Hydrogenase Biomimetics with Redox-Active Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, and Electrocatalytic Studies on [Fe2(CO)4(κ2-dppn)(µ-edt)] (edt = Ethanedithiolate; dppn = 1,8-bis(Diphenylphosphino)Naphthalene)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Protonation
2.3. Electrochemistry
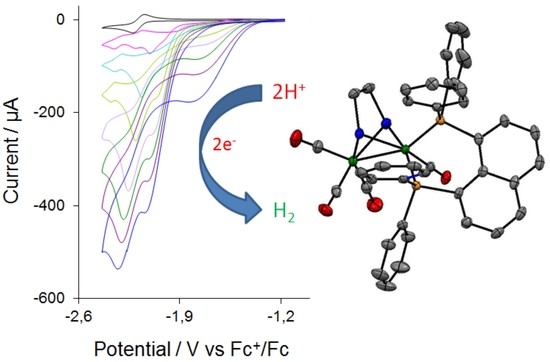
2.4. Catalysis
3. Experimental
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. Protonation Experiments
3.4. X-Ray Crystallography
3.5. Electrochemical Studies
3.6. Computational Methodology and Modeling Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Complex | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C29H21Fe2O5PS2 | C41H32Fe2O4P2S2 |
| Formula weight | 656.25 | 897.33 |
| Temperature (K) | 150(2) | 150(2) |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.71073 | 0.71073 |
| Crystal system | orthorhombic | triclinic |
| Space group | Pbca | P-1 |
| Unit cell dimensions | ||
| a (Å) | 17.2973(10) | 14.310(3) |
| b (Å) | 15.6070(9) | 16.653(4) |
| c (Å) | 20.9270(12) | 18.478(4) |
| α (°) | 90 | 115.075(3) |
| β (°) | 90 | 94.809(4) |
| γ (°) | 90 | 99.124(3) |
| Volume (Å3) | 5649.4(6) | 3881.2(14) |
| Z | 8 | 4 |
| Density (calculated) (Mg/m3) | 1.543 | 1.536 |
| Absorption coefficient (mm−1) | 1.269 | 1.117 |
| F(000) | 2672 | 1832 |
| Crystal size (mm3) | 0.26 × 0.13 × 0.13 | 0.28 × 0.26 × 0.08 |
| θ range for data collection (°) | 2.79 to 28.30 | 2.48 to 28.34 |
| Index ranges | −22 ≤ h ≤ 22, | −18 ≤ h ≤ 18, |
| −20 ≤ k ≤ 20, | −21 ≤ k ≤ 21, | |
| −27 ≤ l ≤ 26 | −23 ≤ l ≤ 23 | |
| Reflections collected | 46753 | 32780 |
| Independent reflections [Rint] | 6896 [Rint = 0.0427] | 17593 [Rint = 0.0379] |
| Max. and min. transmission | 0.8524 and 0.7338 | 0.9159 and 0.7450 |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 6896/0/352 | 17593/0/955 |
| Goodness of fit on F2 | 1.056 | 1.022 |
| Final R indices [I > 2σ(I)] | R1 = 0.0378, | R1 = 0.0512, |
| wR2 = 0.0837 | wR2 = 0.1339 | |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0501, | R1 = 0.0740, |
| wR2 = 0.0879 | wR2 = 0.1484 | |
| Largest diff. peak and hole (e·Å−3) | 0.479 and −0.276 | 1.378 and −0.821 |
References
- Tard, C.; Pickett, C.J. Structural and Functional Analogues of the Active Sites of the [Fe]-, [NiFe]-, and [FeFe]-Hydrogenases. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2245–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Åkermark, B.; Ott, S. Iron hydrogenase active site mimics in supramolecular systems aiming for light-driven hydrogen production. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.J.; Pickett, C.J. Chemistry and the hydrogenases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003, 32, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakaki, I.P.; Thomson, L.M.; Lyon, E.J.; Hall, M.B.; Darensbourg, M.Y. Fundamental properties of small molecule models of Fe-only hydrogenase: Computations relative to the definition of an entatic state in the active site. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 238–239, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauchfuss, T.B. Research on Soluble Metal Sulfides: From Polysulfido Complexes to Functional Models for the Hydrogenases. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ibrahim, S.K.; Tard, C.; Pickett, C.J. Iron-only hydrogenase: Synthetic, structural and reactivity studies of model compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, W.; Ogata, H.; Rudiger, O.; Reijerse, E. Hydrogenases. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4081–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.W.; Lanzilotta, W.N.; Lemon, B.; Seefeldt, L.C. X-ray Crystal Structure of the Fe-only Hydrogenase (CpI) from Clostridium pasteurianum to 1.8 Angstrom Resolution. Science 1998, 282, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolet, Y.; Piras, C.; Legrand, P.; Hatchikian, C.E.; Fontecilla-Camps, J.C. Desulfovibrio desulfuricans iron hydrogenase: The structure shows unusual coordination to an active site Fe binuclear center. Structure 1999, 7, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rauchfuss, T.B. Synthesis of Diiron(I) Dithiolato Carbonyl Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7043–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apfel, U.-P.; Pétillon, F.Y.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J.; Weigand, W. [FeFe] Hydrogenase Models: An Overview. In Bioinspired Catalysis; Schollhammer, P., Weigand, W., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lansing, J.C.; Manor, B.C.; Rauchfuss, T.B. Hydrogenase Models. In Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tschierlei, S.; Ott, S.; Lomoth, R. Spectroscopically Characterized Intermediates of Catalytic H2 Formation by [FeFe] Hydrogenase Models. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2340–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, G.A.N.; Mebi, C.A.; Petro, B.J.; Vannucci, A.K.; Evans, D.H.; Glass, R.S.; Lichtenberger, D.L. Review of Electrochemical Studies of Complexes Containing the Fe2S2 Core Characteristic of [FeFe]-Hydrogenases Including Catalysis by These Complexes of the Reduction of Acids to Form Dihydrogen. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 2681–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloaguen, F. Electrochemistry of Simple Organometallic Models of Iron–Iron Hydrogenases in Organic Solvent and Water. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzaher, S.; Capon, J.-F.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.Y.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J.; Kervarec, N. Influence of a Pendant Amine in the Second Coordination Sphere on Proton Transfer at a Dissymmetrically Disubstituted Diiron System Related to the [2Fe]H Subsite of [FeFe]H2ase. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Jin, K.; Chen, L.; Sun, L. Preparation, Facile Deprotonation, and Rapid H/D Exchange of the μ-Hydride Diiron Model Complexes of the [FeFe]-Hydrogenase Containing a Pendant Amine in a Chelating Diphosphine Ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 11551–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzaher, S.; Capon, J.-F.; Dumontet, N.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.Y.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J. Electrochemical study of the role of a H-bridged, unsymmetrically disubstituted diiron complex in proton reduction catalysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 626, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzaher, S.; Capon, J.-F.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.Y.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J. Evidence for the Formation of Terminal Hydrides by Protonation of an Asymmetric Iron Hydrogenase Active Site Mimic. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 3426–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, F.I.; Hogarth, G.; Kabir, S.E.; Richards, I. Models of the iron-only hydrogenase: Synthesis and protonation of bridge and chelate complexes [Fe2(CO)4{Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2}(μ-pdt)] (n = 2–4)—Evidence for a terminal hydride intermediate. C. R. Chim. 2008, 11, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sanchez, B.E.; Richards, I.; Haque, M.N.; Holt, K.B.; Richmond, M.G.; Hogarth, G. Biomimetics of the [FeFe]-hydrogenase enzyme: Identification of kinetically favoured apical-basal [Fe2(CO)4(μ-H){κ2-Ph2PC(Me2)PPh2}(μ-pdt)]+ as a proton-reduction catalyst. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 812, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hogarth, G.; Hollingsworth, N.; Holt, K.B.; Richards, I.; Richmond, M.G.; Sanchez, B.E.; Unwin, D. Models of the iron-only hydrogenase: A comparison of chelate and bridge isomers of Fe2(CO)4{Ph2PN(R)PPh2}(μ-pdt) as proton-reduction catalysts. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 6775–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, F.I.; Hogarth, G.; Richards, I.; Sanchez, B.E. Models of the iron-only hydrogenase: Structural studies of chelating diphosphine complexes [Fe2(CO)4(µ-pdt)(κ2-P,P′-diphosphine)]. Dalton Trans. 2007, 2495–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, F.I.; Hogarth, G.; Richards, I. Models of the iron-only hydrogenase: Reactions of [Fe2(CO)6(μ-pdt)] with small bite-angle diphosphines yielding bridge and chelate diphosphine complexes [Fe2(CO)4(diphosphine)(μ-pdt)]. J. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 692, 3957–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzaher, S.; Capon, J.-F.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.Y.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J. Electron-Transfer-Catalyzed Rearrangement of Unsymmetrically Substituted Diiron Dithiolate Complexes Related to the Active Site of the [FeFe]-Hydrogenases. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 9863–9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Ghosh, S.; Hossain, M.K.; Rahaman, A.; Hogarth, G.; Kabir, S.E. Hydrogenase biomimetics: Structural and spectroscopic studies on diphosphine-substituted derivatives of Fe2(CO)6(µ-edt) (edt = ethanedithiolate) and Fe2(CO)6(µ-tdt) (tdt = 1,3-toluenedithiolate). Trans. Met. Chem. 2016, 41, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, A.K.; Zampella, G.; Gioia, L.D.; Rauchfuss, T.B.; van der Vlugt, J.I.; Wilson, S.R. Chelate Control of Diiron(I) Dithiolates Relevant to the [Fe−Fe]-Hydrogenase Active Site. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, F.; Ghosh, S.; Hogarth, G.; Hollingsworth, N.; Holt, K.B.; Unwin, D.G. Fluorinated models of the iron-only hydrogenase: An electrochemical study of the influence of an electron-withdrawing bridge on the proton reduction overpotential and catalyst stability. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 703, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauchfuss, T.B. Diiron Azadithiolates as Models for the [FeFe]-Hydrogenase Active Site and Paradigm for the Role of the Second Coordination Sphere. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Rahaman, A.; Holt, K.B.; Nordlander, E.; Richmond, M.G.; Kabir, S.E.; Hogarth, G. Hydrogenase biomimetics with redox-active ligands: Electrocatalytic proton reduction by [Fe2(CO)4(κ2-diamine)(µ-edt)] (diamine = 2,2′-bipy,1,10-phen). Polyhedron 2016, 116, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hogarth, G.; Hollingsworth, N.; Holt, K.B.; Kabir, S.E.; Sanchez, B.E. Hydrogenase biomimetics: Fe2(CO)4(µ-dppf)(µ-pdt)(dppf = 1,1’-bis(diphenylphosphino) ferrocene) both a proton-reduction and hydrogen oxidation catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, C. H2 Binding and Splitting on a New-Generation [FeFe]-Hydrogenase Model Featuring a Redox-Active Decamethylferrocenyl Phosphine Ligand: A Theoretical Investigation. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youtao, S.; Charreteur, K.; Capon, J.-F.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.Y.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J. Non-innocent bma ligand in a dissymetrically disubstituted diiron dithiolate related to the active site of the [FeFe] hydrogenases. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Camara, J.M.; Rauchfuss, T.B. Combining Acid-base, Redox and Substrate Binding Functionalities to Give a Complete Model for the [FeFe]-hydrogenase. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camara, J.M.; Rauchfuss, T.B. Mild Redox Complementation Enables H2 Activation by [FeFe]-Hydrogenase Models. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8098–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tard, C.; Liu, X.M.; Ibrahim, S.K.; Bruschi, M.; Gioia, L.D.; Davies, S.C.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.S.; Sawers, G.; Pickett, C.J. Synthesis of the H-cluster Framework of Iron-only Hydrogenase. Nature 2005, 433, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimbert-Suriñach, C.; Bhadbhade, M.; Colbran, S.B. Bridgehead Hydrogen Atoms Are Important: Unusual Electrochemistry and Proton Reduction at Iron Dimers with Ferrocenyl-Substituted Phosphido Bridges. Organometallics 2012, 31, 3480–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, C.; Gioia, L.D. A Theoretical Study on the Enhancement of Functionally Relevant Electron Transfers in Biomimetic Models of [FeFe]-Hydrogenases. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6987–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orain, P.-Y.; Capon, J.-F.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.Y.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J.; Zampella, G.; Gioia, L.D.; Roisnel, T. Investigation on the Protonation of a Trisubstituted [Fe2(CO)3(PPh3)(κ2-phen)(μ-pdt)] Complex: Rotated versus Unrotated Intermediate Pathways. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzaher, S.; Orain, P.-Y.; Capon, J.-F.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.; Roisnel, T.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J. First Insights into the Protonation of Dissymetrically Disubstituted Di-iron Azadithiolate Models of the [FeFe]H2ases Active Site. Chem. Commun. 2008, 2547–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, J.-F.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.Y.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J. Organometallics Diiron Complex Chemistry Related to the [2Fe]H Subsite of [FeFe]H2ase. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 4671–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orain, P.-Y.; Capon, J.-F.; Kervarec, N.; Gloaguen, F.; Pétillon, F.; Pichon, R.; Schollhammer, P.; Talarmin, J. Use of 1,10-Phenanthroline in Diiron Dithiolate Derivatives Related to the [Fe–Fe] Hydrogenase Active Site. Dalton Trans. 2007, 3754–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Groy, T.L.; Jones, A.K. Biomimetic Model for [FeFe]-hydrogenase: Asymmetrically Disubstituted Diiron Complex with a Redox-active 2,2′-Bipyridyl Ligand. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 3843–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Yen, T.-H.; Chu, K.-T.; Chiang, M.-H. Utilization of Non-Innocent Redox Ligands in [FeFe] Hydrogenase Modeling for Hydrogen Production. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2016, 36, 141–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, G.-H.; Chiang, M.-H. Influence of a Redox-Active Phosphane Ligand on the Oxidations of a Diiron Core Related to the Active Site of Fe-only Hydrogenase. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-H.; Ding, S.; Erdem, Ö.F.; Crouthers, D.J.; Liu, T.; McCrory, C.C.L.; Lubitz, W.; Popescu, C.V.; Reibenspies, J.H.; Hall, M.B.; et al. Redox active iron nitrosyl units in proton reduction electrocatalysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, T.-H.; He, Z.-C.; Lee, G.-H.; Tseng, M.-C.; Shen, Y.-H.; Tseng, T.-W.; Liaw, W.-F.; Chiang, M.-H. Reduced thione ligation is preferred over neutral phosphine ligation in diiron biomimics regarding electronic functionality: A spectroscopic and computational investigation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Yen, T.-H.; Tseng, Y.-J.; Hu, C.-H.; Lee, G.-H.; Chiang, M.-H. Electron Delocalization from the Fullerene Attachment to the Diiron Core within the Active-Site Mimics of [FeFe]Hydrogenase. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 5997–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, T.; Schmidbaur, H. 1,8-Naphthalenediylhis(dimethylphosphane): Steric Influence on Methylation and Borylation. Chem. Ber. 1982, 115, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenske, D.; Becher, H.J. Synthesis and Properties of Derivatives of 2,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)maleic Anhydride as a Contribution to the Problem of Colour, Conjugation, and Complex Formation of this Class of Compounds. Chem. Ber. 1975, 108, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, M.I.; Humphrey, P.A.; Okucu, S.; Schmutzler, R.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Reactions of 1,8-Bis(diphenylphosphino)naphthalene with Os3(CO)12: C–H and C–P Bond Cleavage Reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.E.; Ahmed, F.; Ghosh, S.; Hassan, M.R.; Islam, M.S.; Sharmin, A.; Tocher, D.A.; Haworth, D.T.; Lindeman, S.V.; Siddiquee, T.A.; et al. Reactions of Rhenium and Manganese Carbonyl Complexes with 1,8-Bis(diphenylphosphino) naphthalene: Ligand Chelation, C–H and C–P Bond-cleavage Reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2008, 693, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.E.; Rahman, A.F.M.M.; Parvin, J.; Malik, K.M.A. Reexamination of the Reactivity of Iron Carbonyls with 1,2-Ethanedithiol. Indian J. Chem. 2003, 42A, 2518–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Holt, K.B.; Kabir, S.E.; Richmond, M.G.; Hogarth, G. Electrocatalytic proton reduction catalyzed by the low-valent tetrairon-oxo cluster [Fe4(CO)10(κ2-dppn)(µ4-O)]2− [dppn = 1,1’-bis(diphenylphosphino)naphthalene]. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 5160–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izutsu, K. Acid-Base Dissociation Constants in Dipolar Aprotic Solvents; IUPAC Chemical Data Series No. 35; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mejia-Rodriguez, R.; Chong, D.; Reibenspies, J.H.; Soriaga, M.P.; Darensbourg, M.Y. The Hydrophilic Phosphatriazaadamantane Ligand in the Development of H2 Production Electrocatalysts: Iron Hydrogenase Model Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12004–12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Basak-Modi, S.; Richmond, M.G.; Nordlander, E.; Hogarth, G. Electrocatalytic proton reduction by thiolate-capped triiron clusters [Fe3(CO)9(µ3-SR)(µ-H)] (R = iPr, tBu). Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 480, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, D.; Georgakaki, I.P.; Mejia-Rodriguez, R.; Sanabria-Chinchilla, J.; Soriaga, M.P.; Darensbourg, M.Y. Electrocatalysis of hydrogen production by active site analogues of the iron hydrogenase enzyme: Structure/function relationships. Dalton Trans. 2003, 4158–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, G.A.N.; Vannucci, A.K.; Chen, J.; Lockett, L.T.; Okumura, N.; Petro, B.J.; Zakai, U.I.; Evans, D.H.; Glass, R.S.; Lichtenberger, D.L. Hydrogen Generation from Weak Acids: Electrochemical and Computational Studies of a Diiron Hydrogenase Mimic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12521–12530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Chu, K.-T.; Jhang, R.-L.; Lee, G.-H.; Chiang, M.-H. [FeFe] hydrogenase active site modeling: A key intermediate bearing a thiolate proton and Fe hydride. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4743–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, M.J.; Gray, H.B.; Winkler, J.R. Hydrogen Generation Catalyzed by Fluorinated Diglyoxime−Iron Complexes at Low Overpotentials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8310–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Brunschwig, B.S.; Peters, J.C. Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution at Low Overpotentials by Cobalt Macrocyclic Glyoxime and Tetraimine Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8988–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, G.M.; Yang, J.Y.; Twamley, B.; Wilson, A.D.; Bullock, R.M.; Rakowski-DuBois, M.; DuBois, D.L. Hydrogen Production Using Cobalt-based Molecular Catalysts Containing a Proton Relay in the Second Coordination Sphere. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, M.L.; Stewart, M.P.; Bullock, R.M.; DuBois, M.R.; DuBois, D.L. A Synthetic Nickel Electrocatalyst with a Turnover Frequency above 100,000 s−1 for H2 Production. Science 2011, 333, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.; Zsolnai, L.; Huttner, G. Dinuclear and Trinuclear Carbonyliron Complexes Containing 1,2- and 1,3-Dithiolato Bridging Ligands. Z. Naturforsch. 1982, 37b, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APEX2 Version 2.0-2; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2005.
- SAINT Version 7.23A; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2005.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS Version 2004/1; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Program XS from SHELXTL Package, V. 6.12; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2001.
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dolg, M.; Wedig, U.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Energy-adjusted ab initio pseudopotentials for the second and third row transition elements. J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 86, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, S.; Rana, S.; Hollingsworth, N.; Richmond, M.G.; Kabir, S.E.; Hogarth, G. Hydrogenase Biomimetics with Redox-Active Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, and Electrocatalytic Studies on [Fe2(CO)4(κ2-dppn)(µ-edt)] (edt = Ethanedithiolate; dppn = 1,8-bis(Diphenylphosphino)Naphthalene). Inorganics 2018, 6, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040122
Ghosh S, Rana S, Hollingsworth N, Richmond MG, Kabir SE, Hogarth G. Hydrogenase Biomimetics with Redox-Active Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, and Electrocatalytic Studies on [Fe2(CO)4(κ2-dppn)(µ-edt)] (edt = Ethanedithiolate; dppn = 1,8-bis(Diphenylphosphino)Naphthalene). Inorganics. 2018; 6(4):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040122
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Shishir, Shahed Rana, Nathan Hollingsworth, Michael G. Richmond, Shariff E. Kabir, and Graeme Hogarth. 2018. "Hydrogenase Biomimetics with Redox-Active Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, and Electrocatalytic Studies on [Fe2(CO)4(κ2-dppn)(µ-edt)] (edt = Ethanedithiolate; dppn = 1,8-bis(Diphenylphosphino)Naphthalene)" Inorganics 6, no. 4: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040122
APA StyleGhosh, S., Rana, S., Hollingsworth, N., Richmond, M. G., Kabir, S. E., & Hogarth, G. (2018). Hydrogenase Biomimetics with Redox-Active Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, and Electrocatalytic Studies on [Fe2(CO)4(κ2-dppn)(µ-edt)] (edt = Ethanedithiolate; dppn = 1,8-bis(Diphenylphosphino)Naphthalene). Inorganics, 6(4), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6040122