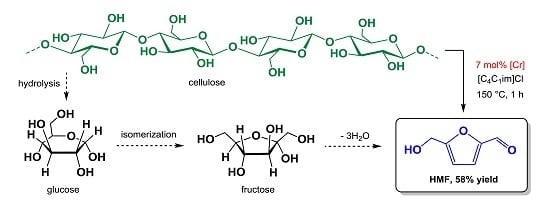
Direct Catalytic Conversion of Cellulose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Using Ionic Liquids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
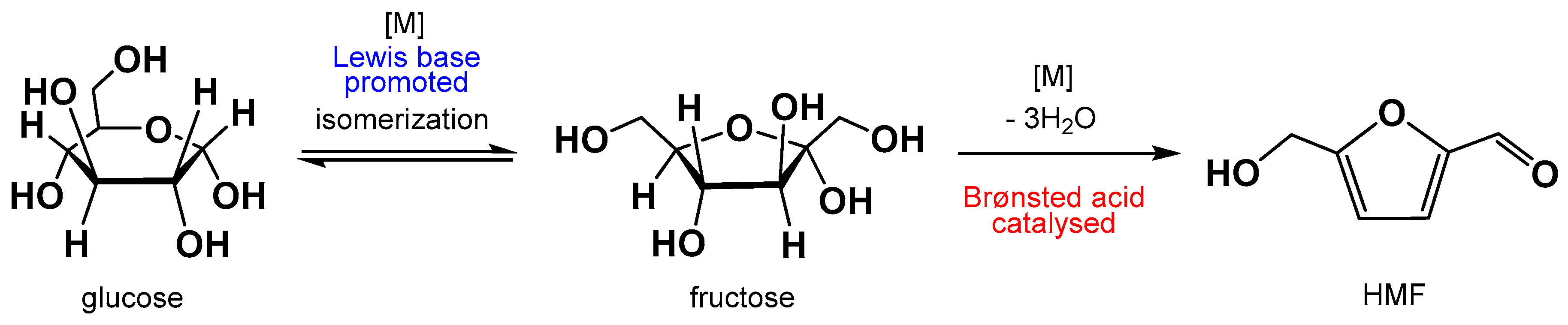
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst and Ionic Liquid Selection
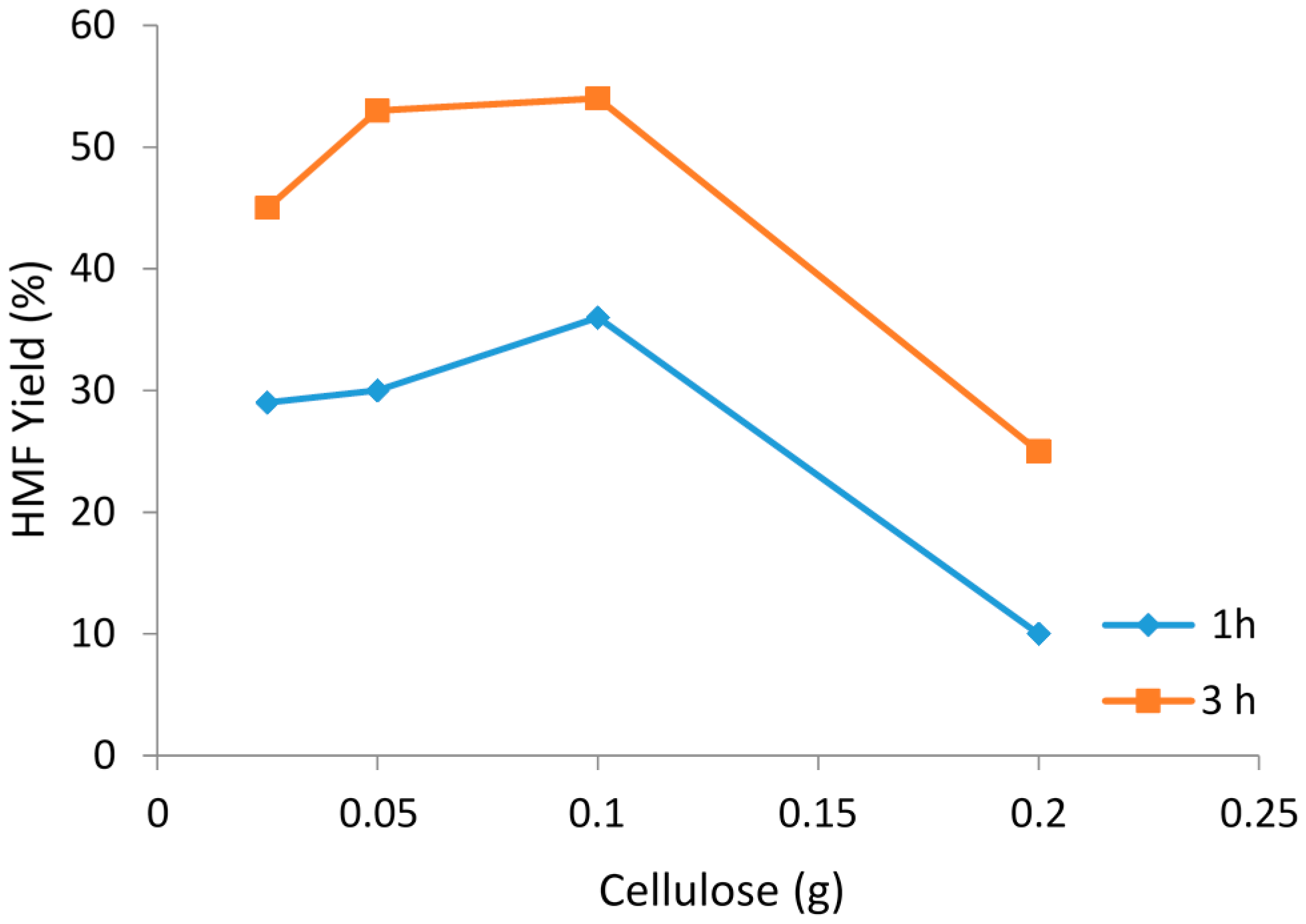
2.2. Cellulose Concentration
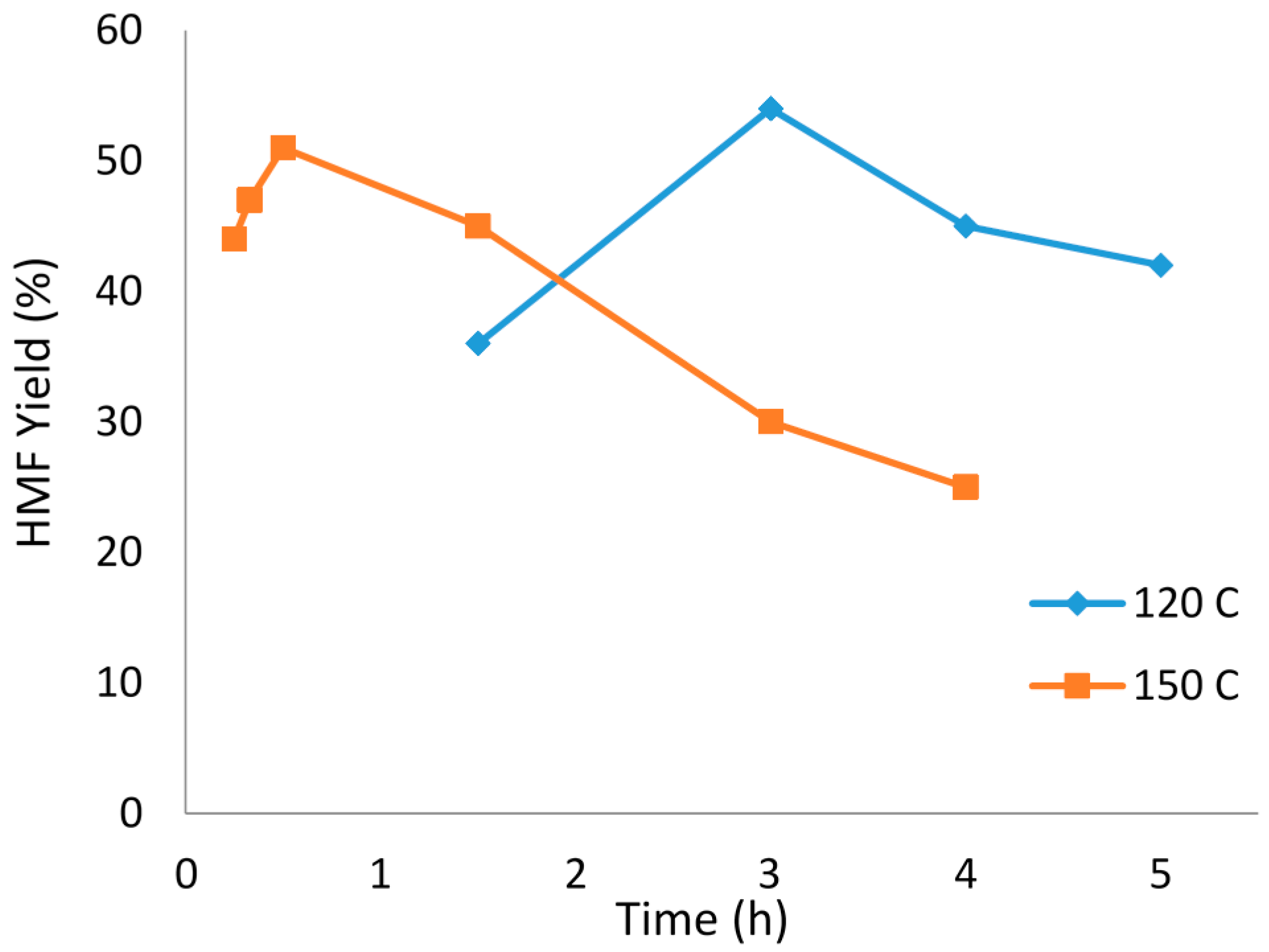
2.3. Reaction Time
2.4. Water and Catalyst Loading
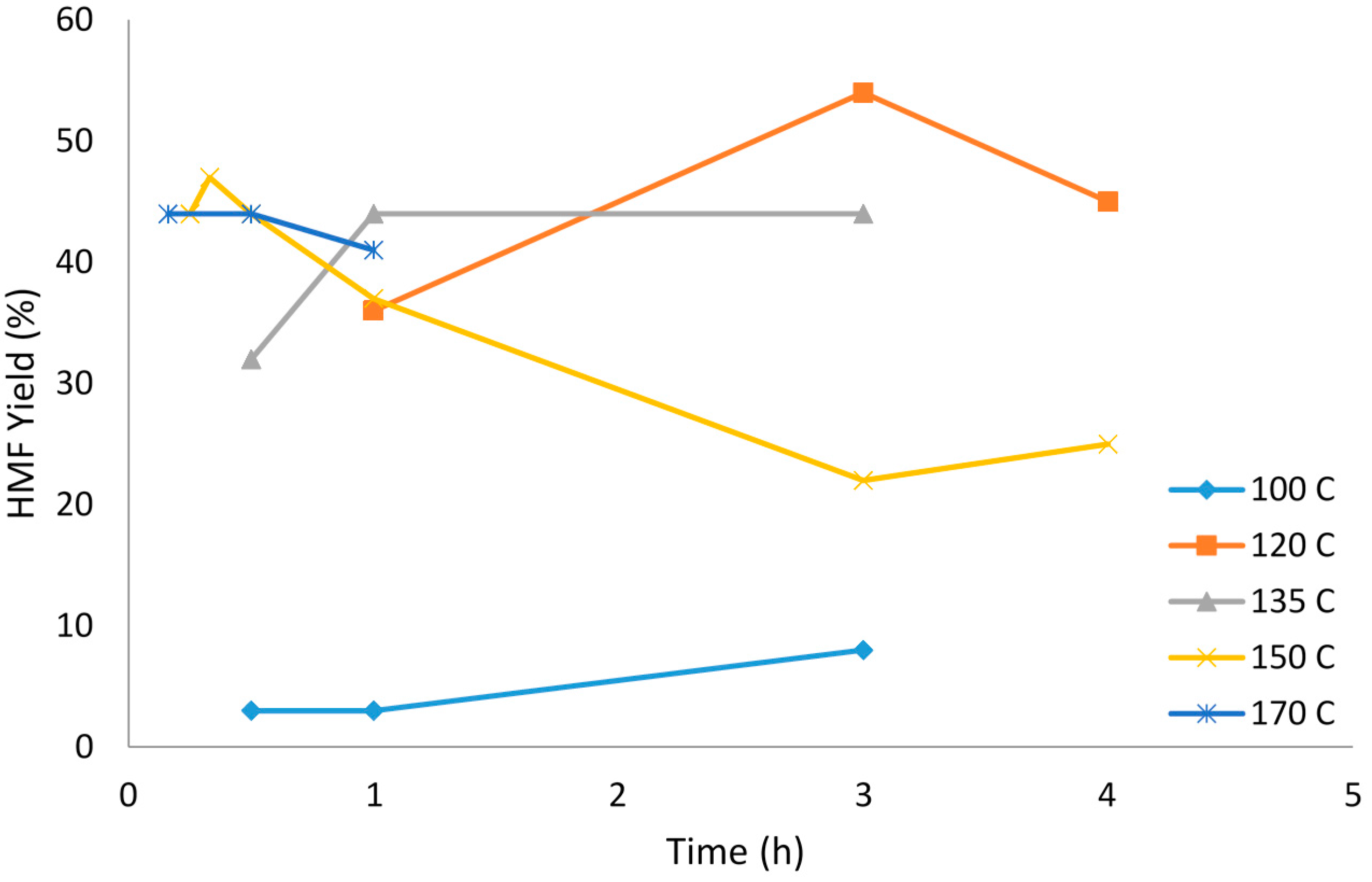
2.5. Reaction Temperature
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Comments
3.2. Catalytic Formation of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) from Cellulose
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ragauskas, A.J.; Williams, C.K.; Davison, B.H.; Britovsek, G.; Cairney, J.; Eckert, C.A.; Frederick, W.J.; Hallett, J.P.; Leak, D.J.; Liotta, C.L. The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 2006, 311, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, G.W.; Iborra, S.; Corma, A. Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: Chemistry, catalysts, and engineering. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román-Leshkov, Y.; Chheda, J.N.; Dumesic, J.A. Phase modifiers promote efficient production of hydroxymethylfurfural from fructose. Science 2006, 312, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, L.J.; Alriksson, B.; Nilvebrant, N.-O. Bioconversion of lignocellulose: Inhibitors and detoxification. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silveira, C.; Trevisan, M.; Rios, J.; Erben, G.; Haubner, R.; Pfundstein, B.; Owen, R. Secondary plant substances in various extracts of the leaves, fruits, stem and bark of caraipa densifolia mart. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, A.; Gräsvik, J.; Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Deconstruction of lignocellulosic biomass with ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 550–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräsvik, J.; Winestrand, S.; Normark, M.; Jönsson, L.J.; Mikkola, J.-P. Evaluation of four ionic liquids for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raut, D.G.; Sundman, O.; Su, W.; Virtanen, P.; Sugano, Y.; Kordas, K.; Mikkola, J.-P. A morpholinium ionic liquid for cellulose dissolution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleteiro, S.; Rivas, S.; Alonso, J.L.; Santos, V.; Parajó, J.C. Utilization of ionic liquids in lignocellulose biorefineries as agents for separation, derivatization, fractionation, or pretreatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8093–8102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, M.H.L.; Morais, A.R.C.; da Costa Lopes, A.M.; Olekszyszen, D.N.; Bogel-Łukasik, R.; Andreaus, J.; Pereira Ramos, L. Current pretreatment technologies for the development of cellulosic ethanol and biorefineries. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 3366–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jogunola, O.; Eta, V.; Hedenström, M.; Sundman, O.; Salmi, T.; Mikkola, J.-P. Ionic liquid mediated technology for synthesis of cellulose acetates using different co-solvents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eta, V.; Mikkola, J.-P. Deconstruction of Nordic hardwood in switchable ionic liquids and acylation of the dissolved cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.; Brandt, A.; Zahari, S.; Klein-Marcuschamer, D.; Parthasarathi, R.; Sun, N.; Sathitsuksanoh, N.; Shi, J.; Stavila, V.; Tran, K. Design of low-cost ionic liquids for biomass pretreatment. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, F.W.; Peters, S. Carbohydrates as green raw materials for the chemical industry. C. R. Chim. 2004, 7, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.H.; Deswarte, F. Introduction to Chemicals from Biomass; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hyvärinen, S.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Murzin, D.Y.; Vaher, M.; Kaljurand, M.; Koel, M. Sugars and sugar derivatives in ionic liquid media obtained from lignocellulosic biomass: Comparison of capillary electrophoresis and chromatographic analysis. Catal. Today 2014, 223, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleteiro, S.; Garrote, G.; Santos, V.; Parajó, J.C. Furan manufacture from softwood hemicelluloses by aqueous fractionation and further reaction in a catalyzed ionic liquid: A biorefinery approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 76, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleteiro, S.; da Costa Lopes, A.M.; Garrote, G.; Parajó, J.C.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Simple and efficient furfural production from xylose in media containing 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 8368–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleteiro, S.; da Costa Lopes, A.M.; Garrote, G.; Bogel-Łukasik, R.; Parajó, J.C. Manufacture of furfural in biphasic media made up of an ionic liquid and a co-solvent. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 77, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.V.; da Costa Lopes, A.M.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Relevance of the acidic 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulphate ionic liquid in the selective catalysis of the biomass hemicellulose fraction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47153–47164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa Lopes, A.M.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Acidic ionic liquids as a sustainable approach of cellulose and lignocellulosic biomass conversion without additional catalysts. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 947–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleteiro, S.; Rivas, S.; Alonso, J.L.; Santos, V.; Parajó, J.C. Furfural production using ionic liquids: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 202, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleteiro, S.; Santos, V.; Garrote, G.; Parajó, J.C. Furfural production from eucalyptus wood using an acidic ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chheda, J.N.; Huber, G.W.; Dumesic, J.A. Liquid-phase catalytic processing of biomass-derived oxygenated hydrocarbons to fuels and chemicals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7164–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centi, G.; Lanzafame, P.; Perathoner, S. Analysis of the alternative routes in the catalytic transformation of lignocellulosic materials. Catal. Today 2011, 167, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Fukuoka, A. Synthesis and utilisation of sugar compounds derived from lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1740–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Green and sustainable manufacture of chemicals from biomass: State of the art. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewkowski, J. Synthesis, chemistry and applications of 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural and its derivatives. ARKIVOC 2001, 1, 17–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Putten, R.-J.; van der Waal, J.C.; de Jong, E.; Rasrendra, C.B.; Heeres, H.J.; de Vries, J.G. Hydroxymethylfurfural, a versatile platform chemical made from renewable resources. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1499–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozell, J.J.; Petersen, G.R. Technology development for the production of biobased products from biorefinery carbohydrates—The US department of energy’s “top 10” revisited. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhlberg, T.; Fu, W.; Woodley, J.M.; Riisager, A. Synthesis of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural in ionic liquids: Paving the way to renewable chemicals. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climent, M.J.; Corma, A.; Iborra, S. Converting carbohydrates to bulk chemicals and fine chemicals over heterogeneous catalysts. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 520–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosatella, A.A.; Simeonov, S.P.; Frade, R.F.; Afonso, C.A. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) as a building block platform: Biological properties, synthesis and synthetic applications. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 754–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, E.; Dam, M.; Sipos, L.; Gruter, G. Furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA), a versatile building block for a very interesting class of polyesters. Biobased Monomers Polym. Mater. 2012, 1105, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Daniel, R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Turner, D.; Wyszynski, M.L.; Richards, P. Combustion and emissions of 2,5-dimethylfuran in a direct-injection spark-ignition engine. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, M.E.; Bogel-Łukasik, E.; Bogel-Łukasik, R. Ionic liquid-mediated formation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural: A promising biomass-derived building block. Chem. Rev. 2010, 111, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyrlik, S.K.; Szerszeń, D.; Olejnik, M.; Danikiewicz, W. Selective dehydration of glucose to hydroxymethylfurfural and a one-pot synthesis of a 4-acetylbutyrolactone from glucose and trioxane in solutions of aluminium salts. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 315, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Aizawa, Y.; Iida, T.; Aida, T.M.; Levy, C.; Sue, K.; Inomata, H. Glucose reactions with acid and base catalysts in hot compressed water at 473 K. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1925–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dee, S.J.; Bell, A.T. A study of the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of cellulose dissolved in ionic liquids and the factors influencing the dehydration of glucose and the formation of humins. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, P.; Dias, A.S.; de Jong, G.-J.G. Furanics: Versatile molecules for biofuels and bulk chemicals applications. Biofuels Technol. 2009, 1, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Osatiashtiani, A.; Lee, A.F.; Brown, D.R.; Melero, J.A.; Morales, G.; Wilson, K. Bifunctional SO4/ZrO2 catalysts for 5-hydroxymethylfufural (5-HMF) production from glucose. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagán-Torres, Y.J.; Wang, T.; Gallo, J.M.R.; Shanks, B.H.; Dumesic, J.A. Production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from glucose using a combination of Lewis and Brønsted acid catalysts in water in a biphasic reactor with an alkylphenol solvent. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonov, S.P.; Coelho, J.A.; Afonso, C.A. An integrated approach for the production and isolation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from carbohydrates. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1388–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Wu, K.; Bi, C.; Cui, Q. Conversion of fructose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) and its derivatives promoted by inorganic salt in alcohol. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 350, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Kwak, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Franz, J.A.; White, J.M.; Holladay, J.E. Effects of crystallinity on dilute acid hydrolysis of cellulose by cellulose ball-milling study. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torget, R.W.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y. Fundamental aspects of dilute acid hydrolysis/fractionation kinetics of hardwood carbohydrates. 1. Cellulose hydrolysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2817–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.H. Solid acids for green chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuhara, T. Water-tolerant solid acid catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3641–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, W.S.L.; Antal, M.J., Jr. Uncatalyzed solvolysis of whole biomass hemicellulose by hot compressed liquid water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, J.; Amin, N.A.S. A review on process conditions for optimum bio-oil yield in hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eminov, S.; Wilton-Ely, J.D.E.T.; Hallett, J.P. Highly selective and near-quantitative conversion of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural using mildly acidic ionic liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Zhou, Y.; Han, B. Efficient conversion of glucose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural catalyzed by a common Lewis acid SnCl4 in an ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1746–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.K. Direct conversion of glucose and cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ionic liquid under microwave irradiation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 5403–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, C.; Musin, I.; Marzialetti, T.; Valenzuela Olarte, M.B.; Agrawal, P.K.; Jones, C.W. Acid-catalyzed conversion of sugars and furfurals in an ionic-liquid phase. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Pidko, E.A.; Hensen, E.J. Molecular aspects of glucose dehydration by chromium chlorides in ionic liquids. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 5281–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Holladay, J.E.; Brown, H.; Zhang, Z.C. Metal chlorides in ionic liquid solvents convert sugars to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Science 2007, 316, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barceloux, D.G. Chromium. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.S.; Woodley, J.M.; Riisager, A. Efficient microwave-assisted synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from concentrated aqueous fructose. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 2568–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Mac Dowell, N.; Welton, T.; Shah, N.; Hallett, J.P. Inexpensive ionic liquids: [HSO4]−-based solvent production at bulk scale. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3098–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eminov, S.; Brandt, A.; Wilton-Ely, J.D.E.T.; Hallett, J.P. Strategies for the highly selective and near-quantitative conversion of glucose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural using ionic liquids. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remsing, R.C.; Swatloski, R.P.; Rogers, R.D.; Moyna, G. Mechanism of cellulose dissolution in the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride: A 13C and 35/37Cl NMR relaxation study on model systems. Chem. Commun. 2006, 1271–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids are not always green: Hydrolysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Brown, H.M.; Huang, X.; Zhou, X.-D.; Amonette, J.E.; Zhang, Z.C. Single-step conversion of cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), a versatile platform chemical. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 361, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, H.; Zhan, S.; Wang, S. Catalytic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in ionic liquid. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4179–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Thushara, D.; Ren, Q.L. Entrainer-intensified vacuum reactive distillation process for the separation of 5-hydroxylmethylfurfural from the dehydration of carbohydrates catalyzed by a metal salt-ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, M.; Bell, A.T. A two-step approach for the catalytic conversion of glucose to 2,5-dimethylfuran in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Lin, J. Hydrolysis of cellulose in ionic liquids catalysed by a magnetically-recoverable solid acid catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiwale, K.Y.; Galande, N.D.; Thakur, P.; Sawant, S.D.; Zambre, V.P.; Bokade, V.V. One-Pot Synthesis of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural by Cellulose Hydrolysis over Highly Active Bimodal Micro/Mesoporous H-ZSM-5 Catalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liang, R.; Ma, Z.; Wu, T.; Wu, Y. Conversion of cellulose to HMF in ionic liquid catalyzed by bifunctional ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.; Huang, C.; Xu, J. Microwave-assisted conversion of microcrystalline cellulose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural catalyzed by ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 162, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
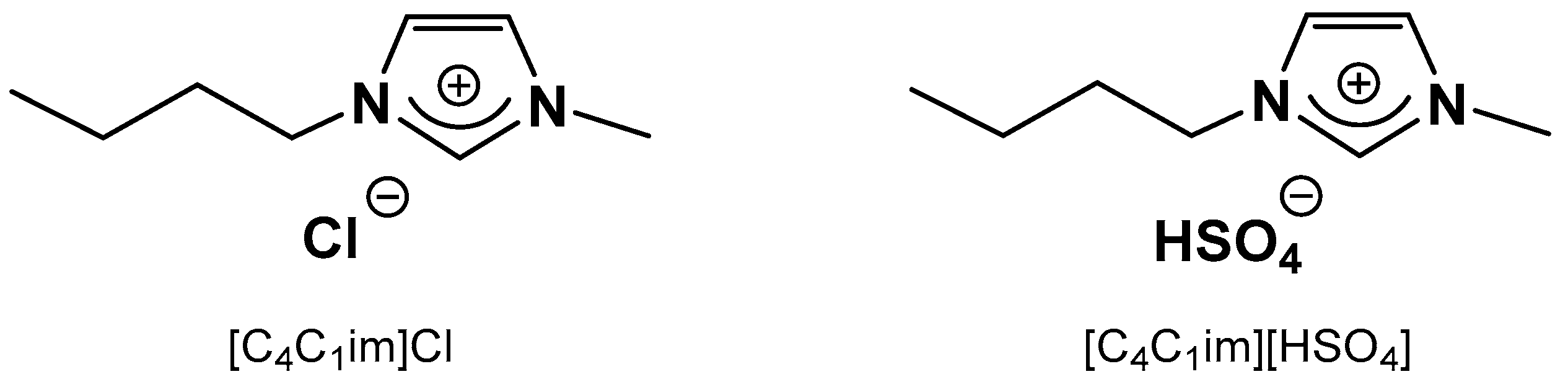

| Entry | Ionic Liquid | Catalyst | 1.5 h | 3 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [C4C1im][HSO4] | CrCl3·6H2O | <5 | <5 |
| 2 | [C4C1im][HSO4] | CrCl3·6H2O + CuCl2 (1:1) | <5 | <5 |
| 3 | [C4C1im][HSO4] | No catalyst | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | [C4C1im]Cl | CrCl3·6H2O | 36 | 54 |
| 5 | [C4C1im]Cl | CrCl3·6H2O + CuCl2 (1:1) | 11 | 11 |
| 6 | [C4C1im]Cl | No catalyst | <3 | <3 |
| 7 | [C4C1im]Cl + [C4C1im][HSO4] (1:1) | CrCl3·6H2O | <3 | <5 |
| 8 | [C4C1im]Cl | ZnCl2 | 0 | 3 |
| 9 | [C4C1im]Cl | CrCl3·6H2O + ZnCl2 (1:1) | 8 | 30 |
| Entry | Ionic Liquid | Catalyst (mol %) | 0.5 h | 1 h | 3 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [C4C1im]Cl + H2O (1:1) | 7 | - | 22 | 28 |
| 2 | [C4C1im]Cl + H2O (3:1) | 7 | - | 51 | 44 |
| 3 | [C4C1im]Cl | 7 | 51 | 45 | 30 |
| 4 | [C4C1im]Cl | 21 | 44 | 37 | 22 |
| Entry | Ionic Liquid | Cellulose (g) | Temp. (°C) | 10 min | 0.5 h | 1 h | 3 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [C4C1im]Cl | 0.025 | 150 | 40 | 52 | 58 | 58 |
| 2 | [C4C1im]Cl | 0.015 | 150 | 25 | 45 | 57 | 51 |
| 3 | [C4C1im]Cl | 0.1 | 170 | 44 | 44 | 41 | - |
| 4 | [C4C1im]Cl | 0.015 | 170 | 31 | 50 | 50 | - |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eminov, S.; Filippousi, P.; Brandt, A.; Wilton-Ely, J.D.E.T.; Hallett, J.P. Direct Catalytic Conversion of Cellulose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Using Ionic Liquids. Inorganics 2016, 4, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4040032
Eminov S, Filippousi P, Brandt A, Wilton-Ely JDET, Hallett JP. Direct Catalytic Conversion of Cellulose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Using Ionic Liquids. Inorganics. 2016; 4(4):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4040032
Chicago/Turabian StyleEminov, Sanan, Paraskevi Filippousi, Agnieszka Brandt, James D. E. T. Wilton-Ely, and Jason P. Hallett. 2016. "Direct Catalytic Conversion of Cellulose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Using Ionic Liquids" Inorganics 4, no. 4: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4040032
APA StyleEminov, S., Filippousi, P., Brandt, A., Wilton-Ely, J. D. E. T., & Hallett, J. P. (2016). Direct Catalytic Conversion of Cellulose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Using Ionic Liquids. Inorganics, 4(4), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4040032