Myocardial Adiponectin Isoform Shift in Dogs with Congestive Heart Failure—A Comparison to Hibernating Brown Bears (Ursus arctos horribilis)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dogs
2.2. Bears
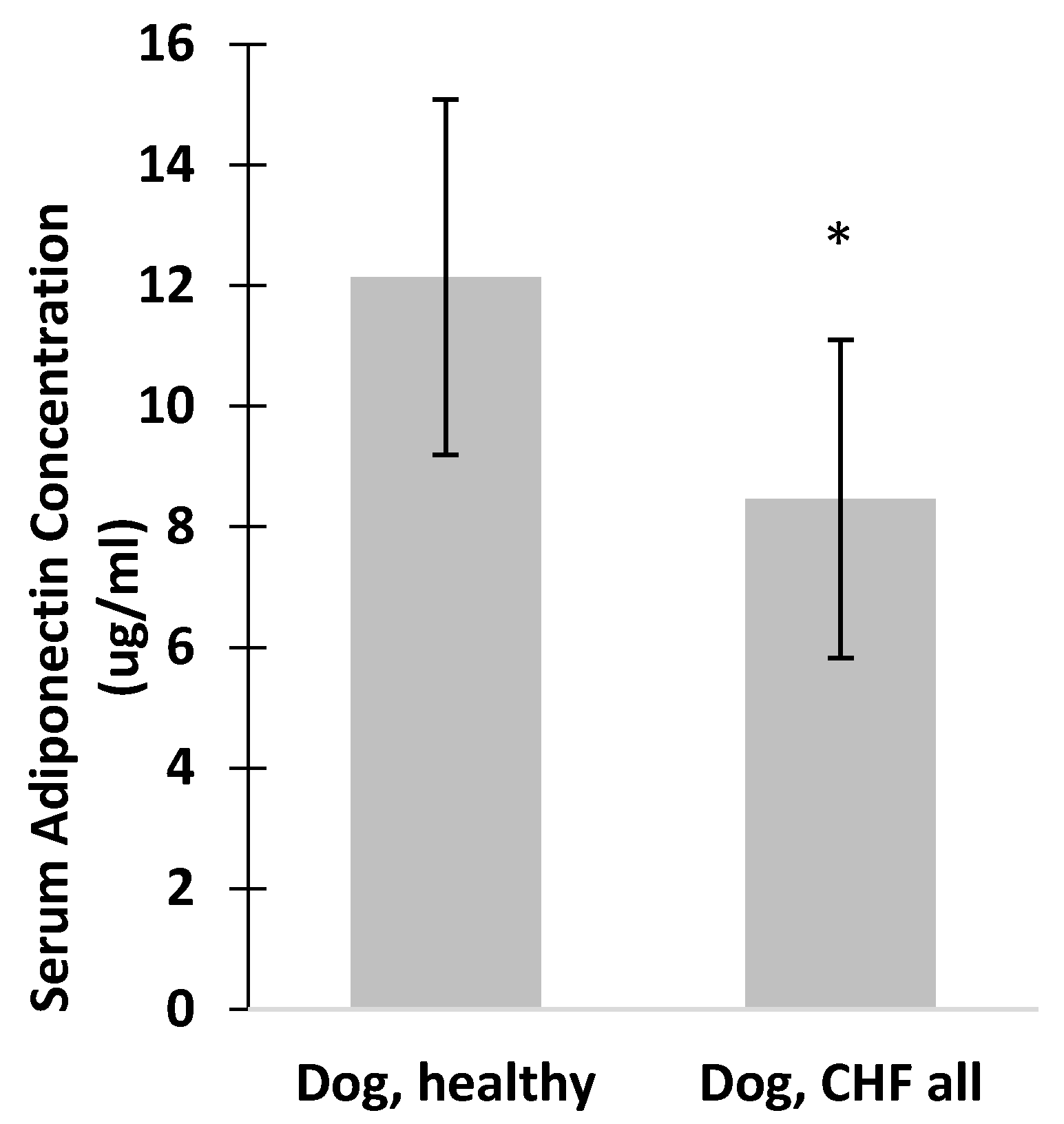
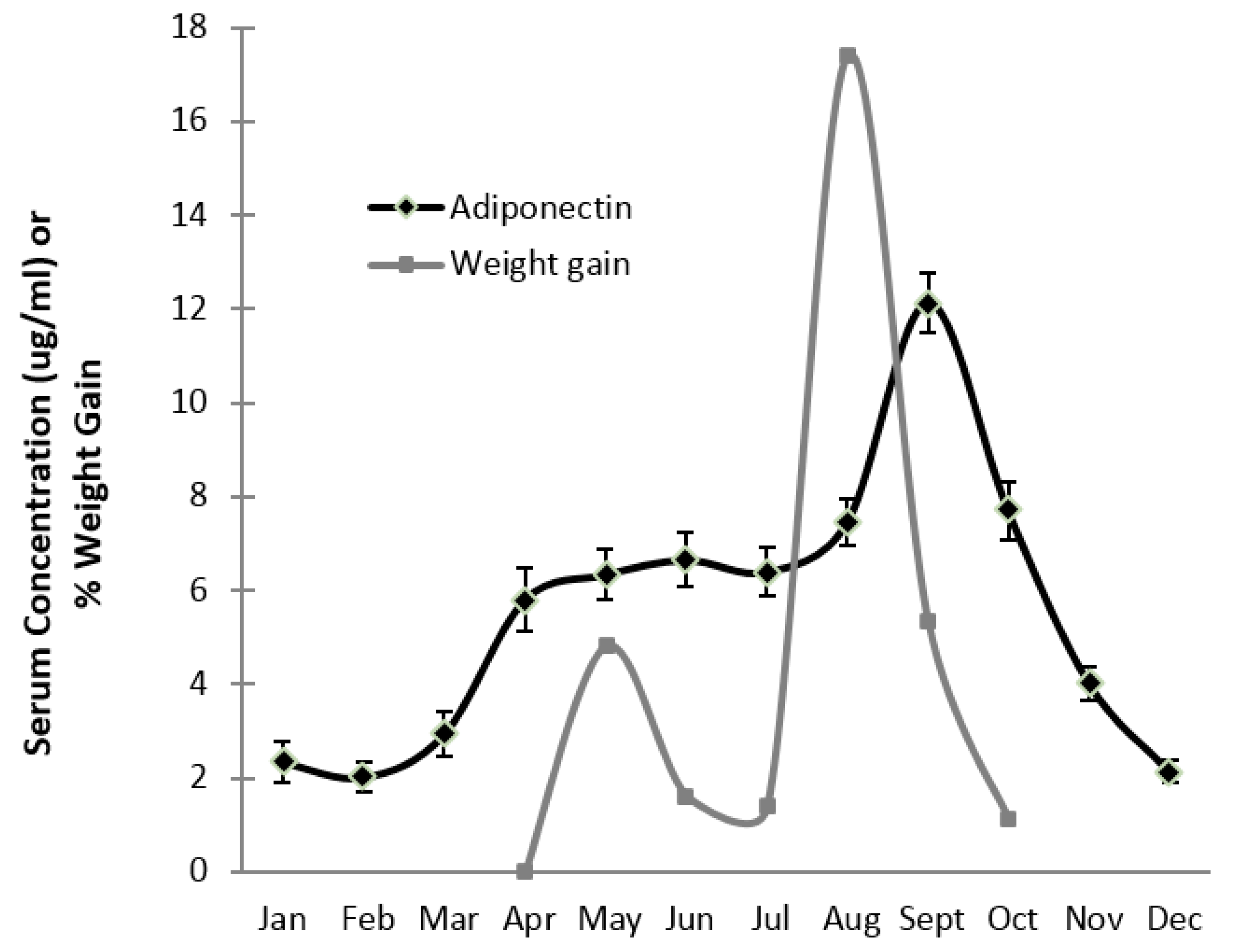
2.3. Serum Adiponectin
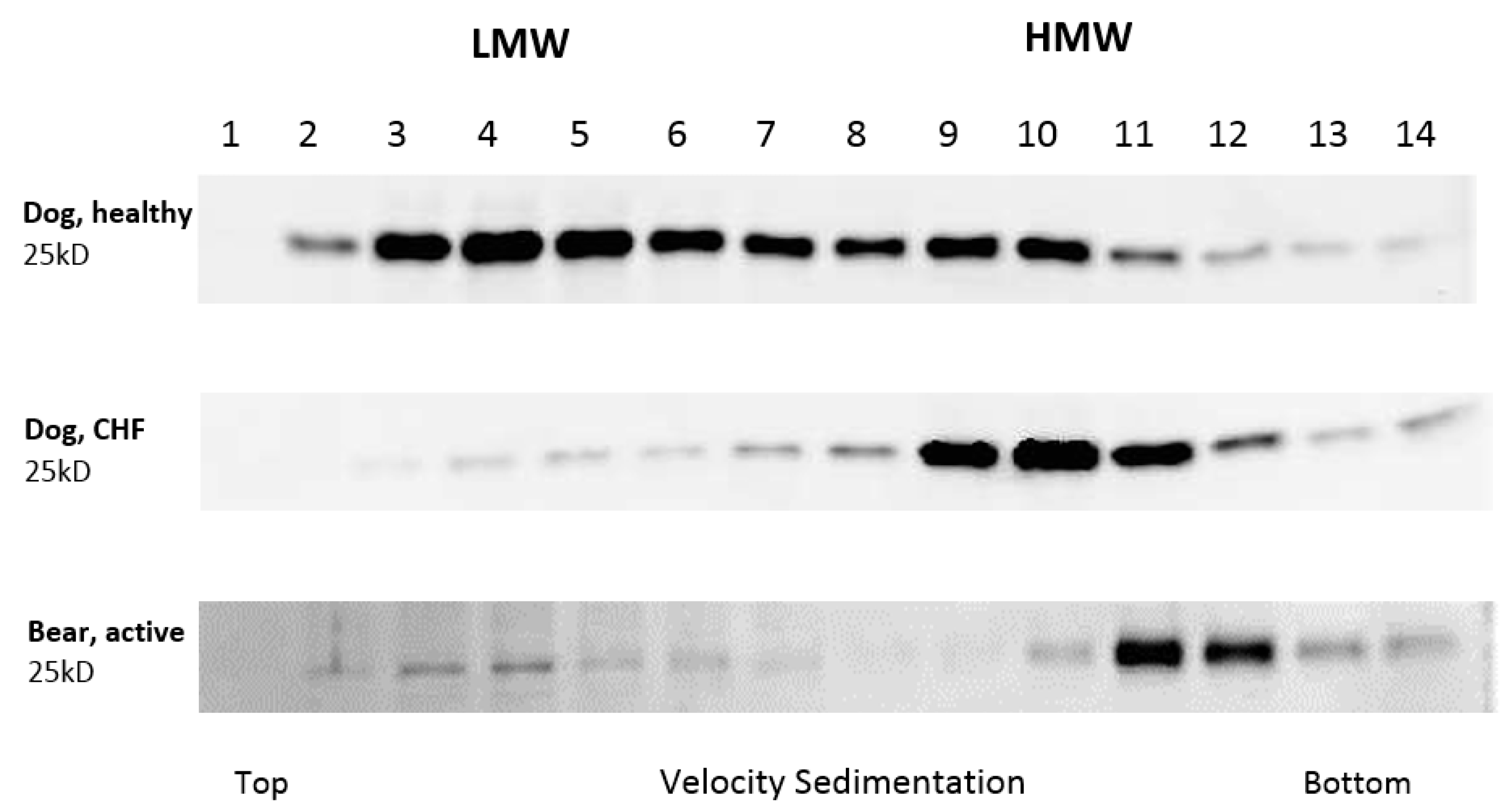
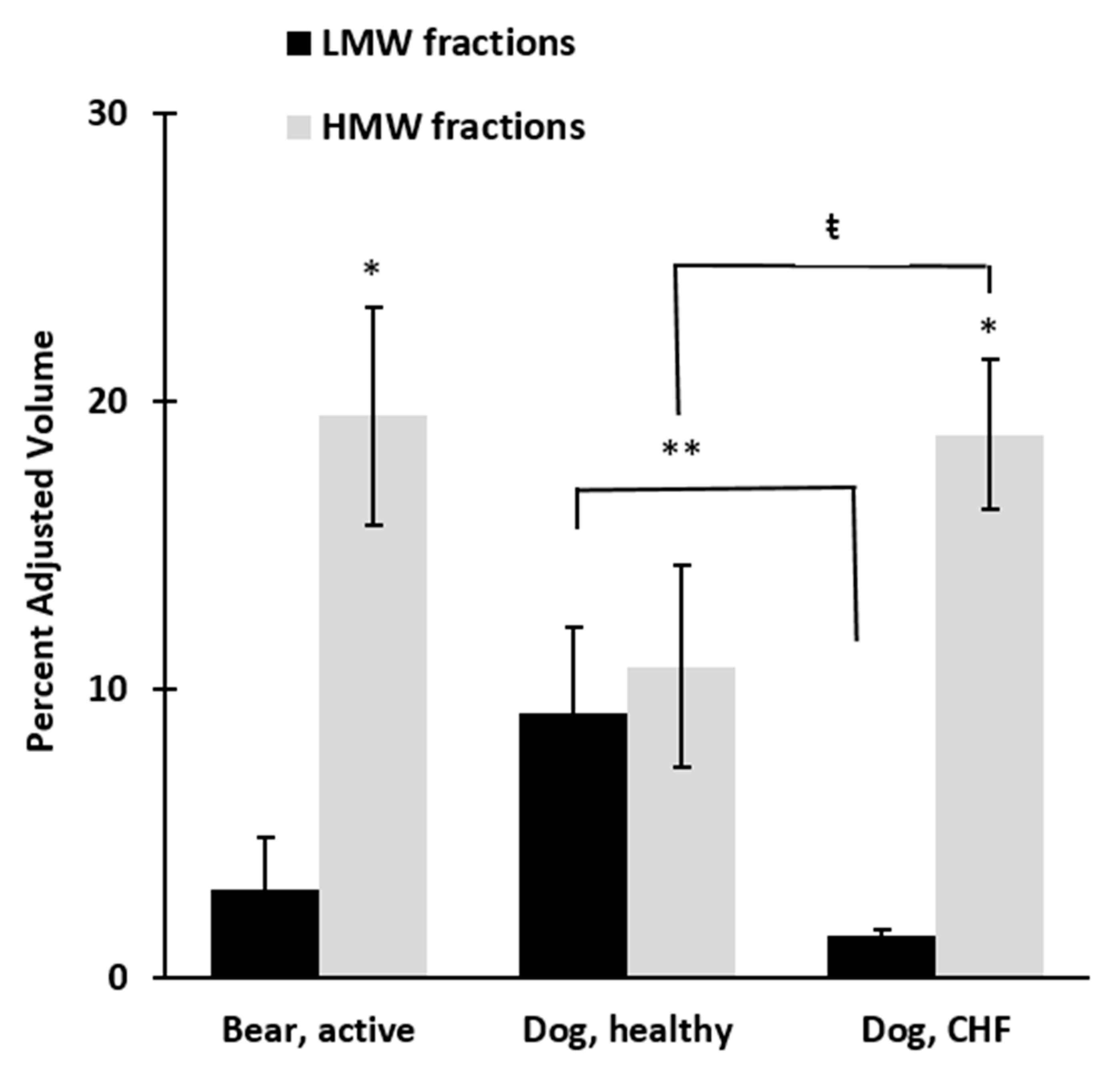
2.4. Western Blot Protocol
2.5. Statistical Analysis
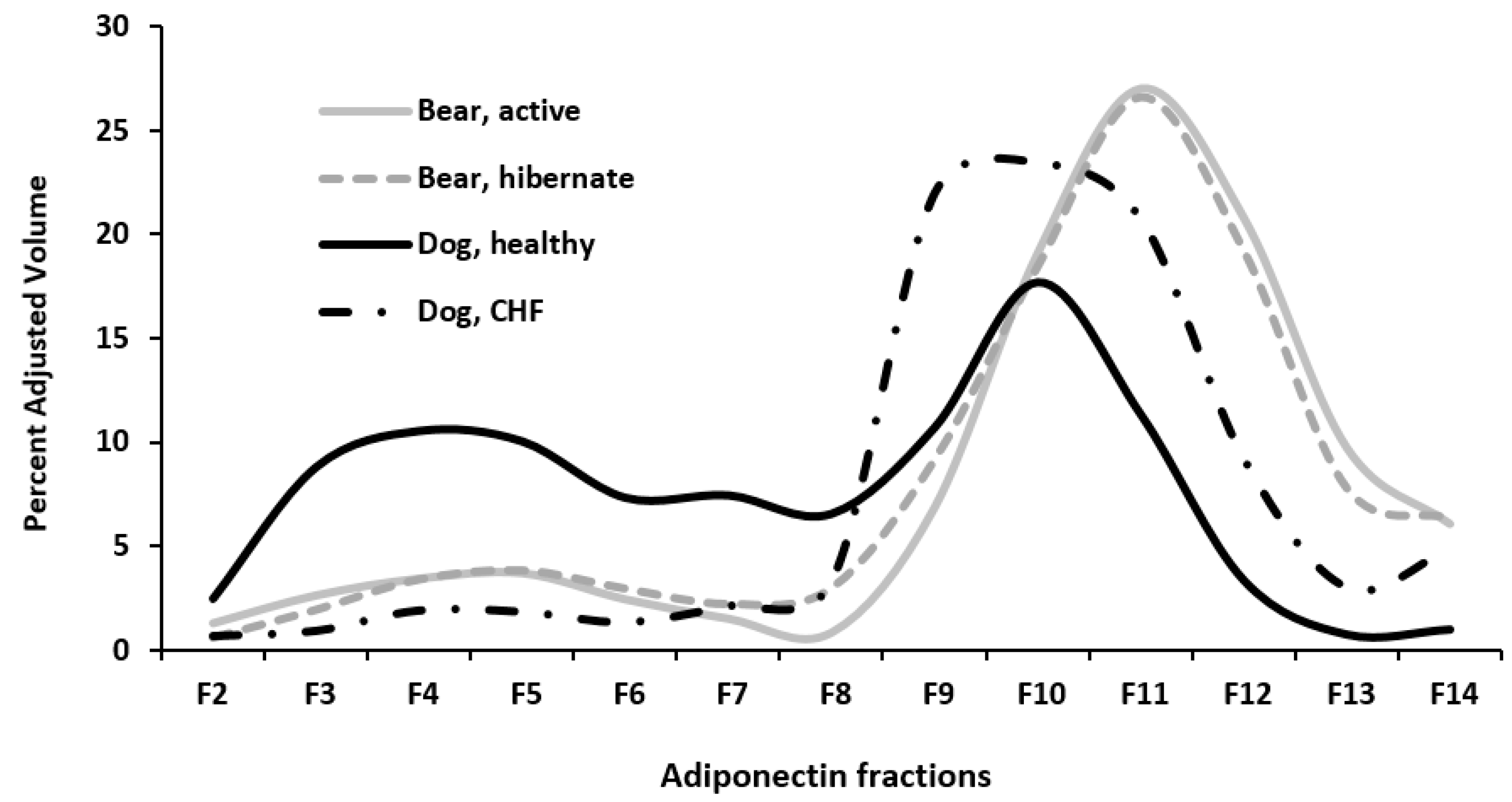
3. Results
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balsan, G.A.; Vieira, J.L.; Oliveira, A.M.; Portal, V.L. Relationship between adiponectin, obesity and insulin resistance. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2015, 61, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker-Duffen, J.L.; Walsh, K. Cardiometabolic effects of adiponectin. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.K.; Ciaraldi, T.; Henry, R.R. Adiponectin in health and disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florant, G.L.; Porst, H.; Peiffer, A.; Hudachek, S.F.; Pittman, C.; Summers, S.A.; Rajala, M.W.; Scherer, P.E. Fat-cell mass, serum leptin and adiponectin changes during weight gain and loss in yellow-bellied marmots (Marmota flaviventris). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2004, 174, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigano, K.S.; Gehring, J.L.; Evans Hutzenbiler, B.D.; Chen, A.V.; Nelson, O.L.; Vella, C.A.; Robbins, C.T.; Jansen, H.J. Life in the fat lane: Seasonal regulation of insulin sensitivity, food intake, and adipose biology in brown bears. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2017, 187, 649–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.W.; Wang, J.; Hug, C.; Tsao, T.S.; Lodish, H.F. A family of Acrp30/adiponectin structural and functional paralogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10302–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitten, M.; Robin, J.P.; Oudart, H.; Pévet, P.; Habold, C. Hormonal changes and energy substrate availability during the hibernation cycle of Syrian hamsters. Horm. Behav. 2013, 64, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffes, M.W.; Gross, M.D.; Schreiner, P.J.; Yu, X.; Hilner, J.E.; Gingerich, R.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Serum adiponectin in young adults—Interactions with central adiposity, circulating levels of glucose, and insulin resistance: The CARDIA study. Ann. Epidemiol. 2004, 14, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, T.A.; Ouchi, N.; Shibata, R.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin actions in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 74, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.H.; Combs, T.P.; Du, X.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyer, C.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hotta, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Pratley, R.E.; Tataranni, P.A. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, B.K.; Lim, Y.H.; Kim, M.K.; Choi, B.Y.; Shin, J. The relationship between adiponectin and left ventricular mass index varies with the risk of left ventricular hypertrophy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Patal, S.; Wexler, D.; Sharabi, Y.; Peleg, E.; Kamari, Y.; Grossman, E.; Sheps, D.; Keren, G.; Roth, A. Circulating adiponectin concentrations in patients with congestive heart failure. Heart 2006, 92, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Novartis Found. Symp. 2007, 286, 164–176, discussion 76–82, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Nio, Y.; Maki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takazawa, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; et al. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzel, M.S.; Scimia, M.C.; Zumstein, P.M.; Walsh, K.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin is critical for adiponectin-mediated cardioprotection in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 120, 4342–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, C.; Wang, J.; Ahmad, N.S.; Bogan, J.S.; Tsao, T.S.; Lodish, H.F. T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10308–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, T.S.; Tomas, E.; Murrey, H.E.; Hug, C.; Lee, D.H.; Ruderman, N.B.; Heuser, J.E.; Lodish, H.F. Role of disulfide bonds in Acrp30/adiponectin structure and signaling specificity. Different oligomers activate different signal transduction pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50810–50817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waki, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Kita, S.; Ito, Y.; Hada, Y.; Uchida, S.; Tsuchida, A.; Takekawa, S.; Kadowaki, T. Generation of globular fragment of adiponectin by leukocyte elastase secreted by monocytic cell line THP-1. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.H.; Quon, M.J.; Kim, J.A.; Koh, K.K. Adiponectin and cardiovascular disease: Response to therapeutic interventions. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Hawkins, M.; Combs, T.P.; Rajala, M.W.; Doebber, T.; Berger, J.P.; Wagner, J.A.; Wu, M.; Knopps, A.; Xiang, A.H.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Kahn, S.E.; Olefsky, J.M.; Buchanan, T.A.; Scherer, P.E. Complex distribution, not absolute amount of adiponectin, correlates with thiazolidinedione-mediated improvement in insulin sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12152–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissebah, A.H.; Sonnenberg, G.E.; Myklebust, J.; Goldstein, M.; Broman, K.; James, R.G.; Marks, J.A.; Krakower, G.R.; Jacob, H.J.; Weber, J.; Martin, L.; Blangero, J.; Comuzzie, A.G. Quantitative trait loci on chromosomes 3 and 17 influence phenotypes of the metabolic syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14478–14483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidemann, C.; Sun, Q.; van Dam, R.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Zhang, C.; Tworoger, S.S.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Hu, F.B. Total and high-molecular-weight adiponectin and resistin in relation to the risk for type 2 diabetes in women. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 149, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanayakkara, G.; Kariharan, T.; Wang, L.; Zhong, J.; Amin, R. The cardio-protective signaling and mechanisms of adiponectin. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 2, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Shibata, R.; Walsh, K. Cardioprotection by adiponectin. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 16, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Takashima, S.; Maeda, N.; Ouchi, N.; Komamura, K.; Shimomura, I.; Hori, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Kitakaze, M. Exacerbation of heart failure in adiponectin-deficient mice due to impaired regulation of AMPK and glucose metabolism. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 67, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, R.; Ouchi, N.; Ito, M.; Kihara, S.; Shiojima, I.; Pimentel, D.R.; Kumada, M.; Sato, K.; Schiekofer, S.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Adiponectin-mediated modulation of hypertrophic signals in the heart. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skurk, C.; Wittchen, F.; Suckau, L.; Witt, H.; Noutsias, M.; Fechner, H.; Schultheiss, H.P.; Poller, W. Description of a local cardiac adiponectin system and its deregulation in dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, H.; Obata, J.E.; Kodama, Y.; Kitta, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Mende, A.; Kawabata, K.; Saito, Y.; Fujioka, D.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Adiponectin is released from the heart in patients with heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 132, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Sweeney, G. Direct effects of adipokines on the heart: Focus on adiponectin. Heart Fail. Rev. 2013, 18, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinmura, K. Is adiponectin a bystander or a mediator in heart failure? The tangled thread of a good-natured adipokine in aging and cardiovascular disease. Heart Fail. Rev. 2010, 15, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, G.; Li, W.; Guo, R.; Yang, J.G.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Peng, Y.G.; Wang, Z.W. Serum total adiponectin level and the risk of cardiovascular disease in general population: A meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sente, T.; Gevaert, A.; Van Berendoncks, A.; Vrints, C.J.; Hoymans, V.Y. The evolving role of adiponectin as an additive biomarker in HFrEF. Heart Fail. Rev. 2016, 21, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, T.; Hashimura, K.; Asakura, M.; Ogai, A.; Amaki, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Kanzaki, H.; Sonoda, M.; Nishizawa, H.; Funahashi, T.; Kitakaze, M. Dynamic changes in plasma total and high molecular weight adiponectin levels in acute heart failure. J. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, C.; Bonagura, J.; Ettinger, S.; Fox, P.; Gordon, S.; Haggstrom, J.; Hamlin, R.; Keene, B.; Luis-Fuentes, V.; Stepien, R. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of canine chronic valvular heart disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgarelli, M.; Savarino, P.; Crosara, S.; Santilli, R.A.; Chiavegato, D.; Poggi, M.; Bellino, C.; La Rosa, G.; Zanatta, R.; Haggstrom, J.; Tarducci, A. Survival characteristics and prognostic variables of dogs with mitral regurgitation attributable to myxomatous valve disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2008, 22, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, L.H.; Fredholm, M.; Pedersen, H.D. Epidemiology and inheritance of mitral valve prolapse in Dachshunds. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1999, 13, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, L.; Häggström, J.; Kvart, C.; Juneja, R.K. Relationship between parental cardiac status in Cavalier King Charles spaniels and prevalence and severity of chronic valvular disease in offspring. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1996, 208, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laske, T.G.; Garshelis, D.L.; Iaizzo, P.A. Monitoring the wild black bear's reaction to human and environmental stressors. BMC Physiol. 2011, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, O.L.; Robbins, C.T. Cardiac function adaptations in hibernating grizzly bears (Ursus arctos horribilis). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2010, 180, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, O.L.; Robbins, C.T. Cardiovascular function in large to small hibernators: Bears to ground squirrels. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2015, 185, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toien, O.; Blake, J.; Edgar, D.M.; Grahn, D.A.; Heller, H.C.; Barnes, B.M. Hibernation in black bears: Independence of metabolic suppression from body temperature. Science 2011, 331, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusby, A.L.; Kania, S.A.; Abd-Eldaim, M.; Bartges, J.W.; Kirk, C.A. Detection of serum adiponectin in the cat, bear, and horse using antibody from a commerical ELISA kit. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Du, X.; Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Rajala, M.W.; Schulthess, T.; Engel, J.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. Structure-function studies of the adipocyte-secreted hormone Acrp30/adiponectin. Implications fpr metabolic regulation and bioactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9073–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Winter, J.C. Using the Student’s t-test with extremely small sample sizes. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2013, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Ceron, J.J.; Holden, S.L.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Biourge, V.; Morris, P.J.; German, A.J. Obesity-related metabolic dysfunction in dogs: A comparison with human metabolic syndrome. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Carrillo-Sanchez, J.D.; García-Martinez, J.D.; Tecles, F.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; German, A.J.; Ceron, J.J. Measurement of salivary adiponectin concentrations in dogs. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 43, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nelson, O.L.; Wood, R.M.; Häggström, J.; Kvart, C.; Robbins, C.T. Myocardial Adiponectin Isoform Shift in Dogs with Congestive Heart Failure—A Comparison to Hibernating Brown Bears (Ursus arctos horribilis). Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4030035
Nelson OL, Wood RM, Häggström J, Kvart C, Robbins CT. Myocardial Adiponectin Isoform Shift in Dogs with Congestive Heart Failure—A Comparison to Hibernating Brown Bears (Ursus arctos horribilis). Veterinary Sciences. 2017; 4(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleNelson, O. Lynne, Rachael M. Wood, Jens Häggström, Clarence Kvart, and Charles T. Robbins. 2017. "Myocardial Adiponectin Isoform Shift in Dogs with Congestive Heart Failure—A Comparison to Hibernating Brown Bears (Ursus arctos horribilis)" Veterinary Sciences 4, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4030035
APA StyleNelson, O. L., Wood, R. M., Häggström, J., Kvart, C., & Robbins, C. T. (2017). Myocardial Adiponectin Isoform Shift in Dogs with Congestive Heart Failure—A Comparison to Hibernating Brown Bears (Ursus arctos horribilis). Veterinary Sciences, 4(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4030035




