Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Like Protein in Human Wound Tissue and Its Biological Functionality in Human Keratinocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
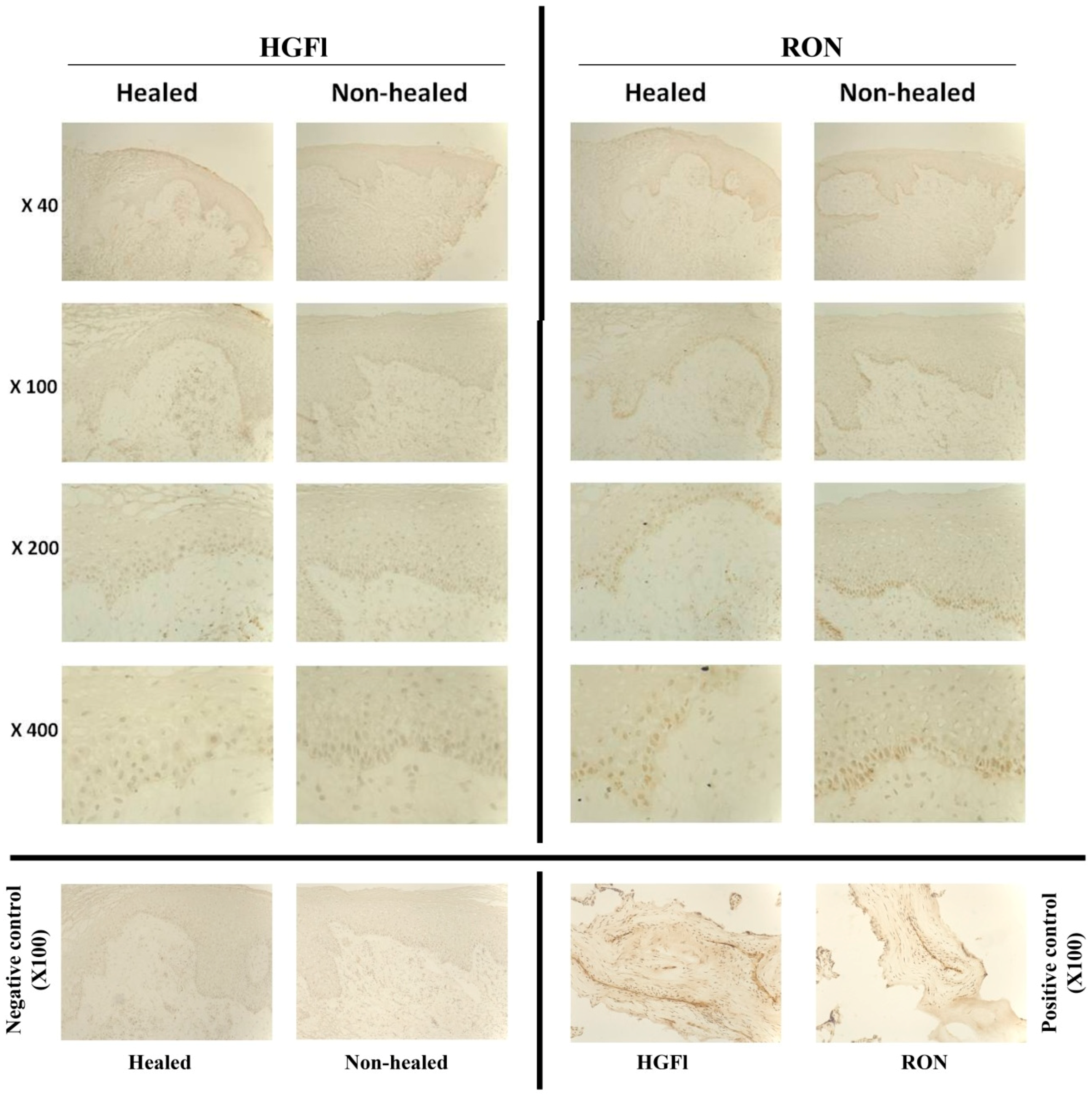
2.1. Expression Profile of HGFl/RON in Clinical Wound Samples
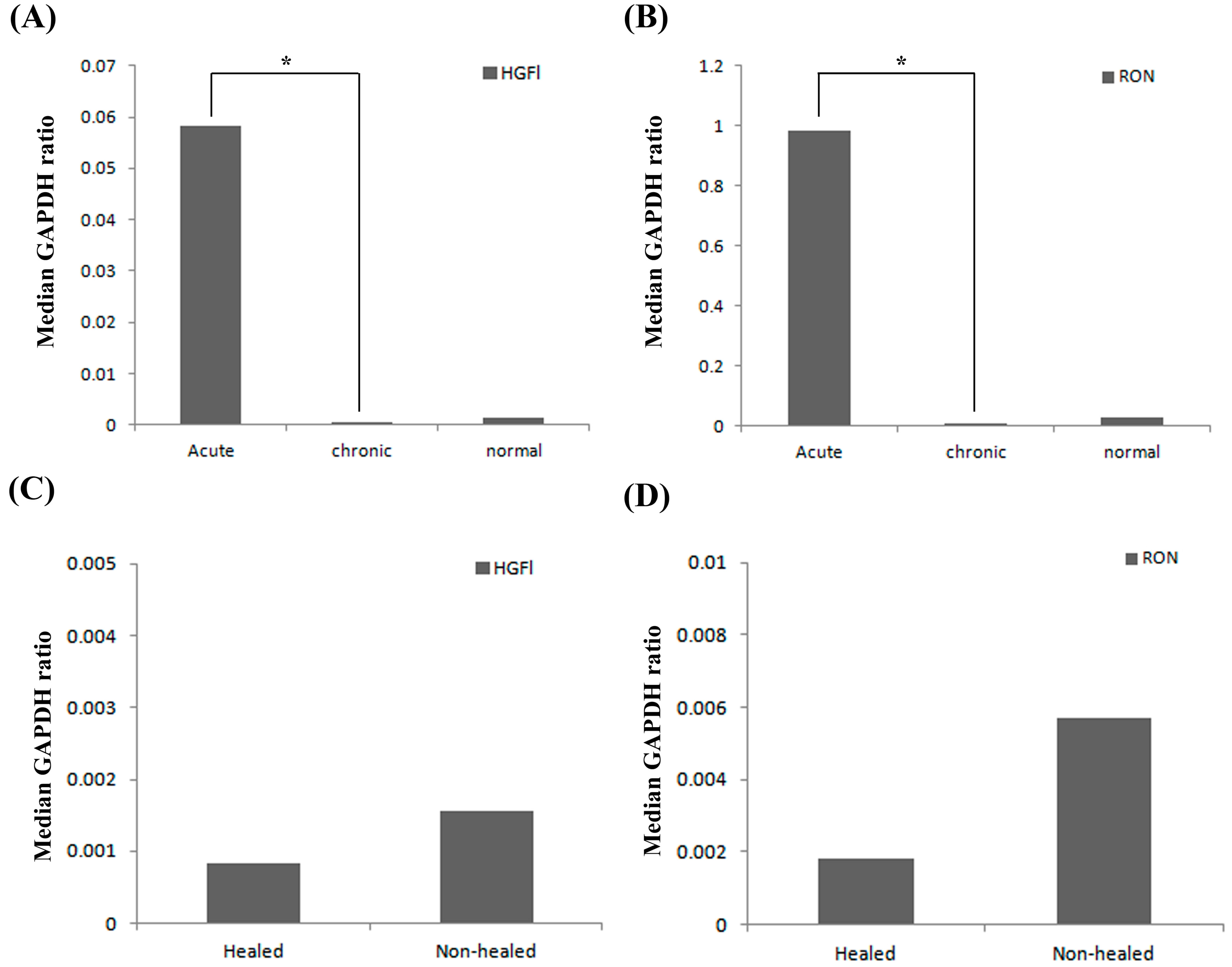
2.2. Expression Pattern of HGFl/RON in Human Keratinocytes and Impact on Cell Growth

2.3. HGFl Impacts on HaCaT Cell Migration
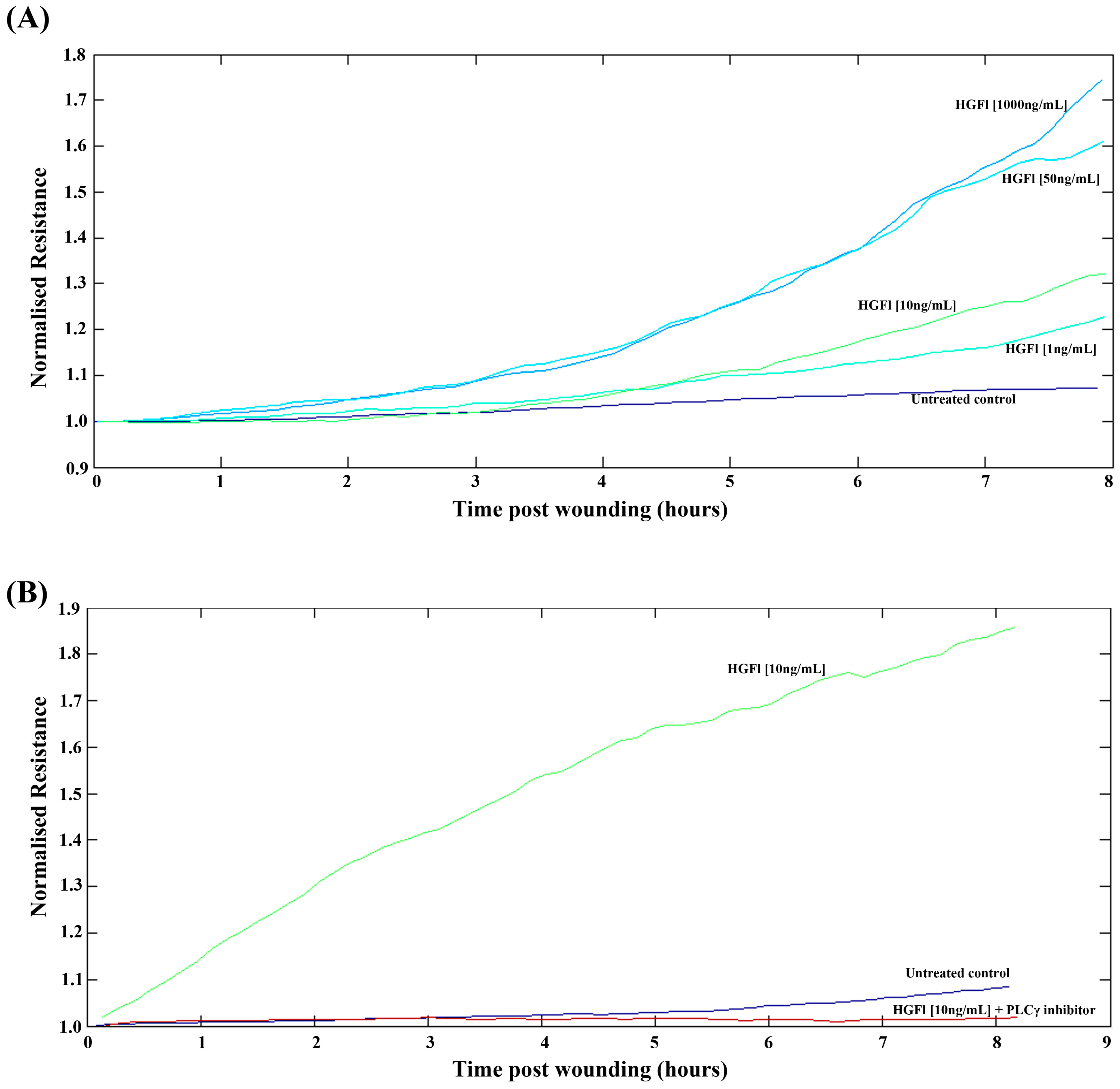
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Wound Edge Biopsies
4.2. Materials for Cell Culture
4.3. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and Quantitative RT-PCR
| Primer | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| HGFl | AGGTGCAGTTTGAGAAGTGT | CTGTGTCATTACCCGTACCT |
| RON | CATCCACCCAGTGCCAAC | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACACCACACAGTCAGCCACAG |
| cMET | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACAGAGCCAAAGTCCTTTCAT | ATCGAATGCAATGGATGAT |
| HGF | TACTGCAGACCAATGTGCTA | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACAGCATTGTTTTCTCGCTTTAT |
| PLCγ | AGAACGACATCAGCAACTCT | GCATATGAGTTGGGTTCATT |
| GAPDH (PCR) | AGCTTGTCATCAATGGAAAT | CTTCACCACCTTCTTGATGT |
| HGFl | GACCAGGCGCCATCAATC | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACACTTGGAACGCCGCTGATC |
| GAPDH (Q-PCR) | CTGAGTACGTCGTGGAGTC | ACTGAACCTGACCGTACACAGAGATGATGACCCTTTTG |
4.4. Immunohistochemical Staining of Wound Tissue
4.5. In Vitro Growth Assay
4.6. Electric Cell–Substrate Impedance Sensing Analysis of Cellular Migration
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baum, C.L.; Arpey, C.J. Normal cutaneous wound healing: Clinical correlation with cellular and molecular events. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 674–686, discussion 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, K.G.; Morris, H.L.; Patel, G.K. Science, medicine and the future: Healing chronic wounds. BMJ 2002, 324, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posnett, J.; Gottrup, F.; Lundgren, H.; Saal, G. The resource impact of wounds on health-care providers in europe. J. Wound Care 2009, 18, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosanquet, D.C.; Ye, L.; Harding, K.G.; Jiang, W.G. Expressed in high metastatic cells (ehm2) is a positive regulator of keratinocyte adhesion and motility: The implication for wound healing. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 71, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.G.; Ye, L.; Patel, G.; Harding, K.G. Expression of waves, the wasp (wiskott-aldrich syndrome protein) family of verprolin homologous proteins in human wound tissues and the biological influence on human keratinocytes. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, A.J.; Jiang, D.G.; Jiang, W.G.; Harding, K.G.; Patel, G.K. Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule impacts on clinical wound healing and inhibits hacat migration. Int. Wound J. 2011, 8, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, J.A.; Han, S.; Danton, M.J.; Degen, S.J. Are hepatocyte growth factor-like protein and macrophage stimulating protein the same protein? Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeel, A.; Yoshimura, T.; Showalter, S.D.; Tanaka, S.; Appella, E.; Leonard, E.J. Macrophage stimulating protein: Purification, partial amino acid sequence, and cellular activity. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 173, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, E.J. Biological aspects of macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) and its receptor. Ciba Found. Symp. 1997, 212, 183–191, discussion 192–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.B.; Ray, M.; Lutz, M.; Sharda, D.; Xu, J.; Hankey, P.A. The RON receptor tyrosine kinase regulates ifn-gamma production and responses in innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, J.A.; Laney, D.W., Jr.; Degen, S.J. Increased expression of mrna for hepatocyte growth factor-like protein during liver regeneration and inflammation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, C.G.; Smith, D.I.; Shridhar, V.; Wang, M.H.; Emanuel, R.L.; Patidar, K.; Graham, S.A.; Zhang, F.; Hatch, V.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; et al. Differential screening of a human chromosome 3 library identifies hepatocyte growth factor-like/macrophage-stimulating protein and its receptor in injured lung. Possible implications for neuroendocrine cell survival. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2979–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Paddock, G.V. Expression of the hepatocyte growth factor-like protein gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma and interleukin-6-induced increased expression in hepatoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1449, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretschmann, K.L.; Eyob, H.; Buys, S.S.; Welm, A.L. The macrophage stimulating protein/RON pathway as a potential therapeutic target to impede multiple mechanisms involved in breast cancer progression. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.H.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.Q. Oncogenic and invasive potentials of human macrophage-stimulating protein receptor, the RON receptor tyrosine kinase. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanteti, R.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Catenacci, D.; Tan, Y.H.; E.L.-Hashani, E.; Cervantes, G.; Husain, A.N.; Tretiakova, M.; Vokes, E.E.; Huet, H.; et al. Differential expression of RON in small and non-small cell lung cancers. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012, 51, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.T.; Babicky, M.; Jaquish, D.; French, R.; Marayuma, K.; Mose, E.; Niessen, S.; Hoover, H.; Shields, D.; Cheresh, D.; et al. The RON-receptor regulates pancreatic cancer cell migration through phosphorylation-dependent breakdown of the hemidesmosome. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauder, S.E.; Santell, L.; Mai, E.; Wright, L.Y.; Luis, E.; N’Diaye, E.N.; Lutman, J.; Ratti, N.; Sa, S.M.; Maun, H.R.; et al. Functional consequences of the macrophage stimulating protein 689c inflammatory bowel disease risk allele. PLoS One 2013, 8, e83958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanney, L.B.; Skeel, A.; Luan, J.; Polis, S.; Richmond, A.; Wang, M.H.; Leonard, E.J. Proteolytic cleavage and activation of pro-macrophage-stimulating protein and upregulation of its receptor in tissue injury. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 111, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowin, A.J.; Kallincos, N.; Hatzirodos, N.; Robertson, J.G.; Pickering, K.J.; Couper, J.; Belford, D.A. Hepatocyte growth factor and macrophage-stimulating protein are upregulated during excisional wound repair in rats. Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 306, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, J.A.; Carrick, T.L.; Degen, J.L.; Witte, D.; Degen, S.J. Biological effects of targeted inactivation of hepatocyte growth factor-like protein in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.H.; Dlugosz, A.A.; Sun, Y.; Suda, T.; Skeel, A.; Leonard, E.J. Macrophage-stimulating protein induces proliferation and migration of murine keratinocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 226, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.H.; Montero-Julian, F.A.; Dauny, I.; Leonard, E.J. Requirement of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase for epithelial cell migration activated by human macrophage stimulating protein. Oncogene 1996, 13, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santoro, M.M.; Gaudino, G.; Marchisio, P.C. The MSP receptor regulates alpha6beta4 and alpha3beta1 integrins via 14-3-3 proteins in keratinocyte migration. Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, T.; Yuhki, N.; Wang, M.H.; Skeel, A.; Leonard, E.J. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of human macrophage stimulating protein (MSP, mst1) confirms MSP as a member of the family of kringle proteins and locates the MSP gene on chromosome 3. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 15461–15468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Stuart, L.A.; Degen, S.J. Characterization of the dnf15s2 locus on human chromosome 3: Identification of a gene coding for four kringle domains with homology to hepatocyte growth factor. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 9768–9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwama, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Suda, T. STK/RON receptor tyrosine kinase mediates both apoptotic and growth signals via the multifunctional docking site conserved among the hgf receptor family. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5866–5875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Xie, M.H.; Yang, B.; Mahapatra, K.; Liu, J.; Marsters, S.; Bodepudi, S.; Ashkenazi, A. Distinct involvement of the gab1 and grb2 adaptor proteins in signal transduction by the related receptor tyrosine kinases RON and met. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 32762–32774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronsin, C.; Muscatelli, F.; Mattei, M.G.; Breathnach, R. A novel putative receptor protein tyrosine kinase of the met family. Oncogene 1993, 8, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.P.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, M.H. MSP-RON signalling in cancer: Pathogenesis and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follenzi, A.; Bakovic, S.; Gual, P.; Stella, M.C.; Longati, P.; Comoglio, P.M. Cross-talk between the proto-oncogenes met and RON. Oncogene 2000, 19, 3041–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuti, S.; Lazzari, L.; Arnesano, A.; Li Chiavi, G.; Gentile, A.; Comoglio, P.M. RON kinase transphosphorylation sustains met oncogene addiction. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Orikawa, H.; Baba, T.; Fukushima, T.; Kataoka, H. Hepatocyte growth factor activator is a serum activator of single-chain precursor macrophage-stimulating protein. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 3481–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, M.H. Requirement of both tyrosine residues 1330 and 1337 in the c-terminal tail of the RON receptor tyrosine kinase for epithelial cell scattering and migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 267, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, K.; Price, P.; Harding, K.G.; Jiang, W.G. The molecular and clinical impact of hepatocyte growth factor, its receptor, activators, and inhibitors in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2006, 14, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, K.; Ruge, F.; Price, P.; Harding, K.G.; Jiang, W.G. Hepatocyte growth factor regulation: An integral part of why wounds become chronic. Wound Repair Regen. 2007, 15, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosanquet, D.C.; Harding, K.G.; Ruge, F.; Sanders, A.J.; Jiang, W.G. Expression of il-24 and il-24 receptors in human wound tissues and the biological implications of il-24 on keratinocytes. Wound Repair Regen. 2012, 20, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzio, R.; Piantelli, M.; Falasca, M. Role of phospholipase c in cell invasion and metastasis. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2013, 53, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, G.; Martin, T.A.; Ye, L.; Lewis-Russell, J.M.; Mason, M.D.; Jiang, W.G. Phospholipase-c gamma-1 (plcgamma-1) is critical in hepatocyte growth factor induced in vitro invasion and migration without affecting the growth of prostate cancer cells. Urol. Oncol. 2008, 26, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.G.; Hiscox, S.; Hallett, M.B.; Scott, C.; Horrobin, D.F.; Puntis, M.C. Inhibition of hepatocyte growth factor-induced motility and in vitro invasion of human colon cancer cells by gamma-linolenic acid. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 71, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, C.; Watkins, G.; Mansel, R.E.; Jiang, W.G. The hepatocyte growth factor regulatory factors in human breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, J.; Keese, C.R.; Giaever, I. Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) as a noninvasive means to monitor the kinetics of cell spreading to artificial surfaces. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 259, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glasbey, J.C.; Sanders, A.J.; Bosanquet, D.C.; Ruge, F.; Harding, K.G.; Jiang, W.G. Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Like Protein in Human Wound Tissue and Its Biological Functionality in Human Keratinocytes. Biomedicines 2015, 3, 110-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3010110
Glasbey JC, Sanders AJ, Bosanquet DC, Ruge F, Harding KG, Jiang WG. Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Like Protein in Human Wound Tissue and Its Biological Functionality in Human Keratinocytes. Biomedicines. 2015; 3(1):110-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3010110
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlasbey, James C., Andrew J. Sanders, David C. Bosanquet, Fiona Ruge, Keith G. Harding, and Wen G. Jiang. 2015. "Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Like Protein in Human Wound Tissue and Its Biological Functionality in Human Keratinocytes" Biomedicines 3, no. 1: 110-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3010110
APA StyleGlasbey, J. C., Sanders, A. J., Bosanquet, D. C., Ruge, F., Harding, K. G., & Jiang, W. G. (2015). Expression of Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Like Protein in Human Wound Tissue and Its Biological Functionality in Human Keratinocytes. Biomedicines, 3(1), 110-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines3010110





