Modeling and Simulation of Optimal Resource Management during the Diurnal Cycle in Emiliania huxleyi by Genome-Scale Reconstruction and an Extended Flux Balance Analysis Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Software
2.2. Genome-Scale Model of E. huxleyi
2.3. diuFBA


2.4. Phenotypic Phase Plane Plots
2.5. Example Model

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Genome-Scale Model
| Category | No. of Reactions |
|---|---|
| Derived from annotated genome | 221 |
| Derived from literature | 9 |
| Gap filling | 72 |
| Transport reactions | 86 |
| Chemical equilibrium reactions | 5 |
| Build-up of biomass precursors | 18 |
| Overlap with other reconstructions | |
| iAF1260 [4] | 103 |
| AraGEM [7] | 60 |
| AlgaGEM [8] | 93 |

3.2. Analysis of the Example Model
3.3. Analysis of the E. huxleyi Model
| Biomass Component | Literature | diuFBA | diuFBA (Protein fixed) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth rate [1/d] | 0.81 | 0.924 | 0.893 |
| Proteins | 1.52 | 3.96 | 1.52 |
| Lipids | 8.62 | 6.69 | 6.69 |
| Long chain molecules | 6.74 | 2.98 | 2.98 |
| Low molecular weight molecules | 7.77 | 9.17 | 12.28 |
| Total carbon | 24.65 | 22.80 | 25.91 |
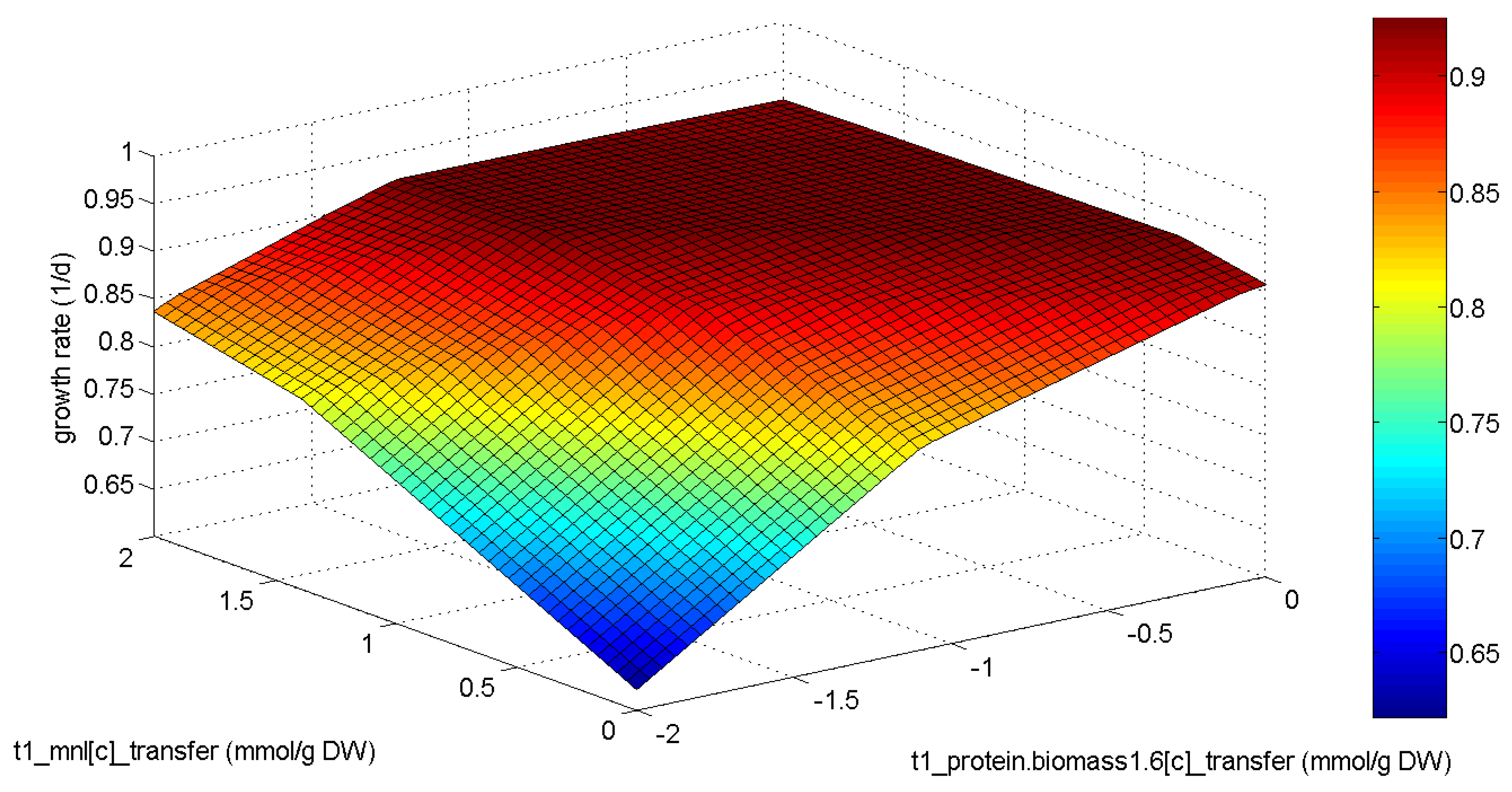

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westbroek, P.; Brown, C.W.; van Bleijswijk, J.; Brownlee, C.; Brummer, G.J.; Conte, M.; Egge, J.; Fernández, E.; Jordan, R.; Knappertsbusch, M.; et al. A model system approach to biological climate forcing. The example of Emiliania huxleyi. Glob. Planet Chang. 1993, 8, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsanti, L.; Gualtieri, P. Algae: Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Read, B.A.; Kegel, J.; Klute, M.J.; Kuo, A.; Lefebvre, S.C.; Maumus, F.; Mayer, C.; Miller, J.; Monier, A.; Salamov, A.; et al. Pan genome of the phytoplankton Emiliania underpins its global distribution. Nature 2013, 499, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feist, A.M.; Henry, C.S.; Reed, J.L.; Krummenacker, M.; Joyce, A.R.; Karp, P.D.; Broadbelt, L.J.; Hatzimanikatis, V.; Palsson, B. A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction for Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 that accounts for 1260 ORFs and thermodynamic information. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, J.D.; Conrad, T.M.; Na, J.; Lerman, J.A.; Nam, H.; Feist, A.M.; Palsson, B.Ø. A comprehensive genome-scale reconstruction of Escherichia coli metabolism—2011. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, J.; Famili, I.; Fu, P.; Palsson, B.; Nielsen, J. Genome-scale reconstruction of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic network. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Dal’Molin, C.G.; Quek, L.E.; Palfreyman, R.W.; Brumbley, S.M.; Nielsen, L.K. AraGEM, a genome-scale reconstruction of the primary metabolic network in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Dal’Molin, C.G.; Quek, L.E.; Palfreyman, R.W.; Nielsen, L.K. AlgaGEM—A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of algae based on the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii genome. BMC Genom. 2011, 12 (Suppl. 4), S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, K.J.; Prakash, P.; Edwards, J.S. Advances in flux balance analysis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, K.; Chandra, N. Flux balance analysis of biological systems: Applications and challenges. Brief. Bioinf. 2009, 10, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, J.D.; Thiele, I.; Palsson, B. What is flux balance analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.S.; Ramakrishna, R.; Palsson, B.O. Characterizing the metabolic phenotype: A phenotype phase plane analysis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 77, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, R.; Edwards, J.S.; Doyle, F.J. Dynamic Flux Balance Analysis of Diauxic Growth in Escherichia coli. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Palsson, B.O. Stoichiometric flux balance models quantitatively predict growth and metabolic by-product secretion in wild-type Escherichia coli W3110. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3724–3731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.M.; Poolman, M.G.; Fell, D.A.; Ratcliffe, R.G.; Sweetlove, L.J. A diel flux balance model captures interactions between light and dark metabolism during day-night cycles in C3 and crassulacean acid metabolism leaves. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellenberger, J.; Que, R.; Fleming, R.M.T.; Thiele, I.; Orth, J.D.; Feist, A.M.; Zielinski, D.C.; Bordbar, A.; Lewis, N.E.; Rahmanian, S.; et al. Quantitative prediction of cellular metabolism with constraint-based models: The COBRA Toolbox v2.0. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1290–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorleifsson, S.G.; Thiele, I. rBioNet: A COBRA toolbox extension for reconstructing high-quality biochemical networks. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2009–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurobi Optimization, Inc. Gurobi Optimizer Reference Manual. Available online: http://www.gurobi.com/documentation/6.0/refman/ (accessed on 22 October 2015).
- Thiele, I.; Palsson, B.O. A protocol for generating a high-quality genome-scale metabolic reconstruction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 93–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, A.; Boesch, B.W.; Palsson, B.O. Stoichiometric interpretation of Escherichia coli glucose catabolism under various oxygenation rates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Le Novere, N.; Hucka, M.; Mi, H.; Moodie, S.; Schreiber, F.; Sorokin, A.; Demir, E.; Wegner, K.; Aladjem, M.I.; Wimalaratne, S.M.; et al. The systems biology graphical notation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinder, L.; Wheeler, G.; Schroeder, D.; von Dassow, P.; Riebesell, U.; Brownlee, C. Expression of biomineralization-related ion transport genes in Emiliania huxleyi. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 3250–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimer, N.; Merrett, M. Calcification rate in Emiliania huxleyi Lohmann in response to light, nitrate and availability of inorganic carbon. New Phytol. 1993, 123, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Marañón, E.; Balch, W.M. Intracellular carbon partitioning in the coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi. J. Mar. Syst. 1996, 9, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlund, T.M.; Hadaegh, A.R.; Clark, R.; Nguyen, B.; Fanelli, M.; Read, B.A. Analysis of Expressed Sequence Tags from Calcifying Cells of Marine Coccolithophorid (Emiliania huxleyi). Mar. Biotechnol. 2004, 6, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riebesell, U.; Revill, A.T.; Holdsworth, D.G.; Volkman, J.K. The effects of varying CO 2 concentration on lipid composition and carbon isotope fractionation in Emiliania huxleyi. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 4179–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, T.; Schoenefeld, S.; Krahnert, I.; Bergmann, S.; Scheffel, A.; Fernie, A.R. Gas-chromatography mass-spectrometry (GC-MS) based metabolite profiling reveals mannitol as a major storage carbohydrate in the coccolithophorid alga Emiliania huxleyi. Metabolites 2013, 3, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Suzuki, I.; Shiraiwa, Y. Quantitative Analysis of Carbon Flow into Photosynthetic Products Functioning as Carbon Storage in the Marine Coccolithophore, Emiliania huxleyi. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zondervan, I.; Rost, B.; Riebesell, U. Effect of CO2 concentration on the PIC/POC ratio in the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi grown under light-limiting conditions and different daylengths. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 272, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokitta, S.D.; Rost, B. Effects of CO2 and their modulation by light in the life-cycle stages of the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebesell, U.; Zondervan, I.; Rost, B.; Tortell, P.D.; Zeebe, R.E.; Morel, F.M. Reduced calcification of marine plankton in response to increased atmospheric CO2. Nature 2000, 407, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlrogge, J.; Browse, J. Lipid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocher, D.; Leaver, M.; Hodgson, P. Recent advances in the biochemistry and molecular biology of fatty acyl desaturases. Prog. Lipid Res. 1998, 37, 73–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Balch, W.M.; Marañón, E.; Holligan, P.M. High rates of lipid biosynthesis in cultured, mesocosm and coastal populations of the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 1994, 114, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knies, D.; Wittmüß, P.; Appel, S.; Sawodny, O.; Ederer, M.; Feuer, R. Modeling and Simulation of Optimal Resource Management during the Diurnal Cycle in Emiliania huxleyi by Genome-Scale Reconstruction and an Extended Flux Balance Analysis Approach. Metabolites 2015, 5, 659-676. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5040659
Knies D, Wittmüß P, Appel S, Sawodny O, Ederer M, Feuer R. Modeling and Simulation of Optimal Resource Management during the Diurnal Cycle in Emiliania huxleyi by Genome-Scale Reconstruction and an Extended Flux Balance Analysis Approach. Metabolites. 2015; 5(4):659-676. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5040659
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnies, David, Philipp Wittmüß, Sebastian Appel, Oliver Sawodny, Michael Ederer, and Ronny Feuer. 2015. "Modeling and Simulation of Optimal Resource Management during the Diurnal Cycle in Emiliania huxleyi by Genome-Scale Reconstruction and an Extended Flux Balance Analysis Approach" Metabolites 5, no. 4: 659-676. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5040659
APA StyleKnies, D., Wittmüß, P., Appel, S., Sawodny, O., Ederer, M., & Feuer, R. (2015). Modeling and Simulation of Optimal Resource Management during the Diurnal Cycle in Emiliania huxleyi by Genome-Scale Reconstruction and an Extended Flux Balance Analysis Approach. Metabolites, 5(4), 659-676. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5040659





