Identifying Freshness of Spinach Leaves Stored at Different Temperatures Using Hyperspectral Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Hyperspectral Imaging System
2.3. Hyperspectral Image Acquisition and Correction
2.4. Spectral Data Preprocessing and Extraction
2.5. Data Analysis Methods
2.5.1. Principal Component Analysis
2.5.2. Effective Wavelength Selection
2.5.3. Discriminant Models
2.6. Software and Model Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Spectral Profile
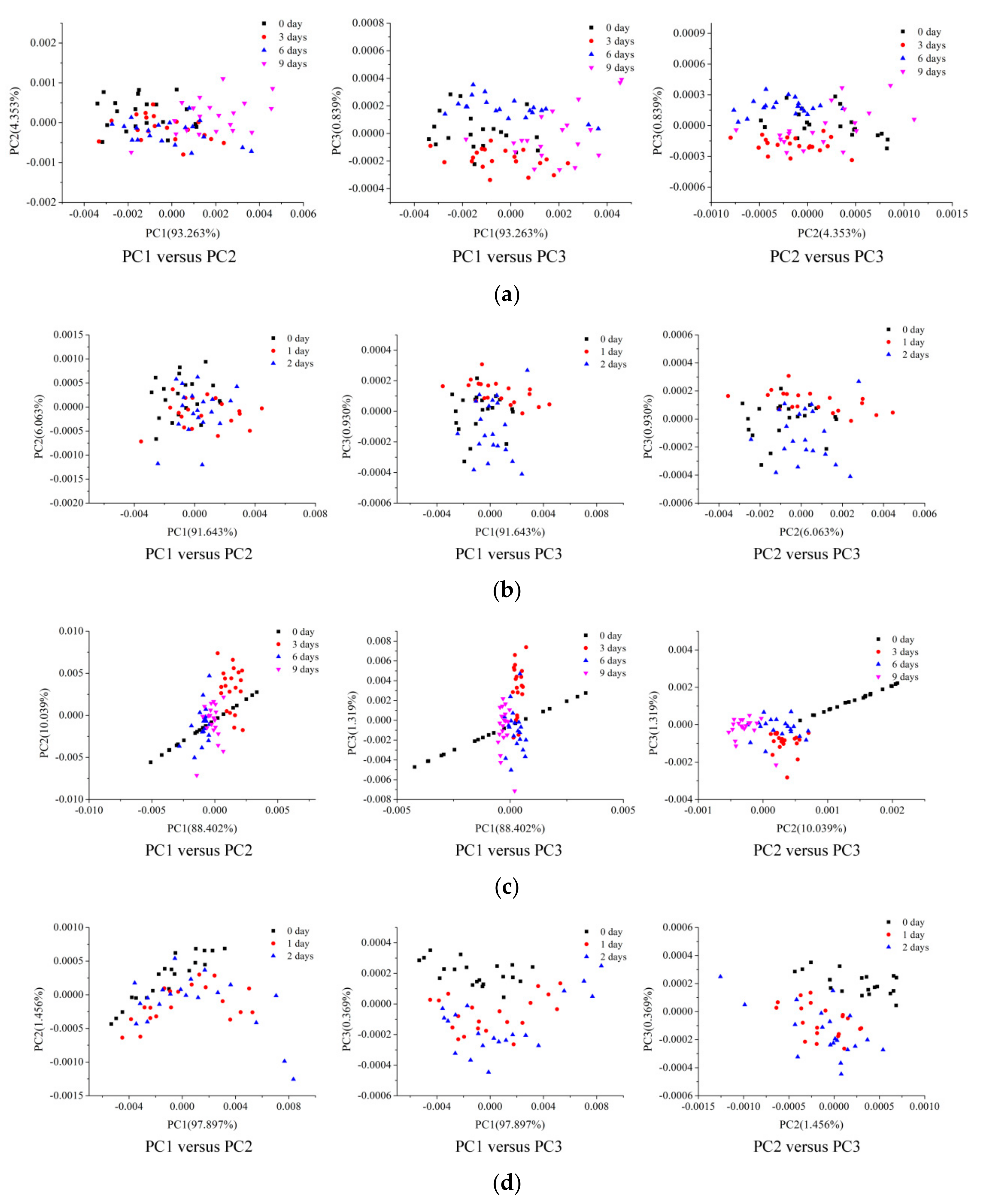
3.2. PCA Scores Scatter Plot Analysis
3.3. Effective Wavelength Selection
3.4. Classification Models Using Vis-NIR and NIR Spectra
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodman, R.M. The Nutrition of Spinach. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2010, 29, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuka, S.; Takahiko, H.; Tomoko, B.; Minako, S.; Hisami, Y.; Hironori, Y.; Taketani1, T.; Eiji, T. Protective effects of glycoglycerolipids extracted from spinach on 5-fluorouracil induced intestinal mucosal injury. J. Med. Investig. 2010, 57, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dosari, M.S. Antioxidant and protective effects of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) leaves against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury. Clin. Exp. Med. J. 2010, 4, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.T.; Yao, M.W.Y.; Wong, Y.C.; Wong, T.; Mok, C.S.; Sin, D.W.M. Evaluation of chemical indicators for monitoring freshness of food and determination of volatile amines in fish by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 224, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péneau, S.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Escher, F.; Nuessli, J. A comprehensive approach to evaluate the freshness of strawberries and carrots. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 45, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safren, O.; Alchanatis, V.; Ostrovsky, V.; Levi, O. Detection of Green Apples in Hyperspectral Images of Apple-Tree Foliage Using Machine Vision. Trans. Asabe 2007, 50, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.L.; Yang, W.Z.; Wang, S.L. Classification of foreign fibers in cotton lint using machine vision and multi-class support vector machine. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 74, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Paulsen, M.R. Corn whiteness measurement and classification using machine vision. Trans. Asae 2000, 43, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burks, T.F.; Shearer, S.A.; Green, J.D.; Heath, J.R. Influence of weed maturity levels on species classification using machine vision. Weed Sci. 2002, 50, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cozzolino, D.; Cynkar, W.U.; Gishen, M.; Colby, C.B. Geographic classification of Spanish and Australian Tempranillo red wines by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy combined with multivariate analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6754–6759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.P.; Zhou, Y.; Ying, Y.B.; Lu, H.; Xu, H. Discrimination of pear varieties using three classification methods based on near-infrared spectroscopy. Trans. Asabe 2007, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Tao, W.; Zhengjun, Q.; Jiyu, P.; Chu, Z.; Yong, H. Fast detection of striped stem-borer (Chilo suppressalis Walker) infested rice seedling based on visible/near-infrared hyperspectral imaging system. Sensors 2017, 17, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.J.; Lamb, D.W.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, J.H. Identification of yellow rust in wheat using in-situ spectral reflectance measurements and airborne hyperspectral imaging. Precis. Agric. 2007, 8, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, D.; Aleixos, N.; Gómez-Sanchis, J.; Cubero, S.; García-Navarrete, O.L.; Blasco, J. Recent advances and applications of hyperspectral imaging for fruit and vegetable quality assessment. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2012, 5, 1121–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.L.; Ma, Y.S.; Li, L.L.; Cheng, J.H. Rapid and Non-destructive Determination of Oil Content of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Using Hyperspectral Imaging Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmasry, G.; Wang, N.; Vigneault, C.; Qiao, J.; Elsayed, A. Early detection of apple bruises on different background colors using hyperspectral imaging. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wan, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Q. Detection of insect-damaged vegetable soybeans using hyperspectral transmittance image. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovenzana, V.; Beghi, R.; Buratti, S.; Civelli, R.; Guidetti, R. Monitoring of fresh-cut Valerianella locusta Laterr. shelf life by electronic nose and VIS–NIR spectroscopy. Talanta 2014, 120, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, M.A.; Lleó, L.; Diezma-Iglesias, B.; Roger, J.M.; Ruiz-Altisent, M. Monitoring spinach shelf-life with hyperspectral image through packaging films. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, M.T.; Pérez-Marín, D.; Flores-Rojas, K.; Guerrero, J.E.; Garrido-Varo, A. Use of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy for shelf-life discrimination of green asparagus stored in a cool room under controlled atmosphere. Talanta 2009, 78, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, R. What is principal component analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bro, R.; Smilde, A.K. Principal component analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Q.; Cheng, J.H.; Sun, D.W.; Zeng, X.A. Advances in Feature Selection Methods for Hyperspectral Image Processing in Food Industry Applications: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1368–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, X.P.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; He, Y.; Zhou, W.J. Mid-infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics to detect Sclerotinia stem rot on oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) leaves. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burges, C.J.C. A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1998, 2, 121–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; He, Y. Identification of coffee bean varieties using hyperspectral imaging: Influence of preprocessing methods and pixel-wise spectra analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.-K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüello, F.; Heras, D.B. ELM-based spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral images using extended morphological profiles and composite feature mappings. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Keydan, G.P.; Merzlyak, M.N.; Gitelson, C. Three-band model for noninvasive estimation of chlorophyll carotenoids and anthocyanin contents in higher plant leaves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganathan, G.K.; Cluff, K.; Samal, A.; Calkins, C.R.; Jones, D.D.; Meyer, G.E.; Subbiah, J. Three dimensional chemometric analyses of hyperspectral images for beef tenderness forecasting. J. Food Eng. 2015, 169, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Heitschmidt, G.W.; Ni, X.Z.; Windham, W.R.; Hawkins, S.; Chu, X. Identification of aflatoxin B1 on maize kernel surfaces using hyperspectral imaging. Food Control 2014, 42, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Lawrence, K.C.; Heitschmidt, G.W.; Windham, W.R.; Peng, Y.K.; Xuan, C.; Zhang, N.N. Classification of Different Level of Aflatoxin B1 on Corn Kernels Surface Using Short-Wave Infrared Reflectance Hyperspectral Imaging; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.R.; He, Y. Application of near-infrared hyperspectral imaging to discriminate different geographical origins of Chinese wolfberries. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.P.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, P.; He, Y. Discrimination of Transgenic Maize Kernel Using NIR Hyperspectral Imaging and Multivariate Data Analysis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gila, D.M.; Marchal, P.C.; Garcia, J.G.; Ortega, J.G. Hyperspectral imaging for determination of some quality parameters for olive oil. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automation & Computing, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
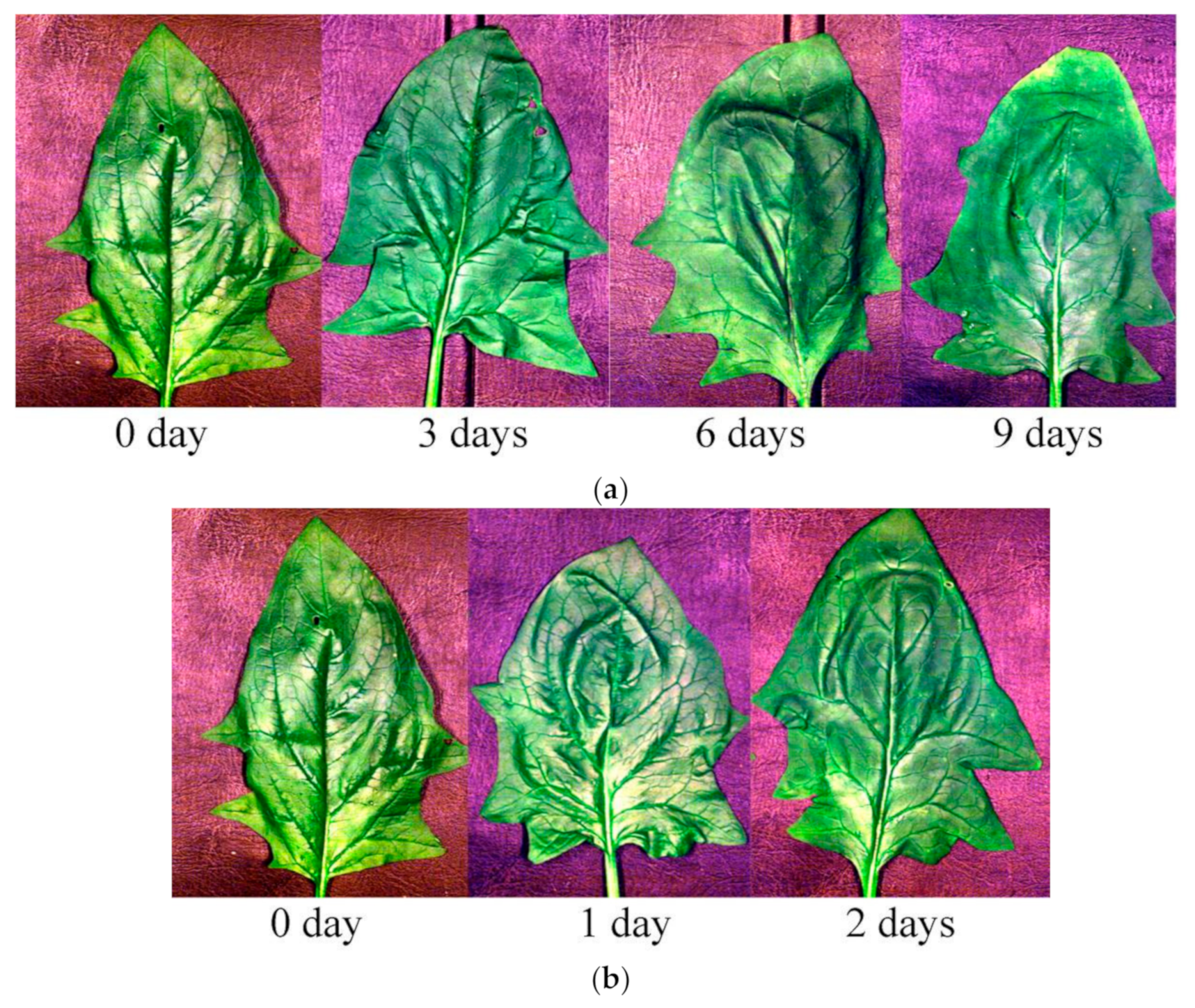



| Hyperspectral Imaging System | Temperature (°C) | No. | Effective Wavelengths (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vis-NIR | 4 | 15 | 506, 518, 538, 566, 636, 643, 697, 704, 707, 711, 714, 719, 739, 753, 765 |
| 20 | 12 | 506, 518, 538, 636, 643, 698, 709, 714, 720, 739, 753, 765 | |
| NIR | 4 | 14 | 988, 1032, 1132, 1164, 1204, 1321, 1348, 1375, 1406, 1429, 1460, 1473, 1511, 1632 |
| 20 | 13 | 995, 1032, 1136, 1164, 1200, 1311, 1348, 1375, 1406, 1429, 1460, 1473, 1632 |
| Temperature (°C) | Classifier | Parameter 1 | Full Spectra (%) | Parameter | Effective Wavelengths (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Prediction | Calibration | Prediction | ||||
| 4 | PLS-DA | 12 | 100 | 100 | 11 | 100 | 100 |
| SVM | (108, 1) | 100 | 100 | (106, 102) | 95 | 92.5 | |
| ELM | 10 | 100 | 100 | 11 | 100 | 100 | |
| 20 | PLS-DA | 11 | 100 | 100 | 12 | 100 | 96.67 |
| SVM | (106, 102) | 98.33 | 100 | (104, 105) | 95.00 | 86.67 | |
| ELM | 13 | 100 | 100 | 19 | 100 | 100 | |
| Temperature (°C) | Classifier | Parameter 1 | Full Spectra (%) | Parameter | Effective Wavelengths (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Prediction | Calibration | Prediction | ||||
| 4 | PLS-DA | 10 | 100 | 100 | 10 | 98.75 | 100 |
| SVM | (106, 103) | 100 | 97.50 | (106, 104) | 98.75 | 92.50 | |
| ELM | 12 | 100 | 100 | 18 | 100 | 100 | |
| 20 | PLS-DA | 4 | 100 | 100 | 4 | 100 | 100 |
| SVM | (103, 103) | 100 | 100 | (103, 105) | 100 | 100 | |
| ELM | 7 | 100 | 100 | 8 | 100 | 100 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Feng, L.; Zhang, C.; Bao, Y.; He, Y. Identifying Freshness of Spinach Leaves Stored at Different Temperatures Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Foods 2019, 8, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090356
Zhu S, Feng L, Zhang C, Bao Y, He Y. Identifying Freshness of Spinach Leaves Stored at Different Temperatures Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Foods. 2019; 8(9):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090356
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Susu, Lei Feng, Chu Zhang, Yidan Bao, and Yong He. 2019. "Identifying Freshness of Spinach Leaves Stored at Different Temperatures Using Hyperspectral Imaging" Foods 8, no. 9: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090356
APA StyleZhu, S., Feng, L., Zhang, C., Bao, Y., & He, Y. (2019). Identifying Freshness of Spinach Leaves Stored at Different Temperatures Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Foods, 8(9), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8090356








