Progressive Genomic Approaches to Explore Drought- and Salt-Induced Oxidative Stress Responses in Plants under Changing Climate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mining Approaches for Salt and Drought Stress Response Genes
2.1. Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Analysis
2.2. Forward Genetics and the Candidate Gene Strategy
2.3. Transcriptomics Analysis
2.4. Association Mapping
2.5. Genome-Wide Association
2.6. Next-Generation Sequencing
3. Functional Genomics Approaches
3.1. Epigenetic Regulators
3.2. Gain-of-Function Lines
3.3. Gene Silencing and RNA Interference Techniques for Salinity and Drought Stress
3.4. Genome Engineering (TALENs, ZFNs, CRISPR/Cas)
3.5. CRISPR-Mediated Base Editing and Prime Genome Editor
4. The Development of Salt- and Drought-Tolerant Crops with High Yielding Capacity
4.1. Genetics Engineering
4.2. Gene Introgression
4.3. Marker-Assisted Breeding and Transference of Genes
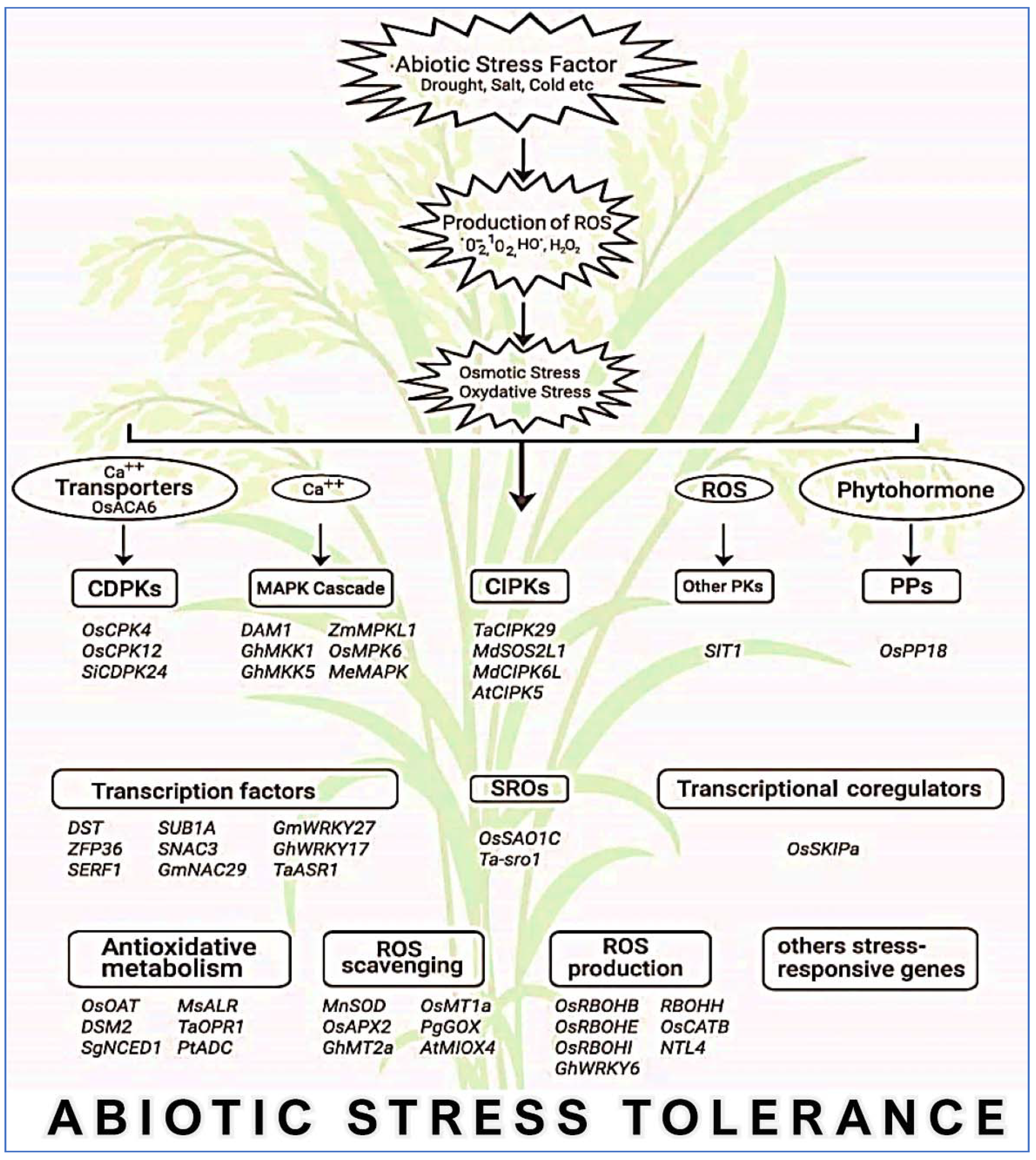
5. Involvement of Genes in the Regulation of ROS in Abiotic Stress Tolerance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rozema, J.; Flowers, T. Crops for a Salinized World. Science 2008, 322, 1478–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, G.; Long, W.; Zou, X.; Li, F.; Nishio, T. Recent progress in drought and salt tolerance studies in Brassica crops. Breed. Sci. 2014, 64, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Athar, H.R.; Ashraf, M. Strategies for Crop Improvement against Salinity and Drought Stress: An Overview. In Salinity and Water Stress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Catlin, P.; Hoffman, G.; Mead, R.; Johnson, R. Long-term response of mature plum trees to salinity. Irrig. Sci. 1993, 13, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. Unlocking the Water Potential of Agriculture. 2003. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=XF2006444621 (accessed on 7 April 2006).
- EL Sabagh, A.; Islam, M.S.; Skalicky, M.; Raza, M.A.; Singh, K.; Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, A.; Mahboob, W.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ratnasekera, D.; et al. Adaptation and Management Strategies of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Against Salinity Stress to Increase Yield and Quality. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.V.; Roy, A.; Vijayan, R.; Banerjee, P.; Verma, V.; Nalia, A.; Pramanik, M.; Mukherjee, B.; Ghosh, A.; Reja, H.; et al. Drought and Heat Stress in Cool-Season Food Legumes in Sub-Tropical Regions: Consequences, Adaptation, and Mitigation Strategies. Plants 2021, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, T.R. Challenges in breeding for yield increase for drought. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbai, R.; Subramaniyam, S.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Yang, D.C. Functional genomic approaches in plant research. In Plant Bioinformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 215–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kartseva, T.; Dobrikova, A.; Kocheva, K.; Alexandrov, V.; Georgiev, G.; Brestič, M.; Misheva, S. Optimal Nitrogen Supply Ameliorates the Performance of Wheat Seedlings under Osmotic Stress in Genotype-Specific Manner. Plants 2021, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Tong, J.; He, X.; Xu, Z.; Xu, L.; Wei, P.; Huang, Y.; Ebrestic, M.; Ema, H.; Eshao, H.-B. A Novel Soybean Intrinsic Protein Gene, GmTIP2;3, Involved in Responding to Osmotic Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- dos Reis, S.P.; Marques, D.N.; Barros, N.L.F.; Costa, C.d.N.M.; de Souza, C.R.B. Genetically engineered food crops to abiotic stress tolerance. In Genetically Engineered Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 247–279. [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor, D.W. Genetic engineering to improve plant performance under drought: Physiological evaluation of achievements, limitations, and possibilities. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasel, M.; Tahjib-Ul-Arif, M.; Hossain, M.A.; Hassan, L.; Farzana, S.; Brestic, M. Screening of Salt-Tolerant Rice Landraces by Seedling Stage Phenotyping and Dissecting Biochemical Determinants of Tolerance Mechanism multidimensional roles in salt-stressed plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaut, Z.; Edelstein, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Overcoming Salinity Barriers to Crop Production Using Traditional Methods. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2013, 32, 250–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gepts, P. The contribution of genetic and genomic approaches to plant domestication studies. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 18, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Lafitte, H.R.; Archibald, R.L.; Yang, M.; Hakimi, S.M.; Mo, H.; Habben, J.E. ARGOS8 variants generated by CRISPR-Cas9 improve maize grain yield under field drought stress conditions. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 15, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibrahimova, U.; Zivcak, M.; Gasparovic, K.; Rastogi, A.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Yang, X.; Brestic, M. Electron and proton transport in wheat exposed to salt stress: Is the increase of the thylakoid membrane proton conductivity responsible for decreasing the photosynthetic activity in sensitive genotypes? Photosynth. Res. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Salaria, N.; Thakur, K.; Kukreja, S.; Gautam, S.; Goutam, U. Functional genomic approaches to improve crop plant heat stress tolerance. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Shao, H.; Shao, C.; Chen, P.; Zhao, S.; Brestic, M.; Chen, X. Physiological adaptive mechanisms of plants grown in saline soil and implications for sustainable saline agriculture in coastal zone. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Doerge, R.W.; Borevitz, J. Novel Resampling Improves Statistical Power for Multiple-Trait QTL Mapping. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aktar, S.; Hossain, N.; Azam, M.G.; Billah, M.; Biswas, P.L.; Latif, M.A.; Rohman, M.; Bagum, S.A.; Uddin, M.S. Phenotyping of Hybrid Maize (Zea mays L.) at Seedling Stage under Drought Condition. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 2154–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, A.; Subudhi, P.; Rosenow, D.; Nguyen, H. Mapping QTLs associated with drought resistance in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, N.; Singh, A.; Dixit, S.; Cruz, M.T.S.; Maturan, P.C.; Jain, R.K.; Kumar, A. Identification and mapping of stable QTL with main and epistasis effect on rice grain yield under upland drought stress. BMC Genet. 2014, 15, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prohens, J.; Gramazio, P.; Plazas, M.; Dempewolf, H.; Kilian, B.; Diez, M.J.; Fita, A.; Herraiz, F.J.; Rodríguez-Burruezo, A.; Soler, S.; et al. Introgressiomics: A new approach for using crop wild relatives in breeding for adaptation to climate change. Euphytica 2017, 213, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, B.P.M.; Shamsudin, N.A.A.; Rahman, S.N.A.; Mauleon, R.; Ratnam, W.; Cruz, M.T.S.; Kumar, A. Association Mapping of Yield and Yield-related Traits Under Reproductive Stage Drought Stress in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 2017, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelraheem, A.; Thyssen, G.N.; Fang, D.D.; Jenkins, J.N.; Mccarty, J.C.; Wedegaertner, T.; Zhang, J. GWAS reveals consistent QTL for drought and salt tolerance in a MAGIC population of 550 lines derived from intermating of 11 Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) parents. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 296, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Shao, B.; Chen, W.; Guo, Z.; Gong, H.; Sang, X.; Wang, J.; Ye, W.W. SSR-based association mapping of salt tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, gmr.15027370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.; Reynolds, M.P.; Mullan, D.; Izanloo, A.; Kuchel, H.; Langridge, P.; Schnurbusch, T. Detection of two major grain yield QTL in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under heat, drought and high yield potential environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 1473–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Fan, Y.; Mak, M.; Babla, M.; Holford, P.; Wang, F.; Chen, G.; Scott, G.; Wang, G.; Shabala, S.; et al. QTLs for stomatal and photosynthetic traits related to salinity tolerance in barley. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Shabala, S.; Ma, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhou, M. Using QTL mapping to investigate the relationships between abiotic stress tolerance (drought and salinity) and agronomic and physiological traits. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Courtois, B.; McLaren, G.; Sinha, P.; Prasad, K.; Yadav, R.; Shen, L. Mapping QTLs associated with drought avoidance in upland rice. Mol. Breed. 2000, 6, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuguna, R.N.; Gupta, P.; Bagri, J.; Singh, D.; Dewi, A.K.; Tao, L.; Islam, M.; Sarsu, F.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Forward and reverse genetics approaches for combined stress tolerance in rice. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 23, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.K.; Sahoo, K.K.; Ghosh, A.; Tripathi, A.K.; Anwar, K.; Das, P.; Singh, A.K.; Pareek, A.; Sopory, S.K.; Singla-Pareek, S.L. Manipulation of glyoxalase pathway confers tolerance to multiple stresses in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 41, 1186–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Prashat, R.; Sharma, P.C.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Physiological characterization of gamma-ray induced mutant population of rice to facilitate biomass and yield improvement under salinity stress. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 21, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Atienza, J.; Jiang, X.; Garciadeblas, B.; Mendoza, I.; Zhu, J.-K.; Pardo, J.M.; Quintero, F.J. Conservation of the Salt Overly Sensitive Pathway in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 143, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mickelbart, M.V.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Bailey-Serres, J. Genetic mechanisms of abiotic stress tolerance that translate to crop yield stability. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutan, K.K.; Kumar, G.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. A Salt Overly Sensitive Pathway Member from Brassica juncea BjSOS3 Can Functionally Complement ΔAtsos3 in Arabidopsis. Curr. Genom. 2017, 19, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olías, R.; Eljakaoui, Z.; Pardo, J.M.; Belver, A. The Na+/H+ exchanger SOS1 controls extrusion and distribution of Na+ in tomato plants under salinity conditions. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.-J.; Ding, L.; Zhu, J.-K. SOS1, a genetic locus essential for salt tolerance and potassium acquisition. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumenberg, M. Introductory Chapter: Transcriptome Analysis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gahlaut, V.; Jaiswal, V.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, P.K. Transcription factors involved in drought tolerance and their possible role in developing drought tolerant cultivars with emphasis on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 2019–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, M.J.; Park, W.; Bauer, P.; Udall, J.A.; Page, J.T.; Raney, J.; Scheffler, B.; Jones, D.C.; Campbell, B.T. RNA-Seq Transcriptome Profiling of Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Root Tissue under Water-Deficit Stress. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rong, W.; Qi, L.; Wang, A.; Ye, X.; Du, L.; Liang, H.; Xin, Z.; Zhang, Z. The ERF transcription factor Ta ERF 3 promotes tolerance to salt and drought stresses in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.-Q.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.-S.; Zhao, C.-P.; Li, L.; Xu, H.-J.; Tang, Y.-M.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.-Z. The soybean GmbZIP1 transcription factor enhances multiple abiotic stress tolerances in transgenic plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 75, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Moon, S.-J.; Han, S.; Kim, B.-G.; Park, S.R.; Lee, S.-K.; Yoon, H.-J.; Lee, H.E.; Kwon, H.-B.; Baek, D.; et al. Expression of StMYB1R-1, a Novel Potato Single MYB-Like Domain Transcription Factor, Increases Drought Tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2010, 155, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Ji, D.; Li, S.; Wang, P.; Li, Q.; Xiang, F. The Dynamic Changes of DNA Methylation and Histone Modifications of Salt Responsive Transcription Factor Genes in Soybean. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.-J.; Wei, W.; Song, Q.-X.; Chen, H.-W.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Wang, F.; Zou, H.-F.; Lei, G.; Tian, A.; Zhang, W.-K.; et al. Soybean NAC transcription factors promote abiotic stress tolerance and lateral root formation in transgenic plants. Plant J. 2011, 68, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Rong, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, T.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Chai, R.; et al. Expression of TaWRKY44, a wheat WRKY gene, in transgenic tobacco confers multiple abiotic stress tolerances. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, T.; Fujita, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Mogami, J.; Todaka, D.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Four A rabidopsis AREB/ABF transcription factors function predominantly in gene expression downstream of SnRK2 kinases in abscisic acid signalling in response to osmotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 38, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Singh, A.K. Marker-Assisted Plant Breeding: Principles and Practices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; p. 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrama, H.A.; Eizenga, G.C.; Yan, W. Association mapping of yield and its components in rice cultivars. Mol. Breed. 2007, 19, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edae, E.A.; Byrne, P.F.; Manmathan, H.; Haley, S.D.; Reynolds, M.P. Association Mapping and Nucleotide Sequence Variation in Five Drought Tolerance Candidate Genes in Spring Wheat. Plant Genome 2013, 6, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeed, M.; Wangzhen, G.; Tianzhen, Z. Association mapping for salinity tolerance in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) germplasm from US and diverse regions of China. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2014, 8, 338–346. [Google Scholar]
- Purcărea, C.; Cachiţă-Cosma, D. Studies regarding the effects of salicylic acid on maize (Zea mays L.) seedling under salt stress. Studia Univ. Ser. Tiintele Vietii 2010, 20, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wójcik-Jagła, M.; Fiust, A.; Kościelniak, J.; Rapacz, M. Association mapping of drought tolerance-related traits in barley to complement a traditional biparental QTL mapping study. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 131, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Dai, X.-Y.; Zhang, W.-H. Physiological mechanisms underlying OsNAC5-dependent tolerance of rice plants to abiotic stress. Planta 2011, 234, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, C.; Ren, Q.; Chang, X.; Liu, G.; Jing, R. Association mapping of dynamic developmental plant height in common wheat. Planta 2011, 234, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, D.; Skot, L.; Singh, R.; Srivastava, R.K.; Das, S.P.; Taunk, J.; Sharma, P.C.; Pal, R.; Raj, B.; Hash, C.T. Exploring Potential of Pearl Millet Germplasm Association Panel for Association Mapping of Drought Tolerance Traits. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sukumaran, S.; Dreisigacker, S.; Lopes, M.; Chavez, P.; Reynolds, M.P. Genome-wide association study for grain yield and related traits in an elite spring wheat population grown in temperate irrigated environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 128, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossa, J.; Burgueño, J.; Dreisigacker, S.; Vargas, M.; Herrera-Foessel, S.A.; Lillemo, M.; Singh, R.P.; Trethowan, R.; Warburton, M.; Franco, J. Association Analysis of Historical Bread Wheat Germplasm Using Additive Genetic Covariance of Relatives and Population Structure. Genetics 2007, 177, 1889–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasheed, A.; Xia, X.; Ogbonnaya, F.; Mahmood, T.; Zhang, Z.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A.; He, Z. Genome-wide association for grain morphology in synthetic hexaploid wheats using digital imaging analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolvien, T.; Kornak, U.; Linke, S.J.; Amling, M.; Oheim, R. Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies Novel Compound Heterozygous ZNF469 Mutations in Two Siblings with Mild Brittle Cornea Syndrome. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 107, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekklar, C.; Pongpanich, M.; Suriya-Arunroj, D.; Chinpongpanich, A.; Tsai, H.; Comai, L.; Chadchawan, S.; Buaboocha, T. Genome-wide association study for salinity tolerance at the flowering stage in a panel of rice accessions from Thailand. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z. Genome-wide association study of salt tolerance at the seed germination stage in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasan, M.; Skalicky, M.; Jahan, M.; Hossain, N.; Anwar, Z.; Nie, Z.; Alabdallah, N.; Brestic, M.; Hejnak, V.; Fang, X.-W. Spermine: Its Emerging Role in Regulating Drought Stress Responses in Plants. Cells 2021, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voichek, Y.; Weigel, D. Identifying genetic variants underlying phenotypic variation in plants without complete genomes. Biol. Res. 2020, 52, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonnaya, F.C.; Rasheed, A.; Okechukwu, E.C.; Jighly, A.; Makdis, F.; Wuletaw, T.; Hagras, A.; Uguru, M.I.; Agbo, C.U. Genome-wide association study for agronomic and physiological traits in spring wheat evaluated in a range of heat prone environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 1819–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, G.T.; Van Dinh, L.; Nguyen, T.T.; Ta, N.K.; Gathignol, F.; Mai, C.D.; Jouannic, S.; Tran, K.D.; Khuat, T.H.; Do, V.N.; et al. Genome-wide Association Study of a Panel of Vietnamese Rice Landraces Reveals New QTLs for Tolerance to Water Deficit During the Vegetative Phase. Rice 2019, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, F.; Cui, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ali, S.; Xiong, L. Genome-wide analysis of alternative splicing of pre-mRNA under salt stress in Arabidopsis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hübner, S.; Korol, A.B.; Schmid, K.J. RNA-Seq analysis identifies genes associated with differential reproductive success under drought-stress in accessions of wild barley Hordeum spontaneum. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pucholt, P.; Sjödin, P.; Weih, M.; Rönnberg-Wästljung, A.C.; Berlin, S. Genome-wide transcriptional and physiological responses to drought stress in leaves and roots of two willow genotypes. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, A.-T.; Maurer, A.; Pillen, K.; Brien, C.; Dowling, K.; Berger, B.; Eglinton, J.K.; March, T.J. Genome-wide association of barley plant growth under drought stress using a nested association mapping population. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahimova, U.; Kumari, P.; Yadav, S.; Rastogi, A.; Antala, M.; Suleymanova, Z.; Zivcak, M.; Arif, T.U.; Hussain, S.; Abdelhamid, M.; et al. Progress in understanding salt stress response in plants using biotechnological tools. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 329, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-X.; Liu, X.; Boge, W.; Liu, X.-P. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Loci for Salt Tolerance during Germination in Autotetraploid Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Using Genotyping-by-Sequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Fu, B.; Li, Z. DNA methylation changes detected by methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphism in two contrasting rice genotypes under salt stress. J. Genet. Genom. 2011, 38, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M.; Maitra, S.; Alam, M.A.; Abu Syed, M.; Hossain, J.; Sarkar, S.; Saha, S.; Bhadra, P.; et al. Consequences and Mitigation Strategies of Abiotic Stresses in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under the Changing Climate. Agronomy 2021, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzker, M.L. Sequencing technologies—the next generation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unamba, C.I.N.; Nag, A.; Sharma, R.K. Next Generation Sequencing Technologies: The Doorway to the Unexplored Genomics of Non-Model Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grada, A.; Weinbrecht, K. Next-Generation Sequencing: Methodology and Application. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Steinberg, K.M.; Larson, D.; Wilson, R.K.; Mardis, E.R. The Next-Generation Sequencing Revolution and Its Impact on Genomics. Cell 2013, 155, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walter, J.; Hümpel, A. Introduction to epigenetics. In Epigenetics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.W.-L.; Henderson, I.; Jacobsen, S.E. Gardening the genome: DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singroha, G.; Sharma, P. Epigenetic Modifications in Plants under Abiotic Stress. In Epigenetics; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Epigenetic regulation during salinity and drought stress in plants: Histone modifications and DNA methylation. Plant Gene 2017, 11, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Fromm, M.E.; Avramova, Z. Multiple exposures to drought ‘train’ transcriptional responses in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Liu, X.; Thorn, G.; Duan, J.; Tian, L. Expression analysis of histone acetyltransferases in rice under drought stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 443, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-M.; Sasaki, T.; Ueda, M.; Sako, K.; Seki, M. Chromatin changes in response to drought, salinity, heat, and cold stresses in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, L.J.; Azevedo, V.S.; Maroco, J.; Oliveira, M.M.; Santos, A.P. Salt Tolerant and Sensitive Rice Varieties Display Differential Methylome Flexibility under Salt Stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaldis, A.; Tsementzi, D.; Tanriverdi, O.; Vlachonasios, K.E. Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptional co-activators ADA2b and SGF29a are implicated in salt stress responses. Planta 2010, 233, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.-G.; Wang, C.-H.; Guo, H.-S. Application of RNA silencing to plant disease resistance. Silence 2012, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricaño-Rodríguez, J.; Adame-García, J.; Patlas-Martínez, C.I.; Hipólito-Romero, E.; Ramos-Prado, J.M. Plant gene co-suppression; basis of the molecular machinery of interfering RNA. Plant Omics 2016, 9, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.P. Gene silencing: Shrinking the black box of RNAi. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, R137–R140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekele, D.; Tesfaye, K.; Fikre, A. Applications of Virus Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) in Plant Functional Genomics Studies. J. Plant Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, L.; Fan, X.; Xu, P.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Meng, S.; Shen, X.J. Transcription Factor GarWRKY5 Is Involved in Salt Stress Response in Diploid Cotton Species (Gossypium aridum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirungu, J.N.; Magwanga, R.O.; Pu, L.; Cai, X.; Xu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hao, F.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Knockdown of Gh_A05G1554 (GhDHN_03) and Gh_D05G1729 (GhDHN_04) Dehydrin genes, Reveals their potential role in enhancing osmotic and salt tolerance in cotton. Genomics 2019, 112, 1902–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Xin, Z.; Lin, T. Knock-down the expression of TaH2B-7D using virus-induced gene silencing reduces wheat drought tolerance. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.-H.; Leidi, E.; Zhang, Q.; Hwang, S.-M.; Li, Y.; Quintero, F.J.; Jiang, X.; D’Urzo, M.P.; Lee, S.Y.; Zhao, Y. Loss of halophytism by interference with SOS1 expression. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, H.; Liang, M.; Lu, M. Both silencing-and over-expression of pepper CaATG8c gene compromise plant tolerance to heat and salt stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 141, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Wang, P.; Fan, Q.; Fu, W.-D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.-N.; Song, Z.; Zhang, G.-L.; Wu, J.-H. Analysis of the Role of the Drought-Induced Gene DRI15 and Salinity-Induced Gene SI1 in Alternanthera philoxeroides Plasticity Using a Virus-Based Gene Silencing Tool. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yan, J.-M.; Li, Y.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Wang, Q.-L.; Liang, Y. Silencing the SpMPK1, SpMPK2, and SpMPK3 genes in tomato reduces abscisic acid—mediated drought tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21983–21996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manmathan, H.; Shaner, D.; Snelling, J.; Tisserat, N.; Lapitan, N. Virus-induced gene silencing of Arabidopsis thaliana gene homologues in wheat identifies genes conferring improved drought tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirungu, J.N.; Magwanga, R.O.; Lu, P.; Cai, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Peng, R.; Wang, K.; Liu, F. Functional characterization of Gh_A08G1120 (GH3.5) gene reveal their significant role in enhancing drought and salt stress tolerance in cotton. BMC Genet. 2019, 20, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, Y.; Ge, X.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Ma, Z. GhWRKY6 acts as a negative regulator in both transgenic Arabidopsis and cotton during drought and salt stress. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhaj, K.; Chaparro-Garcia, A.; Kamoun, S.; Nekrasov, V. Plant genome editing made easy: Targeted mutagenesis in model and crop plants using the CRISPR/Cas system. Plant Methods 2013, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Xu, J.; Sui, C.; Wei, J. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 in plant biology. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Orbović, V.; Xu, J.; White, F.F.; Jones, J.B.; Wang, N. Genome editing of the disease susceptibility gene CsLOB1 in citrus confers resistance to citrus canker. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 15, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez i Marti, A.; Dodd, R.S. Using CRISPR as a gene editing tool for validating adaptive gene function in tree landscape genomics. Front. Ecol. Evol. Dev. 2018, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debbarma, J.; Sarki, Y.N.; Saikia, B.; Boruah, H.P.D.; Singha, D.L.; Chikkaputtaiah, C. Ethylene response factor (ERF) family proteins in abiotic stresses and CRISPR–Cas9 genome editing of ERFs for multiple abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants: A review. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves-Cordones, M.; Mohamed, S.; Tanoi, K.; Kobayashi, N.I.; Takagi, K.; Vernet, A.; Guiderdoni, E.; Périn, C.; Sentenac, H.; Véry, A.A. Production of low-Cs+ rice plants by inactivation of the K+ transporter Os HAK 1 with the CRISPR-Cas system. Plant J. 2017, 92, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, G.; Xie, L.; Jiao, G.; Wei, X.; Sheng, Z.; Tang, S.; Hu, P. CRISPR/CAS9-mediated editing of the fragrant gene Badh2 in rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2017, 31, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, P.; Lei, C.; Hao, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.-G.; Zhao, K. Enhanced Rice Blast Resistance by CRISPR/Cas9-Targeted Mutagenesis of the ERF Transcription Factor Gene OsERF922. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, T.; Chen, Z.; Kong, D.; Bi, J.; Zhang, F.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Enhanced rice salinity tolerance via CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis of the OsRR22 gene. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, P.; Zhang, B.; Gou, F.; Feng, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N. The CRISPR/C as9 system produces specific and homozygous targeted gene editing in rice in one generation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Song, N.; Sun, S.; Yang, W.; Zhao, H.; Song, W.; Lai, J. Efficiency and Inheritance of Targeted Mutagenesis in Maize Using CRISPR-Cas9. J. Genet. Genom. 2016, 43, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.T. CRISPR/Cas9 Targeted Mutagenesis for Functional Genetics in Maize. Plants 2021, 10, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Alptekin, B.; Budak, H. CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in wheat. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2017, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yu, Q.; Que, Y.; Xu, L.; Guo, J. A Novel Non-specific Lipid Transfer Protein Gene from Sugarcane (NsLTPs), Obviously Responded to Abiotic Stresses and Signaling Molecules of SA and MeJA. Sugar Tech. 2016, 19, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Sun, P.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, B.; Jin, Z. The AGPase Family Proteins in Banana: Genome-Wide Identification, Phylogeny, and Expression Analyses Reveal Their Involvement in the Development, Ripening, and Abiotic/Biotic Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Mao, X.; Huang, C.; Tie, W.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wu, C.; Xia, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhou, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the KUP Family under Abiotic Stress in Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.; Yang, H.; Shi, H.; Wei, Y.; Tie, W.; Ding, Z.; Yan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xia, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. The MAPKKK gene family in cassava: Genome-wide identification and expression analysis against drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, P.; Zhao, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, H.; Yu, J.; Xiao, G. The PIN gene family in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): Genome-wide identification and gene expression analyses during root development and abiotic stress responses. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dass, A.; Abdin, M.Z.; Reddy, V.S.; Leelavathi, S. Isolation and characterization of the dehydration stress-inducible GhRDL1 promoter from the cultivated upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Herrera, A.; Yáñez, F.; Castano, E.; Santamaria, J.; Pereira-Santana, A.; Espadas-Alcocer, J.; Teyer, L.F.S.; Espadas-Gil, F.; Alcaraz, L.D.; López-Gómez, R.; et al. A novel Dreb2-type gene from Carica papaya confers tolerance under abiotic stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 125, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.V.S.; Verma, R.K.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Watts, A.; Rao, M.V.; Chinnusamy, V. CRISPR-Cas9 mediated genome editing of drought and salt tolerance (OsDST) gene in indica mega rice cultivar MTU1010. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Liu, C.; Zhao, R.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, S.; Sheng, J.; Shen, L. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated SlNPR1 mutagenesis reduces tomato plant drought tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, S.; Qin, X.; Luo, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Usman, B.; Nawaz, G.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, R. CRISPR/Cas9-Induced Mutagenesis of Semi-Rolled Leaf1,2 Confers Curled Leaf Phenotype and Drought Tolerance by Influencing Protein Expression Patterns and ROS Scavenging in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anzalone, A.V.; Randolph, P.B.; Davis, J.R.; Sousa, A.A.; Koblan, L.; Levy, J.M.; Chen, P.; Wilson, C.; Newby, G.A.; Raguram, A.; et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 2019, 576, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiens, C.P.; Shabala, L.; Zhang, J.; Pottosin, I.; Bose, J.; Zhu, M.; Fuglsang, A.T.; Velarde, A.; Massart, A.; Hill, C. Cell-type specific H+-ATPase activity enables root K+ retention and mediates acclimatation to salinity. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, M.B.; Zeng, F.; Shabala, L.; Zhang, G.; Fan, Y.; Shabala, S.; Zhou, M. Cell-Based Phenotyping Reveals QTL for Membrane Potential Maintenance Associated with Hypoxia and Salinity Stress Tolerance in Barley. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monneveux, P.; Reynolds, M.P.; Aguilar, J.G.; Singh, R.P.; Weber, W.E. Effects of the 7DL.7Ag translocation from Lophopyrum elongatum on wheat yield and related morphophysiological traits under different environments. Plant Breed. 2003, 122, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Crop breeding for salt tolerance in the era of molecular markers and marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed. 2012, 132, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- thi Lang, N.; Buu, B.; Ismail, A. Molecular mapping and marker-assisted selection for salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). OmonRice 2008, 16, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, S.J.; Beena, R.; Gomez, S.M.; Senthivel, S.; Babu, R.C. Mapping Consistent Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Yield QTLs under Drought Stress in Target Rainfed Environments. Rice 2015, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhai, L.; Zheng, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Z. QTL mapping and candidate gene analysis of peduncle vascular bundle related traits in rice by genome-wide association study. Rice 2018, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamsudin, N.A.A.; Swamy, B.P.M.; Ratnam, W.; Cruz, M.T.S.; Raman, A.; Kumar, A. Marker assisted pyramiding of drought yield QTLs into a popular Malaysian rice cultivar, MR219. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badu-Apraku, B.; Talabi, A.O.; Fakorede, M.A.B.; Fasanmade, Y.; Gedil, M.; Magorokosho, C.; Asiedu, R. Yield gains and associated changes in an early yellow bi-parental maize population following genomic selection for Striga resistance and drought tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.; Mao, X.; Jing, R. Functional Analysis and Marker Development of TaCRT-D Gene in Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bimpong, I.K.; Manneh, B.; Sock, M.; Diaw, F.; Amoah, N.K.A.; Ismail, A.M.; Gregorio, G.; Singh, R.K.; Wopereis, M. Improving salt tolerance of lowland rice cultivar ‘Rassi’ through marker-aided backcross breeding in West Africa. Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Yin, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Struik, P.C. Linking ecophysiological modelling with quantitative genetics to support marker-assisted crop design for improved yields of rice (Oryza sativa) under drought stress. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gill, S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhamdi, A.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species in plant development. Development 2018, 145, dev164376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, J.; Chan, Z. ROS Regulation During Abiotic Stress Responses in Crop Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keunen, E.; Peshev, D.; Vangronsveld, J.; Ende, W.V.D.; Cuypers, A. Plant sugars are crucial players in the oxidative challenge during abiotic stress: Extending the traditional concept. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Redox Homeostasis and Antioxidant Signaling: A Metabolic Interface between Stress Perception and Physiological Responses. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Chu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, X. Cotton GhMKK1 Induces the Tolerance of Salt and Drought Stress, and Mediates Defence Responses to Pathogen Infection in Transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Li, X.; Hicks, L.; Xiong, L. A Raf-Like MAPKKK Gene DSM1 Mediates Drought Resistance through Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2009, 152, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Wang, N.; Cui, F.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Xiong, L. Characterization of the β-Carotene Hydroxylase Gene DSM2 Conferring Drought and Oxidative Stress Resistance by Increasing Xanthophylls and Abscisic Acid Synthesis in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 1304–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadarajah, K.K. ROS Homeostasis in Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongdong, L.; Ming, Z.; Lili, H.; Xiaobo, C.; Yang, G.; Xingqi, G.; Han, L. GhMAPKKK49, a novel cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) MAPKKK gene, is involved in diverse stress responses. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 38, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Liu, J.; Bi, D.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. MEKK1, MKK1/MKK2 and MPK4 function together in a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to regulate innate immunity in plants. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bundó, M.; Coca, M. Enhancing blast disease resistance by overexpression of the calcium-dependent protein kinaseOsCPK4in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 14, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asano, T.; Hayashi, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Aoki, N.; Miyao, A.; Mitsuhara, I.; Ichikawa, H.; Komatsu, S.; Hirochika, H.; Kikuchi, S.; et al. A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK12 oppositely modulates salt-stress tolerance and blast disease resistance. Plant J. 2011, 69, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.-F.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Fu, J.-D.; Liu, Y.-W.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Ma, Y.-Z.; Xu, Z.-S.; Xi, Y.-J. Genome-Wide Analysis of CDPK Family in Foxtail Millet and Determination of SiCDPK24 Functions in Drought Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Hu, W.; Wei, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, F.; Han, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Fang, B.; et al. TaCIPK29, a CBL-Interacting Protein Kinase Gene from Wheat, Confers Salt Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.-K.; Li, L.-L.; Cao, Z.-H.; Zhao, Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Hao, Y.-J. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel apple MdCIPK6L gene reveals its involvement in multiple abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 79, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.-G.; Ma, Q.-J.; Sun, C.-H.; Sun, M.-H.; You, C.-X.; Hao, Y.-J. Overexpression of MdSOS2L1, a CIPK protein kinase, increases the antioxidant metabolites to enhance salt tolerance in apple and tomato. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 156, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Shukla, P.; Kirti, P.B. A CBL-interacting protein kinase AdCIPK5 confers salt and osmotic stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-H.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Zhang, L.-Q.; Ai, L.-F.; Han, Y.-F.; Sun, D.-Y.; Zhang, S.-W.; Sun, Y. The receptor-like kinase SIT1 mediates salt sensitivity by activating MAPK3/6 and regulating ethylene homeostasis in rice. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2538–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueno, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Kishi-Kaboshi, M.; Matsushita, A.; Jiang, C.-J.; Goto, S.; Takahashi, A.; Hirochika, H.; Takatsuji, H. Abiotic Stresses Antagonize the Rice Defence Pathway through the Tyrosine-Dephosphorylation of OsMPK6. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; Chang, Y.; Pei, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Yang, H.; Qin, F.; Song, C.; et al. MAPK-like protein 1 positively regulates maize seedling drought sensitivity by suppressing ABA biosynthesis. Plant J. 2019, 102, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, L.; Ding, Z.; Tie, W.; Ding, X.; Zeng, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, H.; Peng, M.; Hu, W. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Gene Family in Cassava. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Pan, J.; Kong, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, D. ZmMKK3, a novel maize group B mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase gene, mediates osmotic stress and ABA signal responses. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Zong, W.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Xiong, L. A SNAC1-regulated protein phosphatase gene OsPP18 modulates drought and oxidative stress tolerance through ABA-independent reactive oxygen species scavenging in rice. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 2100–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deveshwar, P.; Prusty, A.; Sharma, S.; Tyagi, A.K. Phytohormone-Mediated Molecular Mechanisms Involving Multiple Genes and QTL Govern Grain Number in Rice. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 586462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Chao, D.-Y.; Gao, J.-P.; Zhu, M.-Z.; Shi, M.; Lin, H.-X. A previously unknown zinc finger protein, DST, regulates drought and salt tolerance in rice via stomatal aperture control. Genes Dev. Chang. 2009, 23, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wen, F.; Yao, D.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Ni, L.; Zhang, A.; Tan, M.; Jiang, M. A novel rice C2H2-type zinc finger protein, ZFP36, is a key player involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence and oxidative stress tolerance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5795–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Maruyama, K.; Todaka, D.; Kidokoro, S.; Abo, M.; Yoshimura, E.; Shinozaki, K.; Nakashima, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. OsTZF1, a CCCH-Tandem Zinc Finger Protein, Confers Delayed Senescence and Stress Tolerance in Rice by Regulating Stress-Related Genes. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhou, X.; Chu, C.; Wang, X. OsWRKY30 is activated by MAP kinases to confer drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjunath, K.; Mahadeva, A.; Sreevathsa, R.; Ramachandra Swamy, N.; Swamy, N. In Vitro Screening and Identification of Putative Sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) Transformants Expressing ECNAC1 Gene by Salt Stress Method. Trends Biosci. 2013, 6, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Seo, P.J.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, C.-M. A NAC transcription factor NTL4 promotes reactive oxygen species production during drought-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2012, 70, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babitha, K.; Vemanna, R.S.; Nataraja, K.N.; Udayakumar, M. Overexpression of EcbHLH57 transcription factor from Eleusine coracana L. in tobacco confers tolerance to salt, oxidative and drought stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhangwu, H.; Liu, W.; Wan, L.; Li, F.; Dai, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, R. Functional analyses of ethylene response factor JERF3 with the aim of improving tolerance to drought and osmotic stress in transgenic rice. Transgenic Res. 2010, 19, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKersie, B.D.; Bowley, S.R.; Harjanto, E.; Leprince, O. Water-Deficit Tolerance and Field Performance of Transgenic Alfalfa Overexpressing Superoxide Dismutase. Plant Physiol. 1996, 111, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Cui, M.; Xin, X.; Ming, X.; Jing, L.; WU, J.-X. Overexpression of a cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase gene, OsAPX2, increases salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 2500–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, T.; Manna, M.; Reddy, M.K. Glutathione Peroxidase of Pennisetum glaucum (PgGPx) Is a Functional Cd2+ Dependent Peroxiredoxin that Enhances Tolerance against Salinity and Drought Stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberschall, A.; Deák, M.; Török, K.; Sass, L.; Vass, I.; Kovács, I.; Fehér, A.; Dudits, D.; Horváth, G.V. A novel aldose/aldehyde reductase protects transgenic plants against lipid peroxidation under chemical and drought stresses. Plant J. 2000, 24, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, N.; Yactayo-Chang, J.P.; Medina-Jiménez, K.; Acosta-Gamboa, L.M.; González-Romero, M.E.; Arteaga-Vázquez, M.A.; Lorence, A. Mechanisms underlying the enhanced biomass and abiotic stress tolerance phenotype of an Arabidopsis MIOX over-expresser. Plant Direct 2019, 3, e00165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, K.; Niu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R. Genome-wide Identification of PP2C Genes and Their Expression Profiling in Response to Drought and Cold Stresses in Medicago truncatula. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kong, D.; Li, T.; Yu, S.; Mei, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; et al. A novel gene OsAHL1 improves both drought avoidance and drought tolerance in rice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, F.; Qin, T.; Wang, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhang, A.; Tan, M.; Jiang, M. OsHK3 is a crucial regulator of abscisic acid signaling involved in antioxidant defense in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 57, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, B.; Chen, M.; Li, S. Isolation and Identification of Ipomoea cairica (L.) Sweet Gene IcSRO1 Encoding a SIMILAR TO RCD-ONE Protein, Which Improves Salt and Drought Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, N.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. ABA Controls H2O2 Accumulation Through the Induction of OsCATB in Rice Leaves Under Water Stress. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamauchi, T.; Yoshioka, M.; Fukazawa, A.; Mori, H.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Tsutsumi, N.; Yoshioka, H.; Nakazono, M. An NADPH Oxidase RBOH Functions in Rice Roots during Lysigenous Aerenchyma Formation under Oxygen-Deficient Conditions. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Jia, H.; Liu, D.; Hao, L.; Guo, X. A cotton Raf-like MAP3K gene, GhMAP3K40, mediates reduced tolerance to biotic and abiotic stress in Nicotiana benthamiana by negatively regulating growth and development. Plant Sci. 2015, 240, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, Y.-J.; Choi, H.-K.; Park, M.Y.; Choi, S.-W.; Vo, K.T.X.; Jeon, J.-S.; Kim, S.Y. OsMAPKKK63 is involved in salt stress response and seed dormancy control. Plant Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, e1578633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Liang, Y.-H.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Cheng, Z.-M. Cloning, molecular and functional characterization by overexpression in Arabidopsis of MAPKK genes from grapevine (Vitis vinifera). BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodzik, P.; Tajdel-Zielinska, M.; Cieśla, A.; Marczak, M.; Ludwikow, A. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascades in Plant Hormone Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, S.; Azam, F. Co-Existence of Salt and Drought Tolerance in Triticeae. Hereditas 2004, 135, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Baranwal, V.K.; Khurana, P. Genome-wide analysis of bZIP transcription factors in wheat and functional characterization of a TabZIP under abiotic stress. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.-S.; Liu, J.-H.; Chen, X.-J. Overexpression of PtrABF gene, a bZIP transcription factor isolated from Poncirus trifoliata, enhances dehydration and drought tolerance in tobacco via scavenging ROS and modulating expression of stress-responsive genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joo, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Song, S.I. Overexpression of the rice basic leucine zipper transcription factor OsbZIP12 confers drought tolerance to rice and makes seedlings hypersensitive to ABA. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 8, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-Y.; Choi, H.-I.; Im, M.-Y.; Kim, S.Y. Arabidopsis Basic Leucine Zipper Proteins That Mediate Stress-Responsive Abscisic Acid Signaling. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Kang, J.; Lv, B.; Dong, Q.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q. Tartary Buckwheat Transcription Factor FtbZIP5, Regulated by FtSnRK2.6, Can Improve Salt/Drought Resistance in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Mao, B.; Ou, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Chu, C.; Wang, X. OsbZIP71, a bZIP transcription factor, confers salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 84, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Gao, C.; Zheng, X.; Han, B. Identification of OsbZIP72 as a positive regulator of ABA response and drought tolerance in rice. Planta 2008, 229, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Ran, Q.; Xie, G.; Wang, B.; Fang, S.; Chu, J.; Zhang, J. ZmbZIP4 Contributes to Stress Resistance in Maize by Regulating ABA Synthesis and Root Development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Xiong, L. Constitutive activation of transcription factor OsbZIP46 improves drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1755–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Y.; Tang, N.; Du, H.; Ye, H.; Xiong, L. Characterization of OsbZIP23 as a key player of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family for conferring abscisic acid sensitivity and salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1938–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babitha, K.; Ramu, S.; Pruthvi, V.; Mahesh, P.; Nataraja, K.N.; Udayakumar, M. Co-expression of at bHLH17 and at WRKY 28 confers resistance to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2013, 22, 327–341. [Google Scholar]
- Dombrecht, B.; Xue, G.P.; Sprague, S.J.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Ross, J.J.; Reid, J.B.; Fitt, G.P.; Sewelam, N.; Schenk, P.M.; Manners, J.M.; et al. MYC2 Differentially Modulates Diverse Jasmonate-Dependent Functions inArabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2225–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, X.; Tang, S.; Liu, S.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. A novel bHLH transcription factor PebHLH35 from Populus euphratica confers drought tolerance through regulating stomatal development, photosynthesis and growth in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Vishal, B.; Khoo, K.; Rajappa, S.; Loh, C.-S.; Kumar, P.P. Expression of AoNHX1 increases salt tolerance of rice and Arabidopsis, and bHLH transcription factors regulate AtNHX1 and AtNHX6 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Hir, R.; Castelain, M.; Chakraborti, D.; Moritz, T.; Dinant, S.; Bellini, C. At bHLH68 transcription factor contributes to the regulation of ABA homeostasis and drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 160, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, J.-S.; Joo, J.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, Y.-K.; Nahm, B.H.; Song, S.I.; Cheong, J.-J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.-K.; Choi, Y.D. OsbHLH148, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, interacts with OsJAZ proteins in a jasmonate signaling pathway leading to drought tolerance in rice. Plant J. 2011, 65, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Sun, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Deng, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q. Overexpression of Fagopyrum ta-taricum FtbHLH2 enhances tolerance to cold stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 125, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, P.-F.; Li, C.-L.; Zhao, X.-R.; Li, M.-F.; Zhao, H.-X.; Guo, J.-Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q. Overexpression of a Tartary Buckwheat Gene, FtbHLH3, Enhances Drought/Oxidative Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shoucheng, C.; Chai, S.; McIntyre, C.; Xue, G.-P. Overexpression of a predominantly root-expressed NAC transcription factor in wheat roots enhances root length, biomass and drought tolerance. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 37, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Baek, K.H.; Jung, H.; Ha, S.-H.; Choi, Y.D.; Kim, M.; Reuzeau, C.; Kim, J.-K. Root-Specific Expression of OsNAC10 Improves Drought Tolerance and Grain Yield in Rice under Field Drought Conditions. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Redillas, M.C.F.R.; Jang, G.; Jung, H.; Bang, S.W.; Choi, Y.D.; Ha, S.-H.; Reuzeau, C.; Kim, J.-K. OsNAC5overexpression enlarges root diameter in rice plants leading to enhanced drought tolerance and increased grain yield in the field. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2012, 11, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Chung, P.J.; Jeong, J.S.; Jang, G.; Bang, S.W.; Jung, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Ha, S.H.; Choi, Y.D.; Kim, J.K. The rice Os NAC 6 transcription factor orchestrates multiple molecular mechanisms involving root structural adaptions and nicotianamine biosynthesis for drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Sugahara, S.; Yamada, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Yoshiba, Y.; Hirano, H.-Y.; Tsutsumi, N. OsNAC6, a member of the NAC gene family, is induced by various stresses in rice. Genes Genet. Syst. 2005, 80, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redillas, M.C.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Jung, H.; Bang, S.W.; Choi, Y.D.; Ha, S.H.; Reuzeau, C.; Kim, J.K. The overexpression of OsNAC9 alters the root architecture of rice plants enhancing drought resistance and grain yield under field conditions. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2012, 10, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnejat-Bushehri, S.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Balazadeh, S. Arabidopsis NAC transcription factor JUNGBRUNNEN1 affects thermomemory-associated genes and enhances heat stress tolerance in primed and unprimed conditions. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, L.-S.; Nakashima, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Simpson, S.D.; Fujita, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Fujita, M.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Isolation and Functional Analysis of Arabidopsis Stress-Inducible NAC Transcription Factors That Bind to a Drought-Responsive cis-Element in the early responsive to dehydration stress 1 Promoter. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2481–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Gong, Z.; Wang, C.; Xue, F.; Zhang, H.; Ji, W. Wheat NAC transcription factor TaNAC29 is involved in response to salt stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 96, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kim, M.Y.; Ha, J.; Lee, S.-H. Overexpression of the Soybean NAC Gene GmNAC109 Increases Lateral Root Formation and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Saeed, U.H.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, D.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Molecular and Functional Characterization of CaNAC035, an NAC Transcription Factor From Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubouzet, J.G.; Sakuma, Y.; Ito, Y.; Kasuga, M.; Dubouzet, E.G.; Miura, S.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. OsDREBgenes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J. 2003, 33, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, E.-J.; Cheng, M.-C.; Lin, T.-P. Functional characterization of an abiotic stress-inducible transcription factor AtERF53 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jisha, V.; Dampanaboina, L.; Vadassery, J.; Mithöfer, A.; Kappara, S.; Ramanan, R. Overexpression of an AP2/ERF Type Transcription Factor OsEREBP1 Confers Biotic and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Rice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. OsERF71 confers drought tolerance via modulating ABA signaling and proline biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2018, 270, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Seymour, G.B.; Lu, C.; Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, G. An ethylene response factor (ERF5) promoting adaptation to drought and salt tolerance in tomato. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 31, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, C.; Doherty, C.J.; Gilmour, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Thomashow, M.F. Regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF regulon by a complex low-temperature regulatory network. Plant J. 2015, 82, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, F.; Kakimoto, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Osakabe, Y.; Tran, L.S.P.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Regu-lation and functional analysis of ZmDREB2A in response to drought and heat stresses in Zea mays L. Plant J. 2007, 50, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; He, R.J.; Xie, Q.L.; Zhao, X.H.; Deng, X.M.; He, J.B.; Song, L.; He, J.; Marchant, A.; Chen, X.Y. Ethylene Response Factor 74 (ERF74) plays an essential role in controlling a respiratory burst oxidase homolog D (RbohD)-dependent mechanism in response to different stresses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Su, L.; Hu, B.; Li, L.J. Expression of AhDREB1, an AP2/ERF transcription factor gene from peanut, is af-fected by histone acetylation and increases abscisic acid sensitivity and tolerance to osmotic stress in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, M.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y. Overexpression of the soybean GmERF3 gene, an AP2/ERF type transcription factor for increased tolerances to salt, drought, and diseases in transgenic tobacco. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 3781–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, S.; Si, T.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.-K. Mutational Evidence for the Critical Role of CBF Transcription Factors in Cold Acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2744–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, M.H.; Yoo, K.S.; Hyoung, S.; Nguyen, H.T.K.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Ok, S.H.; Yoo, S.D.; Shin, J.S. An Arabidopsis R2R3-MYB transcription factor, AtMYB20, negatively regulates type 2C serine/threonine protein phosphatases to enhance salt tolerance. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, C.; Seo, J.S.; Han, S.W.; Koo, Y.J.; Kim, C.H.; Song, S.I.; Nahm, B.H.; Choi, Y.D.; Cheong, J.-J. Overexpression of AtMYB44 Enhances Stomatal Closure to Confer Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007, 146, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.B.; Kim, H.; Kim, R.J.; Suh, M.C. Overexpression of Arabidopsis MYB96 confers drought resistance in Camelina sativa via cuticular wax accumulation. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Zou, H.-F.; Wang, H.-W.; Zhang, W.-K.; Ma, B.; Zhang, J.-S.; Chen, S.-Y. Soybean GmMYB76, GmMYB92, and GmMYB177 genes confer stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Qi, T.; Huang, H.; Ren, Q.; Wu, D.; Chang, C.; Peng, W.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Xie, D. The Jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins interact with the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB24 to affect Jasmonate-regulated stamen development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Bao, X.; Zhi, Y.; Wu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yin, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; et al. Overexpression of a MYB Family Gene, OsMYB6, Increases Drought and Salinity Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vannini, C.; Locatelli, F.; Bracale, M.; Magnani, E.; Marsoni, M.; Osnato, M.; Mattana, M.; Baldoni, E.; Coraggio, I. Overex-pression of the rice Osmyb4 gene increases chilling and freezing tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Plant J. 2004, 37, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Duan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ali, J.; Li, Z. Overexpression of OsMYB48-1, a Novel MYB-Related Transcription Factor, Enhances Drought and Salinity Tolerance in Rice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, N.; Cheng, S.; Liu, X.; Du, H.; Dai, M.; Zhou, D.-X.; Yang, W.; Zhao, Y. The R2R3-type MYB gene OsMYB91 has a function in coordinating plant growth and salt stress tolerance in rice. Plant Sci. 2015, 236, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.-H.; Xu, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Liu, J.-M.; Li, P.-S.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.-Z.; Xu, Z.-S. Drought-responsive WRKY transcription factor genes TaWRKY1 and TaWRKY33 from wheat confer drought and/or heat resistance in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Xu, H.; Dai, Y.; Deng, D.; Chen, J. ZmWRKY33, a WRKY maize transcription factor conferring enhanced salt stress tolerances in Arabidopsis. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 70, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzid, R.; Zorrig, W.; ben Ayed, R.; Ben Hamed, K.; Ayadi, M.; Damak, Y.; Lauvergeat, V.; Hanana, M. The grapevine VvWRKY2 gene enhances salt and osmotic stress tolerance in transgenic Nicotiana tabacum. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yu, D. Over-expression of the stress-induced OsWRKY45 enhances disease resistance and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Environ. Exp. Exp. Bot. 2009, 65, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, C.; Esposito, S.; D’Amelia, V.; Garramone, R.; Alioto, D.; Zoina, A.; Aversano, R.; Carputo, D. WRKY genes family study reveals tissue-specific and stress-responsive TFs in wild potato species. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Shiroto, Y.; Kishitani, S.; Ito, Y.; Toriyama, K. Enhanced heat and drought tolerance in transgenic rice seedlings overexpressing OsWRKY11 under the control of HSP101 promoter. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R.; Vanderauwera, S.; Gollery, M.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-H.; Sei, S.-C.; Su, Y.-H.; Chiang, C.-M. Overexpression of the Arabidopsis and winter squash superoxide dismutase genes enhances chilling tolerance via ABA-sensitive transcriptional regulation in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, 1685728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, C.; Fu, H.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Lin, Y.; Lai, Z.; Guo, Y. Genome-wide investigation of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family and their regulatory miRNAs reveal the involvement in abiotic stress and hormone response in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caverzan, A.; Passaia, G.; Rosa, S.B.; Ribeiro, C.W.; Lazzarotto, F.; Margis-Pinheiro, M. Plant responses to stresses: Role of ascorbate peroxidase in the antioxidant protection. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 35, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, S.; Fartyal, D.; Agarwal, A.; Shukla, T.; James, D.; Kaul, T.; Negi, Y.K.; Arora, S.; Reddy, M.K. Abiotic stress toler-ance in plants: Myriad roles of ascorbate peroxidase. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.-X.; Feng, K.; Duan, A.-Q.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.-Q.; Xu, Z.-S.; Xiong, A.-S. Isolation, purification and characterization of an ascorbate peroxidase from celery and overexpression of the AgAPX1 gene enhanced ascorbate content and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Bao, H.; Cai, J.; Han, J.; Zhou, L. A Novel Thylakoid Ascorbate Peroxidase from Jatrophacurcas Enhances Salt Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 15, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Yang, F.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, L. Ascorbate peroxidase from Jatropha curcas enhances salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 4879–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiz, E.; Ozyigit, I.I.; Saracoglu, I.A.; Uras, M.E.; Sen, U.; Yalcin, B. Abiotic stress-induced regulation of antioxidant genes in different Arabidopsis ecotypes: Microarray data evaluation. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, Q.; Gao, G.-L.; Fan, Q.-J.; Qiao, G.; Wen, X.-P.; Liu, T.; Peng, Z.-J.; Cai, Y.-Q. Isolation and characterization of a catalase gene “HuCAT3” from pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) and its expression under abiotic stress. Gene 2015, 563, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Hu, L. CsCAT3, a catalase gene from Cucumis sativus, confers resistance to a variety of stresses to Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2017, 31, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milla, M.A.R.; Maurer, A.; Huete, A.R.; Gustafson, J.P. Glutathione peroxidase genes in Arabidopsis are ubiquitous and reg-ulated by abiotic stresses through diverse signaling pathways. Plant J. 2003, 36, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Yang, Y. Identification and Characterization of the Glutathione Peroxidase (GPX) Gene Family in Watermelon and Its Expression under Various Abiotic Stresses. Agronomy 2018, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diao, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, G.; Yu, A.; Yu, X.; Hu, W.; Zheng, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z. Cloning a glutathione peroxidase gene from Nelumbo nucifera and enhanced salt tolerance by overexpressing in rice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4919–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fang, G.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. A Thioredoxin-Dependent Glutathione Peroxidase (OsGPX5) Is Required for Rice Normal Development and Salt Stress Tolerance. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 35, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Khew, C.Y.; Morshed, M.; Namasivayam, P.; Napis, S.; Ho, C.-L. Overexpression of monodehydroascorbate reductase from a mangrove plant (AeMDHAR) confers salt tolerance on rice. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 169, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltayeb, A.E.; Kawano, N.; Badawi, G.H.; Kaminaka, H.; Sanekata, T.; Shibahara, T.; Inanaga, S.; Tanaka, K. Overexpression of monodehydroascorbate reductase in transgenic tobacco confers enhanced tolerance to ozone, salt and polyethylene glycol stresses. Planta 2006, 225, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.H.; Wang, M.-H. Expression Pattern of Two Dehydroascorbate Reductase Genes from Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) in Response to Stress. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2010, 53, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Wang, X.; Zong, Y.; Wen, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, H. Enzymatic activity and functional analysis under multiple abiotic stress conditions of a dehydroascorbate reductase gene derived from Liriodendron Chinense. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 167, 103850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, D.; Li, Y.; McPhee, D.J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, L.; et al. Clones of FeSOD, MDHAR, DHAR Genes from White Clover and Gene Expression Analysis of ROS-Scavenging Enzymes during Abiotic Stress and Hormone Treatments. Molecules 2015, 20, 20939–20954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
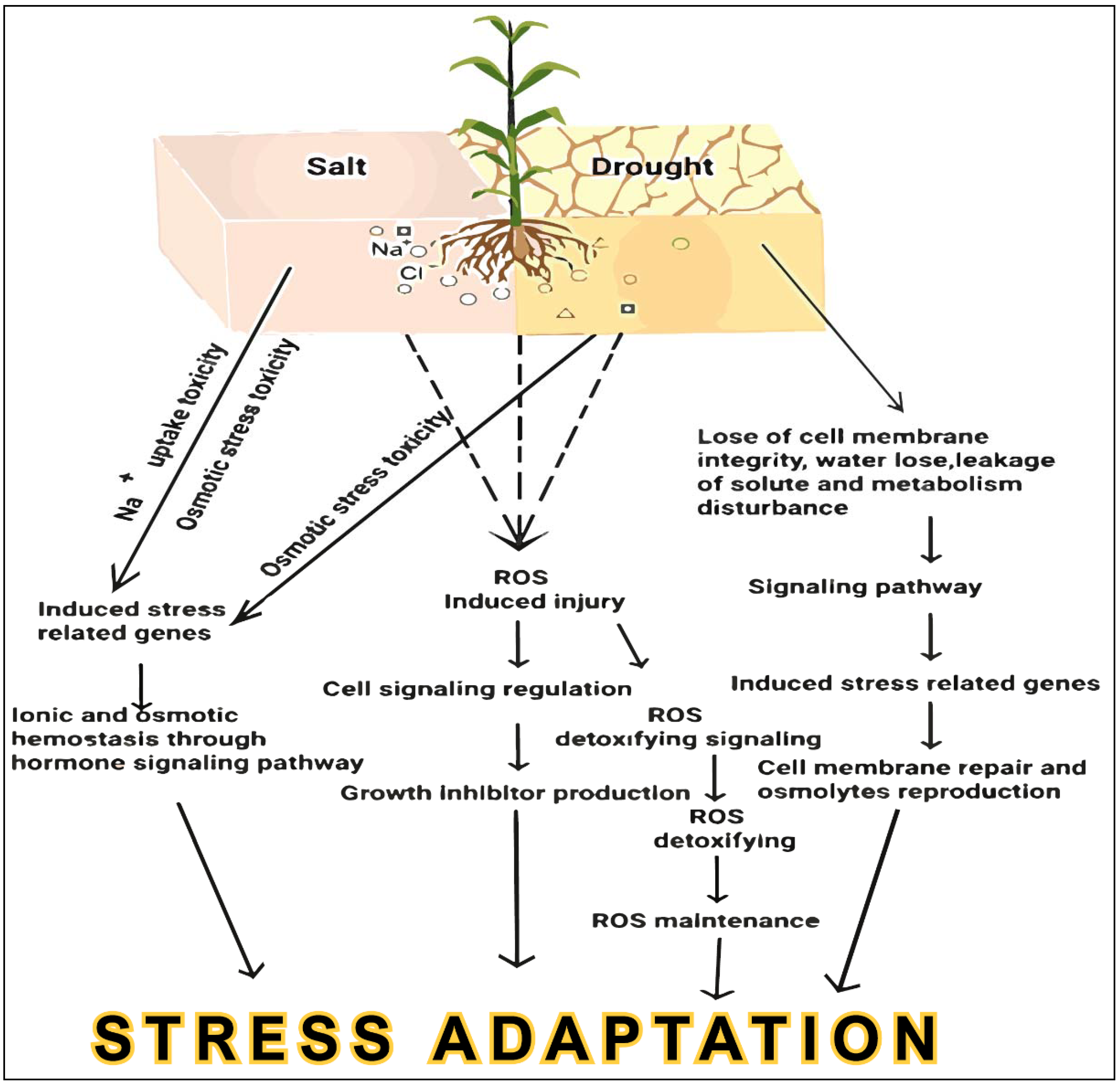
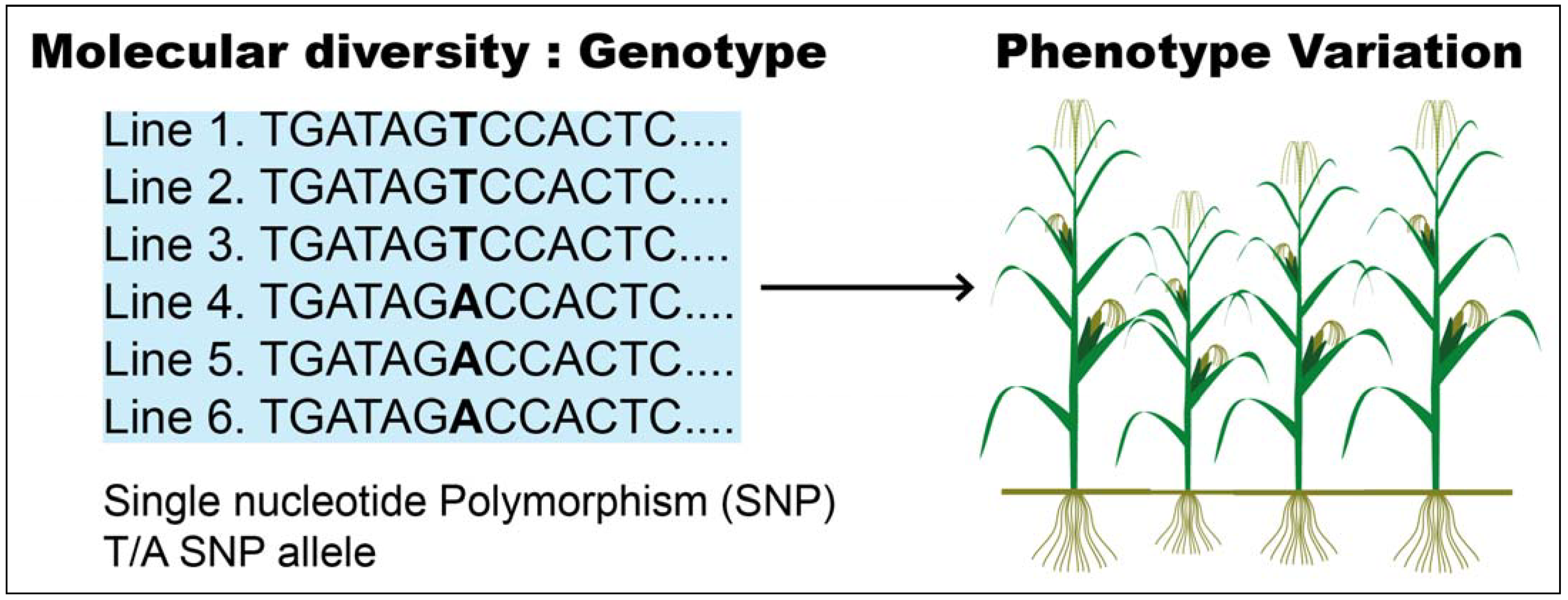


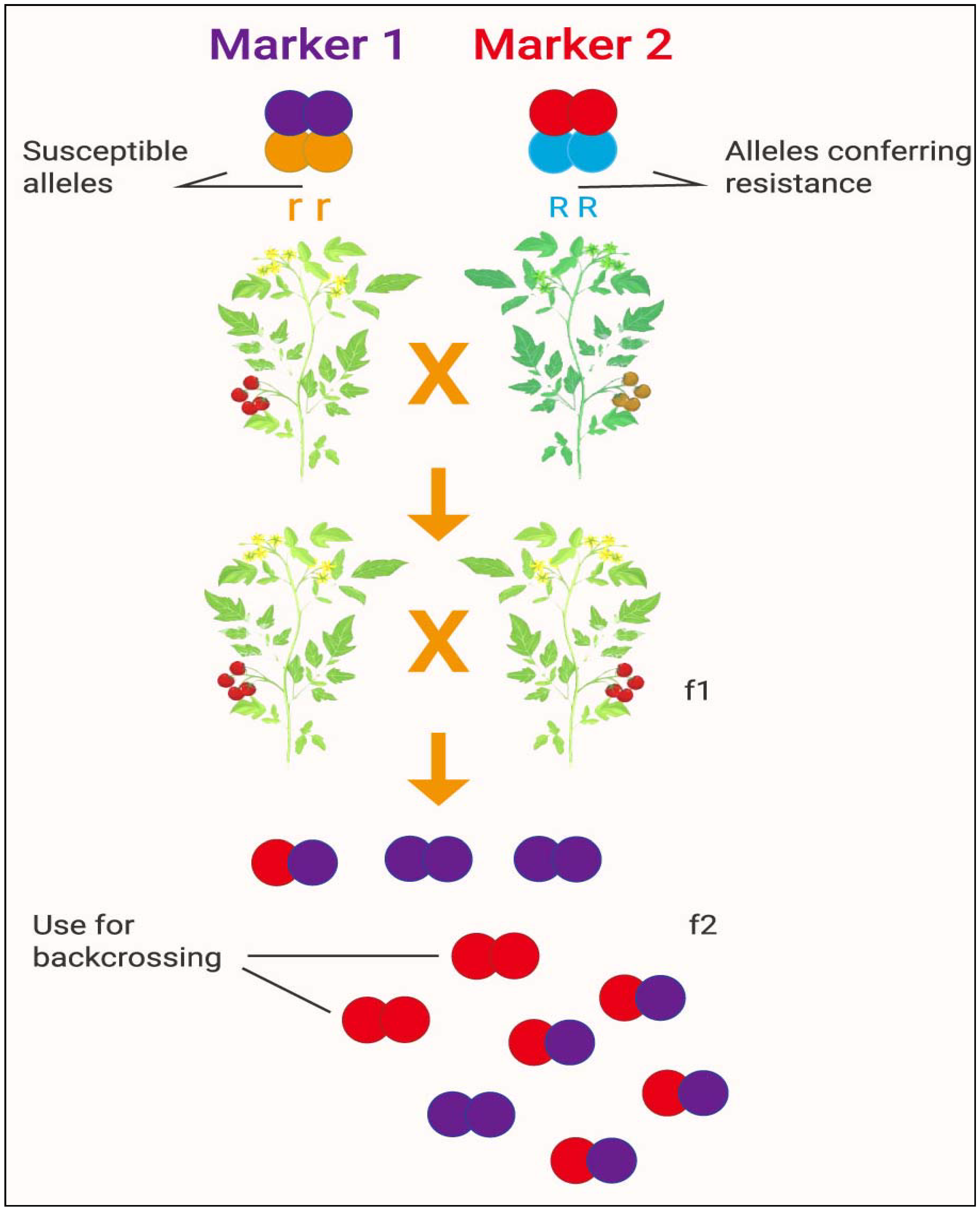
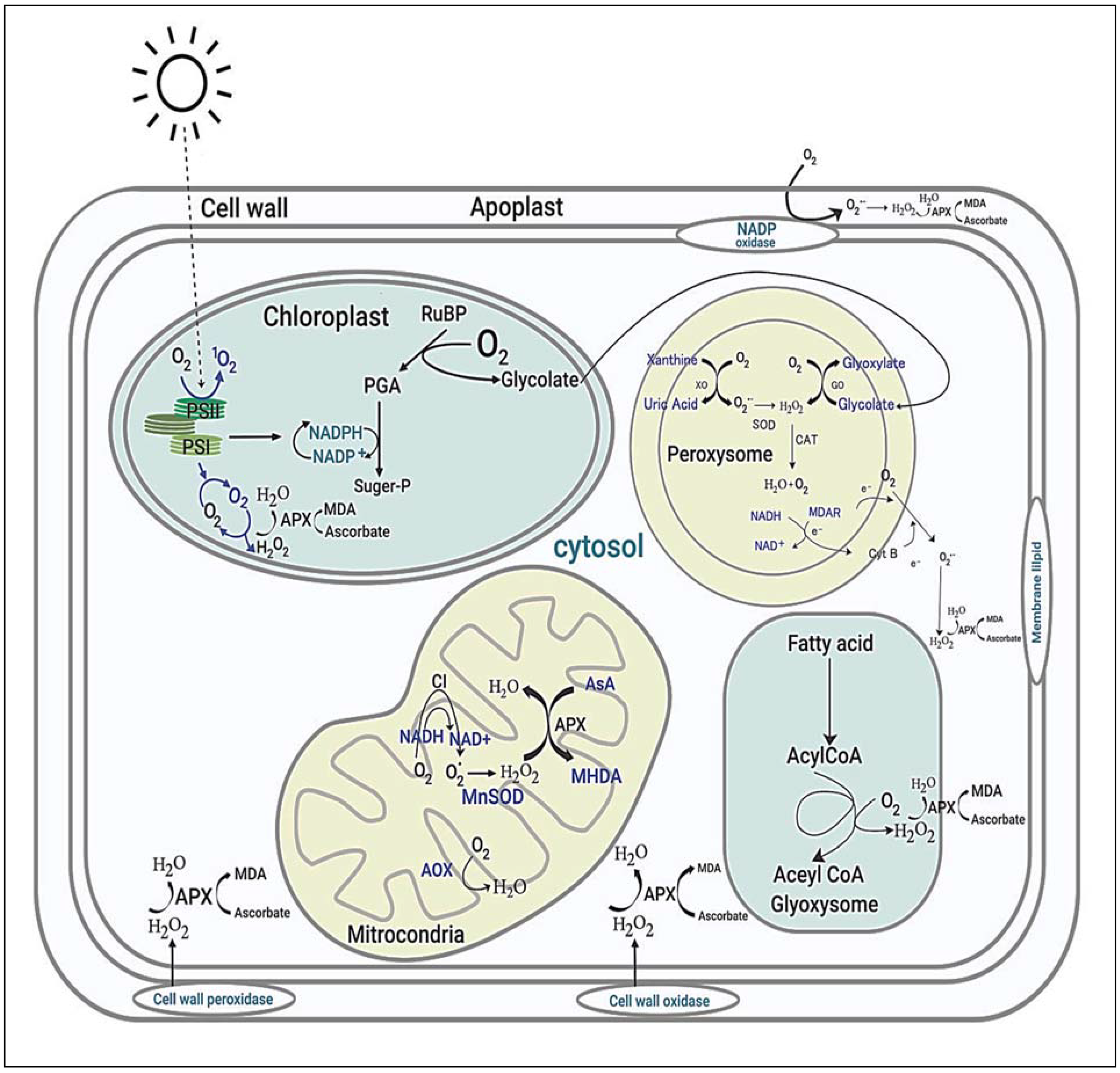
| Stresses | Crops | Major Effect/Finding | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drought stress | Cowpea | Detected QTL relevant to salt-tolerant and sensitive varieties | [29] |
| Drought stress | Wheat | Detected genetic loci to major morpho-physiological traits, components of yield, and grain yield | [30] |
| Salinity | Barley | Detected QTLs related to stomatal and photosynthetic traits associated with salinity tolerance | [31] |
| Drought | Sorghum | Identified QTLs associated with flowering and drought resistance | [24] |
| Drought | Rice | Improved crop yield under drought tolerance | [25] |
| Drought and submergence tolerance | Rice (TDK1) | Drought and submergence tolerance and yield stability | [25] |
| Drought and flood | Rice | Detected drought and salinity tolerance varieties based on developmental and physiological traits | [32] |
| Salinity | Rice (Pusa Basmati 1121) | Detected two QTLs for drought and one QTL for salt stress | [32] |
| Drought | Upland rice | Identified QTLs relevant to leaf rolling, leaf drying, leaf relative water content, and relative growth rate under water stress | [33] |
| SL No. | TF Family | Gene ID | Crop Variety | Target Stresses | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AP2/EREBP | TaERF3 | Triticum aestivum | Drought, Salt | [45] |
| 2 | bZIP | GmbZIP1, | Glycine max | Drought, Salinity, | [46] |
| 3 | MYB/MYC | StMYB1R-1 | Solanum tuberosum | Drought | [47] |
| 4 | NAC | OsNAC5, GmNAC20 | Oryza sativa, Glycine max | Drought | [48,49] |
| 5 | WRKY | TaWRKY44 | Triticum aestivum | Drought, Salt | [50] |
| 6 | AREB/ABF | AREB1, AREB2/ABF4 and ABF3 | Arabidopsis thaliana, | Drought | [51] |
| Stresses | Crops | Target Gene | Major Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) | Association mapping for salt tolerance at germination and seedling stages and the identification of SNP markers associated with salt tolerance in cowpea | [58] | |
| Drought | Wheat | RM223 | Demonstrated a strong power of joint association analysis and linkage mapping for the identification of important drought response genes in wheat | [59] |
| Salinity | Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) | Provided reference data for the use of MAS for salt tolerance in cotton | [55] | |
| Salinity | Cotton (Gossypium arboretum) | (Cotton_A_37775 and Cotton_A_35901) | Provided fundamental information to produce novel salt-tolerant cultivars | [54] |
| Drought | Pearl Millet | PMiGAP | Development of high-yielding drought- and submergence-tolerant rice varieties using marker-assisted introgression | [60] |
| Stresses | Crop Variety | Major Effect/Finding | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat prone | Spring wheat | Yield stability | [69] |
| Drought | Rice (indica and japonica) | Identified QTL containing promising candidate genes related to drought tolerance by osmotic stress adjustment | [70] |
| Salt stress | Arabidopsis thaliana | Provided a comprehensive view of AS under salt stress and revealed novel insights into the potential roles of AS in plant response to salt stress | [71] |
| Salinity | Rice | Candidate genes can be identified by QTL | [65] |
| Drought | Barley (Hordeum spontaneum) | Exploring the genomic basis of reproductive success under stress in wild progenitors with expected ecological and economic applications | [72] |
| Drought | Willow (paper-mulberry) | A core set of candidate genes encoding proteins with a putative function in drought response was identified | [73] |
| Salinity | Wild barley | Across many traits, QTLs that increased phenotypic values were identified | [74]. |
| Salinity | Rice | Unveiled genomic regions/candidate genes regulating salinity stress tolerance in rice | [75] |
| Drought | Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) | Improved alfalfa cultivars with enhanced resistance to drought and salt stresses | [76] |
| Drought | Rice | Drought-induced alterations to DNA methylation that may influence epigenetics | [77] |
| Drought | Wheat | Thirty-seven of the significant marker-traits were detected under the drought-stressed condition | [67] |
| Drought | Wheat | Identified a QL on chromosome 4H | [78] |
| Stresses | Crops | Silencing Gene | Major Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold, drought, salt stress | Rice | OsNAC5 | RNAi lines became less tolerant of these stresses than control plants | [58] |
| Salinity | Arabidopsis | sos1 | thsos1-RNAi lines of Thellungiella were highly salt-sensitive | [99] |
| Salinity | pepper | CaATG8c | The silencing of CaATG8c made pepper seedlings more sensitive to salt stress | [100] |
| Salinity | Alternanthera philoxeroides | ApSI1 | Significantly decreased tolerance to salinity | [101] |
| Drought | Alternanthera philoxeroides | ApDRI15 | Plants were more sensitive to drought stress than the control plants | [101] |
| Drought | Tomato | SpMPK1, SpMPK2, and SpMPK3 | Reduced drought tolerance in tomato plants | [102] |
| Drought | wheat | Era1 and Sal1 | Played imperative roles in conferring drought tolerance | [103] |
| Drought, salt stress | Cotton | GH3.17 | Enhanced drought and salt stress | [104] |
| Salinity | Cotton | GhWRKY6 | Downregulation of GhWRKY6 increased salt tolerance | [105] |
| Target Genes | Crops | Target Stresses | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| TaDREB2 and TaERF3 | Wheat | Abiotic stress response | [118] |
| ScNsLTP | Sugarcane | Drought and chilling resistance | [119] |
| MaAPS1 and MaAPL3 | Banana | Cold and salt | [120] |
| MeKUP | Cassava | Salt, osmosis, cold, and drought resistance | [121] |
| MeMAPKK | Cassava | Drought resistance | [122] |
| GhPIN1–3 and GhPIN2 | Cotton | Drought resistance | [123] |
| GhRDL1 | Cotton | Drought resistance | [124] |
| CpDreb2 | Papaya | Drought, heat, and cold resistance | [125] |
| OsDST | Indica mega rice cultivar | Salt and Drought | [126] |
| SlNPR1 | Tomato | Drought | [127] |
| Leaf1,2 | Rice | Drought | [128] |
| Stresses | Crops | Target Genes | Major Effect/Finding | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drought and Salt | Cotton | Significant associations between polymorphic markers and drought and salt tolerant traits were observed using the general linear model (GLM) | [48] | |
| Salinity | Rice | RM223 | Transferring genes from one variety to another and their use in MAS | [134] |
| Drought | Rice | Developed high-yielding rice cultivars suitable for water-limited environments through marker-assisted breeding | [135] | |
| Salinity | Rice | NAL1 | High yield through optimizing transportation efficiency of photosynthetic products by marker-assisted selection | [136] |
| Drought and flood | Rice | Developed high-yielding drought- and submergence-tolerant rice varieties using marker-assisted introgression | [25] | |
| Drought | Rice | Provided a higher yield advantage | [137] | |
| Drought | maize | Improved grain yield under drought stress conditions | [138] | |
| Drought and salt | Wheat | TaCRT-D | Increased plant stress tolerance and the functional markers of TaCRT-D for marker-assisted selection in wheat breeding | [139] |
| Salinity | Rice | Developed new salt-tolerant rice germplasm using speed-breeding | [140] | |
| Drought | Rice | Stimulated 10–36% higher yield among different inbred lines | [141] |
| Genes | Origin | Transformation Receptor | Protein Function | Major Functions | Signaling Hormone | Approaches Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GhMKK1 | G. hirsutum | N. benthamiana | MAPKK | Influences oxidative, ROS scavenging, salt and drought tolerance | Abscisic acid (ABA) | Reverse genetics | [147] |
| DSM1 | O. sativa | O. sativa | MAPKKK | Influences oxidative, ROS scavenging, drought tolerance | ABA | RNA interference, Reverse genetics | [148] |
| DSM2 | O. sativa | O. sativa | MAPKKK | Influences oxidative, ROS scavenging, drought tolerance | ABA | RNA interference, Reverse genetics | [149] |
| MEKK1 | Arabidopsis | Arabidopsis | MAPKKK | Influences oxidative, ROS scavenging, abiotic stress tolerance | ABA | Reverse genetics | [150] |
| GhMAPKKK49 | G. hirsutum | G. hirsutum | MAPKKK | ROS scavenging, salt, drought, and wounding stresses | ABA, gibberellins (GB), methyl jasmonate (JA), salicylic acid (SA), 6-benzyl amino purine, a-naphthyl acetic acid, and ethylene (ET) | Transcriptome | [151] |
| MKK1, MKK2, MKK6 | Arabidopsis | MAPKK | Stimulate oxidative, ROS scavenging, abiotic stresses | SA | RNA interference | [150,152] | |
| OsCPK4 | O. sativa | O. sativa | Calcium-dependent protein kinase | ROS scavenging, drought, and salt stress | SA | Reverse genetics | [153] |
| OsCPK12 | O. sativa | O. sativa | Calcium-dependent protein kinase | ROS scavenging, influences oxidative salt stress | ABA | RNA interference, Reverse genetics | [154] |
| SiCDPK24 | Setaria italica | Arabidopsis | Calcium-dependent protein kinase | ROS scavenging, drought stress | ABA | Reverse genetics | [155] |
| TaCIPK29 | T. aestivum | N. benthamiana | CBL-interacting protein | ROS scavenging, salt stress | ABA and ET | Reverse genetics | [156] |
| MdCIPK6L | Apple | Arabidopsis | CBL-interacting protein kinase | ROS scavenging, salt, osmotic/drought and chilling stresses | ABA | Reverse genetics | [157] |
| MdSOS2L1 | Apple | tomato | CBL-interacting protein kinase | ROS scavenging, salt stresses | ABA | Reverse genetics | [158] |
| AtCIPK5 | Arachis diogoi | Arabidopsis | CBL-interacting protein kinase | Salt and osmotic stress tolerance | NA | Reverse genetics | [159] |
| SIT1 | O. sativa | O. sativa | Lectin receptor-like kinase | ROS production, salt sensitivity | ET | Reverse genetics | [160] |
| OsMPK6 | O. sativa | O. sativa | MAPK | ROS scavenging, salt stresses | SA | RNA interference | [161] |
| ZmMPKL1 | Zea mays | Zea mays | MAPK | ROS production, drought sensitivity | ABA | CRISPR/Cas9, Reverse genetics | [162] |
| MeMAPK | Cassava | NA | MAPK | osmotic, salt, cold, oxidative stressors | ABA | Transcriptome | [163] |
| ZmMKK3 | Zea mays | N. benthamiana | MAPK | ROS scavenging, osmotic tolerance | ABA | Reverse genetics | [164] |
| OsPP18 | O. sativa | O. sativa | Protein phosphatase 2C | ROS scavenging, drought and oxidative stress | ABA | RNA interference, Reverse genetics | [165] |
| DST | O. sativa | O. sativa | zinc finger C2H2 | ROS scavenging, drought and salt stress | Cytokinins | QTL, RNA interference, Reverse genetics | [166,167] |
| ZFP36 | O. sativa | O. sativa | zinc finger C2H2 | ROS scavenging, stress and oxidative stress | ABA | RNA interference, Reverse genetics | [168] |
| OsTZF1 | O. sativa | O. sativa | Zinc Finger Protein CCCH | ROS scavenging, drought, high-salt stress | ABA | RNA interference | [169] |
| OsWRKY30 | O. sativa | O. sativa | WRKY | ROS scavenging, drought tolerance | SA | Reverse genetics | [170] |
| GhWRKY6 | G. hirsutum | Arabidopsis | WRKY | ROS production, drought and salt stress | ABA | Transcriptome, VIGS, Reverse genetics | [105] |
| EcNAC1 | Helianthus annus | Helianthus annus | NAC | ROS scavenging, salt stress | ABA | Reverse genetics | [171] |
| NTL4 | Arabidopsis | Arabidopsis | NAC | ROS production, drought stress | ABA | RNA interference, Reverse genetics | [172] |
| EcbHLH57 | Eleusine coracana | N. benthamiana | bHLH | ROS scavenging, salt, oxidative and drought stress | ABA | Reverse genetics | [173] |
| JERF3 | O. sativa | O. sativa | Ethylene response factor (ERF) | Drought and osmotic stress | ET | Reverse genetics | [174] |
| MnSOD | N. plumbaginifolia | M. sativa | MnSOD | ROS scavenging drought stress | NA | Reverse genetics | [175] |
| OsAPX2 | Medicago sativa | Medicago sativa | APX | ROS scavenging, salt tolerance | ABA | Reverse genetics | [176] |
| PgGPX | Pennisetum glaucum | O. sativa | GPX | ROS scavenging, salinity and drought stress | SA | Reverse genetics | [177] |
| MsALR | M. sativa | N. benthamiana | NADPH-dependent aldose/aldehyde reductase | Antioxidative metabolism, drought and oxidative stress | NA | Reverse genetics | [178] |
| AtMIOX4 | Arabidopsis | Arabidopsis | MIOX | ROS scavenging, salt tolerance | ABA | Reverse genetics | [179] |
| MtPP2C | Medicago truncatula | NA | PP2C | ROS scavenging, drought and cold stress responses | ABA | Transcriptome | [180] |
| OsAHL1 | O. sativa | O. sativa | AHL | ROS scavenging, drought resistance | ABA, SA | GWAS, Reverse genetics | [181] |
| OsHK3 | O. sativa | NA | HK | ROS scavenging, salinity and drought stress | ABA | RNA interference | [182] |
| IcSRO1 | Ipomoea cairica | Arabidopsis | SRO | ROS scavenging, salt and drought tolerance | ABA | Transcriptome, Reverse genetics | [183] |
| OsCATB | O. sativa | O. sativa | CATB | ROS production, drought stress | ABA | Transcriptome | [184] |
| RBOHH | O. sativa | O. sativa | NADPH Oxidase | ROS production, drought stress | ET | CRISPR/Cas9, Reverse genetics | [185] |
| Functional Category | List of Genes | Type of Stress | Biological Function and Signaling Pathway | Tools Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein kinase | |||||
| MAPKKK | MEKK1, MEKK2, MEKK3, MEKK4, MAPKKK18, GhMAP3K40, OsMAPKKK63, GhMAPKKK49 DSM1, DSM2 | Influences oxidative, abiotic, and biotic stress. | Growth and development; ABA | RNA interference, reverse genetics | [150,186,187] |
| MAPKK | MKK1, MKK2, MKK6, GhMKK1, | Influences oxidative, salt and drought | Growth and development; SA | Transcriptome, reverse genetics | [150,188] |
| MKK3, GhMKK3 | Influences oxidative, salt, and drought stresses | Growth and development; SA | RNA interference, reverse genetics | ||
| MKK4, MKK5 GhMKK4, GhMKK5, | Influences oxidative, drought | Growth and development; JA | RNA interference, reverse genetics | ||
| MKK7, MKK8, MKK9, MKK10, RhMKK9, GhMKK9, ZmMKK10 | Salt and/or drought | Growth and development; ET | Reverse genetics | ||
| VvMKK2, VvMKK4 | Influences oxidative, salt, and drought | Growth and development; SA | Reverse genetics | [177] | |
| MAPK | MPK3, MPK6, MPK10 OsMPK6, ZmMPK3, RhMPK6, ZmMPK6-2, OsMPK3, ZmMPK3 | Influences oxidative, abiotic, and biotic stresses | Cell cycle regulation, cell division; JA and ET | RNA interference, reverse genetics | [150,189] |
| MPK4, MPK5, MPK11, MPK12, MPK13, OsMPK4ZmMPK4-1, OsMPK5, OsMPK5, ZmMPK5 | Influences oxidative, salt, and/or drought | Cell cycle regulation; SA | RNA interference, reverse genetics | [150] | |
| MPK1, MPK2, MPK7, MPK14, ZmMPK7, OsMPK2AtMPK7, OsMPK7, GhMPK7 | Influences oxidative, salt, drought | Circadian-rhythm-regulated; JA, SA | RNA interference, reverse genetics | [150] | |
| MPK8, MPK9, MPK15/16/17/18/19/20 GhMPK17, ZmMPK17 | Influences oxidative, salt, drought | Cell cycle regulation; JA | RNA interference, reverse genetics | [161] | |
| CDPK | OsCPK4 OsCPK12 SiCDPK24 FaCDPK4, FaCDPK11 StCDPK3, StCDPK23 | Influences oxidative, salt, drought | Responses to developmental and environmental cues; SA, ABA | Transcriptome, RNA interference, reverse genetics | [190] |
| CIPK | TaCIPK29 MdCIPK6L MdSOS2L1 AtCIPK5 | ROS scavenging, salt and osmotic stress tolerance | tissue and organ development; ABA | Reverse genetics | [167,168,169,170] |
| Transcription factor | |||||
| bZIP | ABF3, BF4 ABF3, ABF4 FtbZIP5, PtrABF OsbZIP23, OsbZIP12, OsbZIP71, OsbZIP46 OsbZIP72, ZmbZIP4 OsbZIP62, TabZIP | Salt, drought | Light signaling, seed maturation, flower development; ABA | Transcriptome, RNA interference reverse genetics | [191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200] |
| bHLH | MYC2, AtbHLH17, AtbHLH68, AtbHLH122, FtbHLH2, FtbHLH3, PebHLH35, OsbHLH148 | Salt, drought | Growth, development, response to various stresses; JA, ABA | Transcriptome, RNA interference, reverse genetics | [201,202,203,204,205,206,207,208] |
| NAC | ANAC019, ANAC055, ANAC072, ANAC042, TaNAC29, OsNAC6, OsNAC5, OsNAC9, OsNAC10, TaRNAC1, GmNAC109, CaNAC035 | Salt, drought | Plant growth and development range from the formation of shoot apical meristem, floral organ development, reproduction, lateral shoot development; ABA | Transcriptome, RNA interference, reverse genetics | [209,210,211,212,213,214,215,216,217,218,219] |
| AP2/ERF | CBF1, CBF2, CBF3, AtERF53, AtERF74, AhDREB1, OsDREB1, OsEREBP1, OsERF7, GmERF3, ZmDREB2A, SlERF5 | Salt, drought | Regulation of plant growth and development; ABA | Transcriptome, RNA interference reverse genetics | [220,221,222,223,224,225,226,227,228,229,230] |
| MYB | AtMYB44, AtMYB96, AtMYB20, OsMYB4, OsMYB6, OsMYB48-1, OsMYB91, GmMYB76, GmMYB92, GmMYB177 | Abiotic stresses | Circadian rhythm, regulation of primary and secondary metabolism; ABA, JA | Transcriptome, RNA interference reverse genetics | [231,232,233,234,235,236,237,238,239] |
| WRKY | OsWRKY11, OsWRKY45, TaWRKY1, TaWRKY33, cWRKY023, ZmWRKY33, VvWRKY2 | Salt, drought | Growth and development; ABA | Transcriptome, RNA interference reverse genetics | [240,241,242,243,244,245] |
| ROS-scavenging | |||||
| SOD | FSD1, FSD2, FSD3 CSD1, CSD2, CSD3 MSD1 | Salt, drought | Antioxidant defense against oxidative stress; ABA | RNA interference, Reverse genetics | [246] |
| CmSOD | Oxidative stress | ABA | reverse genetics | [247] | |
| CsSOD | Drought | JA and gibberellin (GA3) | Transcriptome | [248] | |
| APX | APX1-APX7 | Salt and or drought | Growth regulation; ABA | Transcriptome | [246] |
| OsAPX1, OsAPX2 | Oxidative, Salt, drought | ABA | Transcriptome | [249] | |
| OsAPX3, OsAPX4 | Salt and drought | ABA | Transcriptome | [249] | |
| OsAPX5, OsAPX6 and OsAPX7 | salinity | ABA | Transcriptome | [250] | |
| AgAPX1 | Drought | NA | Reverse genetics | [251] | |
| TbAPX | Salt | ABA | Reverse genetics | [252] | |
| CytAPX | Salt | ABA | Reverse genetics | [253] | |
| CAT | CAT2, CAT3, ScCAT1 | Salt and/or drought | ABA | Transcriptome | [254] |
| HuCAT3 | Salt and drought | NA | Transcriptome | [255] | |
| VsCat | Salt | Salt | CRISPR/C as9 | [198] | |
| CsCAT3 | Tolerance to heat, cold, salinity and osmotic condition | ABA | Transcriptome, Reverse genetics | [256] | |
| GPX | GPX1, GPX2, GPX5, GPX6 and GPX7 | Abiotic stress | Plant development, multiple signaling pathways | Transcriptome | [257,258] |
| PgGPx | Salinity and Drought | NA | Reverse genetics | [177] | |
| ClGPX | Salinity and Drought | ABA | Transcriptome | [258] | |
| NnGPX | Salt | NA | Reverse genetics | [259] | |
| OsGPX5 | Salt | ABA | Transcriptome, RNA interference | [260] | |
| MDHAR | MDAR2-4 | Salt | Stress protection; ABA | Transcriptome | [256] |
| AeMDHAR | Salt | NA | Reverse genetics | [261] | |
| AtMDAR1 | Ozone, salt and drought stress | ABA | Reverse genetics | [262] | |
| TrMDHAR | salt | ABA | Transcriptome | [261] | |
| DHAR | SlDHAR1 and SlDHAR2 | salt | Stress protection; NA | Transcriptome | [263] |
| DHAR1 and DHAR3 | Salt | ABA | Transcriptome | [256] | |
| LcDHAR | Salt and drought | NA | Transcriptome, Reverse genetics | [264] | |
| TrDHAR | Salt | ABA | Transcriptome | [265] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Billah, M.; Aktar, S.; Brestic, M.; Zivcak, M.; Khaldun, A.B.M.; Uddin, M.S.; Bagum, S.A.; Yang, X.; Skalicky, M.; Mehari, T.G.; et al. Progressive Genomic Approaches to Explore Drought- and Salt-Induced Oxidative Stress Responses in Plants under Changing Climate. Plants 2021, 10, 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091910
Billah M, Aktar S, Brestic M, Zivcak M, Khaldun ABM, Uddin MS, Bagum SA, Yang X, Skalicky M, Mehari TG, et al. Progressive Genomic Approaches to Explore Drought- and Salt-Induced Oxidative Stress Responses in Plants under Changing Climate. Plants. 2021; 10(9):1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091910
Chicago/Turabian StyleBillah, Masum, Shirin Aktar, Marian Brestic, Marek Zivcak, Abul Bashar Mohammad Khaldun, Md. Shalim Uddin, Shamim Ara Bagum, Xinghong Yang, Milan Skalicky, Teame Gereziher Mehari, and et al. 2021. "Progressive Genomic Approaches to Explore Drought- and Salt-Induced Oxidative Stress Responses in Plants under Changing Climate" Plants 10, no. 9: 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091910








