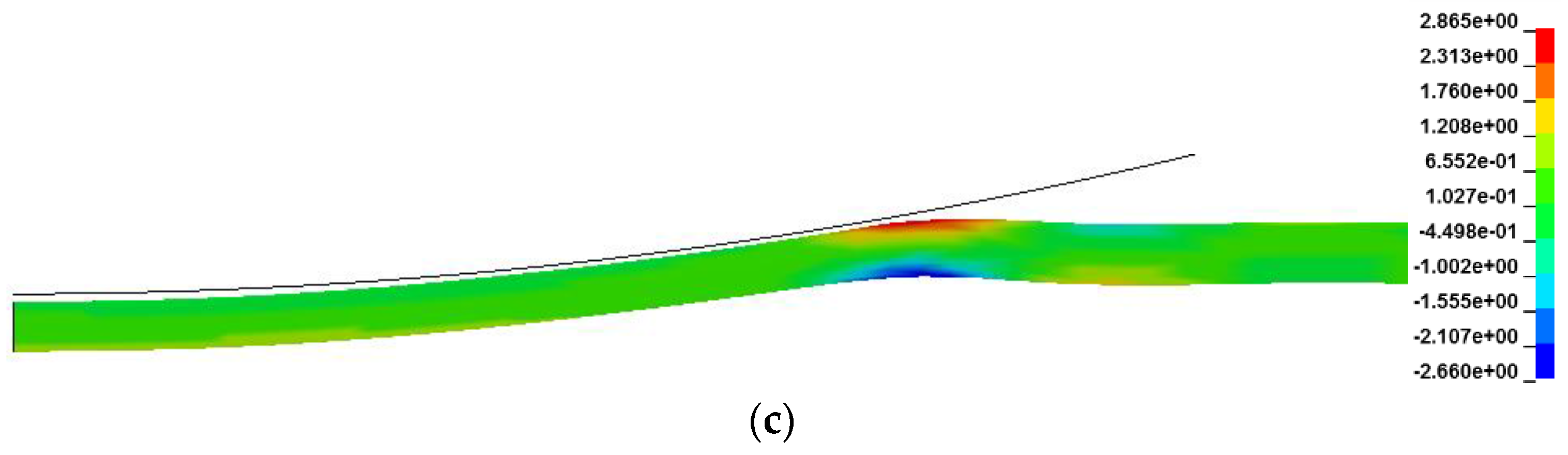
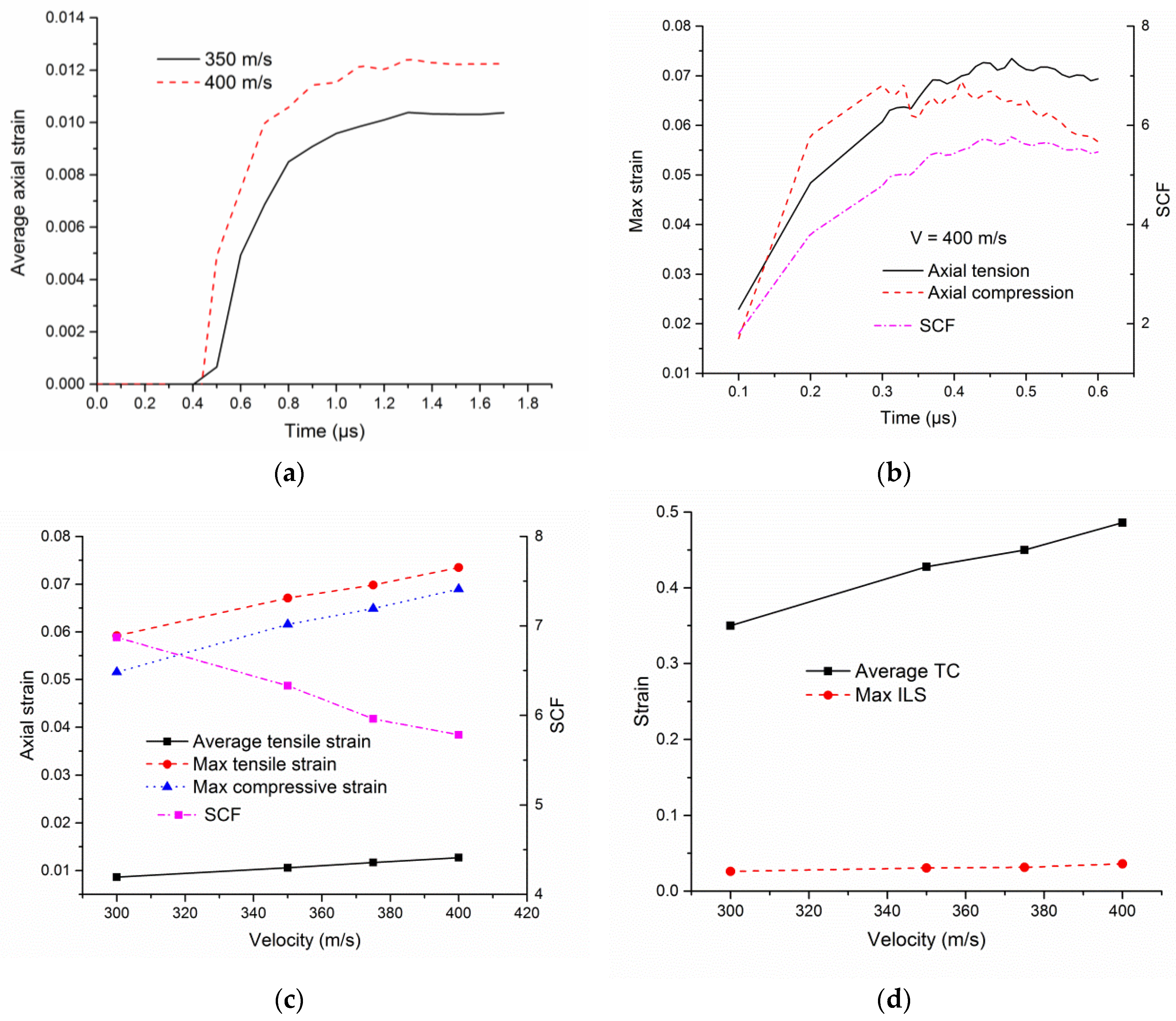
3.1. Cylindrical Projectile Impact
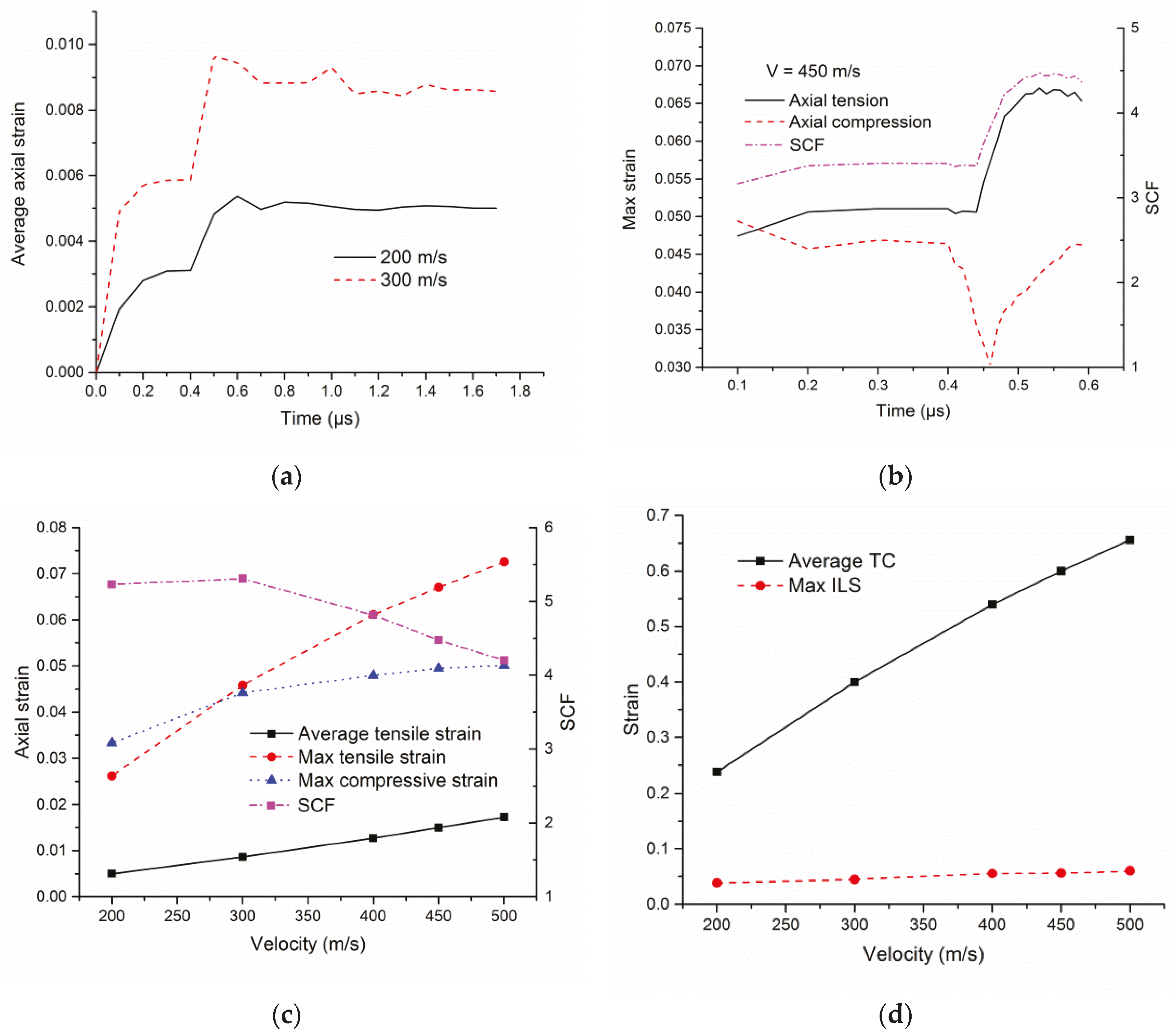
3.2. FSP Impact
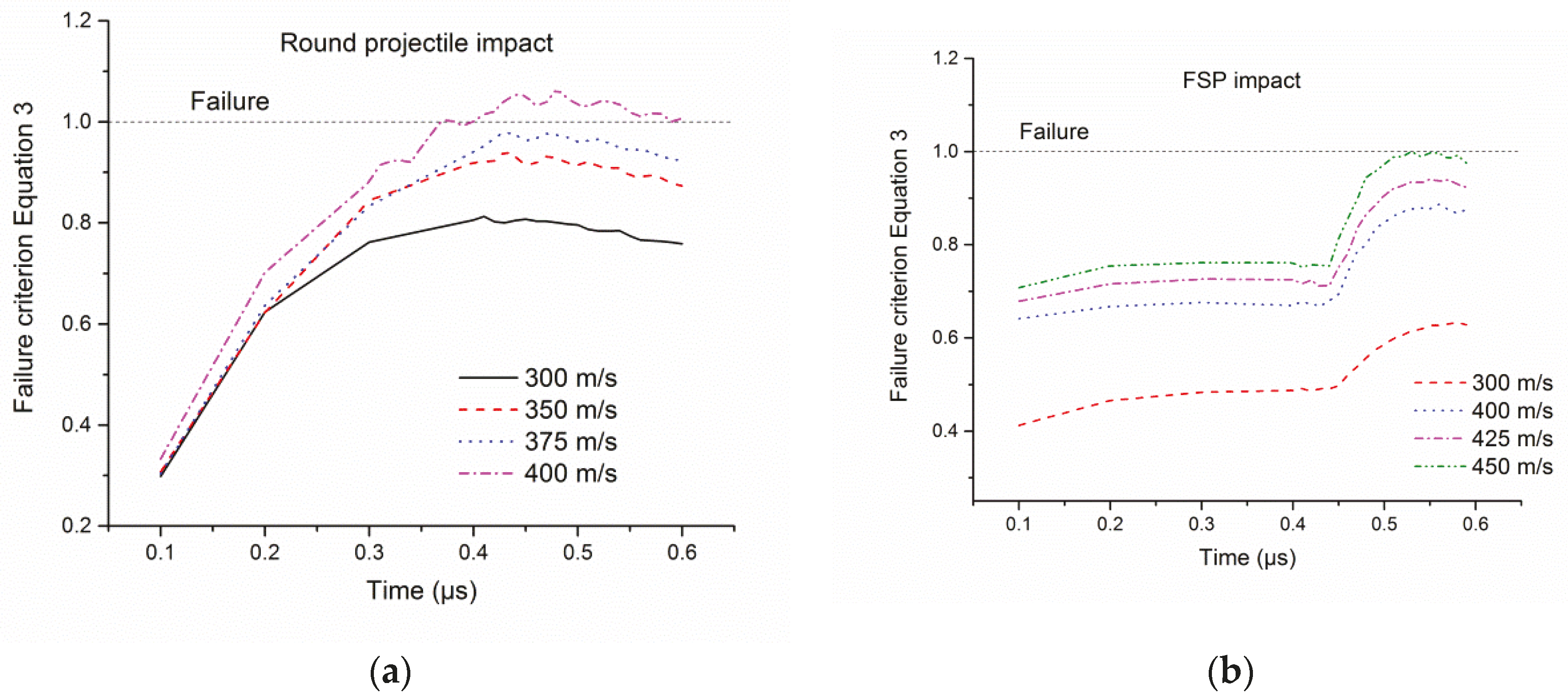
3.3. Failure Criterion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnan, K.; Sockalingam, S.; Bansal, S.; Rajan, S. Numerical simulation of ceramic composite armor subjected to ballistic impact. Compos. B 2010, 41, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Chowdhury, S.C.; Gillespie, J.W.; Keefe, M. Recent advances in modeling and experiments of Kevlar ballistic fibrils, fibers, yarns and flexible woven textile fabrics—A review. Text. Res. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.C.; McCrackin, F.L.; Schiefer, H.F. Stress-Strain Relationships in Yarns Subjected to Rapid Impact Loading: Part V: Wave Propagation in Long Textile Yarns Impacted Transversely. Text. Res. J. 1958, 28, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocron, S.; Kirchdoerfer, T.; King, N.; Freitas, C.J. Modeling of fabric impact with high speed imaging and nickel-chromium wires validation. J. Appl. Mech. 2011, 78, 051007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.D.; Chocron, S. Why impacted yarns break at lower speed than classical theory predicts. J. Appl. Mech. 2011, 78, 051021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, M.; Chu, J.; Jewell, E.; Lim, B.; Ytuarte, E.; Tsutsui, W.; Horner, S.; Zheng, J.; Chen, W. Effect of projectile nose geometry on the critical velocity and failure of yarn subjected to transverse impact. Text. Res. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.A. Dynamic Behavior of Materials; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, R.A.; Cohen, S.H.; Segars, R.A. Heat as a factor in the penetration of cloth ballistic panels by 0.22 caliber projectiles. Text. Res. J. 2000, 70, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, V.; Lim, C.; Cheong, C. Perforation of high-strength fabric by projectiles of different geometry. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2003, 28, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr.; Keefe, M. Dynamic modeling of Kevlar KM2 single fiber subjected to transverse impact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 67–68, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr.; Keefe, M. On the transverse compression response of Kevlar KM2 using fiber-level finite element model. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 2504–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Gillespie, J.W.; Keefe, M. Modeling the fiber length-scale response of Kevlar KM2 yarn during transverse impact. Text. Res. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, Q.P.; Gillespie, J.W.; VanLandingham, M.R. Evaluation of the three-dimensional properties of Kevlar across length scales. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 1824–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Bremble, R.; Gillespie, J.W.; Keefe, M. Transverse compression behavior of Kevlar KM2 single fiber. Compos. A 2016, 81, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.P.; Nilakantan, G.; Keefe, M.; Powers, B.M.; Bogetti, T.A. Global/Local Modeling of Ballistic Impact onto Woven Fabrics. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilakantan, G.; Keefe, M.; Bogetti, T.A.; Adkinson, R.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr. On the finite element analysis of woven fabric impact using multiscale modeling techniques. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 2300–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr.; Keefe, M. Influence of multiaxial loading on the failure of Kevlar KM2 single fiber. Text. Res. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, M.; Li, D.; Spatola, J.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J. The effects of off-axis transverse deflection loading on the failure strain of various high-performance fibers. Text. Res. J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heru Utomo, B.; Broos, J. Dynamic material behavior determination using single fiber impact. In Proceedings of the 25th Conference and Exposition on Structural Dynamics 2007, IMAC-XXV, Orlando, FL, USA, 19–22 February 2007; p. 7.
- Hallquist, J.O. LS-DYNA Theory Manual; Livermore Software Technology Corporation: Livermore, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Chen, W.; Weerasooriya, T. Mechanical Properties of Kevlar® KM2 Single Fiber. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2005, 127, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.A.; Deitzel, J.M.; Gillespie, J.W. Compressive strength analysis for high performance fibers with different modulus in tension and compression. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, M.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J. Why the Smith theory over-predicts instant rupture velocities during fiber transverse impact. Text. Res. J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, M.C. Multi-Axial Failure of High-Performance Fiber during Transverse Impact. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nilakantan, G.; Obaid, A.A.; Keefe, M.; Gillespie, J.W. Experimental evaluation and statistical characterization of the strength and strain energy density distribution of Kevlar KM2 yarns: Exploring length-scale and weaving effects. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1749–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanborn, B.; Weerasooriya, T. Quantifying damage at multiple loading rates to Kevlar KM2 fibers due to weaving, finishing, and pre-twist. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2014, 71, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.C.; Haque, B.Z.; van Duin, A.C.T.; Bogetti, T.A.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr. Study of the Mechanical Properties of Kevlar Fibril using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. In Proceedings of the SAMPE Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 18–21 May 2015.
- Cheng, M.; Chen, W.; Weerasooriya, T. Experimental investigation of the transverse mechanical properties of a single Kevlar® KM2 fiber. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2004, 41, 6215–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, A.A.; Yarlagadda, S.; Gillespie, J. Combined effects of kink bands and hygrothermal conditioning on tensile strength of polyarylate liquid crystal co-polymer and aramid fibers. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 50, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, S.; Goncharuk, G.; Bobrov, A. Effect of transverse compression on the tensile strength of aramid yarns. Dokl. Phys. Chem. 2015, 462, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, P.B.; Sockalingam, S.; Deitzel, J.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr.; Keefe, M.; Bogetti, T.A.; Casem, D.T.; Weerasooriya, T. The effect of fiber meso/nanostructure on the transverse compression response of ballistic fibers. Compos. A 2017, 94, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Sockalingam, S.; Gu, B.; Sun, B.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr.; Chou, T. Electromechanical behavior of carbon nanotube fibers under transverse compression. J. Phys. D 2017, 50, 085303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sockalingam, S.; Gillespie, J.W.,.; Keefe, M. Role of Inelastic Transverse Compressive Behavior and Multiaxial Loading on the Transverse Impact of Kevlar KM2 Single Fiber. Fibers 2017, 5, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib5010009
Sockalingam S, Gillespie JW,, Keefe M. Role of Inelastic Transverse Compressive Behavior and Multiaxial Loading on the Transverse Impact of Kevlar KM2 Single Fiber. Fibers. 2017; 5(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib5010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleSockalingam, Subramani, John W., Gillespie, and Michael Keefe. 2017. "Role of Inelastic Transverse Compressive Behavior and Multiaxial Loading on the Transverse Impact of Kevlar KM2 Single Fiber" Fibers 5, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib5010009
APA StyleSockalingam, S., Gillespie, J. W. ,., & Keefe, M. (2017). Role of Inelastic Transverse Compressive Behavior and Multiaxial Loading on the Transverse Impact of Kevlar KM2 Single Fiber. Fibers, 5(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib5010009







