Optical Measuring Methods for the Investigation of High-Pressure Homogenisation
Abstract
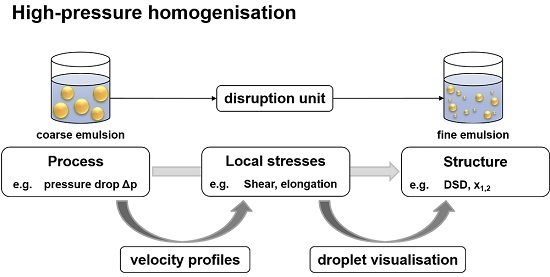
:1. Motivation
2. Background
2.1. Why Do We Need Detailed Information on the HPH Process?
2.2. Optical Measurment Methods for the Characterisation of the HPH Process
2.2.1. High-Speed Image Processing (HSIP)
2.2.2. Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV)
2.2.3. Micro Particle Image Velocimetry (µPIV)
2.2.4. Visualisation of Cavitation
3. Optical Methods for Investigating High-Pressure Homogenisation
3.1. Visualisation of Droplet Deformation and Break-up Using High-Speed Image Processing (HSIP)
3.2. Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) Mesurements to Investigate Velocity Profiles and Droplet Break-up
3.3. Micro-PIV Mesurements
3.4. Visualisation of Cavitation during the HPH Process
4. Summary
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HPH | High-pressure homogenisation |
| DSD | Droplet size distribution |
| HSIP | High-speed image processing |
| PIV | Particle image velocimetry |
| TI | Turbulent inertial |
| TV | Turbulent viscous |
| SCL | Sono-chemiluminescence |
| SG | Shadowgraphy |
| HPSM | High-pressure microsystems |
References
- Clausse, M.; Becher, P. Encyclopedia of Emulsion Technology, Volume 1; Becher, P., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA; Basel, Switzerland, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Karbstein, H. Untersuchungen zum Herstellen und Stabilisieren von Öl-in-Wasser-Emulsionen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Karlsruhe, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, C.; Robins, M.M. Homogenisation of oil-in-water emulsions: Effect of pressure and composition on droplet size distribution. Trans. IChemE 1991, 69, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Phipps, L.W. Homogenizing valve design and its influence on milk fat globule dispersion II. High rate of flow. J. Dairy Res. 1982, 49, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstra, P.; Smulders, P.E.A. Emulsion Formation. In Modern Aspects of Emulsion Science; Binks, B.P., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 1998; pp. 56–99. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.J. Method of Forming a Microemulsion; Biotechnology Development Corporation: Newton, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.J.; Lagace, A.P. Apparatus for Forming Emulsions; Biotechnology Development Corporation: Newton Upper Falls, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Klinksiek, B.; Schleenstein, D.; Hovestadt, W.; Vom Felde, M. Verstellbarer Strahldispergator zur Herstellung Wässriger 2-Komponeten-Polyurethanloack-Emulsionen; Bayer Ag: Leverkusen, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, F.; Köhler, K.; Schubert, H.; Schuchmann, H.P. Herstellen von Emulsionen in einfachen und modifizierten Lochblenden: Einfluss der Geometrie auf die Effizienz der Zerkleinerung und Folgen für die Maßstabsvergrößerung. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2008, 80, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, J.L. Formulation Considerations in Emulsion Preparations and Stability. In Food Emulsions and Foams: Theory and Practice; Wan, P.J., Barfod, N.M., Eds.; American Institute of Chemical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chanana, G.D. Particle size reduction of emulsions by formulation design II: Effect of oil and surfactant concentration. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 1995, 49, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.A. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practice and Techniques; McClements, D.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA; Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tesch, S.; Freudig, B.; Schubert, H. Production of emulsions in high-pressure homogenizers—Part I: Disruption and stabilization of droplets. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2003, 26, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumscheidt, F.D.; Mason, S.G. Particle motions in sheared suspensions. XII. Deformation and burst of fluid drops in shear and hyperbolic flow. J. Colloid Sci. 1961, 16, 238–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomotika, S. On the instability of a cylindrical thread of a viscous liquid surrounded by another viscous fluid. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1935, 150, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, B.J.; Leal, L.G. An experimental investigation of drop deformation and breakup in steady, two-dimensional linear flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 167, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floury, J.; Bellettre, J.; Legrand, J.; Desrumaux, A. Analysis of a new type of high pressure homogeniser. A study of the flow pattern. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesch, S.; Schubert, H. Droplet deformation and disruption during the emulsification in a high-pressure homogenizer with an orifice valve. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2001, 73, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiber, A.; Kiefer, P. Kavitation und Turbulenz als Zerkleinerungsmechanismen bei der Homogenisation von O/W-Emulsionen. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1976, 48, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, K.H. High-pressure Homogenization. Part I. Liquid-liquid dispersion in turbulence fields of high energy density. J. Food Eng. 1987, 6, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudig, B.; Tesch, S.; Schubert, H. Production of emulsions in high-pressure homogenizers—Part II: Influence of cavitation on droplet breakup. Eng. Life Sci. 2003, 6, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzhals, H.A.; Reuter, H. Untersuchungen über die physikalisch-technischen Vorgänge beim Homogenisieren von Milch in Hochdruck-Homogenisiermaschinen. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1979, 51, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, M. Homogenisation von Milch und Milchkonzentraten mit einer Lavaldüse. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Budde, C.; Schaffner, D.; Walzel, P. Drop breakup in liquid-liquid dispersions at an orifice plate observed in a large-scale model. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2002, 25, 1164–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, G.; Wagner, G.; Ulrich, J. Untersuchungen zum Aufbruch von Einzeltropfen in Dispergiereinheiten zur Emulsionsherstellung. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2001, 73, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, G.E. Zur Emulsionsherstellung in Blendensystemen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Galinat, S.; Masbernat, O.; Guiraud, P.; Dalmazzone, C.; Noik, C. Drop break-up in turbulent pipe flow downstream of a restriction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 6511–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innings, F.; Tragardh, C. Visualization of the drop deformation and break-up process in a high pressure homogenizer. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2005, 28, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innings, F.; Tragardh, C. Analysis of the flow field in a high-pressure homogenizer. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2007, 32, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innings, F.; Fuchs, L.; Tragardh, C. Theoretical and experimental analyses of drop deformation and break-up in a scale model of a high-pressure homogenizer. J. Food Eng. 2011, 103, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A.; Fuchs, L.; Innings, F.; Revstedt, J.; Tragardh, C.; Bergenstahl, B. High resolution experimental measurement of turbulent flow field in a high pressure homogenizer model and its implications on turbulent drop fragmentation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1790–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A.; Fuchs, L.; Innings, F.; Revstedt, J.; Trägårdh, C.; Bergenståhl, B. On flow-fields in a high pressure homogenizer and its implication on drop fragmentation. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A.; Fuchs, L.; Innings, F.; Revstedt, J.; Trägårdh, C.; Bergenståhl, B. Velocity measurements of turbulent two-phase flow in a high-pressure homogenizer model. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2013, 200, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothsch, T.; Schilcher, C.; Richter, C.; Beinert, S.; Dietzel, A.; Büttgenbach, S.; Kwade, A. High-pressure microfluidic systems (HPMS): Flow and cavitation measurements in supported silicon microsystems. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, K.; Crowther, F.E.; Cierpka, C.; Hecht, L.L.; Kähler, C.J.; Schuchmann, H.P. Investigations on the characterization of laminar and transitional flow conditions after high pressure homogenization orifices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 18, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, K.; Gepperth, S.; Koch, R.; Bauer, H.-J.; Schuchmann, H.P. On the visualization of droplet deformation and breakup during high-pressure homogenization. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2015, 19, 1139–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollhoff, R.T.; Kelemen, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Local Multiphase Flow Characterization with Micro Particle Image Velocimetry Using Refractive Index Matching. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2015, 38, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A.; Fuchs, L.; Innings, F.; Revstedt, J.; Bergenstahl, B.; Tragardh, C. Visual observations and acoustic measurements of cavitation in an experimental model of a high-pressure homogenizer. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlender, M.; Spengler, A.; Schuchmann, H.P. High-pressure emulsion formation in cylindrical coaxial orifices: Influence of cavitation induced pattern on oil drop size. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2015, 74, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlender, M.; Minke, K.; Spiegel, B.; Schuchmann, H.P. High-pressure double stage homogenization processes: Influences of plant setup on oil droplet size. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 131, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlender, M.; Minke, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Sono-chemiluminescence (SCL) in a high-pressure double stage homogenization processes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 142, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothsch, T.; Richter, C.; Beinert, S.; Schilcher, C.; Schilde, C.; Büttgenbach, S.; Kwade, A. Effect of cavitation on dispersion and emulsification process in high-pressure microsystems (HPMS). Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 144, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Danner, T. Role of surfactant type and concentration for the mean drop size during emulsification in turbulent flow. Langmuir 2004, 20, 7444–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walstra, P. Emulsions. In Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science: Soft Colloids; Lyklema, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lemenand, T.; Dupont, P.; Della Valle, D.; Peerhossaini, H. Comparative efficiency of shear, elongation and turbulent droplet breakup mechanisms: Review and application. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 2587–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Håkansson, A. Experimental methods for measuring coalescence during emulsification—A critical review. J. Food Eng. 2016, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Interfacial interactions and the stability of oil-in-water emulsions. Pure Appl. Chem. 1992, 64, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöblom, J. Emulsions and Emulsion Stability; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Vankova, N.; Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Ivanov, I.B.; Vulchev, V.D.; Danner, T. Emulsification in turbulent flow, 1. Mean and maximum drop diameters in inertial and viscous regimes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 312, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, T.; Schubert, H. Coalescence Processes in Emulsions. In Food Colloids: Fundamentals of Formulation; Dickinson, E., Miller, R., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2001; pp. 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, H.P. Dispersion phenomena in high-viscosity immiscible fluid systems and application of static mixers as dispersion devices in such systems. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1982, 14, 225–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumscheidt, F.D.; Mason, S.G. Particle motions in sheared suspensions XI. Internal circulation in fluid droplets (experimental). J. Colloid Sci. 1961, 16, 210–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhab, E.J.; Dressler, M.; Feigl, K.; Fischer, P.; Megias-Alguacil, D. Emulsion processing-from single-drop deformation to design of complex processes and products. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 2101–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erni, P.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Deformation of single emulsion drops covered with a viscoelastic adsorbed protein layer in simple shear flow. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 244104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, S.F.M.; Feigl, K.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Investigation and Visualization of Droplet Deformation and Breakup in Complex Laminar Flow Fields; International Symposium on Food Rheology & Structure: Montpellier, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Megias-Alguacil, D.; Feigl, K.; Dressler, M.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Droplet deformation under simple shear investigated by experiment, numerical simulation and modelling. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2004, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.A.; Bentley, B.J.; Leal, L.G. An experimental-study of transient effects in the breakup of viscous drops. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 173, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innings, F.; Hamberg, L.; Tragardh, C. Dynamic modelling of the deformation of a drop in a four-roll mill. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 4771–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigl, K.; Kaufmann, S.F.M.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. A numerical procedure for calculating droplet deformation in dispersing flows and experimental verification. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 58, 2351–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigl, K.; Megias-Alguacil, D.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Simulation and experiments of droplet deformation and orientation in simple shear flow with surfactants. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 3242–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, P.J.; Puel, F.; Dubbelboer, A.; Janssen, J.; Sheibat-Othman, N. Coupled population balance–CFD simulation of droplet breakup in a high pressure homogenizer. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2014, 68, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. The formation of emulsions in definable fields of flow. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1934, 146, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Über die Zerstäubung von Tropfen in einer turbulenten Strömung. In Sammelband zur Statistischen Theorie der Turbulenz: Übersetzt Abgedruckt; Goering, H., Ed.; Akademie-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1958; p. 825. [Google Scholar]
- Hinze, J.O. Fundamentals of the hydrodynamic mechanism of splitting in dispersion processes. AIChE J. 1955, 1, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.X.; Lucas, D. A literature review of theoretical models for drop and bubble breakup in turbulent dispersions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3389–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.J.D.; Halliwell, N.A. Laser speckle photography and particle image velocimetry: Photographic film noise. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, R.J. Scattering particle characteristics and their effect on pulsed laser measurements of fluid flow: Speckle velocimetry vs particle image velocimetry. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 1690–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, R.J.; Westerweel, J. Particle Image Velocimetry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, M.; Willert, C.E.; Wereley, S.T.; Kompenhans, J. Particle Image Velocimetry. A Practical Guide; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Particle Image Velocimetry. New Developments and Recent Applications; Schröder, A.; Willert, C.E. (Eds.) Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008.
- Adrian, R.J. Twenty years of particle image velocimetry. Exp. Fluids 2005, 39, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.T.; Fiedler, H.E.; Wang, J.J. Limitation and improvement of PIV. Exp. Fluids 1993, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kähler, C.J.; Scharnowski, S.; Cierpka, C. On the resolution limit of digital particle image velocimetry. Exp. Fluids 2012, 52, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kähler, C.J.; Scharnowski, S.; Cierpka, C. On the uncertainty of digital PIV and PTV near walls. Exp. Fluids 2012, 52, 1641–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H. The wide variety of possible applications of micro-thermofluid control. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2005, 1, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, J.G.; Wereley, S.T.; Meinhart, C.D.; Beebe, D.J.; Adrian, R.J. A particle image velocimetry system for microfluidics. Exp. Fluids 1998, 25, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhart, C.D.; Wereley, S.T.; Santiago, J.G. PIV measurements of a microchannel flow. Exp. Fluids 1999, 27, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsiaris, A.G.; Mathioulakis, D.S.; Tsangaris, S. Microscope PIV for velocity-field measurement of particle suspensions flowing inside glass capillaries. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielnik, M.M.; Saetran, L.R. Micro Particle Image velocimetry—An overview. Turbulence 2004, 10, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lindken, R.; Rossi, M.; Grosse, S.; Westerweel, J. Micro-Particle Image Velocimetry (microPIV): Recent developments, applications, and guidelines. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2551–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cierpka, C.; Rossi, M.; Segura, R.; Mastrangelo, F.; Kähler, C.J. A comparative analysis of the uncertainty of astigmatism-mu PTV, stereo-mu PIV, and mu PIV. Exp. Fluids 2012, 52, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, H.; Eberle, A.; Hofemeier, P. Micro-PIV for high velocity flows. In Proceedings of the 15th Int Symposium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, Lissabon, Portugal, 5–8 July 2010.
- Wereley, S.T.; Meinhart, C.D. Recent advances in micro-particle image velocimetry. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2010, 42, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settles, G.S. Schlieren and Shadowgraph Techniques. Visualizing Phenomena in Transparent Media; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann, A. Charakterisierung von Kavitationsblasenpopulationen. Ph.D. Thesis, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, A.L.; Waite, T.D. Chemiluminescence of luminol in the presence of iron (ii) and oxygen: Oxidation mechanism and implications for its analytical use. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5909–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innings, F. Drop Break-Up in High-Pressure Homogenisers. Ph.D. Thesis, Lund University, Faculty of Engineering, Lund, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wieth, L.; Kelemen, K.; Braun, S.; Koch, R.; Bauer, H.-J.; Schuchmann, H.P. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) simulation of a high-pressure homogenization process. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2016, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, K. Inline-Messung des Tropfenaufbruchs in Hochdruckblenden: Möglichkeiten und Limitierungen der µPIV. Ph.D. Thesis, Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT), Karlsruhe, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Finke, J.H.; Niemann, S.; Richter, C.; Gothsch, T.; Kwade, A.; Büttgenbach, S.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Multiple orifices in customized microsystem high-pressure emulsification: The impact of design and counter pressure on homogenization efficiency. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, C.C.; Slatter, W.L.; Powell, R.W. A Study of the Cavitation Effect in the homogenization of dairy products 1, 2. J. Dairy Sci. 1950, 33, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinig, A.R.; Middelberg, A.P. The correlation of cell disruption with homogenizer valve pressure gradient determined by computational fluid dynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 5103–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.J.; Chen, X.D. Visualization of the flow patterns in a high-pressure homogenizing valve using a CFD package. J. Food Eng. 1997, 33, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, L.W. Cavitation and separated flow in a simple homogenizing valve and their influence on the break-up of fat globules in milk. J. Dairy Res. 1974, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, L.W. Some operating characteristics of a simple homogenizing poppet valve; pressure profiles and separation: Zone of fat globule dispersion. J. Dairy Res. 1974, 41, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, K.H. High-pressure homogenization. Part II. The influence of cavitation on liquid-liquid dispersion in turbulence fields of high energy density. J. Food Eng. 1987, 6, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesch, S.; Freudig, B.; Schubert, H. Herstellen von Emulsionen in Hochdruckhomogenisatoren—Teil 1: Zerkleinern und Stabilisieren von Tropfen. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2002, 74, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, J.H.; Schur, J.; Richter, C.; Gothsch, T.; Kwade, A.; Buttgenbach, S.; Muller-Goymann, C.C. The influence of customized geometries and process parameters on nanoemulsion and solid lipid nanoparticle production in microsystems. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A. Scale-down failed—Dissimilarities between high-pressure homogenizers of different scales due to failed mechanistic matching. J. Food Eng. 2017, 195, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| First Author | Measuring Method | Disruption Unit | Scale-Up Factor | Viscosity Ratio | Reynolds Number | Homogenisation Pressure 1 | Primary Droplet Diameter | Investigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Budde [24] | HSIP | orifice | 250 2 | 0.13; 6.3 | 1570 | 0.088–0.112 bar | 3 mm | Droplet deformation |
| Kolb [25,26] | HSIP | orifice | 50 2 | 6; 11; 30 | 1000–8000 | - | 2–3 mm | Droplet deformation |
| Galinat [27] | HSIP | orifice | 5–10 2 | 0.55 | 4000–13,000 | 88–1120 Pa | 2–3 mm | Droplet deformation |
| Innings [28] | PIV | flat valve | 0.6; 2.7 3 | 70 | 3000–6000 | - | 5–50 µm; 300 -350 µm | Droplet deformation |
| Innings [29] | PIV | flat valve | 32 2 | - | 9400 | 0.003 bar | - | Flow pattern |
| Innings [30] | PIV | flat valve | 32 3 | 5.4 | 5000 | 0.65 bar | 5 µm | Droplet deformation |
| Håkansson [31] | PIV | flat valve | 32 3 | - | 27,000 | - | - | Flow pattern |
| Håkansson [32] | PIV | flat valve | 32 3 | - | ? | 30–80 bar | 230 µm 4 | Flow pattern |
| Håkansson [33] | PIV | flat valve | 32 3 | - | 2600 | - | 230 µm 4 | Flow pattern |
| Gothsch [34] | µPIV | HPMS | - | - | ≈12,000 | 100–500 bar | - | Flow pattern |
| Kelemen [35] | µPIV | orifice | 1 2 | - | 330; 1280 | 10–80 bar | - | Flow pattern |
| Kelemen [36] | µPIV | orifice | 1 2 | 2; 14 | 285; 1130 | 10–80 bar | 40 µm | Droplet deformation |
| Kollhoff [37] | µPIV | orifice | 1 2 | 26 | 500 | 10–13 bar | 37 µm | Flow pattern |
| Håkansson [38] | PIV | flat valve | 0.4 3 | - | 5500 | 100 bar | - | Cavitation |
| Schlender [39] | SG | orifice | ≈1 2 | 63 | 18,000–62,000 | 50–550 bar | ≈30 µm | Cavitation |
| Schlender [40] | SG | orifice | ≈1 2 | 63 | >20,000 | 50–250 bar | 20 µm | Cavitation |
| Schlender [41] | SCL | orifice | 1 2 | 63 | - | 50–250 bar | 20 µm | Cavitation |
| Gothsch [34,42] | µPIV | HPMS | - | 79.3 | 5590 | 100–500 bar | 396 nm | Cavitation, flow pattern |
| Measurement Technique | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| HSIP | Droplet deformations and break-ups can be investigated | Velocity profiles cannot be measured, local stresses cannot be calculated |
| PIV | Suitable for investigations in larger dimensions, spatial resolution of droplets | Accessibility for the laser sheet and the camera, time scales cannot be scaled correctly |
| µPIV | Optical accessibility only from one side necessary, dimensions are close to original disruption units | Spatial and temporal resolution limitations, small droplets cannot be visualised |
| SG | Gas bubbles can be visualised, area where cavitation takes place can be determined | Flow changes through gas bubbles cannot be resolved, impact of collapse of gas bubbles cannot be determined |
| SCL | Intensity of collapse of gas bubbles can be measured | Gas bubbles are not visualised, velocity measurements impossible |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bisten, A.; Schuchmann, H.P. Optical Measuring Methods for the Investigation of High-Pressure Homogenisation. Processes 2016, 4, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr4040041
Bisten A, Schuchmann HP. Optical Measuring Methods for the Investigation of High-Pressure Homogenisation. Processes. 2016; 4(4):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr4040041
Chicago/Turabian StyleBisten, Ariane, and Heike P. Schuchmann. 2016. "Optical Measuring Methods for the Investigation of High-Pressure Homogenisation" Processes 4, no. 4: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr4040041
APA StyleBisten, A., & Schuchmann, H. P. (2016). Optical Measuring Methods for the Investigation of High-Pressure Homogenisation. Processes, 4(4), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr4040041