Plant Cell Wall Proteins: A Large Body of Data, but What about Runaways?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A Large Body of Data
| Plant species | Type of proteome | Number of identified CWPs a | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dicots | |||
| Arabidopsis thaliana | cell wall | 913 | [14,17,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] |
| N-glycoproteome | 200 | ||
| 495 | |||
| Brassica napus/oleracea | xylem sap | 147 | [19,39] |
| N-glycoproteome | 92 | [19] | |
| 162 | |||
| Cicer arietinum | cell wall | nd | [40,41,42] |
| Glycine max | cell wall | nd | [43] |
| Gossypium hirsutum | N-glycoproteome | 116 | [44] |
| Helianthus annuus | cell wall | nd | [45] |
| Linum usitatissimum | cell wall | 106 | [46] |
| Medicago sativa | cell wall |  | [16,47] |
| Nicotiana benthamiana | cell wall | nd | [48] |
| Nicotiana tabacum | cell wall | nd | [34,49,50,51] |
| Populus deltoides | cell wall | 144 | [13] |
| P. trichocarpa x P. deltoides (hybrid poplar) | xylem sap | 33 | [52] |
| 142 | |||
| Solanum lycopersicum | cell wall | nd, 60 | [34,53] |
| N-glycoproteome | 104 | [20] | |
| 161 | |||
| Solanum tuberosum | cell wall |  | [54,55] |
| Monocots | |||
| Brachypodium distachyon | cell wall | 689 | [15] |
| 314 | |||
| Oryza sativa | cell wall | 381 | [56,57,58,59,60] |
| 270 | |||
| Saccharum officinarum | cell wall | 69 | [61] |
| Zea mays | cell wall, | nd | [62,63] |
| xylem sap | nd | [64] |
| Stems | Leaves | Fruit pericarp | Fruit cuticle | Xylem sap | Protocols | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dicots | |||||||
| B. napus/oleracea | x | xylem sap | [19] | ||||
| L. usitatissimum | x | - cell wall preparation - extraction of proteins from cell walls with CaCl2, LiCl | [46] | ||||
| M. sativa | x | - cell wall preparation - extraction of proteins from cell walls with EGTA, LiCl | [16] | ||||
| P. deltoides | x | xylem sap | [13] | ||||
| S. lycopersicum | x | chloroform extraction | [53] | ||||
| S. lycopersicum | x | N-glycoproteome (total protein extraction followed by ConA affinity chromatography | [20] | ||||
| S. tuberosum | x | - cell wall preparation - extraction of proteins from cell walls with CaCl2 | [55] | ||||
| Monocots | |||||||
| B. distachyon | x | x | - cell wall preparation - extraction of proteins from cell walls with CaCl2, LiCl | [15] |
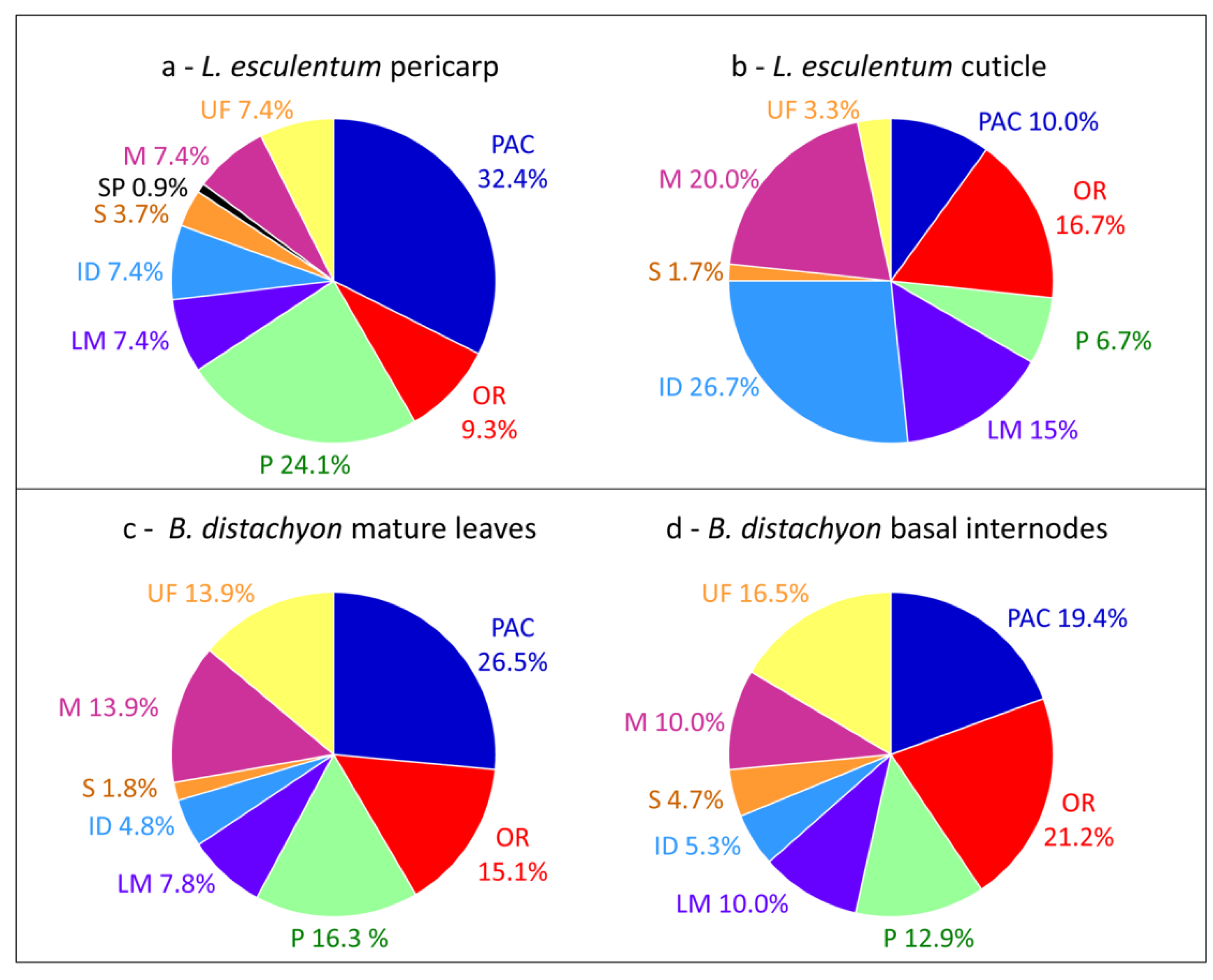
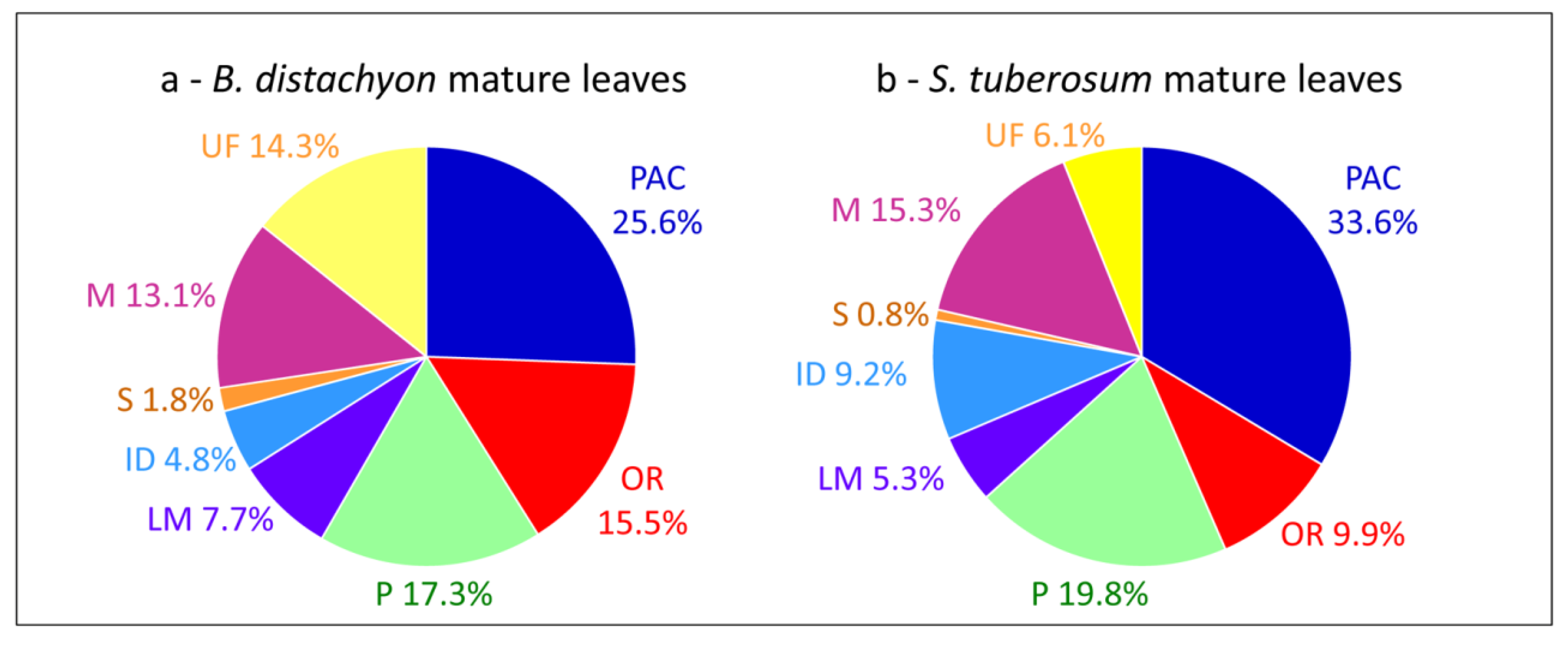
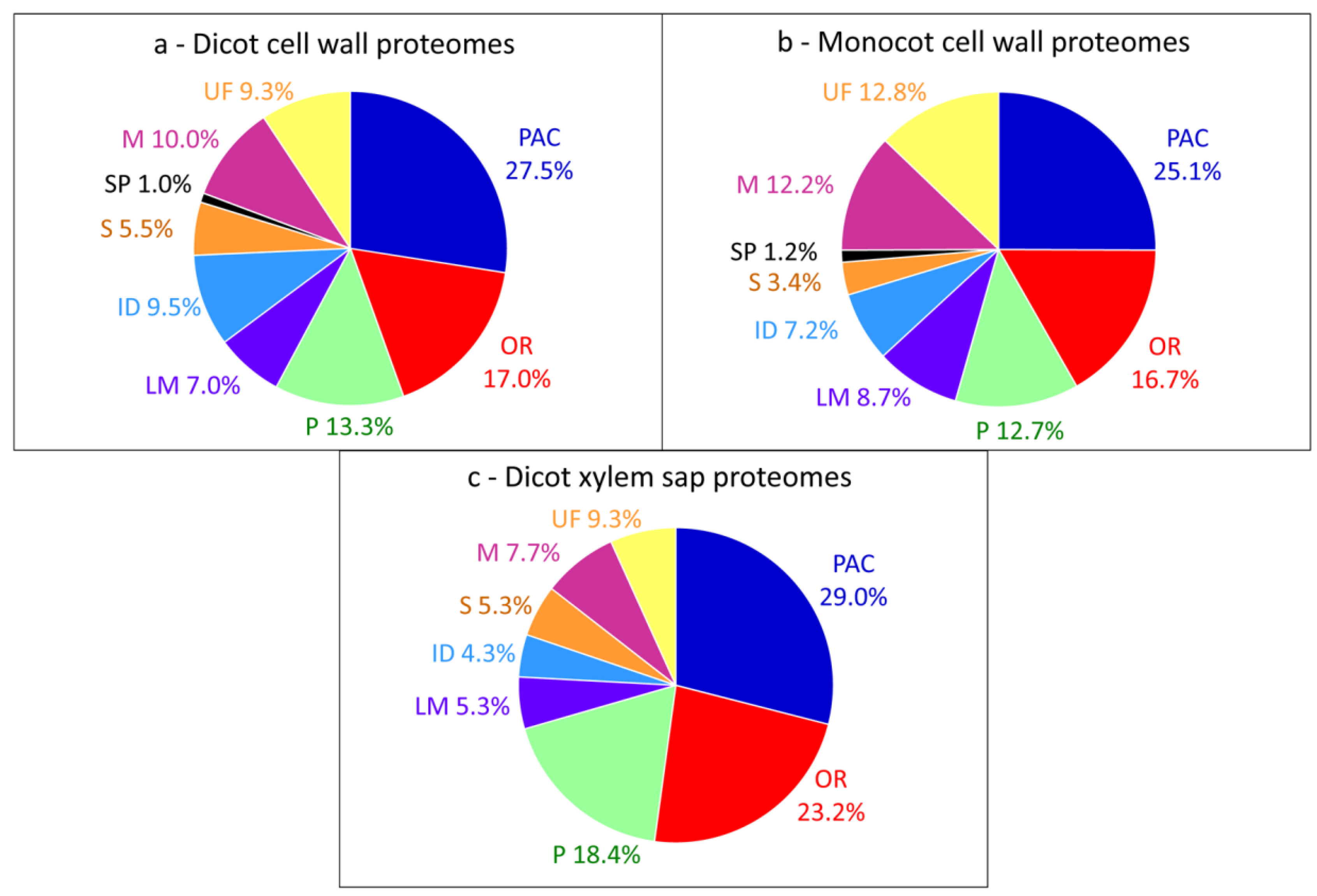
3. The Limitations for Full Coverage of Cell Wall Proteomes
3.1. Loss of Proteins during the Purification of Cell Walls

3.2. Extraction of Proteins by Salt Solutions

3.3. Difficulties to Extract Structural Proteins
| Protein family | Plant | References |
|---|---|---|
| PRP (At5g09530; At5g14920, AtGASA14) | A. thaliana | [14] |
| AGP/PRP (At1g28290, AtAGP31) | A. thaliana | [14,30] |
| LRX (At1g62440, AtLRX2; At4g13340; At3g24480; AtLRX3, AtLRX4; At4g18670, AtLRX5) | A. thaliana | [14,22,38] |
| GRP (At2g05580) | A. thaliana | [14] |
| LRX (Os01g0594300, Os05g0180300, Os06g0704500, Os02g0138000 | O. sativa | [56] |
| GRP (Os07g0688700, Os07g0440100) | O. sativa | [57] |
| THRGP (Os03g0676300, Os04g0418800) | O. sativa | [56,57] |
| AGP/PRP (Lus10015434) | L. usitatissimum | [46] |
| LRX (Medtr8g103700.1, Medtr6g086120.1) | M. sativa | [16] |
| LRX (Solyc11g005150.1) | L. esculentum | [20] |
4. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carpita, N.C.; Gibeaut, D.M. Structural models of primary cell walls in flowering plants, consistency of molecular structure with the physical properties of the walls during growth. J. Plant 1993, 3, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Dixon, R. On-off switches for secondary cell wall biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.P. Revealing the structural and functional diversity of plant cell walls. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Marcus, S.; Knox, J. Cell wall biology: perspectives from cell wall imaging. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roppolo, D.; Geldner, N. Membrane and walls: Who is master, who is servant? Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, S.C. Primary cell wall metabolism: Tracking the careers of wall polymers in living plant cells. New Phytol. 2004, 161, 641–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, G.; Roberts, K. The biology of arabinogalactan proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Smith, S.; de Smet, I. Small signaling peptides in Arabidopsis development: How cells communicate over a short distance. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3198–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Savatin, D.; Sicilia, F.; Gramegna, G.; Cervone, F.; Lorenzo, G. Oligogalacturonides: Plant damage-associated molecular patterns and regulators of growth and development. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, e49. [Google Scholar]
- Albenne, C.; Canut, H.; Jamet, E. Plant cell wall proteomics: The leadership of Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, e111. [Google Scholar]
- Jamet, E.; Albenne, C.; Boudart, G.; Irshad, M.; Canut, H.; Pont-Lezica, R. Recent advances in plant cell wall proteomics. Proteomics 2008, 8, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Saravanan, R.S.; Damasceno, C.M.; Yamane, H.; Kim, B.D.; Rose, J.K. Digging deeper into the plant cell wall proteome. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechanova, O.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Adams, J.; Pechan, T.; Vandervelde, L.; Drnevich, J.; Jawdy, S.; Adeli, A.; Suttle, J.; Lawrence, A.; et al. Apoplast proteome reveals that extracellular matrix contributes to multistress response in poplar. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, e674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Canut, H.; Borderies, G.; Pont-Lezica, R.; Jamet, E. A new picture of cell wall protein dynamics in elongating cells of Arabidopsis thaliana: Confirmed actors and newcomers. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douché, T.; San Clemente, H.; Burlat, V.; Roujol, D.; Valot, B.; Zivy, M.; Pont-Lezica, R.; Jamet, E. Brachypodium distachyon as a model plant toward improved biofuel crops: Search for secreted proteins involved in biogenesis and disassembly of cell wall polymers. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2438–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonk, J.; Hatfield, R.; Sullivan, M. Proteomic analysis of cell walls of two developmental stages of alfalfa stems. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, e279. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, I.S.; Park, A.R.; Bae, M.S.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, N.Y.; Lee, S.; Cheong, H.; Park, O.K. Secretome analysis reveals an Arabidopsis lipase involved in defense against Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2832–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-May, E.; Rose, J. Progress toward the tomato fruit cell wall proteome. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, e159. [Google Scholar]
- Ligat, L.; Lauber, E.; Albenne, C.; San Clemente, H.; Valot, B.; Zivy, M.; Pont-Lezica, R.; Arlat, M.; Jamet, E. Analysis of the xylem sap proteome of Brassica oleracea reveals a high content in secreted proteins. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1798–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalá, C.; Howe, K.; Hucko, S.; Rose, J.; Thannhauser, T. Towards characterization of the glycoproteome of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit using Concanavalin A lectin affinity chromatography and LC-MALDI-MS/MS analysis. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, U.; Francis, J.L.; Whittal, R.W.; Stephens, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Zaiane, O.R.; Goebel, R.; Muench, D.G.; Good, A.G.; Taylor, G.J. Extracellular proteomes of Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus roots: Analysis and comparison by MUdPIT and LC-MS/MS. Plant Soil 2006, 286, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, E.M.; Bottrill, A.R.; Walshaw, J.; Vigouroux, M.; Naldrett, M.J.; Thomas, C.L.; Maule, A.J. Arabidopsis cell wall proteome defined using multidimensional protein identification technology. Proteomics 2006, 6, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borderies, G.; Jamet, E.; Lafitte, C.; Rossignol, M.; Jauneau, A.; Boudart, G.; Monsarrat, B.; Esquerré-Tugayé, M.T.; Boudet, A.; Pont-Lezica, R. Proteomics of loosely bound cell wall proteins of Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspension cultures: A critical analysis. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 3421–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borner, G.H.; Lilley, K.S.; Stevens, T.J.; Dupree, P. Identification of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in Arabidopsis. A proteomic and genomic analysis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudart, G.; Jamet, E.; Rossignol, M.; Lafitte, C.; Borderies, G.; Jauneau, A.; Esquerré-Tugayé, M.-T.; Pont-Lezica, R. Cell wall proteins in apoplastic fluids of Arabidopsis thaliana rosettes: Identification by mass spectrometry and bioinformatics. Proteomics 2005, 5, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasoli, M.; Spadoni, S.; Lilley, K.; Cervone, F.; de Lorenzo, G.; Mattei, B. Identification by 2-D DIGE of apoplastic proteins regulated by oligogalacturonides in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proteomics 2008, 8, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmont, S.; Jamet, E.; Pont-Lezica, R.; Canut, H. Proteomic analysis of secreted proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings: Improved recovery following removal of phenolic compounds. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.-Y.; Blackburn, K.; Lin, Y.-M.; Goshe, M.; Wiliamson, J. Absolute protein quantification by LC/MS for global analysis of salicylic acid-induced plant protein secretion responses. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivasa, S.; Ndimba, B.K.; Simon, W.J.; Robertson, D.; Yu, X.-L.; Knox, J.P.; Bolwell, P.; Slabas, A.R. Proteomic analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana cell wall. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiz, L.; Irshad, M.; Pont-Lezica, R.F.; Canut, H.; Jamet, E. Evaluation of cell wall preparations for proteomics: A new procedure for purifying cell walls from Arabidopsis hypocotyls. Plant Methods 2006, 2, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslam, R.P.; Downie, A.L.; Raventon, M.; Gallardo, K.; Job, D.; Pallett, K.E.; John, P.; Parry, M.A.J.; Coleman, J.O.D. The assessment of enriched apoplastic extracts using proteomic approaches. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2003, 143, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.-K.; Yokoyama, R.; Nishitani, K. A proteomic approach to apoplastic proteins involved in cell wall regeneration in protoplasts of Arabidopsis suspension-cultured cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndimba, B.K.; Chivasa, S.; Hamilton, J.M.; Simon, W.J.; Slabas, A.R. Proteomic analysis of changes in the extracellular matrix of Arabidopsis cell suspension cultures induced by fungal elicitors. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.; Mitchell, G.P.; Gilroy, J.S.; Gerrish, C.; Bolwell, G.P.; Slabas, A.R. Differential extraction and protein sequencing reveals major differences in patterns of primary cell wall proteins from plants. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 15841–15848. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, C.J.; Ferguson, K.L.; Lahnstein, J.; Bacic, A. Post-translational modifications of arabinogalactan-peptides of Arabidopsis thaliana. Endoplasmic reticulum and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchor signal cleavage sites and hydroxylation of proline. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45503–45511. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.; Plaxton, W. Proteomic analysis of alterations in the secretome of Arabidopsis thaliana suspension cells subjected to nutritional phosphate deficiency. Proteomics 2008, 8, 4317–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minic, Z.; Jamet, E.; Negroni, L.; der Garabedian, P.A.; Zivy, M.; Jouanin, L. A sub-proteome of Arabidopsis thaliana trapped on Concanavalin A is enriched in cell wall glycoside hydrolases. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Giboulot, A.; Zivy, M.; Valot, B.; Jamet, E.; Albenne, C. Combining various strategies to increase the coverage of the plant cell wall glycoproteome. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehr, J.; Buhtz, A.; Giavalisco, P. Analysis of xylem sap proteins from Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol. 2005, 5, e11. [Google Scholar]
- Bhushan, D.; Pandey, A.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Choudhary, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Datta, A.; Chakraborty, N. Extracellular matrix proteome of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) illustrates pathway abundance, novel protein functions and evolutionary perspect. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Bhushan, D.; Pandey, A.; Choudhary, M.; Datta, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, N. Comparative proteomics analysis of differentially expressed proteins in chickpea extracellular matrix during dehydration stress. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2007, 6, 1868–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, D.; Jaiswal, D.; Ray, D.; Basu, D.; Datta, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, N. Dehydration-responsive reversible and irreversible changes in the extracellular matrix: Comparative proteomics of chickpea genotypes with contrasting tolerance. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 2027–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nishizawa, K.; Nanjo, Y.; Furukawa, K. Comparative analysis of differentially expressed proteins in soybean cell wall during flooding stress. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, K.; Pandey, P.; Rajamani, V.; Padmalatha, K.; Dhandapani, G.; Kanakachari, M.; Leelavathi, S.; Kumar, P.; Reddy, V. Glycoproteome of elongating cotton fibre cells. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2013, 12, 3777–3789. [Google Scholar]
- Pinedo, M.; Regenten, M.; Elizalde, M.; Quiroga, I.; Pagnussat, L.; Jorrin-Novo, J.; Maldonado, A.; de la Canal, L. Extracellular sunflower proteins: Evidence on non-classical secretion of a jacalin-related lectin. Protein Pept. Lett. 2012, 19, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Day, A.; Fénart, S.; Neutelings, G.; Hawkins, S.; Rolando, C.; Tokarski, C. Identification of cell wall proteins in the flax (Linum usitatissimum) stem. Proteomics 2013, 13, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, B.S.; Lei, Z.; Dixon, R.A.; Sumner, L.W. Proteomics of Medicago sativa cell walls. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1709–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, C.; Goulet, C.; Goulet, M.; Michaud, D. 2-DE proteome maps for the leaf apoplast of Nicotiana benthamiana. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2336–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Dani, V.; Simon, W.J.; Duranti, M.; Croy, R.R. Changes in the tobacco leaf apoplast proteome in response to salt stress. Proteomics 2005, 5, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy, M.; Alves, G.; Vertommen, D.; Ma, J.; Boutry, M.; Navarre, C. Identification of peptidases in Nicotiana tabacum leaf intercellular fluid. Proteomics 2008, 8, 2285–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, D.; Whitelegge, J.; Bindschedler, L.; Rayon, C.; Boudet, A.; Rossignol, M.; Borderies, G.; Bolwell, G. The cell wall and secretory proteome of a tobacco cell line synthesising secondary wall. Proteomics 2009, 9, 2355–2372. [Google Scholar]
- Dafoe, N.; Constabel, P. Proteomic analysis of hybrid poplar xylem sap. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeats, T.; Howe, K.; Matas, A.; Buda, G.; Thannhauser, T.; Rose, J. Mining the surface proteome of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit for proteins associated with cuticle biogenesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3759–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Pagano, M.; Daleo, G.; Guevara, M. Hydrophobic proteins secreted into the apoplast may contribute to resistance agaisnt Phytophtora infestans in potato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 60, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Chisholm, K.; Coffin, R.; Peters, R.; Al-Mughrabi, K.; Wang-Pruski, G.; Pinto, D. Protein profiling in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) leaf tissues by differential centrifugation. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 2594–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kim, S.; Cho, W.; Rim, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Kang, K.; Park, Z.; Kim, J. Proteomics of weakly bound cell wall proteins in rice calli. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 166, 665–685. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, W.; Chen, X.; Chu, H.; Rim, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, Z.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y. The proteomic analysis of the secretome of rice calli. Physiol. Plant. 2009, 135, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-H.; Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, S.; Singh, R.; Lee, J.-E.; Cho, Y.-S.; Agrawal, G.; Rakwal, R.; Jwa, N.-S. Systematic secretome analyzes of rice leaf and seed callus suspension-cultured cells: Workflow development and establishment of high-density two-dimensional gel reference maps. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 5187–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Bokhari, S.; Dong, C.; Liu, J. Comparative proteomics analysis of the root apoplasts of rice seedlings in response to hydrogen peroxide. PLoS One 2011, 6, e16723. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Wang, Y.; Lee, K.; Park, Z.; Park, J.; Wu, J.; Kwon, S.; Lee, Y.; Agrawal, G.; Rakwal, R.; et al. In-depth insight into in vivo apoplastic secretome of rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interaction. J. Proteomics 2013, 78, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderan-Rodrigues, M.; Jamet, E.; Calderan Rodrigues Bonassi, M.; Guidetti-Gonzalez, S.; Carmanhanis Begossi, A.; Vaz Setem, L.; Franceschini, L.; Guimarães Fonseca, J.; Labate, C. Cell wall proteomics of sugarcane cell suspension cultures. Proteomics 2014, 14, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, S.; Alvarez, S.; Asirvatham, V.S.; Schachtman, D.P.; Wu, Y.; Sharp, R.E. Cell wall proteome in the maize primary root elongation zone. I. Extraction and identification of water-soluble and lightly ionically bound proteins. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 311–325. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Alvarez, S.; Marsh, E.; Lenoble, M.; Cho, I.; Sivaguru, M.; Chen, S.; Nguyen, H.; Wu, Y.; Schachtman, D.; et al. Cell wall proteome in the maize primary root elongation zone. II. Region-specific changes in water soluble and lightly ionically bound proteins under water deficit. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 1533–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.; Goodger, J.Q.; Marsh, E.L.; Chen, S.; Asirvatham, V.S.; Schachtman, D.P. Characterization of the maize xylem sap proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamet, E.; Roujol, D.; San Clemente, H.; Irshad, M.; Soubigou-Taconnat, L.; Renou, J.-P.; Pont-Lezica, R. Cell wall biogenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana elongating cells: Transcriptomics complements proteomics. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, e505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamet, E.; Boudart, G.; Borderies, G.; Charmont, S.; Lafitte, C.; Rossignol, M.; Canut, H.; Pont-Lezica, R. Isolation of plant cell wall proteins. In Sample Preparation and Fractionation for 2-D PAGE/Proteomics; Posch, A., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jamet, E.; Canut, H.; Boudart, G.; Pont-Lezica, R. Cell wall proteins: A new insight through proteomics. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.K.C.; Lee, S.-J. Straying off the highway: Trafficking of secreted plant proteins and complexity in the plant cell wall proteome. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 153, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Lobo, A.; Roujol, D.; Zuñiga-Sánchez, E.; Albenne, C.; Piñero, D.; Gamboa de Buen, A.; Jametb, E. The highly conserved spermatophyte cell wall DUF642 protein family: Phylogeny and first evidence of interaction with cell wall polysaccharides in vitro. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 63, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaner, N.; Lin, M.; McKeown, M.; Steinbach, P.; Hazelwood, K.; Davidson, M.; Tsien, R.Y. Improving the photostability of bright monomeric orange and red fluorescent proteins. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showalter, A.; Keppler, B.; Lichtenberg, J.; Gu, D.; Welch, L. A bioinformatics approach to the identification, classification, and analysis of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 485–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, Q.; Cannon, M.C. The cell wall hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein RSH is essential for normal embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, S.; Ricardi, M.; Dorosz, J.; Fernandez, P.; Nadra, A.; Pol-Fachin, L.; Egelund, J.; Gille, S.; Harholt, J.; Ciancia, M.; et al. O-Glycosylated cell wall proteins are essential in root hair growth. Science 2011, 332, 1401–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, D.; Northcote, D. Hydroxyproline in primary cell walls of higher plants. Nature 1960, 188, 665–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, D.; Kieliszewski, M.; Chen, Y.; Cannon, M. Role of the extensin superfamily in primary cell wall architecture. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.; Sadler, I.; Fry, S. Pulcherosine, an oxidatively coupled trimer of tyrosine in plant cell walls: Its role in cross-link formation. Phytochemistry 1998, 47, 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, M.; Terneus, K.; Hall, Q.; Tan, L.; Wang, Y.; Wegenhart, B.; Chen, L.; Lamport, D.; Chen, Y.; Kieliszewski, M. Self-assembly of the plant cell wall requires an extensin scaffold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2226–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabelrauch, L.S.; Kieliszewski, M.J.; Upham, B.L.; Alizedeh, H.; Lamport, D.T.A. Isolation of pI 4.6 extensin peroxidase from tomato cell suspension cultures and identification of Val-Tyr-Lys as putative intermolecular cross-link site. Plant J. 1996, 9, 477–489. [Google Scholar]
- Stafstrom, J.P.; Staehelin, L.A. The role of carbohydrate in maintaining extensin in an extended conformation. Plant Physiol. 1986, 81, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Y.; Behrens, B.X.; West, P.R.; Mort, A.J. Solubilization and partial characterization of extensin fragments from cell walls of cotton suspension-cultures, evidence for a covalent cross-link between extensin and pectin. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez, A.; Fishman, M.; Fortis, L.; Cooke, P.; Hotchkiss, A.J. Identification of extensin protein associated with sugar beet pectin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10951–10958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringli, C. The hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein domain of the Arabidopsis LRX1 requires Tyr for function but not for insolubilization in the cell wall. Plant J. 2010, 63, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassab, G.I. Plant cell wall proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 281–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, K.; Schmidt, A.; Marcus, A. Characterization of two soybean repetitive proline-rich proteins and a cognate cDNA from germinated axes. Plant Cell 1989, 1, 945–952. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, D.J.; Kjellbom, P.; Lamb, C.J. Elicitor-induced and wound induced oxidative cross-linking of a proline rich plant cell wall protein: a novel, rapid defense response. Cell 1992, 70, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, L.F.; Tenhaken, R.; Lamb, C. Function of oxidative cross linking of cell wall structural proteins in plant disease resistance. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Frueauf, J.; Dolata, M.; Leykam, J.; Lloyd, E.; Gonzales, M.; VandenBosch, K.; Kieliszewski, M. Peptides isolated from cell walls of Medicago truncatula nodules and uninfected root. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringli, C.; Keller, B.; Ryser, U. Glycine-rich proteins as structural components of plant cell walls. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1430–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangeon, A.; Junqueira, R.; Sachetto-Martins, G. Functional diversity of the plant glycine-rich proteins superfamily. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringli, C.; Hauf, G.; Keller, B. Hydrophobic interactions of the structural protein GRP1.8 in the cell wall of protoxylem elements. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Showalter, A.; Egelund, J.; Hernandez-Sanchez, A.; Doblin, M.; Bacic, A. Arabinogalactan-proteins and the research challenges for these enigmatic plant cell surface proteoglycans. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, e140. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Eberhard, S.; Pattathil, S.; Warder, C.; Glushka, J.; Yuan, C.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Avci, U.; Miller, J.; et al. An Arabidopsis cell wall proteoglycan consists of pectin and arabinoxylan covalently linked to an arabinogalactan protein. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, D.T.A.; Kieliszewski, M.J.; Showalter, A.M. Salt stress upregulates periplasmic arabinogalactan proteins: using salt stress to analyze AGP function. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, D. Life behind cell walls: Paradigm lost, paradigm regained. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1363–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Clemente, H.; Pont-Lezica, R.; Jamet, E. Bioinformatics as a tool for assessing the quality of sub-cellular proteomic strategies and inferring functions of proteins: Plant cell wall proteomics as a test case. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2009, 3, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Albenne, C.; Canut, H.; Hoffmann, L.; Jamet, E. Plant Cell Wall Proteins: A Large Body of Data, but What about Runaways? Proteomes 2014, 2, 224-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes2020224
Albenne C, Canut H, Hoffmann L, Jamet E. Plant Cell Wall Proteins: A Large Body of Data, but What about Runaways? Proteomes. 2014; 2(2):224-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes2020224
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbenne, Cécile, Hervé Canut, Laurent Hoffmann, and Elisabeth Jamet. 2014. "Plant Cell Wall Proteins: A Large Body of Data, but What about Runaways?" Proteomes 2, no. 2: 224-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes2020224
APA StyleAlbenne, C., Canut, H., Hoffmann, L., & Jamet, E. (2014). Plant Cell Wall Proteins: A Large Body of Data, but What about Runaways? Proteomes, 2(2), 224-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes2020224




