Impact of Storage Temperature on Green Tea Quality: Insights from Sensory Analysis and Chemical Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Materials
2.3. Conventional Sensory Assessment
2.4. Analysis of Biochemical Constituents
2.5. Extraction of Volatile Compounds
2.6. Analysis of Volatile Compounds
2.7. Analysis of the Effect of Moisture Content on Green Tea Quality
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of Storage Temperatures on the Biochemical Characteristics of Green Tea
3.1.1. Amino Acids
3.1.2. Sugar Content
3.1.3. Water Extracts
3.2. Effect of Storage Temperatures on Green Tea Metabolites
3.2.1. Polyphenols
3.2.2. Flavonoids
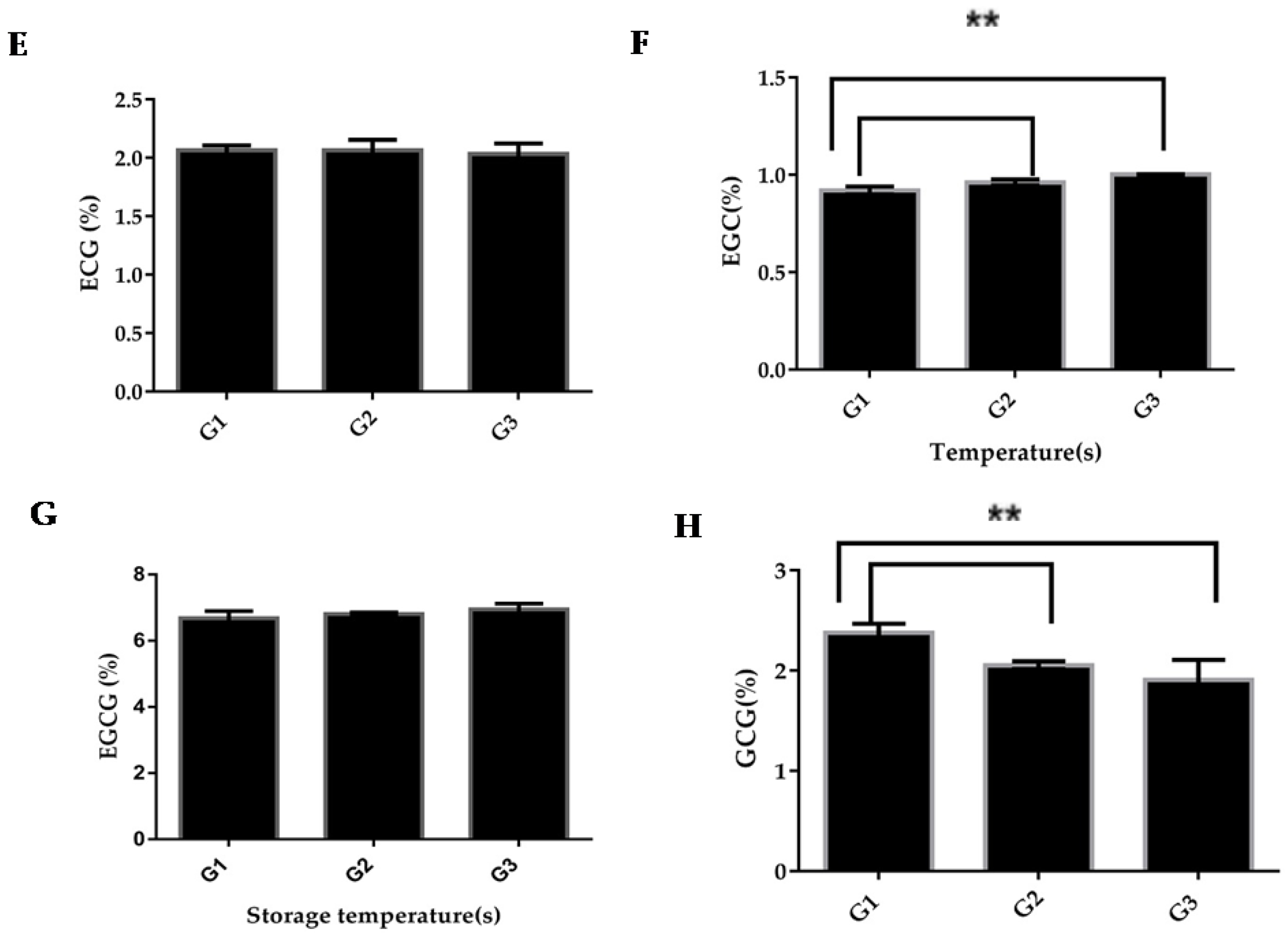
3.2.3. Catechins
3.3. Temperature-Related Changes in Green Tea Phytochemicals
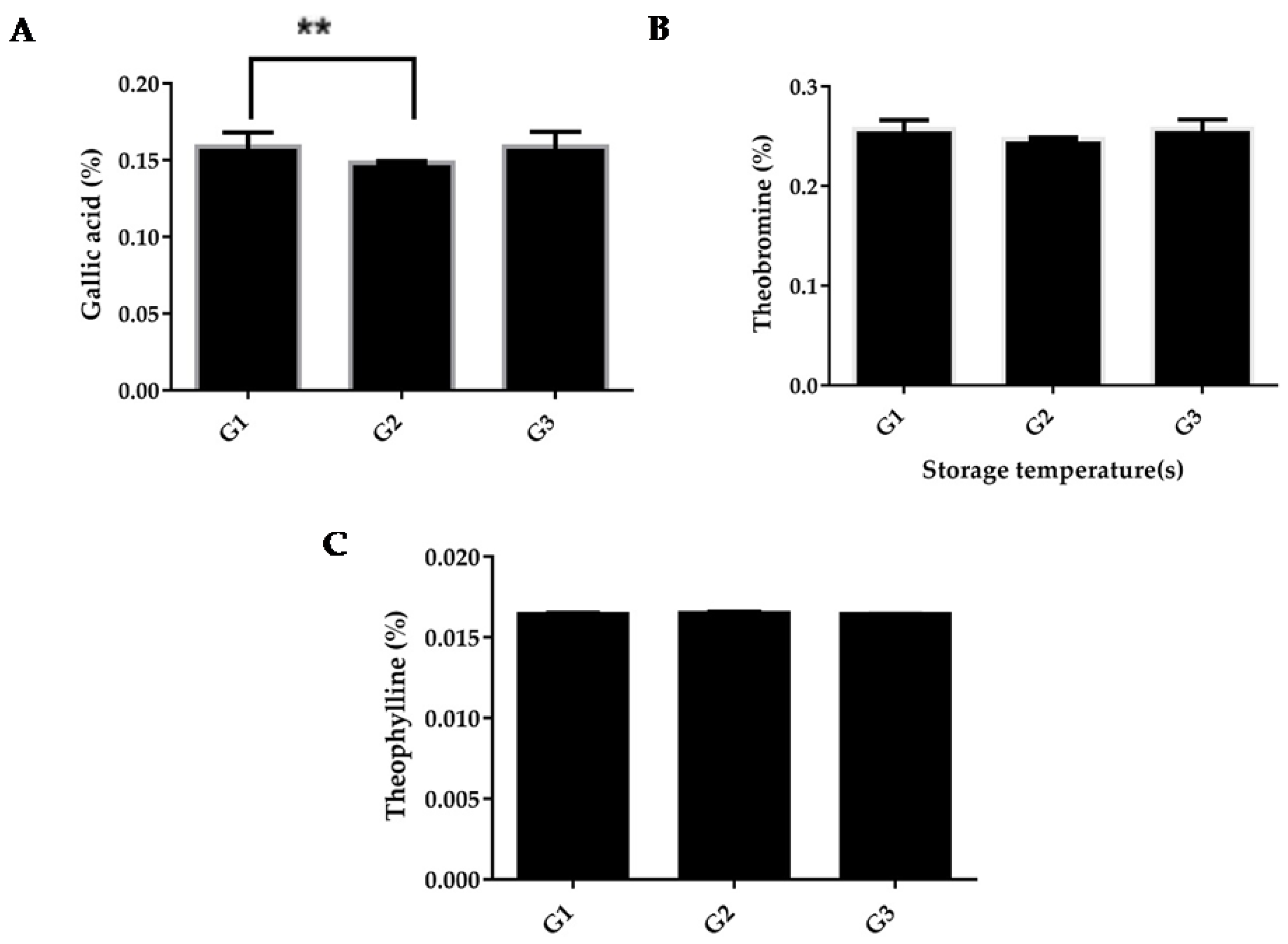
3.3.1. Gallic Acid
3.3.2. Theophylline
3.3.3. Theobromine
3.4. Impact of Temperature during Storage on Volatile Substances
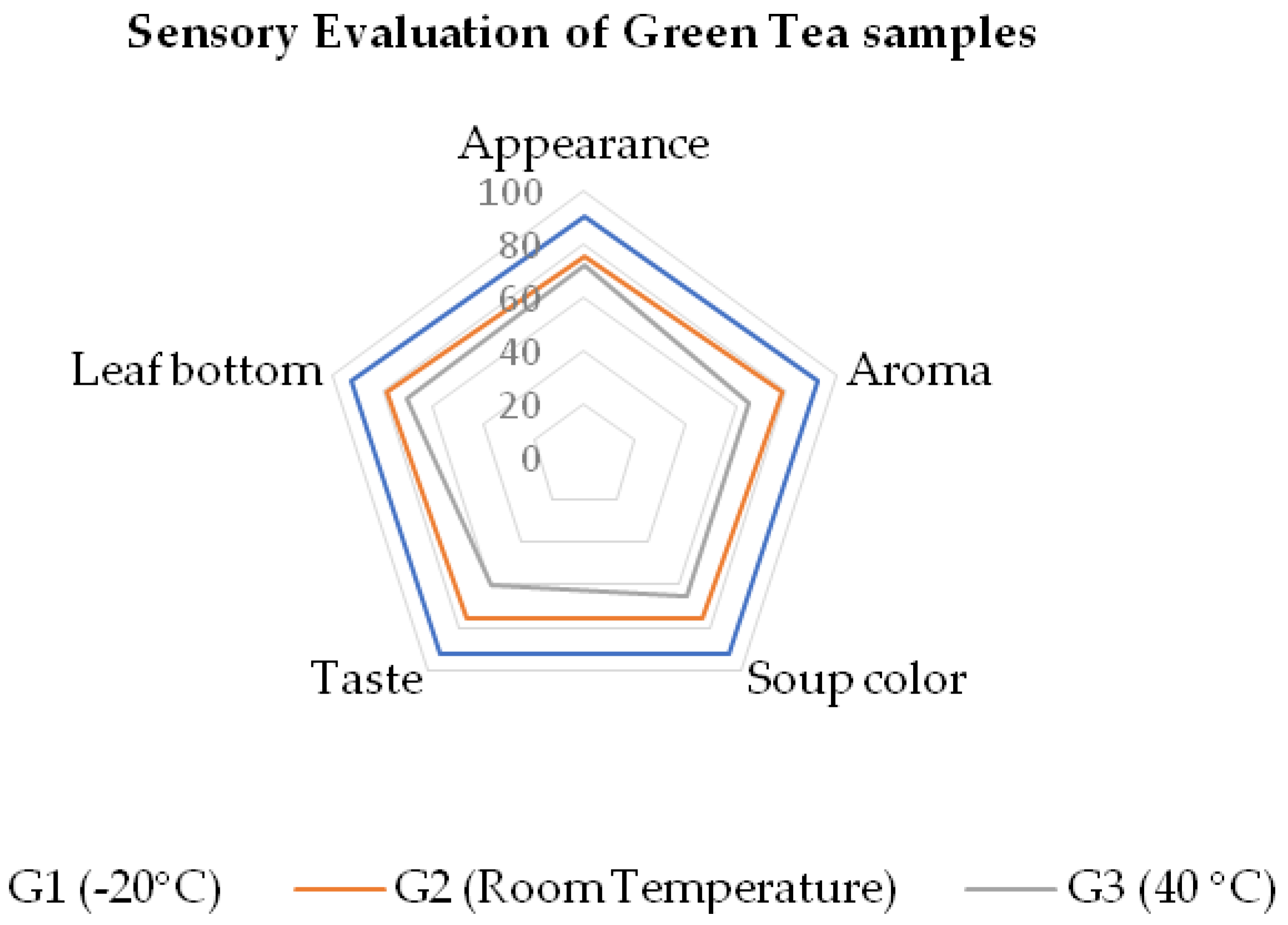
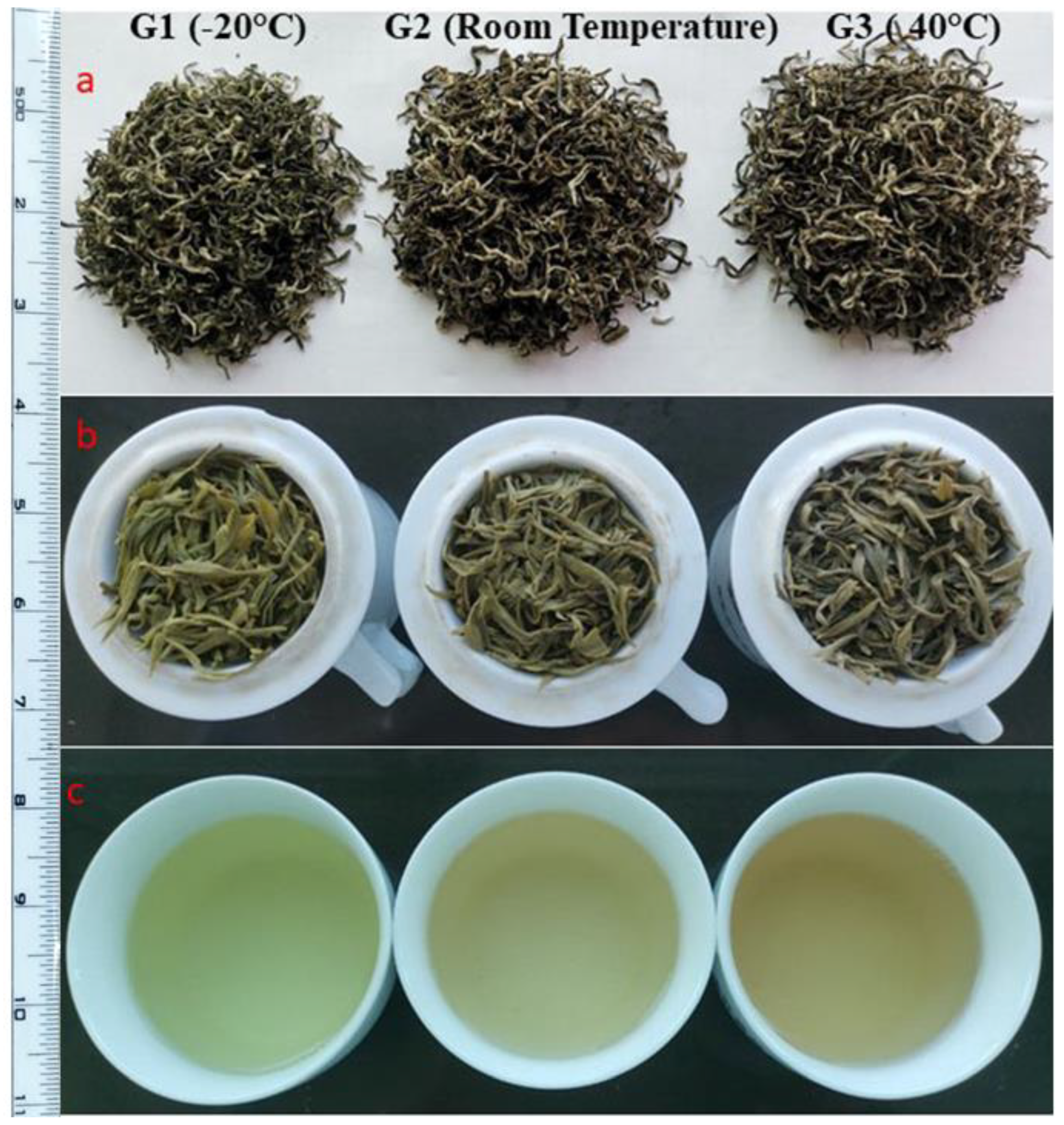
3.5. Changes in Appearance, Aroma, Soup Colour, Taste, and Leaf Bottom
3.6. Effect of Moisture Content on Green Tea Quality
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altunkaya, A. Partial purification and characterization of polyphenoloxidase from Turkish tea leaf (Camellia sinensis L.). Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razic, S.; Kuntic, V. Diverse elements in herbal tea products consumed in serbia using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Arora, D.; Jeet Kaur, G.; Kaur, H. Antibacterial activity of tea and coffee: Their extracts and preparations. Int. J. Food Prop. 2009, 12, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.fao.org/publications/home/fao-flagship-publications/the-state-of-food-and-agriculture/en (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Ho, C.T.; Lin, J.K.; Shahidi, F. Chemistry and health promoting properties. In Tea and Tea Products; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Available online: https://www.routledge.com/Tea-and-Tea-Products-Chemistry-and-Health-Promoting-Properties/Ho-Lin-Shahidi/p/book/9780849380822 (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Damiani, E.; Bacchetti, T.; Padella, L.; Tiano, L.; Carloni, P. Antioxidant activity of different white teas: Comparison of hot and cold tea infusions. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2014, 33, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komes, D.; Horžić, D.; Belščak, A.; Ganić, K.K.; Vulić, I. Green tea preparation and its influence on the content of bioactive compounds. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Jian, L. Tea and Health. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Pasrija, D.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Techniques for Extraction of Green Tea Polyphenols: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 935–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Li, C.W.; Shih, Y.T.; Chuang, L.T. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of lower-polymerized polyphenols in oolong tea. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekal, A.; Drozdz, P.; Pyrzynska, K. Comparison of the antioxidant properties of commonly consumed commercial teas. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.S.; Ahmad, R.S.; Sultan, M.T.; Qayyum, M.M.N.; Naz, A. Green Tea and Anticancer Perspectives: Updates from Last Decade. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda-Yamamoto, M.; Tachibana, H. Anti-Allergic Action of 0-methylated EGCG in Green Tea Cultivar Benifuuki. J. Food Drug Anal. 2012, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Gao, C.; Wu, W.; Kong, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, W. The flavor characteristics and antioxidant capability of aged Jinhua white tea and the mechanisms of its dynamic evolution during long-term aging. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Wen, S.; Sun, L.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, J.; Lai, Z.; Li, Z.; Lai, X.; et al. Metabolomics reveals the effects of different storage times on the acidity quality and metabolites of large-leaf black tea. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Yuan, E.; Chen, R.; Yan, F.; Lai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; et al. Metabolomics and electronic tongue reveal the effects of different storage years on metabolites and taste quality of Oolong Tea. Food Control 2023, 152, 109847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, C.; Cui, L.; Liu, Z.; Liang, J. Effects of Different Expansion Temperatures on the Non-Volatile Qualities of Tea Stems. Foods 2024, 13, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Taylor, L.S.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Mauer, L.J. Kinetic study of catechin stability: Effects of ph, concentration, and temperature. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12531–12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, C.D.; Soysa, P. Extraction Kinetics of phytochemicals and antioxidant activity during black tea (Camellia sinensis L.) brewing. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelebek, H. LC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS characterization of phenolic constituents in Turkish black tea: Effect of infusion time and temperature. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Burillo, S.; Giménez, R.; Rufián-Henares, J.A.; Pastoriza, S. Effect of brewing time and temperature on antioxidant capacity and phenols of white tea: Relationship with sensory properties. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Helliwell, K. Epimerisation of catechins in green tea infusions. Food Chem. 2000, 70, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qu, F.; Wang, P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X. Characterization analysis of flavor compounds in green teas at different drying temperature. LWT 2022, 161, 113394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukatsu, S.; Hara, T. Effect of Storage Condition on the Qualities of Green Tea. ChagyoKenkyuHokoku (Tea Res. J.) 1970, 1970, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Ma, M.; Li, C.; Luo, L. Stability of tea polyphenols solution with different pH at different temperatures. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Huang, W.Y.; Lin, W.S.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, S.L.; Lin, Y.S. Effects of infusion and storage on antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of black tea. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaomei, W.; Han, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, L.; Chen, C.; Han, B.; Wang, M. The Flavor Characteristics, Antioxidant Capability, and Storage Year Discrimination Based on Back propagation Neural Network of Organic Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) during Long-Term Storage. Foods 2024, 13, 753. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Han, S.; Mei, X.; Wang, M.; Han, B. Changes in profiles of volatile compounds and prediction of the storage year of organic green tea during the long-term storage. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Wen, J.; An, K.; Yu, Y.; Zou, B.; Guo, M. A comparative study of aromatic characterization of Yingde Black Tea infusions in different steeping temperatures. LWT 2021, 143, 110860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocieczek, A.; Pukszta, T.; Żyłka, K.; Kirieieva, N. The influence of storage conditions on the stability of selected health-promoting properties of tea. LWT 2023, 184, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhuang, S.; Gu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Xiao, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Y. Effect of storage time on the volatile compounds and taste quality of Meixian green tea. LWT 2023, 173, 114320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.P.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zheng, L.; Yin, P.; Ye, F.; Gui, A.H.; Wang, S.P.; Wang, X.P.; Tang, J.; et al. Characterization of stale odor in green tea formed during storage: Unraveling improvements arising from reprocessing by baking. LWT 2023, 174, 114458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, L.; Liao, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Zeng, L. Effects of brewing conditions on the phytochemical composition, sensory qualities and antioxidant activity of green tea infusion: A study using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, E.; Hua, F.; Schuckers, S.; Andreescu, S.; Bradley, R. Effects of brewing conditions on the antioxidant capacity of twenty-four commercial green tea varieties. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachinello, M.R.; Vital, A.C.P.; Chambo, A.P.S.; Wielewski, P.; Matumoto-Pintro, P.T. Effect of freeze-dried green tea added in hamburgers as source of antioxidant during freezing storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Ni, D. Hot-Air Drying Significantly Improves the Quality and Functional Activity of Orange Black Tea Compared with Traditional Sunlight Drying. Foods 2023, 12, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T, 2013. GB/T 8305-2013; Tea—Determination of Water-Soluble Substance Content. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2013. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/3/39348.html (accessed on 9 January 2024).
- Mao, A.; Su, H.; Fang, S.; Chen, X.; Ning, J.; Ho, C.; Wan, X. Effects of roasting treatment on non-volatile compounds and taste of green tea. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 8313-2018; Method for Detection of Tea Polyphenols and Catechins Content in Tea. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Chang, C.C.; Yang, M.H.; Wen, H.M.; Chern, J.C. Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J. Food Drug Anal. 2002, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; He, W.; Zeng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cheng, H. Catechin contents in tea (Camellia sinensis) as affected by cultivar and environment and their relation to chlorophyll contents. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liao, Y.; Tang, G.; Dong, F.; Zeng, L. Effects of temperature and light on quality-related metabolites in tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze] leaves. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Que, Z. Formation and transformation of Maillard reaction products in black tea during fermentation and baking processes. Food Res. Int. 2014, 57, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Wang, D. Effects of storage conditions on sensory quality and chemical composition of black tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tu, Z.; Chen, L.; Lin, J.Z.; Zhu, H.K.; Ye, Y. Analysis of metabolites in green tea during the roasting process using non-targeted metabolomics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Long, P.P.; Ho, C.T.; Wang, Y.J.; Kan, Z.P.; Cao, L.T.; Zhang, L.; Wan, X.C. LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Reveals the Chemical Changes of Polyphenols during High-Temperature Roasting of Large-Leaf Yellow Tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5405–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Sun, J.; Kan, J.; Jin, C.; Zhang, X. Effects of storage temperature on amino acid degradation in peanut butter. Food Chem. 2018, 259, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Z.; Bai, S.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, X. Effects of storage time and temperature on free sugar contents of tea. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C1602–C1607. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X. Changes in soluble sugar and oligosaccharide compositions in green tea during storage at different temperatures. Food Chem. 2021, 339. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Taylor, L.S.; Mauer, L.J. Degradation kinetics of catechins in green tea powder: Effects of temperature and relative humidity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6082–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lim, S.W.; Cho, S.H.; Choi, S.G.; Heo, H.J.; Lee, S.C. Effect of relative humidity and storage temperature on the quality of green tea powder. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 38, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Wong, Y.F. Antioxidant activity of green tea catechins in vivo and in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3603–3608. [Google Scholar]
- Aslı, C.A.N.; Vural, N.; Şarer, E. Determination of volatile compounds in green tea and black tea from Turkey by using HS-SPME and GC-MS. İstanb. J. Pharm. 2020, 50, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Stavric, B. Methylxanthines: Toxicity to humans. 3. Theobromine, paraxanthine and the combined effects of methylxanthines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1988, 26, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sang, S.; Yuan, L.; Ho, C.T. Identification of theaflavin-3,3′-digallate as the most bioactive compound in black tea extract. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4080–4089. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.L.; Lin, C.C.; Zhang, D.; Jeng, K.C.G.; Yao, P.W.; Chuang, L.T.; Kuo, S.L.; Hou, C.W. Fresh green tea and gallic acid ameliorate oxidative stress in kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2328–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.T.; Zheng, X.; Li, S. Tea aroma formation. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhang, W.G.; Zhao, J.; Yu, R.L. Effect of storage temperature on sensory quality and volatile compound profiles of dry-cured hams from Chinese BaXuyen crossbred pigs. Meat Sci. 2020, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Xie, D.; Xie, J. Identification of key odorants responsible for tea-like aroma quality of green teas and green tea granules. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.P.; Song, Q.S.; Li, D.X.; Wan, X.C. Discrimination of the production season of chinese green tea by chemical analysis in combination with supervised pattern recognition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7064–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.H.; Pang, X.L.; Chen, D.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.S.; Wu, J.H. Evaluation of Chinese tea by the electronic nose and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: Correlation with sensory properties and classification according to grade level. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; Levin, C.E.; Lee, S.U.; Kozukue, N. Stability of green tea catechins in commercial tea leaves during storage for 6 months. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, H. Off-flavor components of green tea during preservation. Int. J. Mater. Form. 1987, 19, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, S.J.; Lorenzo, T.V. Chlorophylls in Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 29, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.G. Effects of low temperature on tea quality in the process of production and storage. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 7957–7958. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.L.; Yin, J.F.; Xu, Y. Application research of calm-holding temperature-far infrared technology for green tea processing. J. Tea Sci. 2013, 33, 336–348. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Q.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, T. Recommended storage temperature for green tea based on sensory quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4333–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higdon, J.V.; Frei, B. Tea Catechins and Polyphenols: Health Effects, Metabolism, and Antioxidant Functions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 43, 89–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Hossain, M.R.; D’Souza, M.J. Sensory characteristics, chemical composition, and consumer acceptance of black tea extracts: A feasibility study. Foods 2018, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.J.; Hua, J.J.; Jiang, Y.W.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Yuan, H.B. Influence of fixation methods on the chestnut-like aroma of green tea and dynamics of key aroma substances. Food Res Int. 2020, 136, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.C. Biochemistry of tea, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 160–180. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.L.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, M.L.; Yang, C.; Xie, D.C.; Tan, J.F. Variation patterns in the content of glycosides during green tea manufacturing by a modification-specific metabolomics approach: Enzymatic reaction promoting an increase in the glycosidically bound volatiles at the pan firing stage. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; He, C.; Zhu, J.Y.; Qu, F.F.; Ran, M.Q.; Ai, Z.Y. Effect of shaping methods on the quality of E-Cha No.10 green tea products. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 2020, 35, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.S.; Mi, X.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Yu, Y.B.; Li, S.L.; Qi, Y.G. Effect of different processing techniques on the quality of “Shaancha 1” green tea. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ji, K.W. Research progress on the relationship between tea shape and quality. Tea Fujian 2000, 22, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Storage Conditions | G1 | G2 | G3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | SD | Average | SD | Average | SD | |
| Theobromine (%) | 0.257 | 0.008 | 0.247 | 0.0016 | 0.257 | 0.009 |
| Gallic acid (%) | 0.158 | 0.009 | 0.148 | 0.001 | 0.158 | 0.0095 |
| Theophylline (%) | 0.016 | 0.0000746 | 0.0164 | 0.0001 | 0.016 | 0.0000187 |
| Soluble sugar content (%) | 5.573 | 0.030 | 5.663 | 0.279 | 5.67 | 0.157 |
| Contents (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL No. | Compound Name | G1 | G2 | G3 |
| 1 | Dimethyl sulphide | 11.96 ± 2.31 | 3.13 ± 1.12 | 0.36 ± 0.16 |
| 2 | 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl- | 7.65 ± 1.09 | 5.05 ± 1.27 | 3.76 ± 0.86 |
| 3 | Indole | 6.65 ± 1.12 | 2.34 ± 0.91 | 3.02 ± 0.29 |
| 4 | Phenylethyl Alcohol | 5.86 ± 0.98 | 17.03 ± 2.93 | 5.86 ± 1.11 |
| 5 | n-Caproic acid vinyl ester | 4.49 ± 1.23 | 4.94 ± 1.39 | 3.49 ± 1.17 |
| 6 | 1,6-Octadien-3-ol, 3,7-dimethyl- | 4.45 ± 1.08 | 5 ± 1.73 | 3.48 ± 0.65 |
| 7 | 2-Cyclopenten-1-one, 3-methyl-2-(2-pentenyl)-, (Z)- | 4.44 ± 0.87 | 4.16 ± 1.23 | 3.75 ± 0.49 |
| 8 | Benzyl Alcohol | 3.84 ± 0.93 | 13.69 ± 2.18 | 15.17 ± 2.11 |
| 9 | Benzaldehyde | 0.57 ± 0.24 | 2.27 ± 0.63 | 6.7 ± 1.44 |
| 10 | 1-Pentanol | 7.32 ± 1.63 | 5.46 ± 1.14 | 0.64 ± 0.76 |
| Conditions | Tea Polyphenols (%) | Amino Acids (%) | Water Extracts (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | SD | Average | SD | Average | SD | |
| 5% MC (Freezing) | 23.54 | 0.29 | 4.54 | 0.08 | 39.25 | 0.24 |
| 3% MC (RT) | 23.2 | 0.67 | 4.52 | 0.05 | 40.95 | 0.09 |
| 5% MC (RT) | 22.73 | 0.35 | 4.58 | 0.07 | 39.99 | 0.02 |
| 7% MC (RT) | 23.01 | 0.03 | 4.38 | 0.08 | 38.72 | 0.31 |
| EGCG | GCG | ECG | ||||
| Average | SD | Average | SD | Average | SD | |
| 5% MC (Freezing) | 4.41 | 0.01 | 2.86 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 0.005774 |
| 3% MC (RT) | 4.46 | 0.02 | 2.59 | 0.01 | 1.23 | 0.01 |
| 5% MC (RT) | 4.293333 | 0.015275 | 2.52 | 0.01 | 1.19 | 0.01 |
| 7% MC (RT) | 4.26 | 0.01 | 2.57 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Yu, P.; Zhong, N.; Huang, H.; Zheng, H. Impact of Storage Temperature on Green Tea Quality: Insights from Sensory Analysis and Chemical Composition. Beverages 2024, 10, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020035
Zhao X, Yu P, Zhong N, Huang H, Zheng H. Impact of Storage Temperature on Green Tea Quality: Insights from Sensory Analysis and Chemical Composition. Beverages. 2024; 10(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xi, Penghui Yu, Ni Zhong, Hao Huang, and Hongfa Zheng. 2024. "Impact of Storage Temperature on Green Tea Quality: Insights from Sensory Analysis and Chemical Composition" Beverages 10, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020035
APA StyleZhao, X., Yu, P., Zhong, N., Huang, H., & Zheng, H. (2024). Impact of Storage Temperature on Green Tea Quality: Insights from Sensory Analysis and Chemical Composition. Beverages, 10(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10020035





