The Nasal Nitric Oxide Response to External Acoustic Energy: A Pilot Study of Sampling Dynamics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subject Recruitment
2.2. Study Procedures
2.2.1. Both Experiments
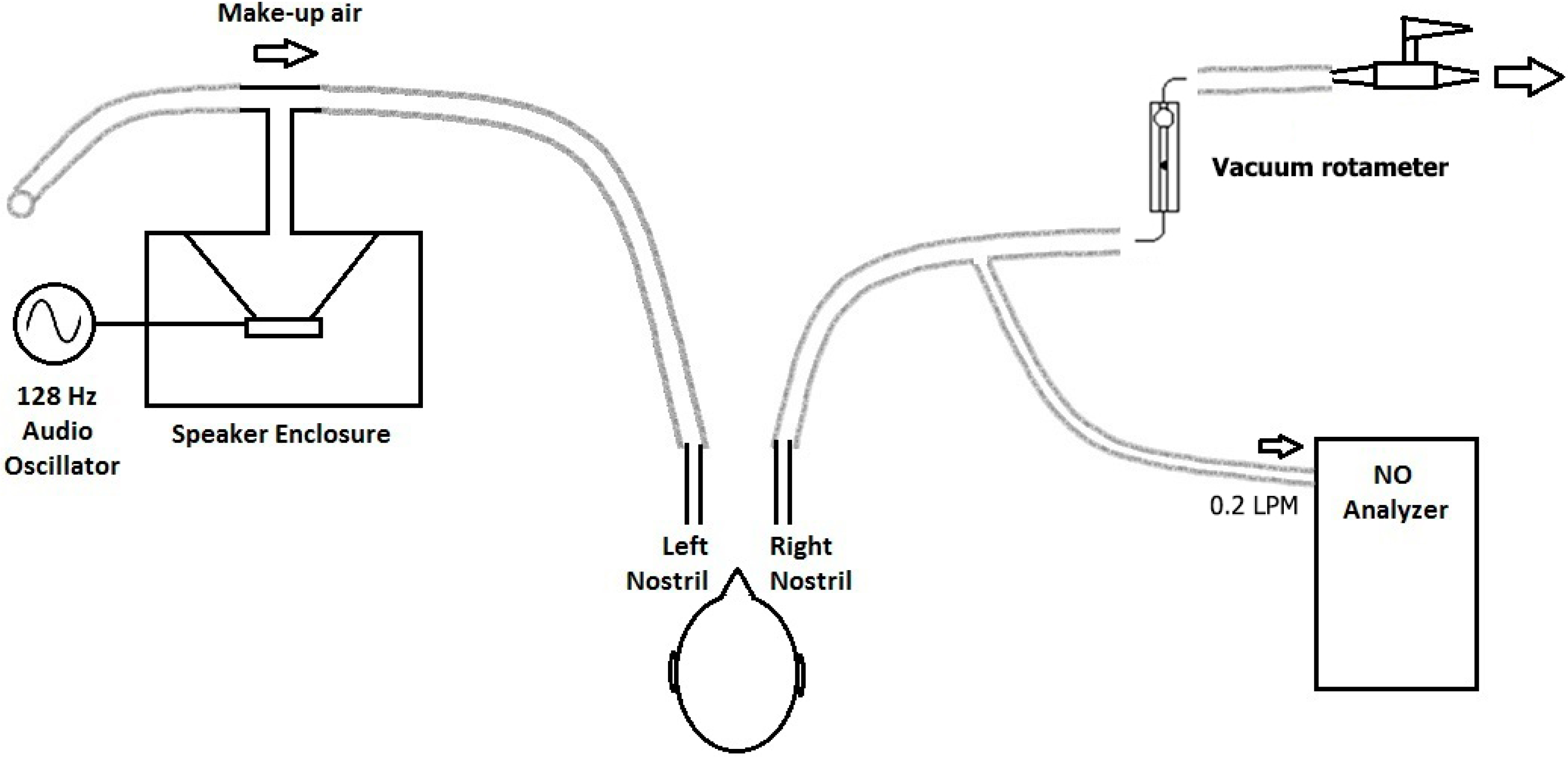
2.2.2. Experiment 1
2.2.3. Experiment 2
2.2.4. Longitudinal Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1

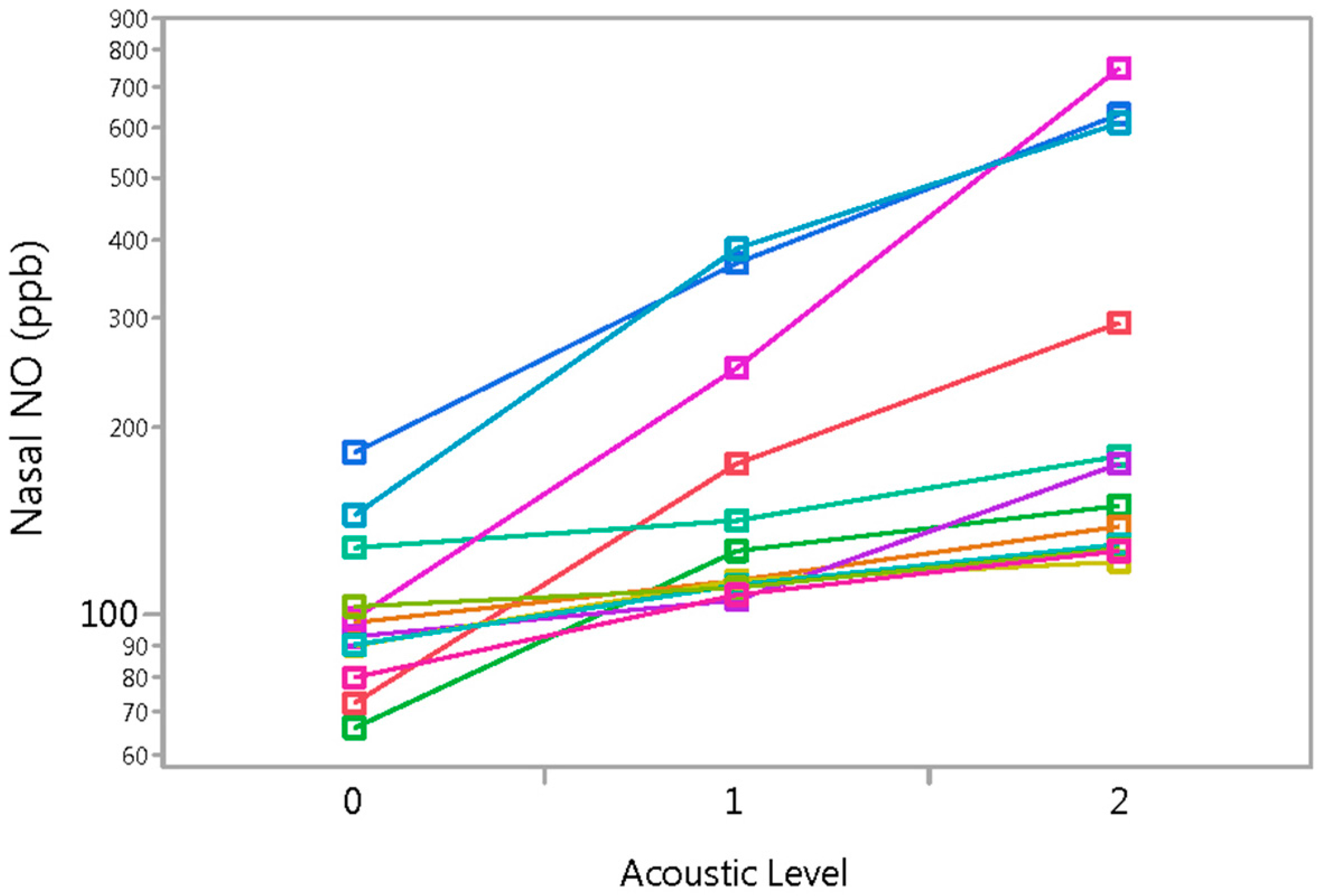
3.2. Experiment 2
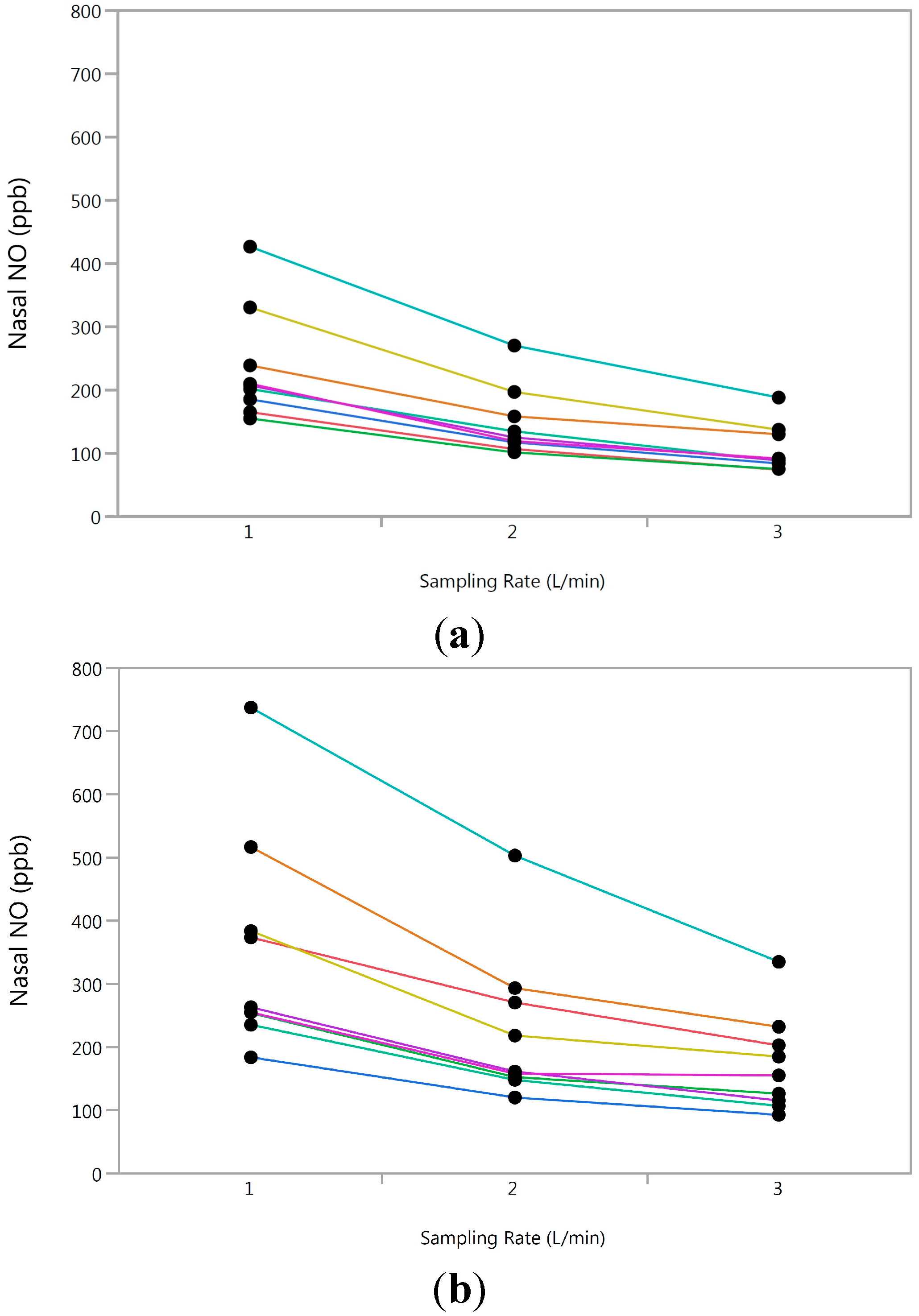
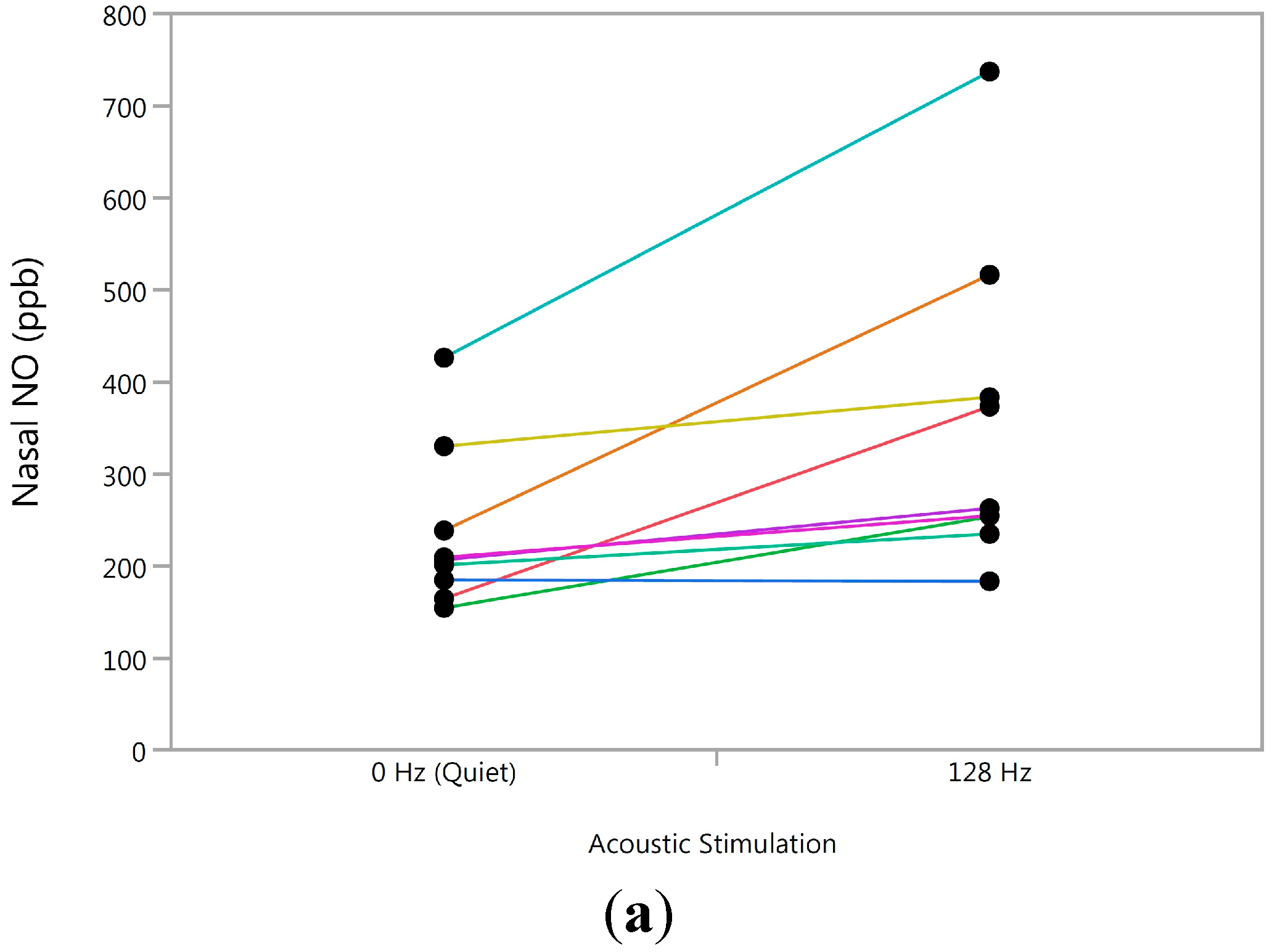

3.3. Longitudinal Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jorissen, M.; Lefevere, L.; Willems, T. Nasal nitric oxide. Allergy 2001, 56, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.G.; Mottram, C. The use of fraction of exhaled nitric oxide in pulmonary practice. Chest 2008, 133, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adappa, N.D.; Zhang, Z.; Palmer, J.N.; Kennedy, D.W.; Doghramji, L.; Lysenko, A.; Reed, D.R.; Scott, T.; Zhao, N.W.; Owens, D.; et al. The bitter taste receptor T2R38 is an independent risk factor for chronic rhinosinusitis requiring sinus surgery. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, J.-F.; Didier, A.; Rami, J.; M’Rini, C.; Charlet, J.-P.; Serrano, E.; Besombes, J.-P. Nasal nitric oxide is increased in allergic rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1997, 27, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kharitonov, S.A.; Rajakulasingam, K.; O’Connor, B.; Durham, S.R.; Barnes, P.J. Nasal nitric oxide is increased in patients with asthma and allergic rhinitis and may be modulated by nasal glucocorticoids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 99, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, U.; Bryden, K.; Devoy, M.; Howarth, P. Increased levels of exhaled nitric oxide during nasal and oral breathing in subjects with seasonal rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 97, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, A.H.; Sue-Chu, M.; Holmen, T.L.; Langhammer, A.; Bjermer, L. Exhaled and nasal NO levels in allergic rhinitis: relation to sensitization, pollen season and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, P.A.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Clearie, K.; Stewart, M.; Lipworth, B.J. Relationship between fractional exhaled nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide in airways disease. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 105, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irander, K.; Palm, J.P.; Borres, M.P.; Ghafouri, B. Clara cell protein in nasal lavage fluid and nasal nitric oxide—Biomarkers with anti-inflammatory properties in allergic rhinitis. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Rinder, J.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.M.; Alving, K. Nasally exhaled nitric oxide in humans originates mainly in the paranasal sinuses. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1994, 152, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.A.; Cervin, A.; Lindberg, S.; Uddman, R.; Cardell, L.O. The paranasal sinuses as reservoirs for nitric oxide. Acta Otolaryngol. 2002, 122, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinlay, L.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Williamson, P.A.; Lipworth, B.J. Nasal nitric oxide as a measure of osteomeatal complex patency in nasal polyps. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 107, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, J.F.; Flores, P.; Rami, J.; Murris-Espin, M.; Bremont, F.; Pasto I Aguilla, M.; Serrano, E.; Didier, A. Nasal nitric oxide concentration in paranasal sinus inflammatory diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommarito, L.; Guida, G.; Heffle, E.; Badiu, I.; Nebiolo, F.; Usai, A.; de Stefani, A.; Rolla, G. Nasal nitric oxide concentration in suspected chronic rhinosinusitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 101, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantonio, D.; Brouillette, L.; Parikh, A.; Scadding, G.K. Paradoxical low nasal nitric oxide in nasal polyposis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degano, B.; Genestal, M.; Serrano, E.; Rami, J.; Arnal, J.F. Effect of treatment on maxillary sinus and nasal nitric oxide concentrations in patients with nosocomial maxillary sinusitis. Chest 2005, 128, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanz, M.J.; Prendes, S.; Peyrou, N.; Toledo, G.; Ferrer, C.M. Nasal nitric oxide as a noninvasive marker in the antibiotic treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragab, S.M.; Lund, V.J.; Saleh, H.A.; Scadding, G. Nasal nitric oxide in objective evaluation of chronic rhinosinusitis therapy. Allergy 2006, 61, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delclaux, C.; Malinvaud, D.; Chevalier-Bidaud, B.; Callens, E.; Mahut, B.; Bonfils, P. Nitric oxide evaluation in upper and lower respiratory tracts in nasal polyposis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deroee, A.F.; Naraghi, M.; Sontou, A.F.; Ebrahimkhani, M.R.; Dehpour, A.R. Nitric oxide metabolites as biomarkers for follow-up after chronic rhinosinusitis surgery. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2009, 23, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O. Humming greatly increases nasal nitric oxide. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struben, V.M.; Wieringa, M.H.; Mantingh, C.J.; Bruinsma, S.M.; de Jongste, J.C.; Feenstra, L. Silent and humming nasal NO measurements in adults aged 18–70 years. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 35, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shusterman, D.J.; Jansen, K.; Weaver, E.M.; Koenig, JQ. Documentation of the nasal nitric oxide response to humming: methods evaluation. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 37, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniscalco, M.; Weitzberg, E.; Sundberg, J.; Sofia, M.; Lundberg, J.O. Assessment of nasal and sinus nitric oxide output using single-breath humming exhalations. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granqvist, S.; Sundberg, J.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Paranasal sinus ventilation by humming. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniscalco, M.; Sofia, M.; Weitzberg, E.; Carratu, L.; Lundberg, J.O. Nasal nitric oxide measurements before and after repeated humming maneuvers. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 33, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, L.; Hess, A.; Bloch, W.; Michel, O.; Schuster, K.D.; Gäbler, R.; Urban, W. Temporal nitric oxide dynamics in the paranasal sinuses during humming. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Maniscalco, M.; Sofia, M.; Lundblad, L.; Weitzberg, E. Humming, nitric oxide, and paranasal sinus obstruction. JAMA 2003, 289, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniscalco, M.; Sofia, M.; Weitzberg, E.; de Laurentiis, G.; Stanziola, A.; Rossillo, V.; Lundberg, J.O. Humming-induced release of nasal nitric oxide for assessment of sinus obstruction in allergic rhinitis: pilot study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 34, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATS (American Thoracic Society). ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [Google Scholar]
- Shusterman, D.J.; Weaver, E.M.; Goldberg, A.N.; Schick, S.F.; Wong, H.H.; Balmes, J.R. Pilot evaluation of the nasal nitric oxide response to humming as an index of osteomeatal patency. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2012, 26, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Rinder, J.; Rudehill, A.; Jansson, O.; Wiklund, N.P.; Lundberg, J.M.; Alving, K. Calcium-independent and steroid-resistant nitric oxide synthase activity in human paranasal sinus mucosa. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 1344–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennie, C.E.; Hood, C.M.; Blenke, E.J.; Schroter, R.S.; Doorly, D.J.; Jones, H.; Towey, D.; Tolley, N.S. Physical and computational modeling of ventilation of the maxillary sinus. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; Williamson, P.; Anderson, K.; Lipworth, B. Effect of systemic steroids on humming nasal nitric oxide in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 105, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniscalco, M.; Pelaia, G.; Sofia, M. Exhaled nasal nitric oxide during humming: Potential clinical tool in sinonasal disease? Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shusterman, D. The Nasal Nitric Oxide Response to External Acoustic Energy: A Pilot Study of Sampling Dynamics. Sinusitis 2016, 1, 13-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis1010013
Shusterman D. The Nasal Nitric Oxide Response to External Acoustic Energy: A Pilot Study of Sampling Dynamics. Sinusitis. 2016; 1(1):13-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis1010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleShusterman, Dennis. 2016. "The Nasal Nitric Oxide Response to External Acoustic Energy: A Pilot Study of Sampling Dynamics" Sinusitis 1, no. 1: 13-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis1010013
APA StyleShusterman, D. (2016). The Nasal Nitric Oxide Response to External Acoustic Energy: A Pilot Study of Sampling Dynamics. Sinusitis, 1(1), 13-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis1010013




