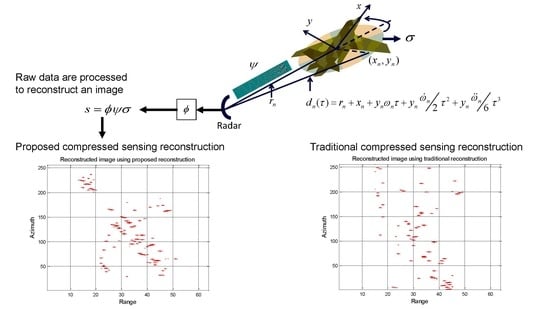
Compressed Sensing ISAR Reconstruction Considering Highly Maneuvering Motion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Compressed Sensing Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar
2.1. Observation Model
2.2. Reconstruction
- The reflectivity vector σ is sparse, which means that many of its entries are zeros or of very small magnitude. This is a valid assumption in CS ISAR imaging as there are a few strong reflecting points in an object for each range bin.
- The matrix should observe the restricted isometric property (RIP), which means that the columns of the matrix should not be very similar, as this would ensure a sufficient number of linearly-independent measurements. This property is satisfied by random Gaussian matrices, Fourier matrices, chirp function matrices [40], etc., the latter two matrices being directly related to CS ISAR imaging and justifying the use of CS for ISAR imaging.
3. Compressed Sensing ISAR Reconstruction in the Presence of High Maneuvering Motion
3.1. Dictionary for High Maneuvering Motion Imaging
- Initialize , repetition number and .
- Correlate each column of the sub-sampled dictionary with and find the column that gives the maximum correlation, i.e., the following correlation is carried out at each repetition k:
- Update by concatenating the selected column of the selected subsampled dictionary, i.e.,
- Find an estimate of the reflectivity corresponding to the updated by solving:
- Update . This update removes the contribution of the estimated reflectivity calculated in the previous step.
- Increment k, and repeat Steps 2–6 until , where υ is a threshold that can be set based upon a perceived SNR: a higher SNR means a lower threshold and vice versa. Other termination conditions may involve running the repetitions a fixed number of times based on expected sparsity, or when there is no significant change in for a number of repetitions. The ratio shows the relative change in energy of when the contribution of the selected dictionary’s column is removed from it, compared to the energy of the initial received data .
- The final result provides an estimate of reflectivity corresponding to each and γ parameter according to Equation (24). This estimate is given as , where K is the final repetition. The 1D reflectivity is estimated by adding the result for all values of rotational acceleration and rotational acceleration rate together as described in Equation (25) to obtain the estimate . This estimate shows the reflectivity for each position given by .
3.2. CS ISAR Dictionary Performance in Terms of Dictionary Mismatch
3.2.1. Performance with Small Mismatch
3.2.2. Performance with Large Mismatch
3.2.3. Performance with Small and Mismatches
3.2.4. Performance with Large and Mismatches
3.3. Modified OMP
3.4. Computational Complexity
4. Results
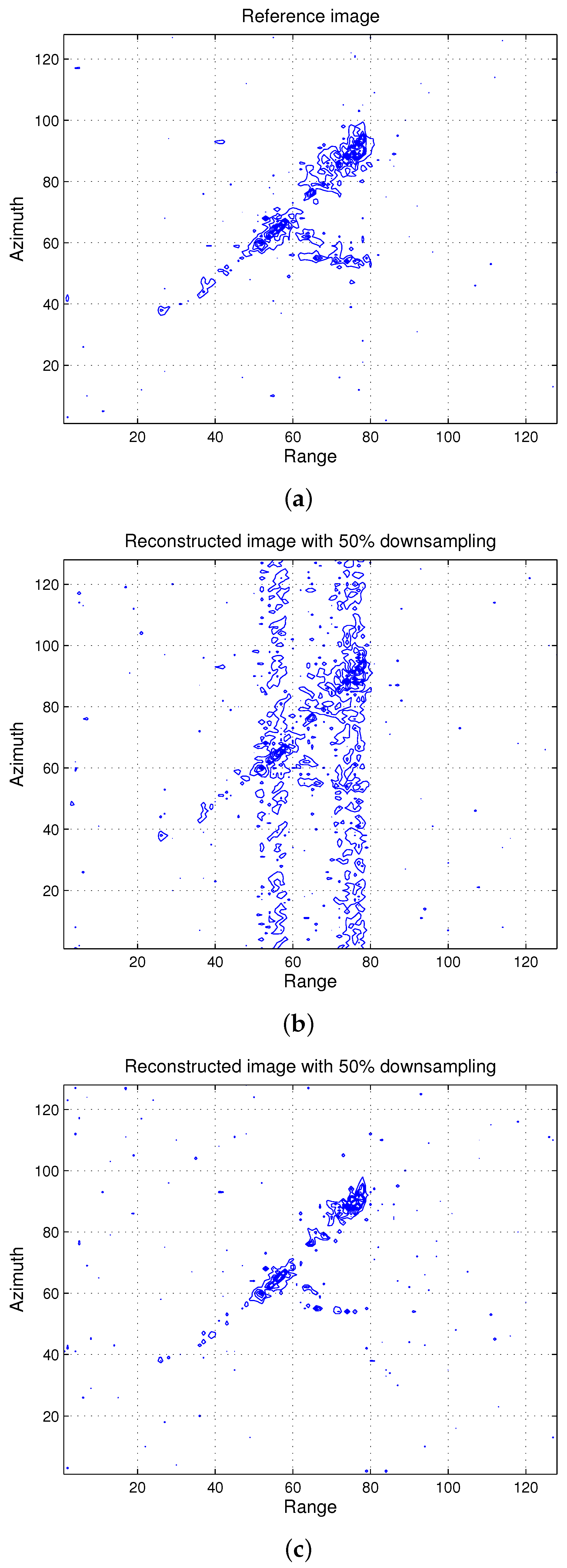
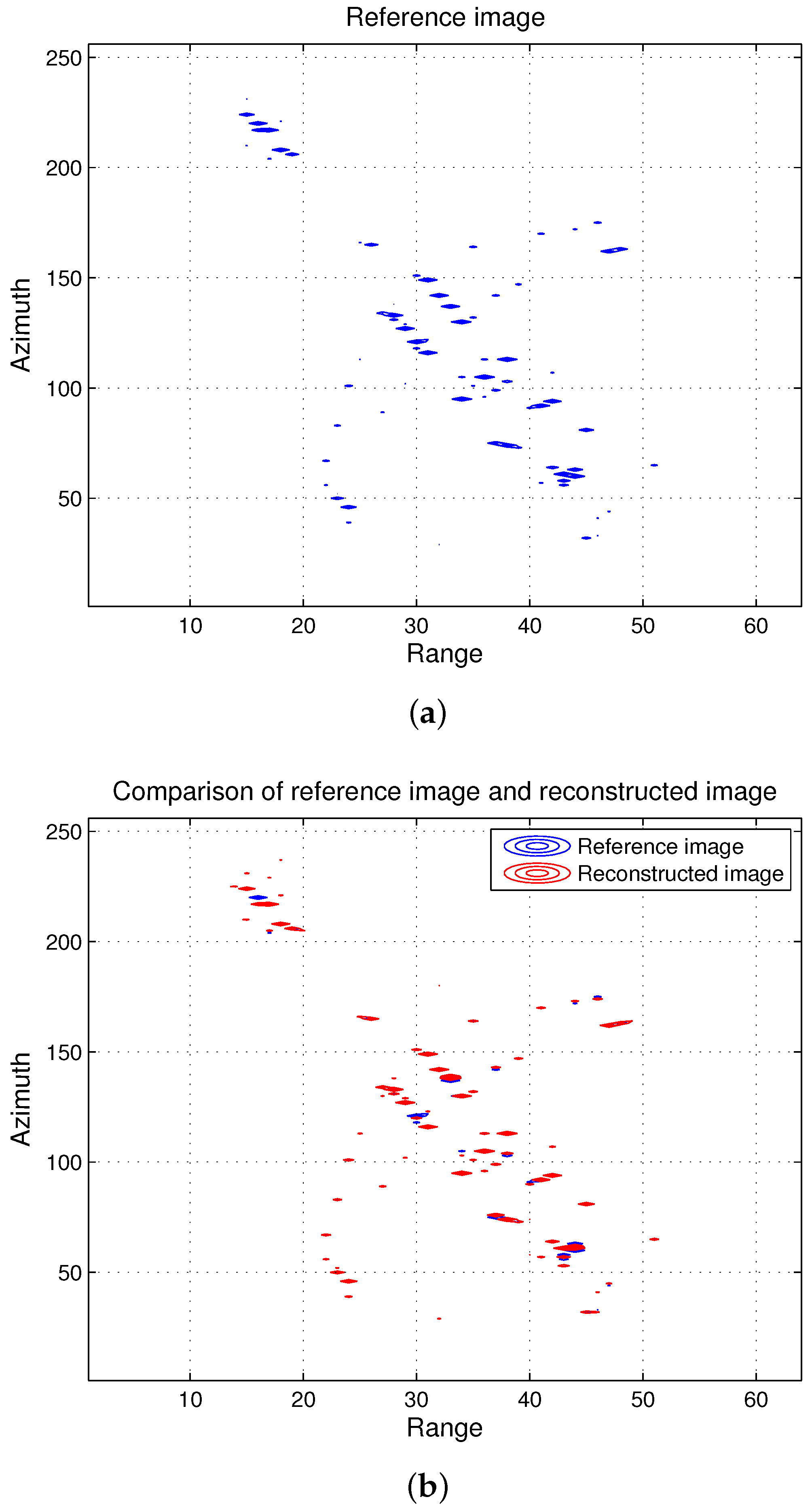
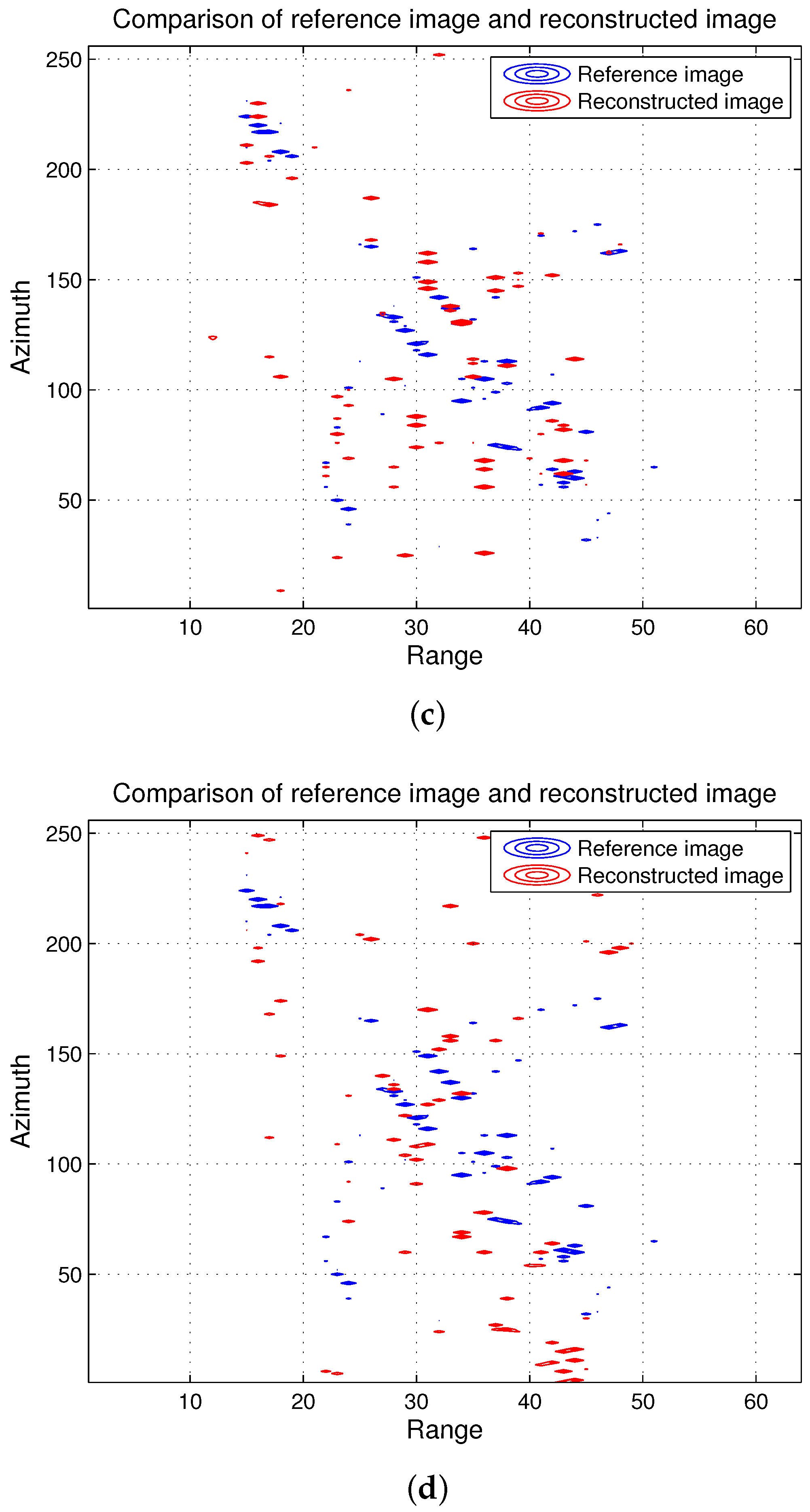
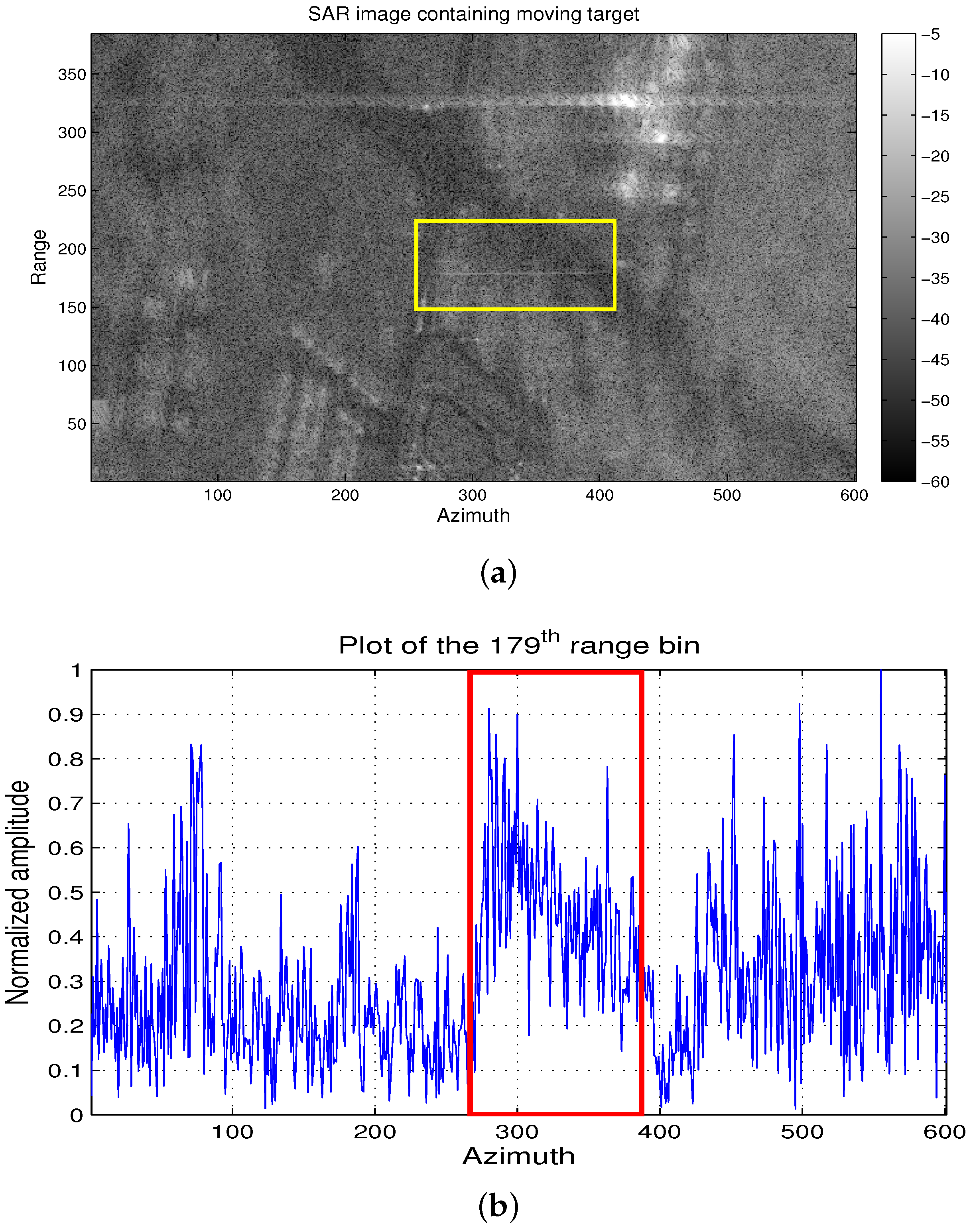
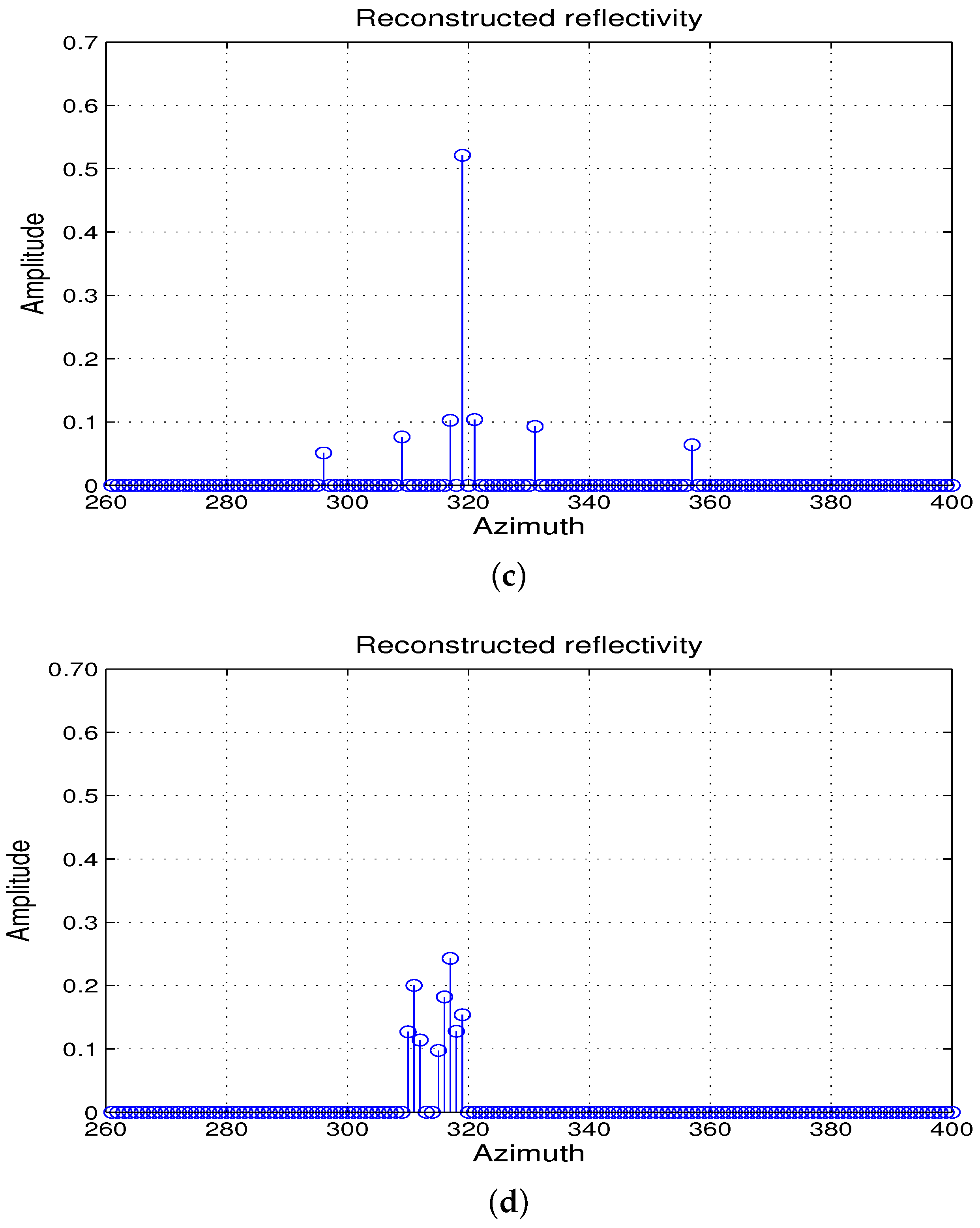
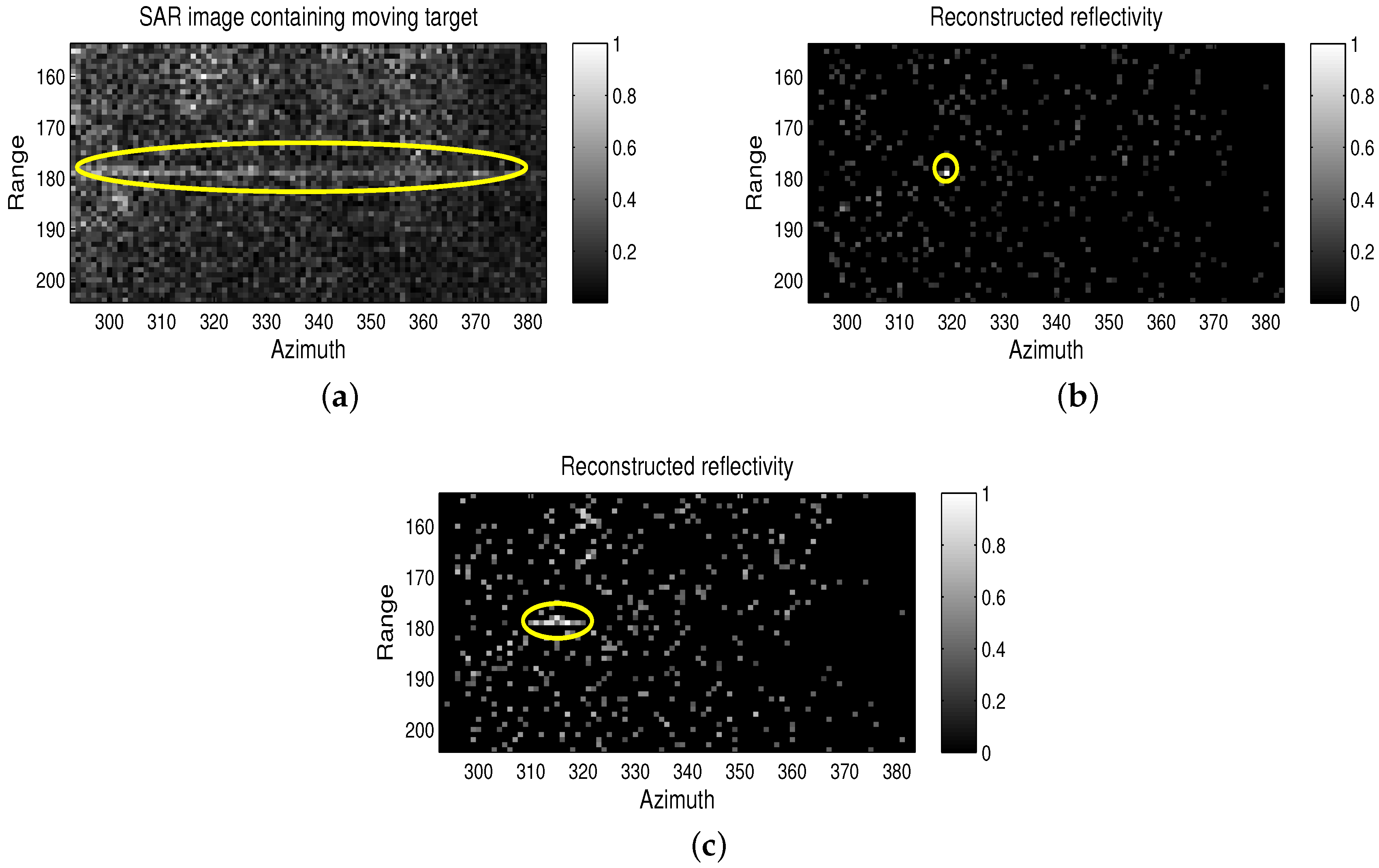
4.1. Imaging Results
4.2. Numerical Results
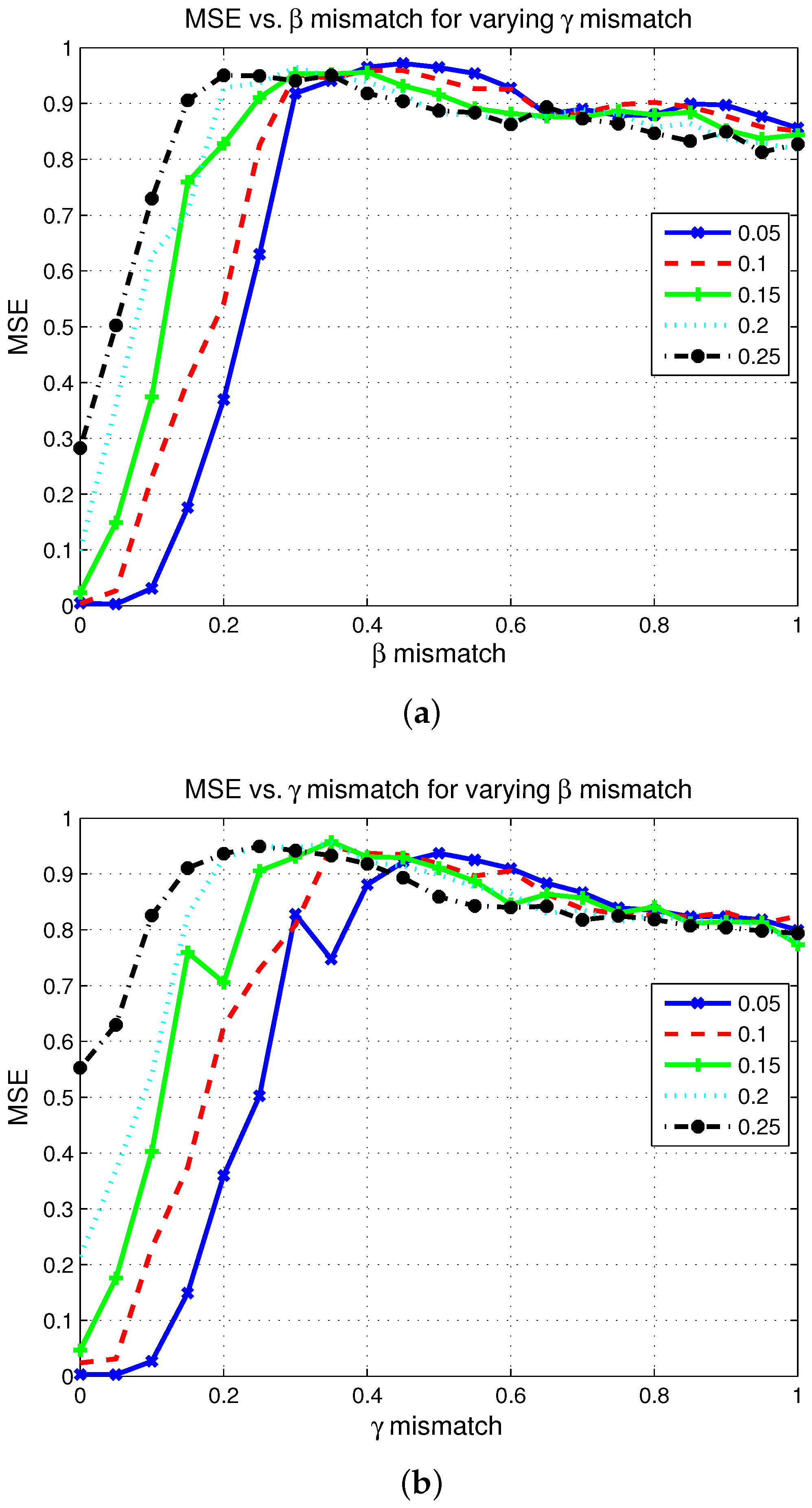
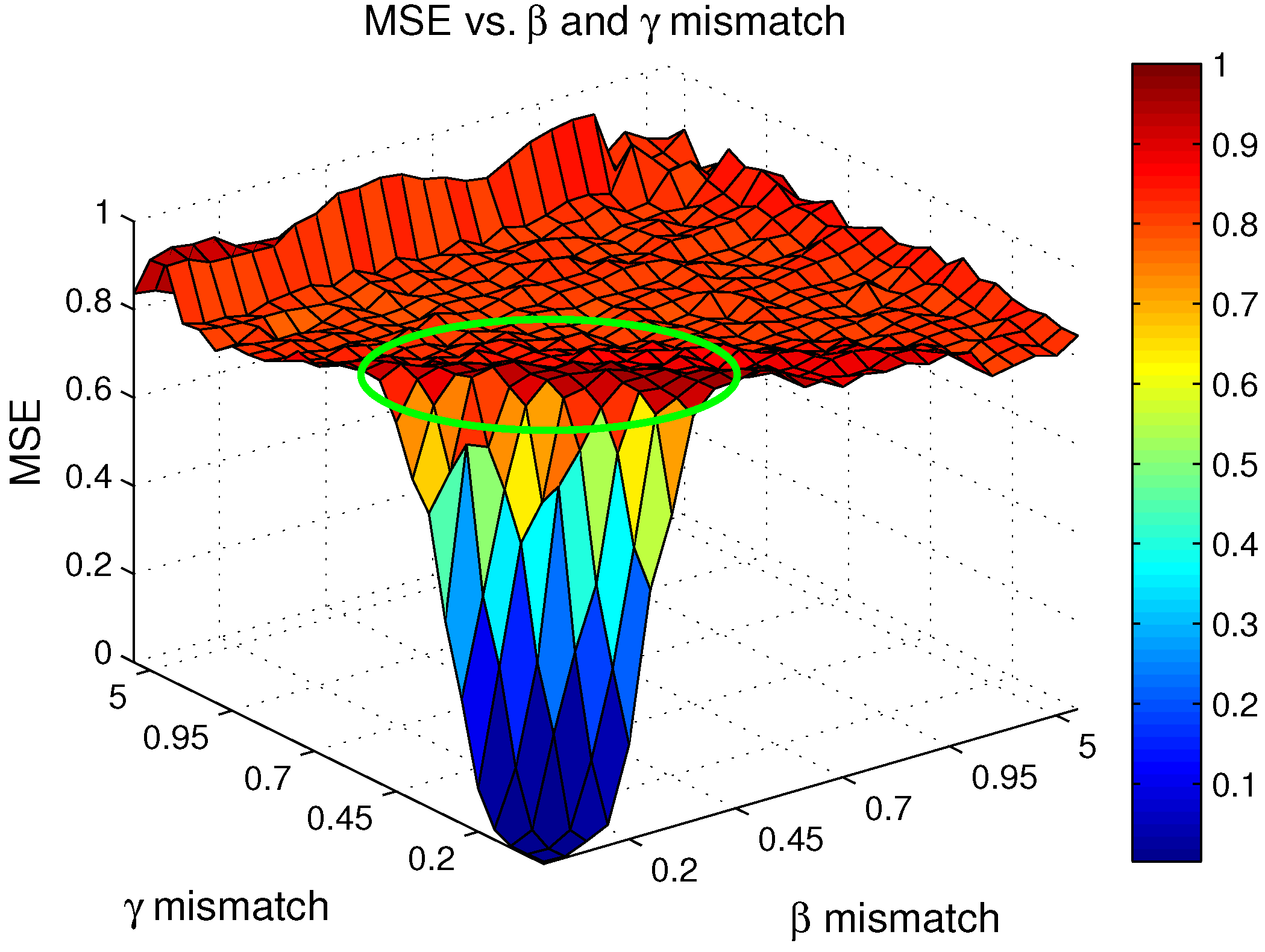
4.2.1. Performance of the CS ISAR Dictionary in the Presence of Mismatch
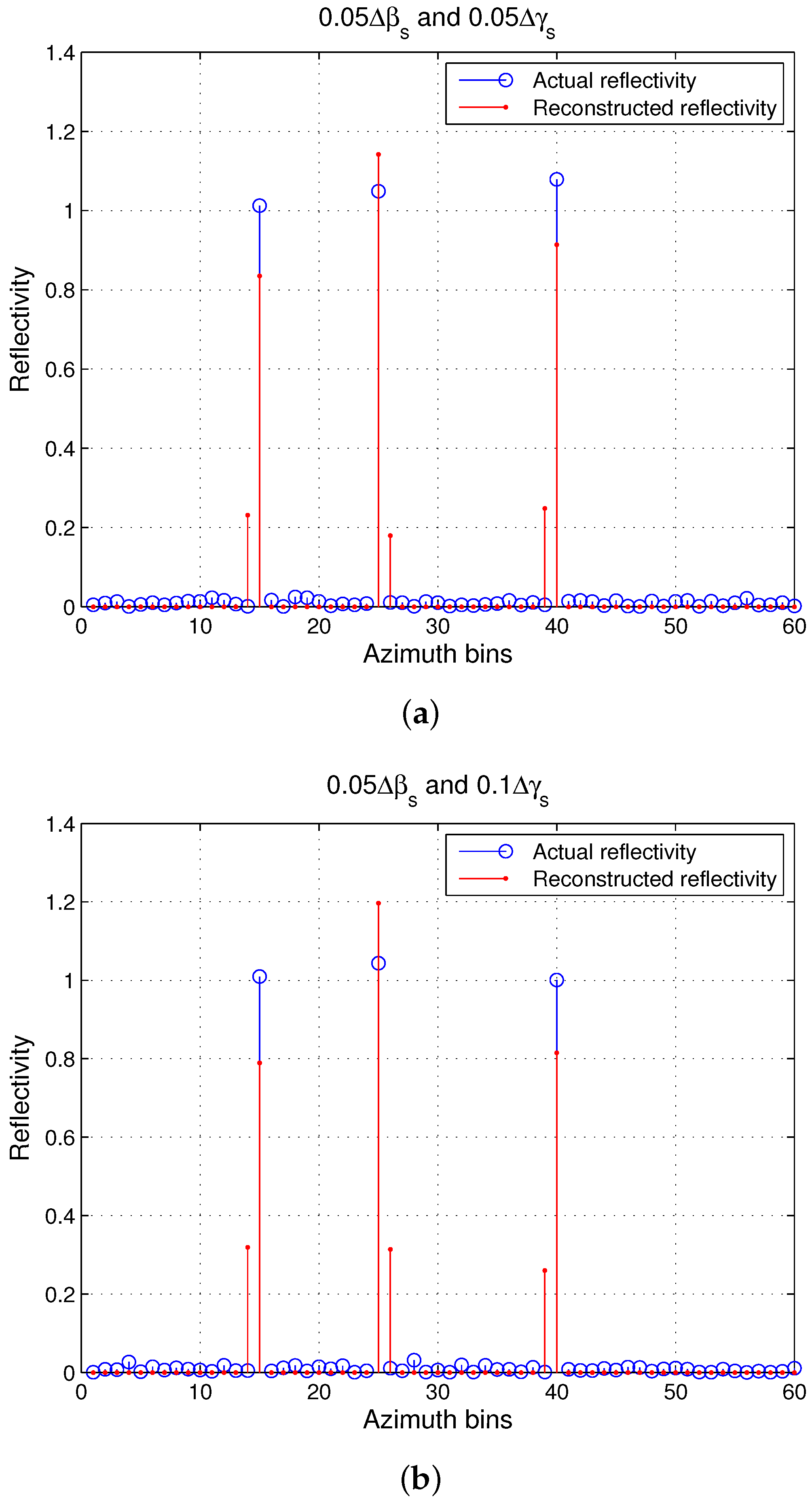
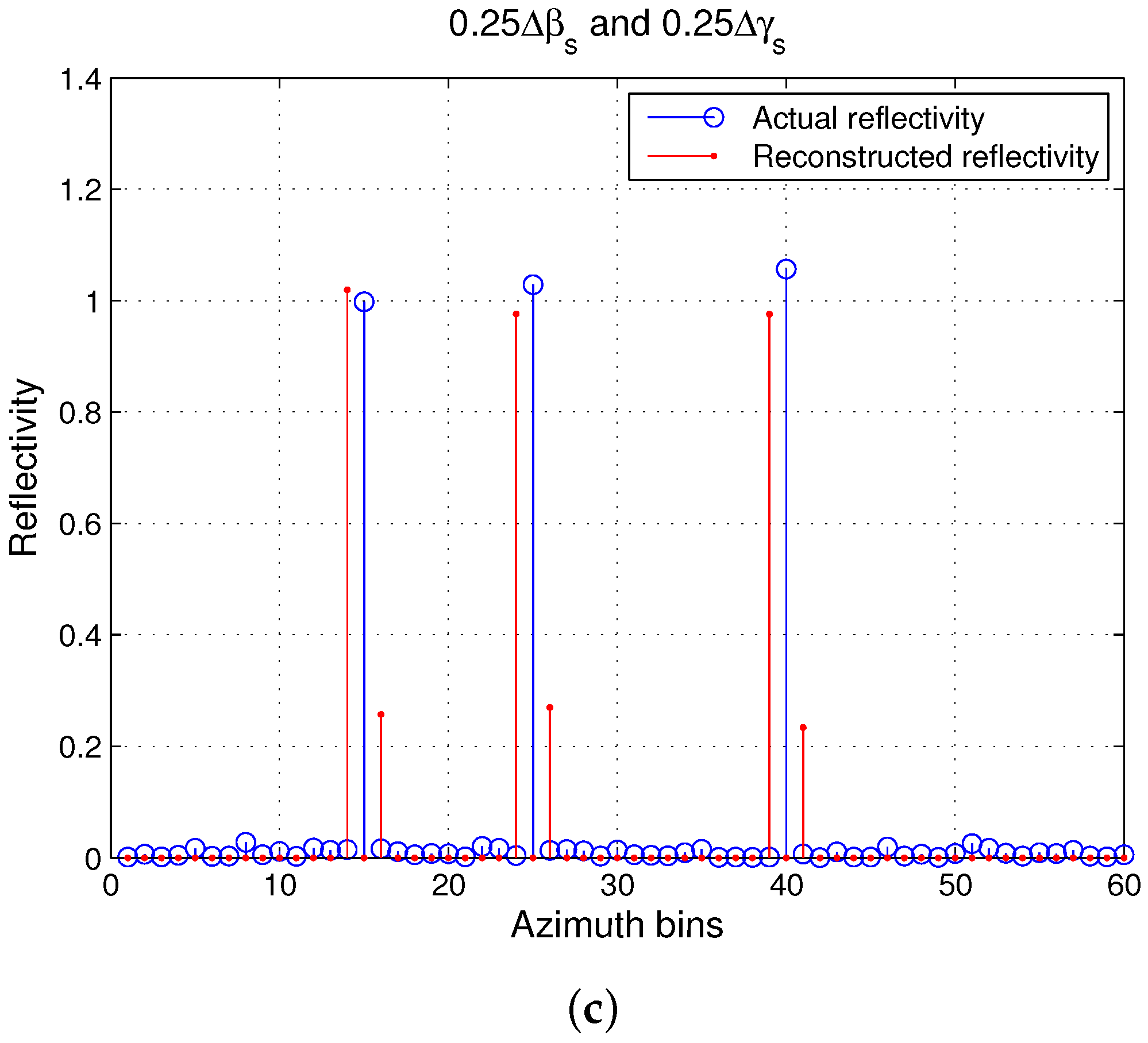
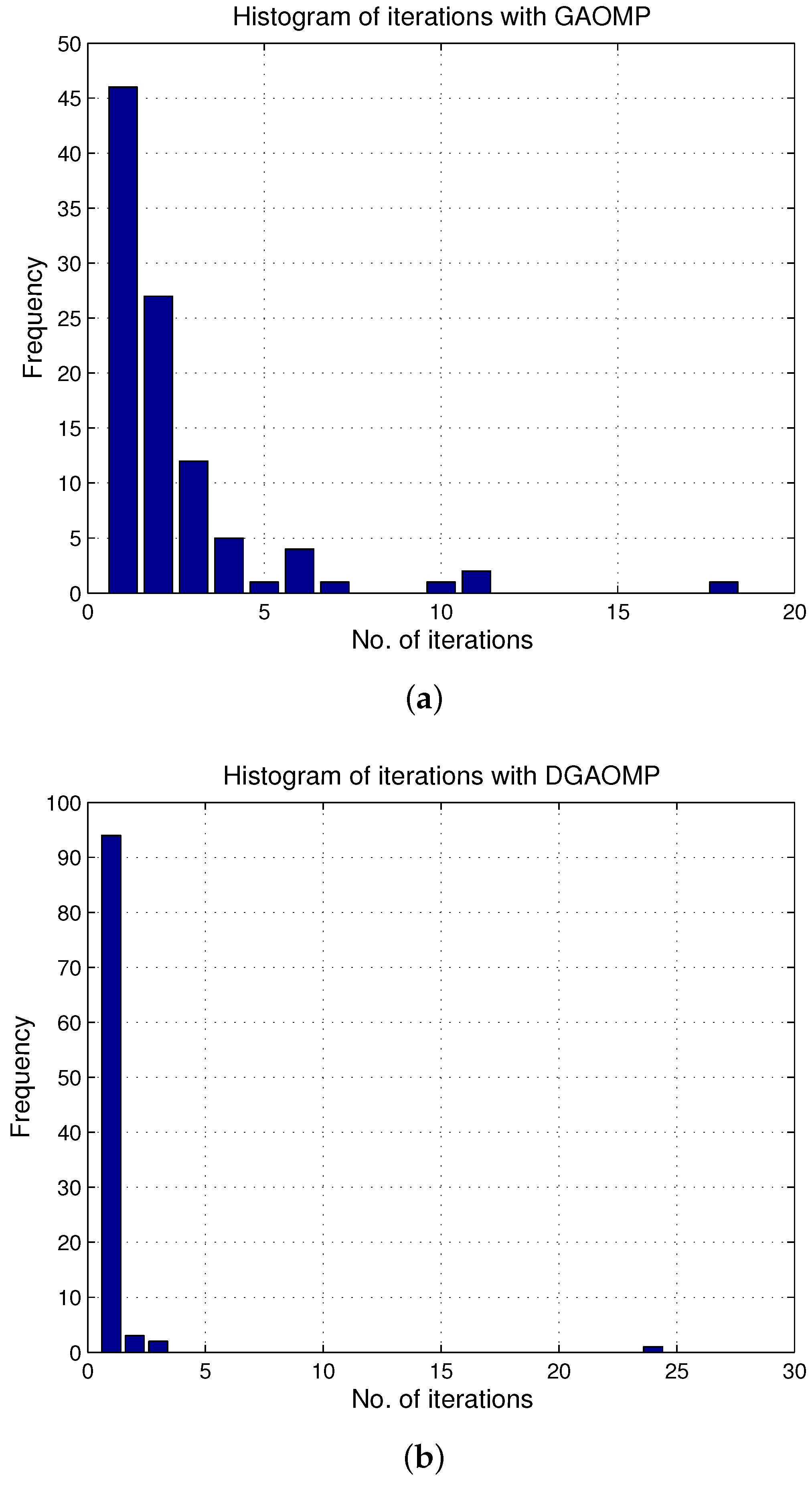
4.2.2. Reconstruction Performance of the Proposed Algorithm
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Candès, E.; Tao, T. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 5406–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.; Romberg, J.; Tao, T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 489–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniuk, R. Compressive sensing [Lecture notes]. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2007, 24, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropp, J.; Gilbert, A. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Xue, Y.; Carin, L. Bayesian compressive sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 2346–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayyani, H.; Babaie-Zadeh, M.; Jutten, C. Bayesian pursuit algorithm for sparse representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2009), Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009.
- Schnitter, P.; Potter, L.; Ziniel, J. Fast Bayesian matching pursuit. In Proceedings of the Information Theory and Applications Workshop, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 January–1 February 2008.
- Cetin, M.; Karl, W. Feature-enhanced synthetic aperture radar image formation based on nonquadratic regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J. Single-pixel remote sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Bamler, R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 247–258. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Ahmad, F.; Amin, M. Joint localization of stationary and moving targets behind walls using sparse scene recovery. J. Electron. Imag. 2013, 22, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, J. On compressive sensing applied to radar signal processing. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Easley, G.; Healy, D.; Chellappa, R. Compressed synthetic aperture radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2010, 4, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M.; Stojanovic, I.; Onhon, N.; Varshney, K.; Samadi, S.; Karl, W.; Willsky, A. Sparsity-driven synthetic aperture radar imaging: Reconstruction, autofocusing, moving targets, and compressed sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M.; Lanterman, A. Region-enhanced passive radar imaging. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2005, 152, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevanovic, M.; Crocco, L.; Djordjevic, A.; Nehorai, A. Higher order sparse microwave imaging of PEC scatterers. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xing, M.; Qiu, C.; Li, J.; Bao, Z. Achieving higher resolution ISAR imaging with limited pulses via compressed sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.-G. ISAR 2-D imaging of uniformly rotating targets via matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.-G. Adaptive sparse recovery by parametric weighted L1 minimization for ISAR imaging of uniformly rotating targets. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. 2013, 6, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiu, B.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Cong, Y.; Bao, Z. Joint ISAR imaging and cross-range scaling method based on compressive sensing with adaptive dictionary. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A.S.; Zhang, X.-P. Compressed Sensing ISAR reconstruction in the presence of rotational acceleration. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. 2014, 7, 2957–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.; Strohmer, T. General deviants: An analysis of perturbations in compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 4, 342–349. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.; Pezeshki, A.; Scharf, L.; Calderbank, A. Sensitivity to basis mismatch in compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 2182–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, L. ISAR image analysis and recovery with unavailable or heavily corrupted data. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y. ISAR imaging of ship target with complex motion based on new approach of parameters estimation for polynomial phase signal. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2011, 2011, 425203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.-G.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Bao, Z. High-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging and scaling with sparse aperture. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. 2015, 8, 4010–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, X.; Li, X. Decoupled ISAR imaging using RSFW based on twice compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 3195–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Bi, G.; Yang, L. An autofocus technique for high-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6392–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Tao, M.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Z. Adaptive translational motion compensation method for ISAR imaging under low SNR based on particle swarm optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. 2015, 8, 5146–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, S.; Bacci, A.; Giusti, E.; Martorella, M.; Berizzi, F. Compressive sensing-based inverse synthetic radar imaging imaging from incomplete data. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.-Q. Bayesian inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging by exploiting sparse probing frequencies. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, Q.; Sun, H. ISAR imaging by two-dimensional convex optimization-based compressive sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 7088–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, T.; Meng, H.; Chen, J. Compressive sensing based ISAR imaging via the combination of the sparsity and nonlocal total variation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.-J.; Xia, X.-G. Motion compensation for airborne SAR via parametric sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.; Ling, H. Time-Frequency Transforms for Radar Imaging and Signal Analysis; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Soumekh, M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Baraniuk, R.; Cevher, V.; Duarte, M.; Hegde, C. Model-Based Compressive Sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2010, 56, 1982–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, A.; Radha, H. Complex sparse projections for compressed sensing. In Proceedings of the 2010 44th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Princeton, NJ, USA, 17–19 March 2010.
- Applebaum, L.; Howard, S.; Searle, S.; Calderbank, R. Chirp sensing codes: Deterministic compressed sensing measurements for fast recovery. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2009, 26, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, R.; Xing, M.; Bao, Z. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of ship target with complex motion. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2008, 2, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M. In An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough, S.; Casteel, C., Jr.; Gorham, L.; Minardi, M.; Majumder, U.; Judge, M.; Zelnio, E.; Bryant, M.; Nichols, H.; Page, D. A challenge problem for SAR-based GMTI in urban environments. In SPIE Proceedings: Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery; The International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7337. [Google Scholar]
- SAR-Based GMTI in Urban Environment Challenge Problem Overview. Available online: https://www.sdms.afrl.af.mil/index.php?collection=gmti (accessed on 9 March 2017).
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. An airborne SAR moving target imaging and motion parameters estimation algorithm with azimuth-dechirping and the second-order Keystone transform applied. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. 2015, 8, 3967–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mismatch | Effects | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | × | × | ✔ | Amplitude degradation if is close to . |
| Case 2 | ✔ | × | ✔ | Amplitude degradation and position shift if and . Position shift only if . |
| Case 3 | × | ✔ | ✔ | No position shift if . Otherwise, amplitude degradation and position shift. |
| Case 4 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Amplitude degradation and position shift if . Otherwise, position shift only. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khwaja, A.S.; Cetin, M. Compressed Sensing ISAR Reconstruction Considering Highly Maneuvering Motion. Electronics 2017, 6, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6010021
Khwaja AS, Cetin M. Compressed Sensing ISAR Reconstruction Considering Highly Maneuvering Motion. Electronics. 2017; 6(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhwaja, Ahmed Shaharyar, and Mujdat Cetin. 2017. "Compressed Sensing ISAR Reconstruction Considering Highly Maneuvering Motion" Electronics 6, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6010021
APA StyleKhwaja, A. S., & Cetin, M. (2017). Compressed Sensing ISAR Reconstruction Considering Highly Maneuvering Motion. Electronics, 6(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6010021