Breath Ethane Concentrations in Healthy Volunteers Correlate with a Systemic Marker of Lipid Peroxidation but Not with Omega-3 Fatty Acid Availability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Human Participants
2.2. Biological Sample Collection
2.3. Analytical Procedures
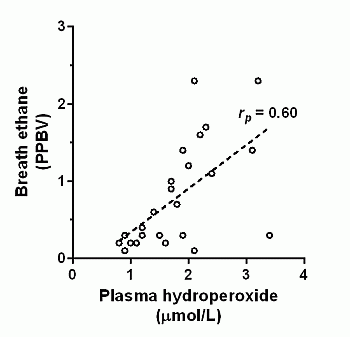
3. Results

| Fatty acid | Mol % | Correlation with breath ethane |
|---|---|---|
| C18:3 n-3 (α-linolenic) | 0.24 ± 0.05 | −0.13 |
| C18:4 n-3 (stearidonic) | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 0.35 |
| C20:3 n-3 (eicosatrienoic) | 0.09 ± 0.05 | 0.11 |
| C20:4 n-3 (eicosatetraenoic) | 0.12 ± 0.05 | −0.03 |
| C20:5 n-3 (eicosapentaenoic) | 0.96 ± 0.26 | 0.31 |
| C22:5 n-3 (docosapentaenoic) | 2.7 ± 0.41 | 0.33 |
| C22:6 n-3 (docosahexaenoic) | 4.5 ± 0.82 | −0.16 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Free Radicals In Biology And Medicine, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, M.W.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Gray, S.G. Targeting oxidative stress in cancer. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 1225–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rains, J.L.; Jain, S.K. Oxidative stress, insulin signaling, and diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, E.J.; Mancini, E.V.; Seth, R.; Yao, X.H.; Netticadan, T. Oxidative stress and heart disease: cardiac dysfunction, nutrition, and gene therapy. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2003, 5, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013. Article 316523. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, B.M.; McKenzie, I.; Glen, I.; Bennett, C.P. Increased levels of ethane, a non-invasive marker of n-3 fatty acid oxidation, in breath of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Nutr. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Mahadik, S.P.; Mukherjee, S. Free radical pathology and antioxidant defense in schizophrenia: A review. Schiz. Res. 1996, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A.; Colombo, R. Protein carbonyl groups as biomarkers of oxidative stress. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2003, 329, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge, J.M. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidants as biomarkers of tissue damage. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, B.M.; Puukila, S.; Malik, I.; Babay, S.; Lecours, M.; Agostino, A.; Wondimu, T.; Khaper, N. The use of SIFT-MS to investigate headspace aldehydes as markers of lipid peroxidation. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2013, 9, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlius, Y.; Ingleman-Sundberg, M. Metabolism of n-pentane by ethanol-inducible cytochrome P-450 in liver microsomes and reconstituted membranes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 161, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.M.; Shah, S.; Peet, M. Increased breath ethane and pentane concentrations in currently unmedicated patients with schizophrenia. Open. J. Psychiatr. 2011, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letteron, P.; Duchatelle, V.; Berson, A.; Fromenty, B.; Fisch, C.; Degott, C.; Benhamou, J.P. Increased ethane exhalation, an in vivo index of lipid peroxidation, in alcohol abusers. Gut 1993, 34, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, S.A.; Barnes, P.J. Biomarkers of some pulmonary diseases in exhaled breath. Biomarkers 2002, 7, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredi, P.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Barnes, P.J. Elevation of exhaled ethane concentration in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1450–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Gorham, K.A.; Mads, P.; Sulbaek, A.; Meinardi, S.; Delfino, R.J.; Staimer, N.; Tjoa, T.; Rowland, F.S.; Blake, D.R. Ethane and n-pentane in exhaled breath are biomarkers of exposure not effect. Biomarkers 2009, 14, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, M.P.; Clements, N.C.; Garewal, H.S. Cigarette smoking and ethane exhalation in humans. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, B.K.; Treasaden, I.H.; Cocchi, M.; Tsaluchidu, S.; Tonello, L.; Ross, B.M. A comparison of oxidative stress in smokers and non-smokers: an in vivo human quantitative study of n-3 lipid peroxidation. BMC Psychiatr. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeleye, O.E.; Watson, R.R.; Eskelson, C.D.; Mufti, S.I. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acid promotes peroxidation and its possible role in the promotion of cancer. In Biological Reactive Intermediates IV; Witmer, C.M., Snyder, R.R., Jollow, D.J., Kalf, G.F., Kocsis, J.J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: London, UK, 1990; pp. 789–791. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, B.M.; Maxwell, R.; Glen, I. Increased breath ethane levels in medicated patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are unrelated to erythrocyte omega-3 fatty acid abundance. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatr. 2011, 30, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, R.; Ward, P.E.; Glen, I.; Roberts, S.J.; Ross, B.M. On the relationship between methylnicotinate-induced skin flush and fatty acids levels in acute psychosis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatr. 2003, 27, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obajimi, O.; Black, K.D.; Glen, I.; Ross, B.M. Antioxidant modulation of oxidant-stimulated uptake and release of arachidonic acid in eicosapentaenoic acid-supplemented human lymphoma U937 cells. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 2007, 76, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.P. Ferrous ion oxidation in the presence of the ferric ion indicator xylenol orange for the measurement of hydroperoxides: the FOX assay. Meth. Enzymol. 1994, 233, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catignani, G.L.; Bieri, J.G. Simultaneous determination of retinol and alpha-tocopherol in serum or plasma by liquid chromatography. Clin. Chem. 1983, 29, 708–712. [Google Scholar]
- Wander, R.; Du, S.-H. Oxidation of plasma proteins is not increased after supplementation with eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 731–737. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Rong, S.; Qu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, D.; Pan, H.; Wang, W. Relation between gastric cancer and protein oxidation, DNA damage, and lipid peroxidation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013. Article 543760. [Google Scholar]
- Nourooz-Zadeh, J.; Tajaddini-Sarmadi, J.; McCarthy, S.; Betteridge, D.J.; Wolff, S.P. Elevated levels of authentic plasma hydroperoxides in NIDDM. Diabetes 1995, 44, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, F.S.; Humphreys, M.H.; DoNascimento, C.A.; Abbasi, F.; Reaven, G.M. Relation between insulin resistance and plasma concentrations of lipid hydroperoxides, carotenoids, and tocopherols. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 776–779. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ross, B.M.; Glen, I. Breath Ethane Concentrations in Healthy Volunteers Correlate with a Systemic Marker of Lipid Peroxidation but Not with Omega-3 Fatty Acid Availability. Metabolites 2014, 4, 572-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4030572
Ross BM, Glen I. Breath Ethane Concentrations in Healthy Volunteers Correlate with a Systemic Marker of Lipid Peroxidation but Not with Omega-3 Fatty Acid Availability. Metabolites. 2014; 4(3):572-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4030572
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoss, Brian M., and Iain Glen. 2014. "Breath Ethane Concentrations in Healthy Volunteers Correlate with a Systemic Marker of Lipid Peroxidation but Not with Omega-3 Fatty Acid Availability" Metabolites 4, no. 3: 572-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4030572
APA StyleRoss, B. M., & Glen, I. (2014). Breath Ethane Concentrations in Healthy Volunteers Correlate with a Systemic Marker of Lipid Peroxidation but Not with Omega-3 Fatty Acid Availability. Metabolites, 4(3), 572-579. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4030572