Twistor Interpretation of Harmonic Spheres and Yang–Mills Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Harmonic Spheres in Kähler Manifolds
2.1. Complex Structures and Kähler Manifolds
2.2. Harmonic Spheres in Kähler Manifolds
2.3. Harmonicity Conditions
3. Twistor Construction of Harmonic Maps
3.1. Penrose Twistor Program
3.2. Hopf Bundle
3.3. Atiyah–Hitchin–Singer Construction
3.4. Harmonic Spheres in Riemannian Manifolds
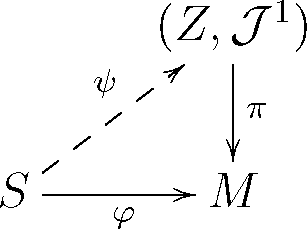
3.5. Twistor Bundles over Riemannian Manifolds
4. Harmonic Spheres in Projective Spaces
4.1. Explicit Construction of Harmonic Spheres in ℙn

4.2. Interpretation in Terms of Flags

5. Harmonic Spheres in Grassmann Manifolds
5.1. Flag Manifolds
5.2. Flag Bundles
5.3. Twistor Construction of Harmonic Spheres in Grassmannians
6. Harmonic Spheres in the Hilbert–Schmidt Grassmannian
6.1. Hilbert–Schmidt Grassmannian
6.2. Harmonic Spheres in Hilbert–Schmidt Grassmannian
- the projection pr+ : Win → H+ is a Fredholm operator of index rk, while the projection pr− : Win → H− is a Hilbert–Schmidt operator;
- the projection pr− : Wout → H− is a Fredholm operator of index rl, while the projection pr+ : Wout → H+ is a Hilbert–Schmidt operator;
- Ei with i = 1, …, k − 1, k + 1, …, l − 1, l + 1, …, m are ri-dimensional vector subspaces in H;
- all subspaces Ei with i = 1, …, m are pairwise orthogonal, and their direct sum is equal to H: E1 ⊕…⊕ Em = H.
7. Harmonic Maps into Loop Spaces
7.1. Loop Spaces
7.2. Harmonic Spheres in Loop Spaces
8. Yang–Mills Fields and Instantons
8.1. Yang–Mills Equations
8.2. Yang–Mills Moduli Spaces
8.3. Twistor Description of Yang–Mills Fields
9. Atiyah–Donaldson Construction and Harmonic Spheres Conjecture
9.1. Atiyah–Donaldson Theorem
9.2. Harmonic Spheres Conjecture
9.3. Twistor Version
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sergeev, A.G. Harmonic Maps; SEC Lecture Courses, 10; Steklov Math. Inst.: Moscow, Russia, 2008; In Russian. [Google Scholar]
- Beloshapka, I.; Sergeev, A. Harmonic spheres in the Hilbert–Schmidt Grassmannian. Am. Math. Soc. Transl. 2014, 234, 13–31. [Google Scholar]
- Atiyah, M.F.; Ward, R.S. Instantons and algebraic geometry. Commun. Math. Phys. 1977, 55, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Atiayh, M.F.; Drinfeld, V.G.; Hitchin, N.J.; Manin, Y.I. Construction of instantons. Phys. Lett. 1978, 65, 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- Manin, Y.I. Gauge Field Theory and Complex Geometry; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, E. An interpretation of classical Yang–Mills fields. Phys. Lett. 1978, 78, 394–398. [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg, J.; Yasskin, P.B.; Green, P.S. Non-self-dual gauge fields. Phys. Lett. 1978, 78, 464–468. [Google Scholar]
- Atiayh, M.F. Instantons in two and four dimensions. Commun. Math. Phys. 1984, 93, 437–451. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, S.K. Instantons and geometric invariant theory. Commun. Math. Phys. 1984, 93, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeev, A.G. Harmonic spheres conjecture. Theor. Math. Phys. 2012, 164, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeev, A.G. Harmonic spheres and Yang-Mills fields, Proceedings of the Conference on Geometry, Integrability and Optimization; Avangard Prima: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2013; pp. 1–23.
- Atiyah, M.F.; Hitchin, N.J.; Singer, I.M. Self-Duality in Four-Dimensional Riemannian Geometry. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. 1978, 362, 425–461. [Google Scholar]
- Atiyah, M.F. Geometry of Yang–Mills Fields; Scuola Normale Superiore: Pisa, Italy, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Eells, J.; Salamon, S. Twistorial constructions of harmonic maps of surfaces into four-manifolds. Ann. Sc. Norm. Super. Pisa. 1985, 12, 589–640. [Google Scholar]
- Rawnsley, J.H. F-structures, f-twistor spaces and harmonic maps. In Lecture Notes Math; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1985; Volume 1164, pp. 84–159. [Google Scholar]
- Eells, J.; Wood, J.C. Harmonic maps from surfaces to complex projective spaces. Adv. Math. 1983, 49, 217–263. [Google Scholar]
- Borel, A.; Hirzebruch, F. Characteristic classes and homogeneous spaces I. Am. J. Math. 1958, 80, 458–538. [Google Scholar]
- Burstall, F.; Salamon, S. Tournaments, flags and harmonic maps. Math. Ann. 1987, 277, 249–265. [Google Scholar]
- Burstall, F. A twistor description of harmonic maps of a 2-sphere into a Grassmannian. Math. Ann. 1986, 274, 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pressley, A.; Segal, G. Loop Groups; Clarendon Press: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeev, A.G. Kähler Geometry of Loop Spaces; Moscow Centre for Continuous Math. Education: Moscow, Russia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bor, G.; Montgomery, R. SO(3) invariant Yang–Mills fields which are not self-dual; UC Berkeley: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, T.H. Non-minimal Yang–Mills fields and dynamics. Invent. Math. 1992, 107, 397–420. [Google Scholar]
- Sadun, L.; Segert, J. Non-self-dual Yang–Mills connections with non-zero Chern number. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1991, 24, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Sibner, L.M.; Sibner, R.J.; Uhlenbeck, K. Solutions to Yang–Mills equations that are not self-dual. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8610–8613. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, T.; Habermann, L. Yang–Mills equations on the two-dimensional sphere. Commun. Math. Phys. 1985, 100, 231–243. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sergeev, A. Twistor Interpretation of Harmonic Spheres and Yang–Mills Fields. Mathematics 2015, 3, 47-75. https://doi.org/10.3390/math3010047
Sergeev A. Twistor Interpretation of Harmonic Spheres and Yang–Mills Fields. Mathematics. 2015; 3(1):47-75. https://doi.org/10.3390/math3010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleSergeev, Armen. 2015. "Twistor Interpretation of Harmonic Spheres and Yang–Mills Fields" Mathematics 3, no. 1: 47-75. https://doi.org/10.3390/math3010047
APA StyleSergeev, A. (2015). Twistor Interpretation of Harmonic Spheres and Yang–Mills Fields. Mathematics, 3(1), 47-75. https://doi.org/10.3390/math3010047




