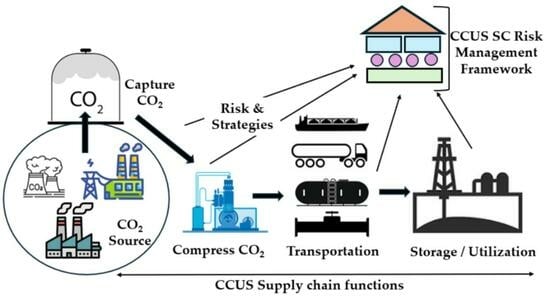
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Risks from Supply Chain Perspective: A Review of the Literature and Conceptual Framework Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review Methodology
2.1. Identifying Research Gap
2.1.1. Descriptive Statistics
2.1.2. Analysis of Risks Based on SC Sectors
2.1.3. Linking with CCUS SC Risk
3. Literature Analysis
3.1. Description of Literature Analysis
3.2. Understanding Literature
4. Review Findings and Discussion
5. Conceptual Framework (CF) of CCUS SC Risk Management
6. Research Implications
6.1. Environmental Implications
6.2. Managerial Implications
6.3. Economic Implications
7. Conclusions
8. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix A
| Work | CO2 Source | Transportation Mode | HR | ENR | RR | ER | TR | SCRM | Optimization | CSC | LCA | CA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | Power plants Cement plants Steel and iron plants | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||||
| [20] | Fossil fuel power Chemical industries Steel, cement plants | Pipeline Ship Tanker | ☑ | |||||||||
| [13] | Industrial processes | Pipeline, truck | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||||
| [83] | Power plant Industrial sites Others | Pipeline, ship, truck, rail | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||
| [84] | Not specified | Not specified | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||||
| [10] | High-emission sources (power plants, industries) and air | Pipeline, ship, truck | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||
| [85] | Industrial and energy sites | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||||
| [86] | Power plant | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||||
| [87] | Power plants, biogas plants, gas processing plants, refineries, cement production plants and others | Road, rail, pipeline | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||||
| [88] | Power plants and multiple other sources | Pipeline, sea carriers, rail, road | ☑ | |||||||||
| [73] | Oil and gas | ☑ | ||||||||||
| [89] | Various industrial and power plants | Pipeline | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||||
| [90] | Not specified | Pipeline | ☑ | |||||||||
| [91] | Not specified | Pipeline | ☑ | |||||||||
| [19] | Not specified | ☑ | ||||||||||
| [92] | European coal and gas power plant | Pipeline | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||||
| [75] | Power plants, cement, iron and steel refineries | Pipeline (tank and ship as alternative) | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||||
| [93] | Not specified | Pipeline | ☑ | |||||||||
| [94] | Power plants | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||||
| [74] | Power plants, steel plants, oil refinery plants, petrochemical plants | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||||
| [95] | Power plants. Iron and steel plants, cement industries | Pipeline, ship, rail, road | ☑ | ☑ | ||||||||
| [96] | Not specified | Pipeline, ship, road, rail | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | |||||||
| [97] | Energy and manufacturing sector | Pipeline | ☑ | ☑ |
References
- Dziejarski, B.; Krzyżyńska, R.; Andersson, K. Current Status of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Technologies in the Global Economy: A Survey of Technical Assessment. Fuel 2023, 342, 127776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhou, S.; Peng, T.; Ou, X. A Review of CO2 Emissions Reduction Technologies and Low-Carbon Development in the Iron and Steel Industry Focusing on China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, J. Optimization-Based Approach for CO2 Utilization in Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Supply Chain. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 139, 106885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, H.; Littlefield, A.A.; Menefee, M.; Kinzer, A.; Hull, T.; Sovacool, B.K.; Bazilian, M.D.; Kim, J.; Griffiths, S. Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage in Review: Sociotechnical Implications for a Carbon Reliant World. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 177, 113215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Han, H.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, G. A Review of Recent Progress of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) in China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Bogle, I.D.L.; Ugo Foscolo, P. Life Cycle Assessment of a Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage Supply Chain in Italy and Germany: Comparison between Carbon Dioxide Storage and Utilization Systems. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 55, 102743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Prospects of Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage for Mitigating Climate Change. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Ashworth, P.; Zhang, S.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y.; Angus, D. China’s Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Policy: A Critical Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Ashworth, P. The Development of Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Research in China: A Bibliometric Perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Teng, F.; McLellan, B.C. A Critical Review on Deployment Planning and Risk Analysis of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) toward Carbon Neutrality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anika, O.C.; Nnabuife, S.G.; Bello, A.; Okoroafor, E.R.; Kuang, B.; Villa, R. Prospects of Low and Zero-Carbon Renewable Fuels in 1.5-Degree Net Zero Emission Actualisation by 2050: A Critical Review. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Dai, S. CCUS As a Second-Best Choice for China’s Carbon Neutrality: An Institutional Analysis. Clim. Policy 2021, 21, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovari, H.; Müller, L.; Mayer, F.; Bardow, A. A Climate-Optimal Supply Chain for CO2 Capture, Utilization, and Storage by Mineralization. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 131750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejski, P.; Chmiel, K.; Subramanian, N.; Kuś, T. Methods and Techniques for CO2 Capture: Review of Potential Solutions and Applications in Modern Energy Technologies. Energies 2022, 15, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Huh, C.; Lee, S.; Chang, D. Comparison of CO2 Liquefaction Pressures for Ship-Based Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Chain. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 52, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminu, M.D.; Nabavi, S.A.; Rochelle, C.A.; Manovic, V. A Review of Developments in Carbon Dioxide Storage. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 1389–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Itakura, K. A State-of-the-Art Review on Technology for Carbon Utilization and Storage. Energies 2023, 16, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishal, V.; Chandra, D.; Singh, U.; Verma, Y. Understanding Initial Opportunities and Key Challenges for CCUS Deployment in India at Scale. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Foscolo, P.U.; Zondervan, E. Optimization of CCUS Supply Chains for Some European Countries under the Uncertainty. Processes 2020, 8, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Aviso, K.B.; Tan, R.R.; Li, Z.; Jia, X. Safety Risk Assessment of the Large-Scale Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Demonstration Project in Dongying, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.I.; Roger, C.B.; Hale, T.N.; Bernstein, S.; Tiberghien, Y.; Balme, R. Making the Paris Agreement: Historical Processes and the Drivers of Institutional Design. Political Stud. 2021, 71, 914–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogelj, J.; Den Elzen, M.; Höhne, N.; Fransen, T.; Fekete, H.; Winkler, H.; Schaeffer, R.; Sha, F.; Riahi, K.; Meinshausen, M. Paris Agreement Climate Proposals Need a Boost to Keep Warming Well below 2 °C. Nature 2016, 534, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savaresi, A. The Paris Agreement: A New Beginning? J. Energy Nat. Resour. Law 2016, 34, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, G.; Gidden, M.J.; Smith, C.J.; Fyson, C.; Nauels, A.; Riahi, K.; Schleußner, C.F. Uncompensated Claims to Fair Emission Space Risk Putting Paris Agreement Goals out of Reach. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 024040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitinjak, C.; Ebennezer, S.; Ober, J. Exploring Public Attitudes and Acceptance of CCUS Technologies in JABODETABEK: A Cross-Sectional Study. Energies 2023, 16, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarhan, L.M.; Alayyar, A.S.; Alqahtani, N.B.; Khdary, N.H. Circular Carbon Economy (CCE): A Way to Invest CO2 and Protect the Environment, a Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ruiz Maraggi, L.; Bhattacharya, S.; Yut, K.; McMahon, T.P.; Haddad, M. Feasibility of CO2 Storage in Depleted Unconventional Oil and Gas Reservoirs: Capacity, Microscale Mechanism, Injectivity, Fault Stability, and Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 11th Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 13–15 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, J.; Zang, X.; Piao, Z.; Li, L.; Kim, K. China’s Low-Carbon Economic Growth: An Empirical Analysis Based on the Combination of Parametric and Nonparametric Methods. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 37219–37232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhao, T.; Hou, D.; Yu, C.W. Challenges and Paths to Enhance Green Efficiency under Low-Carbon Economic and Social Development. Indoor Built Environ. 2023, 32, 1420326X231179835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; D’souza, D.; Londhe, V.Y. Exploring the Concepts of Various Nano-Formulations Loaded with Herbal Drugs Moieties against Breast Cancer Using PRISMA Analysis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Kamble, S.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Gunasekaran, A.; Ndubisi, N.O.; Venkatesh, M. Manufacturing and Service Supply Chain Resilience to the COVID-19 Outbreak: Lessons Learned from the Automobile and Airline Industries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 163, 120447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M. Accelerating Retail Supply Chain Performance against Pandemic Disruption: Adopting Resilient Strategies to Mitigate the Long-Term Effects. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2021, 34, 1844–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Shang, J.; Yang, F.; Ang, S. Measuring Energy Supply Chains’ Efficiency with Emission Trading: A Two-Stage Frontier-Shift Data Envelopment Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1462–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardas, B.B.; Raut, R.D.; Narkhede, B. Determinants of Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Case Study from the Oil and Gas Supply Chain. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2019, 17, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Gonzalez, E.D.R.S. A Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Framework for Agriculture Supply Chain Risk Management under a Circular Economy Context. Manag. Decis. 2021, 59, 1801–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, M.; Bentahar, O. Technological Forecasting & Social Change Digitalization of the Healthcare Supply Chain: A Roadmap to Generate Benefits and Effectively Support Healthcare Delivery. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 167, 120717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmaster, M.; Nettleton, C.; Tom, C.; Xu, B. Risk Management: Rethinking Fashion Supply Chain Management for Multinational Corporations in Light of the COVID-19 Outbreak. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2020, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaqiri, A.; Hossain, N.U.I.; Jaradat, R.; Abutabenjeh, S.; Keating, C.B.; Khasawneh, M.T.; Ariel Pinto, C. A Systemic Approach for Disruption Risk Assessment in Oil and Gas Supply Chains. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. 2019, 15, 230–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alora, A.; Barua, M.K. Development of a Supply Chain Risk Index for Manufacturing Supply Chains. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2022, 71, 477–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behdani, B.; Lukszo, Z.; Srinivasan, R. Agent-Oriented Simulation Framework for Handling Disruptions in Chemical Supply Chains. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 122, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, G.; O’Sullivan, M.J.; Olsen, T.L.; Zhang, A. Agribusiness Supply Chain Risk Management: A Review of Quantitative Decision Models. Omega 2018, 79, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrisandina, N.J.; Vedant, S.; Iakovou, E.; Pistikopoulos, E.N.; El-Halwagi, M.M. Multi-Scale Integration for Enhanced Resilience of Sustainable Energy Supply Chains: Perspectives and Challenges. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 164, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Liu, L. Risk Assessment of Agricultural Supermarket Supply Chain in Big Data Environment. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2020, 28, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, I.; Comes, T.; Nickel, S. A Critical Review on Supply Chain Risk—Definition, Measure and Modeling. Omega 2015, 52, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbiri, S.; Rameezdeen, R.; Chileshe, N.; Statsenko, L. A Novel Taxonomy for Risks in Agribusiness Supply Chains: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Ibne Hossain, N.U.; Jaradat, R.; Hamilton, M. Leveraging a Bayesian Network Approach to Model and Analyze Supplier Vulnerability to Severe Weather Risk: A Case Study of the U.S. Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Following Hurricane Maria. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 49, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, N.; Ibne Hossain, N.U.; Nur, F.; Talluri, S.; Jaradat, R.; Lawrence, J.M. An Assessment of Probabilistic Disaster in the Oil and Gas Supply Chain Leveraging Bayesian Belief Network. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 235, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axon, C.J.; Darton, R.C. Measuring Risk in Fuel Supply Chains. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffron, R.J.; Downes, L.; Bysveen, M.; Brakstad, E.V.; Mikunda, T.; Neele, F.; Eickhoff, C.; Hanstock, D.; Schumann, D. Ownership, Risk and the Law for a CO2 Transport Network for Carbon Capture and Storage in the European Union. J. Energy Nat. Resour. Law 2018, 36, 433–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.G.; Rathi, S.; Patwa, S. Analysis on Supply Chain Risks in Indian Apparel Retail Chains and Proposal of Risk Prioritization Model Using Interpretive Structural Modeling. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2015, 26, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlqvist, V.; Dube, N.; Jahre, M.; Lee, J.S.; Melaku, T.; Moe, A.F.; Olivier, M.; Selviaridis, K.; Viana, J.; Aardal, C. Supply Chain Risk Management Strategies in Normal and Abnormal Times: Policymakers’ Role in Reducing Generic Medicine Shortages. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2022, 53, 206–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friday, D.; Savage, D.A.; Melnyk, S.A.; Harrison, N.; Ryan, S.; Wechtler, H. A Collaborative Approach to Maintaining Optimal Inventory and Mitigating Stockout Risks during a Pandemic: Capabilities for Enabling Health-Care Supply Chain Resilience. J. Humanit. Logist. Supply Chain. Manag. 2021, 11, 248–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, R.; Kargar, B.; Rajabzadeh, M.; Hesabi, F.; Özceylan, E. Hybrid Fuzzy and Data-Driven Robust Optimization for Resilience and Sustainable Health Care Supply Chain with Vendor-Managed Inventory Approach. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 24, 1216–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohmah, D.U.M.; Dania, W.A.P.; Dewi, I.A. Risk Measurement of Supply Chain Organic Rice Product Using Fuzzy Failure Mode Effect Analysis in MUTOS Seloliman Trawas Mojokerto. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 3, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ren, J.; Wang, H. A System Dynamics Simulation Model of Chemical Supply Chain Transportation Risk Management Systems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2016, 89, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Makui, A.; Paydar, M.M. Forward and Reverse Supply Chain Network Design for Consumer Medical Supplies Considering Biological Risk. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 140, 106229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Chaudhuri, A.; Srivastava, R.K. Propagation of Risks and Their Impact on Performance in Fresh Food Retail. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2015, 26, 568–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kbah, Z.; Erdil, N.O.; Aqlan, F. Risk Assessment in Oil and Gas Industry Using Simulation and Bow-Tie Analysis. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Theory Appl. Pract. 2020, 27, 110–123. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, E.A.; Youssef, M.M. Analysis of Risk Factors and Events Linked to the Supply Chain: Case of Automotive Sector in Morocco. J. Logist. Manag. 2017, 6, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rosales, F.P.; Oprime, P.C.; Royer, A.; Batalha, M.O. Supply Chain Risks: Findings from Brazilian Slaughterhouses. Supply Chain. Manag. 2020, 25, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L. Supply Chain Risk’s Impact on Corporate Financial Performance. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 38, 713–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mastragostino, R.; Swartz, C.L.E. Flexibility Analysis of Process Supply Chain Networks. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2016, 84, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Sun, H.; Hu, X.; Jin, K.; Ping, M. Demand Information Sharing in a Two-Echelon Supply Chain with a Risk-Averse Retailer: Retail Price Decision versus Retail Quantity Decision. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2022, 29, 3657–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, G.; O’Sullivan, M.J.; Olsen, T.L.; Zhang, A. Allocation Flexibility for Agribusiness Supply Chains under Market Demand Disruption. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 3524–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.M.; Ma, C.; Shen, B.; Sun, Q. Optimal Pricing in Mass Customization Supply Chains with Risk-Averse Agents and Retail Competition. Omega 2019, 88, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ning, C.; You, F. Data-Driven Distributionally Robust Optimization of Shale Gas Supply Chains under Uncertainty. AIChE J. 2019, 65, 947–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda, E.D.; Nyaga, G.N.; Young, G.J. Supply Chain Risk Management and Hospital Inventory: Effects of System Affiliation. J. Oper. Manag. 2016, 44, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.; Ahmed, W. Understanding Influence of Supply Chain Relationships in Retail Channels on Risk Management. Decision 2022, 49, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlqvist, V.; Norrman, A.; Jahre, M. Supply Chain Risk Governance: Towards a Conceptual Multi-Level Framework. Oper. Supply Chain. Manag. 2020, 13, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhani, R.; Torabi, S.A.; Altay, N. Retail Supply Chain Network Design with Concurrent Resilience Capabilities. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 234, 108042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lan, B. Detect Megaregional Communities Using Network Science Analytics. Urban Sci. 2022, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Shishodia, A.; Kamble, S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Belhadi, A. Agriculture Supply Chain Risks and COVID-19: Mitigation Strategies and Implications for the Practitioners. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Regulations for Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage: Comparative Analysis of Development in Europe, China and the Middle East. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 173, 105722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, I.B.; Han, J. Design under Uncertainty of Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Infrastructure Considering Profit, Environmental Impact, and Risk Preference. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, J. Risk Management Optimization Framework for the Optimal Deployment of Carbon Capture and Storage System under Uncertainty. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 113, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; He, D.; Xu, Q.; Nan, G. Omnichannel Retail Operations with Ship-to-Store and Ship-from-Store Options under Supply Disruption. Front. Eng. Manag. 2023, 10, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Gao, Y.; Tao, Y. Comparison of End-of-Life Tire Treatment Technologies: A Chinese Case Study. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Machado, I.; Magrelli, V.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial Intelligence in Innovation Research: A Systematic Review, Conceptual Framework, and Future Research Directions. Technovation 2023, 122, 102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Jia, F.; Lin, X.; Chen, L. The Role of Technology in Supply Chain Decarbonisation: Towards an Integrated Conceptual Framework. Supply Chain. Manag. 2023, 28, 803–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vögele, S.; Govorukha, K.; Mayer, P.; Rhoden, I.; Rübbelke, D.; Kuckshinrichs, W. Effects of a Coal Phase-out in Europe on Reaching the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 879–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, S.; Fu, X.; Feng, S.; Zhuang, Z. A Sustainable Agricultural Supply Chain Considering Substituting Organic Manure for Chemical Fertilizer. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.R.; Yu, Z.; Golpira, H.; Sharif, A.; Mardani, A. A State-of-the-Art Review and Meta-Analysis on Sustainable Supply Chain Management: Future Research Directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.F.; Zantye, M.S.; Kazi, M.K. Challenges and Opportunities in Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage: A Process Systems Engineering Perspective. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 166, 107925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, B.; Gani, R. Sustainable Synthesis of Integrated Process, Water Treatment, Energy Supply, and CCUS Networks under Uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 157, 107636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Che, L.; Wan, L.; Fei, L. A MULTIMOORA-Based Risk Evaluation Approach for CCUS Projects by Utilizing D Numbers Theory. Axioms 2022, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchino, M.; Popielak, P.; Panowski, M.; Wawrzyńczak, D.; Majchrzak-Kucęba, I.; De Falco, M. The Environmental Impacts of Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage on the Electricity Sector: A Life Cycle Assessment Comparison between Italy and Poland. Energies 2022, 15, 6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kegl, T.; Čuček, L.; Kovač Kralj, A.; Kravanja, Z. Conceptual MINLP Approach to the Development of a CO2 Supply Chain Network–Simultaneous Consideration of Capture and Utilization Process Flowsheets. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Baroudi, H.; Awoyomi, A.; Patchigolla, K.; Jonnalagadda, K.; Anthony, E.J. A Review of Large-Scale CO2 Shipping and Marine Emissions Management for Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage. Appl. Energy 2021, 287, 116510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.H.; Leonzio, G.; Zondervan, E. Supply Chain Optimization Framework for CO2 capture, Utilization, and Storage in Germany. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, C. An Approach of Quantitative Risk Assessment for Release of Supercritical CO2 Pipelines. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 94, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Bogle, D.; Foscolo, P.U.; Zondervan, E. Optimization of CCUS Supply Chains in the UK: A Strategic Role for Emissions Reduction. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 155, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Amore, F.; Bezzo, F. Optimizing the Design of Supply Chains for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Sequestration in Europe: A Preliminary Assessment. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Foscolo, P.U.; Zondervan, E. An Outlook towards 2030: Optimization and Design of a CCUS Supply Chain in Germany. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 125, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguid, A.; Zaluski, W.; El-Kaseeh, G.; Lee, S.Y.; Piercy, M. Well Integrity Risk Assessment to Inform Containment Risk Monitoring for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage, Applied to the Weyburn-Midale Field, Canada. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2019, 86, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Du, J. An Optimization Model for Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage Supply Chain: A Case Study in Northeastern China. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, S.M.; Samsatli, S. Technologies and Infrastructures Underpinning Future CO2 Value Chains: A Comprehensive Review and Comparative Analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 85, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyanarengan Ravi, N.; Van Sint Annaland, M.; Fransoo, J.C.; Grievink, J.; Zondervan, E. Development and Implementation of Supply Chain Optimization Framework for CO2 Capture and Storage in The Netherlands. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2017, 102, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Risks | References | MFSC/PSC | RSC | ESC/PRSC | ASC | HCSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Disaster | [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Changes in Government regulations and Policies | [38,39,43,48,49] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Globalization | [42,50] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Political Instability and Unrest | [39,47,48] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Terrorism and War | [38,39] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Trade Agreement | [42,47] | ☑ | ||||
| Stockout Risk/Shortage | [51,52,53] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Product Return | [54] | ☑ | ||||
| Financial Risk | [38,39,48,50,55] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ||
| Environmental Threat | [38,44,45,47,48] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Inflation and Currency Exchange Risk | [39] | ☑ | ||||
| High Insurance Cost | [38] | ☑ | ||||
| Safety and Human Risk | [38,47,56] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Production Variability | [38,47,56] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ||
| Transportation Delay | [38,43,46,50,57] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | |
| Product Quality | [43,44,48,50,54] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | |
| Supply Delay | [39,44,54,58,59,60] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | |
| Lack of Supplier Coordination | [39,59,61] | ☑ | ||||
| Production Capacity | [38,46,48,62] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Continuous Production | [58] | ☑ | ||||
| Scheduling Problem | [47,56] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Cross-contamination | [57] | ☑ | ||||
| Perishability | [41,57] | ☑ | ||||
| Chemical Contaminants | [54] | ☑ | ||||
| Retail Price Variability | [60,63] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Demand variability | [38,39,41,47,50,54,60,62,63,64,65,66,67] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| Price Volatility | [41,47,60] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Loss of Customer | [43,68] | ☑ | ||||
| Information Flow Management | [39,43,55,59,69] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | |
| Short Product Life Cycle | [39,41,61] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Infrastructure Risk | [38,46,48,50,55,67] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ||
| Processing Unit Disruption | [58] | ☑ | ||||
| Technical Failure | [47] | ☑ | ||||
| Transportation Cost | [47] | ☑ | ||||
| Damage during process | [54] | ☑ | ||||
| SC Interconnection between nodes | [43,52] | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ||
| Unused Retail Capacity | [70] | ☑ | ||||
| Internal Disruption | [39] | ☑ | ||||
| Transport Breakdown | [39,55] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| Labor Strike | [39] | ☑ | ||||
| Storage Technology | [41,58] | ☑ | ||||
| Technological advancement | [47,48] | ☑ | ||||
| Preservation Equipment and Technology | [43] | ☑ | ||||
| Machine Damage | [48,54] | ☑ | ||||
| Picking Technology | [41,43] | ☑ | ||||
| Rapid Changes in Technologies | [1,39,55] | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| MFSC—manufacturing SC PSC—production SC RSC—retail SC | PRSC—process SC ESC—energy SC ASC—agricultural SC HCSC—healthcare SC | |||||
| SC Sectors | References |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing/Production Supply Chain (MFSC/PSC) RM | [31,38,39,42,44,45,47,48,56] |
| Retail SC (RSC) Risk Management | [42,43,50,52,57,60,62,63,67] |
| Energy/Process SC (ESC/PRSC) RM | [38,42,44,45,47,48,54,55,58] |
| Agricultural SC (ASC) RM | [41,43,45,48,54,72] |
| Health Care SC (HCSC) RM | [36,51,52,53,67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabir, M.A.; Khan, S.A.; Kabir, G. Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Risks from Supply Chain Perspective: A Review of the Literature and Conceptual Framework Development. C 2024, 10, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010015
Kabir MA, Khan SA, Kabir G. Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Risks from Supply Chain Perspective: A Review of the Literature and Conceptual Framework Development. C. 2024; 10(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabir, Md Ainul, Sharfuddin Ahmed Khan, and Golam Kabir. 2024. "Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Risks from Supply Chain Perspective: A Review of the Literature and Conceptual Framework Development" C 10, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010015
APA StyleKabir, M. A., Khan, S. A., & Kabir, G. (2024). Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage Risks from Supply Chain Perspective: A Review of the Literature and Conceptual Framework Development. C, 10(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010015