Assessment of Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity among Four Seaweeds, with Focus on Caulerpa lentillifera J.Agardh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Seaweed Extract Preparation
2.3. Cell Lines and Culture
2.4. Luciferase Assay
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay (MTT Assay)
2.6. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA)
2.7. Colony-Forming Assay
2.8. Apoptosis Determination
2.9. Change in Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm)
2.10. Wound Healing Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
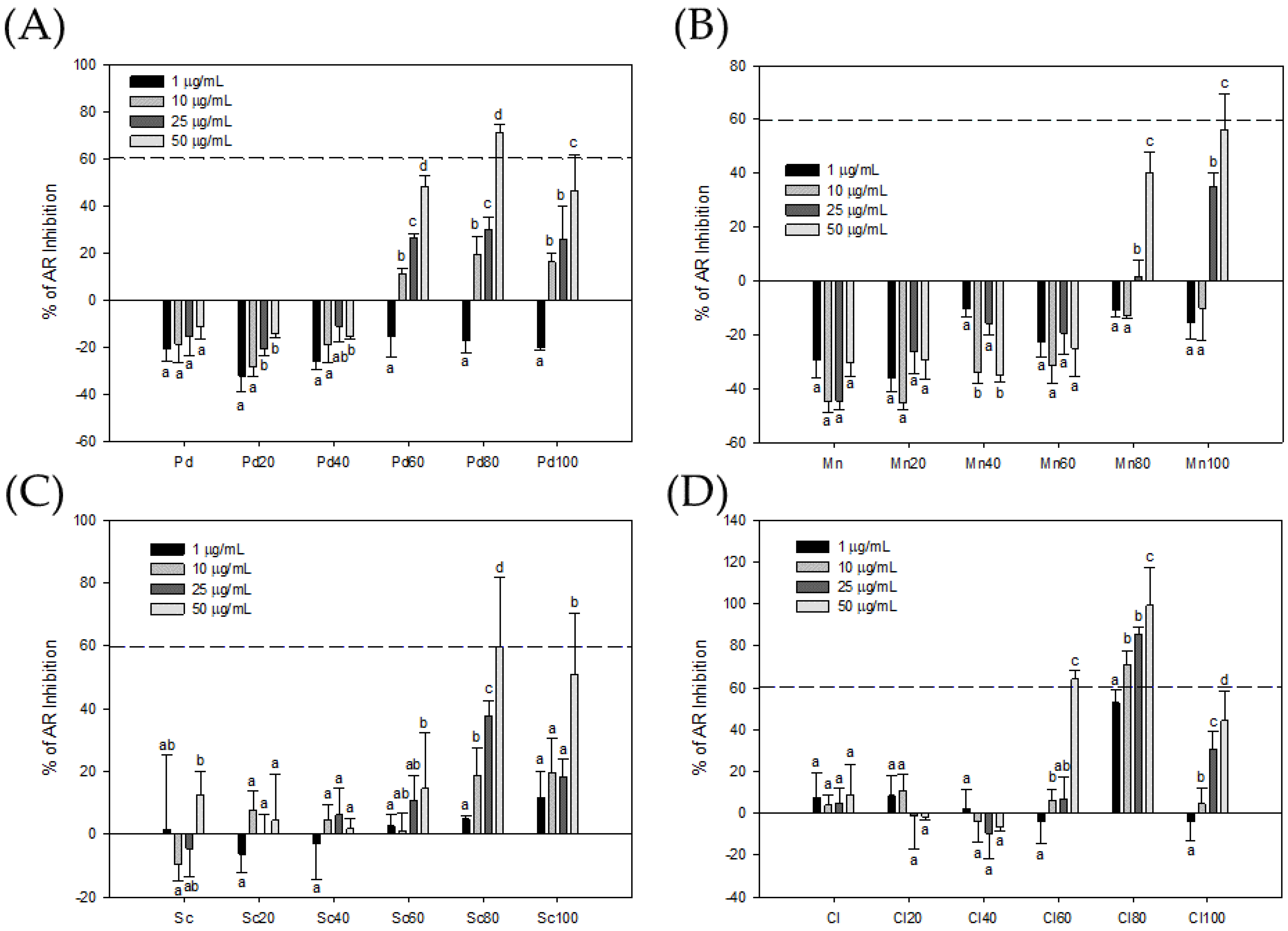
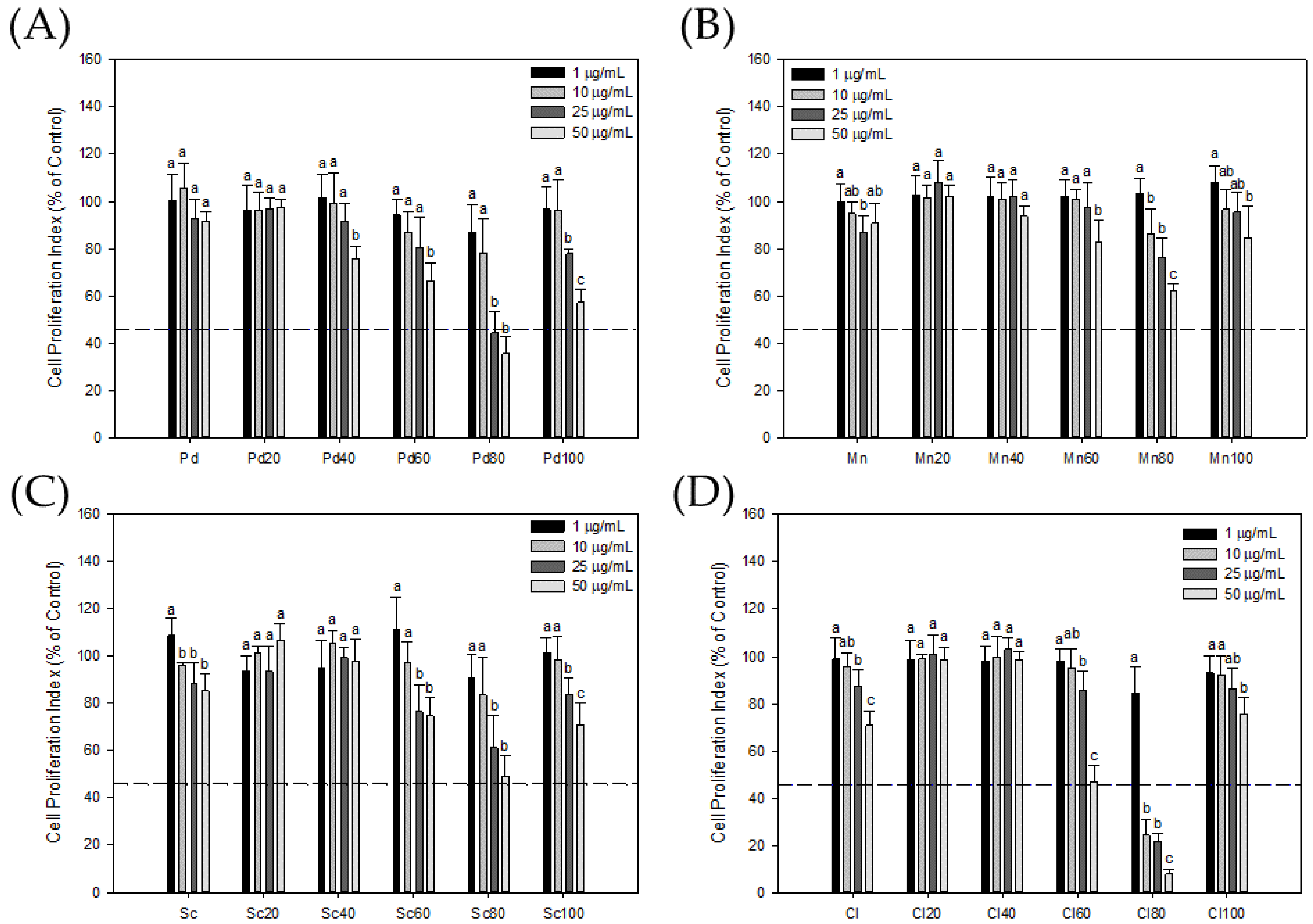
3.1. Bioactivity-Guided Fractionation of Seaweeds
3.2. Effect of Seaweed Extracts on LNCaP Cell Proliferation
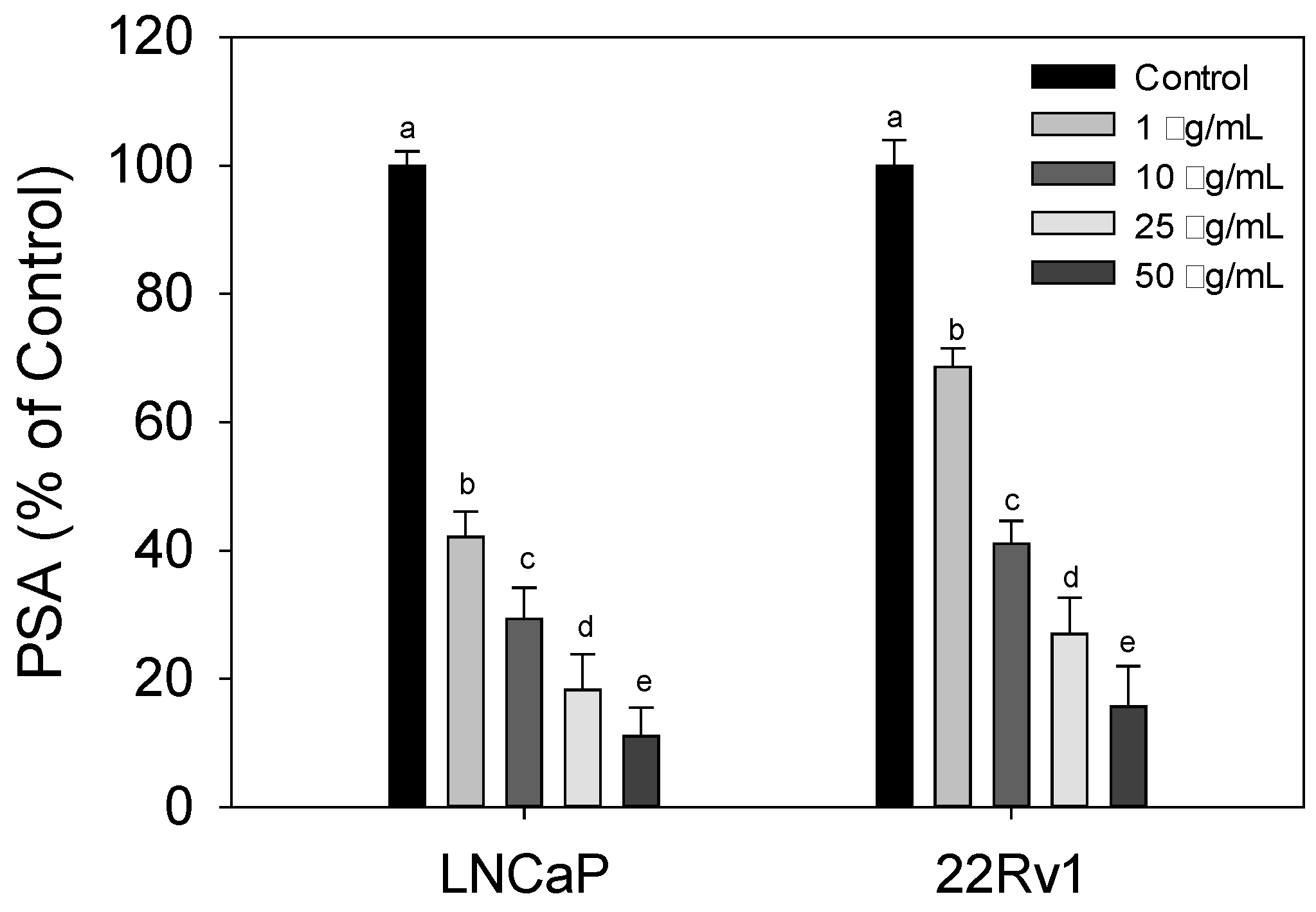
3.3. Effect of Cl80 on PSA Expression
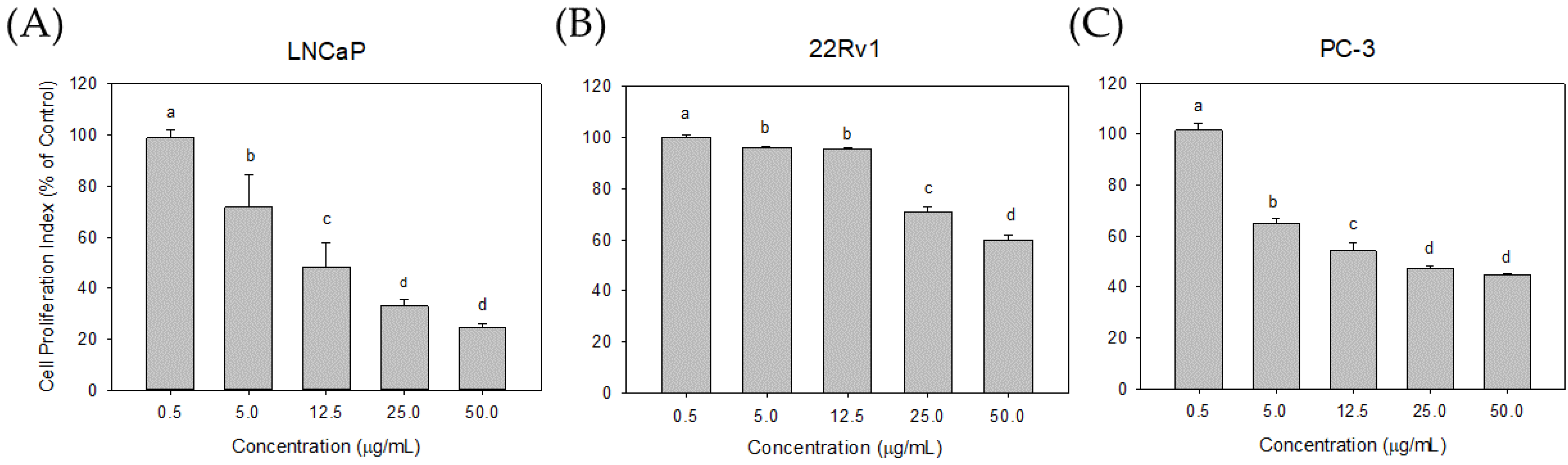
3.4. Effect of Cl80 on PCa Cell Proliferation and Development
3.5. Effect of Cl80 on LNCaP Cell Apoptosis
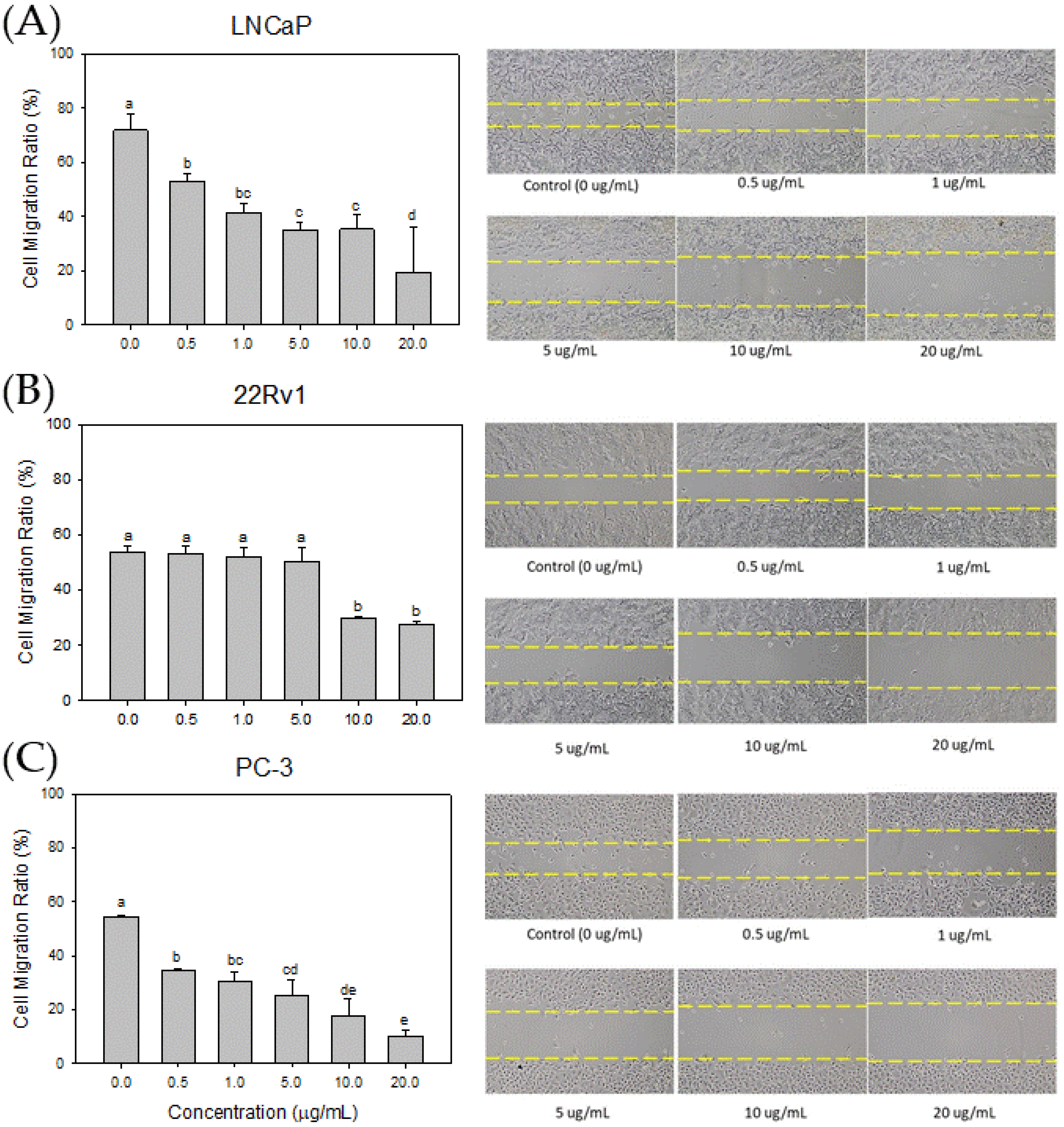
3.6. Effect of Cl80 on PCa cell Migration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinto, V.R.A.; Campos, R.F.D.; Rocha, F.; Emmendoerfer, M.L.; Vidigal, M.C.T.R.; da Rocha, S.J.S.S.; Della Lucia, S.M.; Cabral, L.F.M.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Perrone, I.T. Perceived healthiness of foods: A systematic review of qualitative studies. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavinson, V.; Popovich, I.; Mikhailova, O. Towards realization of longer life. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020054. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkac, J.; Gajdosova, V.; Hroncekova, S.; Bertok, T.; Hires, M.; Jane, E.; Lorencova, L.; Kasak, P. Prostate-specific antigen glycoprofiling as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of prostate cancer. Interface Focus 2019, 9, 20180077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabi, B.R.; Liu, S.Q.; Stoyanova, T. Current and emerging therapies for neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 238, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.X.; Wu, W.H.; Wen, Y.X.; Zhang, L.Z.; Wu, Y.L.; Farid, M.S.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Capanoglu, E.; Zhao, C. Recent advances of natural pigments from algae. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2023, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogel-Castillo, C.; Latorre-Castaneda, M.; Munoz-Munoz, C.; Agurto-Munoz, C. Seaweeds in Food: Current Trends. Plants 2023, 12, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunathilaka, M.D.T.L. Utilization of Marine Seaweeds as a Promising Defense Against COVID-19: A Mini-review. Mar. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Je, J.G.; Huang, C.; Oh, J.Y.; Fu, X.; Wang, K.; Ahn, G.; Xu, J.; Gao, X.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sulfated Polysaccharides Isolated from Codium fragile In Vitro in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and In Vivo in Zebrafish. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, R.S.; Choudhary, B.; Pandey, S.; Pathak, P.K.; Patel, M.K.; Mishra, A. Rehashing Our Insight of Seaweeds as a Potential Source of Foods, Nutraceuticals, and Pharmaceuticals. Foods 2023, 12, 3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Wang, Q.; Luo, H.; Lei, D.; Tang, Z.; Lei, S.; Xiao, H. Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenols-Rich Components from Three Edible Seaweeds on Inflammation and Colon Cancer in vitro. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 856273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besednova, N.N.; Andryukov, B.G.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Kryzhanovsky, S.P.; Fedyanina, L.N.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Shchelkanov, M.Y. Antiviral Effects of Polyphenols from Marine Algae. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, T.; Yang, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhan, F.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, X. Anti-Cancer Activity of Porphyran and Carrageenan from Red Seaweeds. Molecules 2019, 24, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, B.; PBhuyan, P.; Ki, J.S. Immunomodulatory, Antioxidant, Anticancer, and Pharmacokinetic Activity of Ulvan, a Seaweed-Derived Sulfated Polysaccharide: An Updated Comprehensive Review. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.Y.; Hwang, P.A. Clinical applications of fucoidan in translational medicine for adjuvant cancer therapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktar, Z.A.; Oral, S.; Bulut, S.H.; Bayraktar, Y. Effect of perception of sustainability in local food experiences on healthy eating tendency: Mediator and moderator effects. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1150277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.T.; Fu, Y.Z.; Shi, J.; Xie, S.G.; Yang, Y.F. Carbon sink potential and environmental benefits of seaweed: A case study of the seaweed cultivation industry on China coast. Aquaculture 2023, 572, 739494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.M.; Chen, L.R.; Lin, E.H.; Ke, F.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; Hsiao, P.W. Compounds from Wedelia chinensis synergistically suppress androgen activity and growth in prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Verma, P.K.; Shukla, A.; Singh, R.K.; Patel, A.K.; Yadav, L.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, N.; Kaushalendra; Acharya, A. Moringa oleifera L. leaf extract induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondrial apoptosis in Dalton’s Lymphoma: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 302, 115849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Shin, J.Y.; Kang, N.G.; Lee, S. Antiandrogenic activity of Riboflavin 5’-phosphate (FMN) in 22Rv1 and LNCaP human prostate cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 917, 174743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekdaengphanao, P.; Jaiseri, D.; Sriraj, P.; Aukkanimart, R.; Prathumtet, J.; Udonsan, P.; Boonmars, T. Anticancer activity of Terminalia chebula, Terminalia bellirica, and Phyllanthus emblica extracts on cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. J. Herb. Med. 2022, 35, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Verma, P.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Acharya, A. Achyranthes aspera L. leaf extract induced anticancer effects on Dalton’s Lymphoma via regulation of PKC alpha signaling pathway and mitochondrial apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 274, 114060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Kim, J.E.; Xu, Y.; Han, H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J. AKT, a Key Transmitter of HIF-1alpha and AR Signaling Pathways, Has a Critical Role in the Apigetrin-Mediated Anti-Cancer Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1370. [Google Scholar]
- Mroczek, T.; Dymek, A.; Widelski, J.; Wojtanowski, K.K. The Bioassay-Guided Fractionation and Identification of Potent Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors from Narcissus c.v. ‘Hawera’ Using Optimized Vacuum Liquid Chromatography, High Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Bioautography. Metabolites 2020, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auchus, R.J.; Sharifi, N. Sex Hormones and Prostate Cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2020, 71, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorella, E.; Giantulli, S.; Sciarra, A.; Silvestri, I. AR and PI3K/AKT in Prostate Cancer: A Tale of Two Interconnected Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, K.; McManus, J.M.; Sharifi, N. Hormonal Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.M.; Cacciamani, G.E.; Gill, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Abreu, A.; Gill, I.S. Trends in Incidence of Metastatic Prostate Cancer in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e222246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horoszewicz, J.S.; Leong, S.S.; Kawinski, E.; Karr, J.P.; Rosenthal, H.; Chu, T.M.; Mirand, E.A.; Murphy, G.P. LNCaP model of human prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 1809. [Google Scholar]
- van Bokhoven, A.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Korch, C.; Johannes, W.U.; Smith, E.E.; Miller, H.L.; Nordeen, S.K.; Miller, G.J.; Lucia, M.S. Molecular characterization of human prostate carcinoma cell lines. Prostate 2003, 57, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liang, X.; Jiang, G. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of castration resistant prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komendantova, A.S.; Scherbakov, A.M.; Komkov, A.V.; Chertkova, V.V.; Gudovanniy, A.O.; Chernoburova, E.I.; Sorokin, D.V.; Dzichenka, Y.U.; Shirinian, V.Z.; Volkova, Y.A.; et al. Novel steroidal 1,3,4-thiadiazines: Synthesis and biological evaluation in androgen receptor-positive prostate cancer 22Rv1 cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 91, 103142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, S.; Sun, Y.; Squires, J.M.; Zhang, H.; Oh, W.K.; Liang, C.Z.; Huang, J.T. PC3 Is a Cell Line Characteristic of Prostatic Small Cell Carcinoma. Prostate 2011, 71, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.L.; Li, W.B.; Luo, Z.; Chen, K.H.; Cao, J.J.; Yu, C.; Liu, W.J. Isolation and enrichment of PC-3 prostate cancer stem-like cells using MACS and serum-free medium. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.; Bagga, M.; Kaur, A.; Westermarck, J.; Abankwa, D. ColonyArea: An ImageJ Plugin to Automatically Quantify Colony Formation in Clonogenic Assays. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolatabadi, E.N.; Asghariazar, V.; Darvish, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Simvastatin-loaded PCL/PEG nanofibrous scaffold: A prospective approach for suppression 5-fluorouracil resistance in MKN-45 gastric cancer cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Shukla, N.; Kumari, S.; Ansari, M.S.; Gautam, N.K.; Patel, G.K. Cancer stem cell in prostate cancer progression, metastasis and therapy resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, R.; Elbessoumy, A.A.; Chandramoorthy, H.C.; Dera, A.; Al Fayi, M. FCX, an arylidene derivative, induces apoptosis in androgen receptor-selective prostate cancer cells. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, A.P. The change of cellular membranes on apoptosis: Fluorescence detection. Exp. Oncol. 2012, 34, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, N.; Gupta, P.; Verma, A.; Tiwari, R.K.; Madhukar, P.; Kamble, S.C.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S.K.; Gautam, V. Ethyl Acetate Extract of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Promotes Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deborde, S.; Gusain, L.; Powers, A.; Marcadis, A.; Yu, Y.; Chen, C.H.; Frants, A.; Kao, E.; Tang, L.H.; Vakiani, E.; et al. Reprogrammed Schwann Cells Organize into Dynamic Tracks that Promote Pancreatic Cancer Invasion. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molter, C.W.; Muszynski, E.F.; Tao, Y.; Trivedi, T.; Clouvel, A.; Ehrlicher, A.J. Prostate cancer cells of increasing metastatic potential exhibit diverse contractile forces, cell stiffness, and motility in a microenvironment stiffness-dependent manner. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 932510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Hwang, K.A.; Shim, S.M.; Choi, K.C. Growth and migration of LNCaP prostate cancer cells are promoted by triclosan and benzophenone-1 via an androgen receptor signaling pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.-J.; Hsiao, P.-W. Assessment of Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity among Four Seaweeds, with Focus on Caulerpa lentillifera J.Agardh. Foods 2024, 13, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13091411
Wu G-J, Hsiao P-W. Assessment of Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity among Four Seaweeds, with Focus on Caulerpa lentillifera J.Agardh. Foods. 2024; 13(9):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13091411
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guan-James, and Pei-Wen Hsiao. 2024. "Assessment of Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity among Four Seaweeds, with Focus on Caulerpa lentillifera J.Agardh" Foods 13, no. 9: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13091411







