Optimization of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) Growth: From Laboratory Scale to Pilot Scale
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain
2.2. Culture Conditions
2.3. Growth Data
2.4. Biomass Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Culture Media Comparison
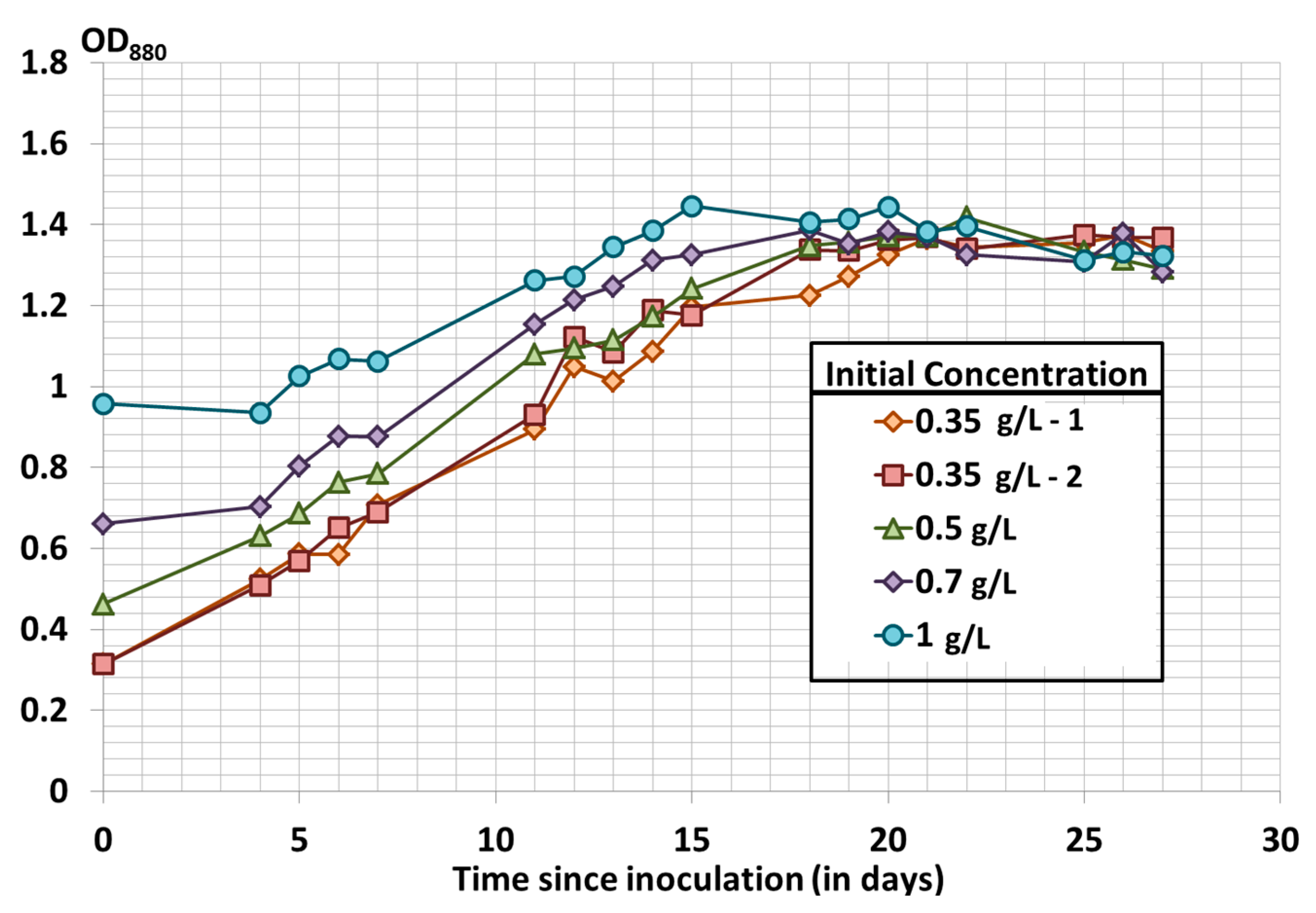
3.2. Effect of the Initial Biomass Concentration on Spirulina Growth Using Modified Zarrouk’s Medium
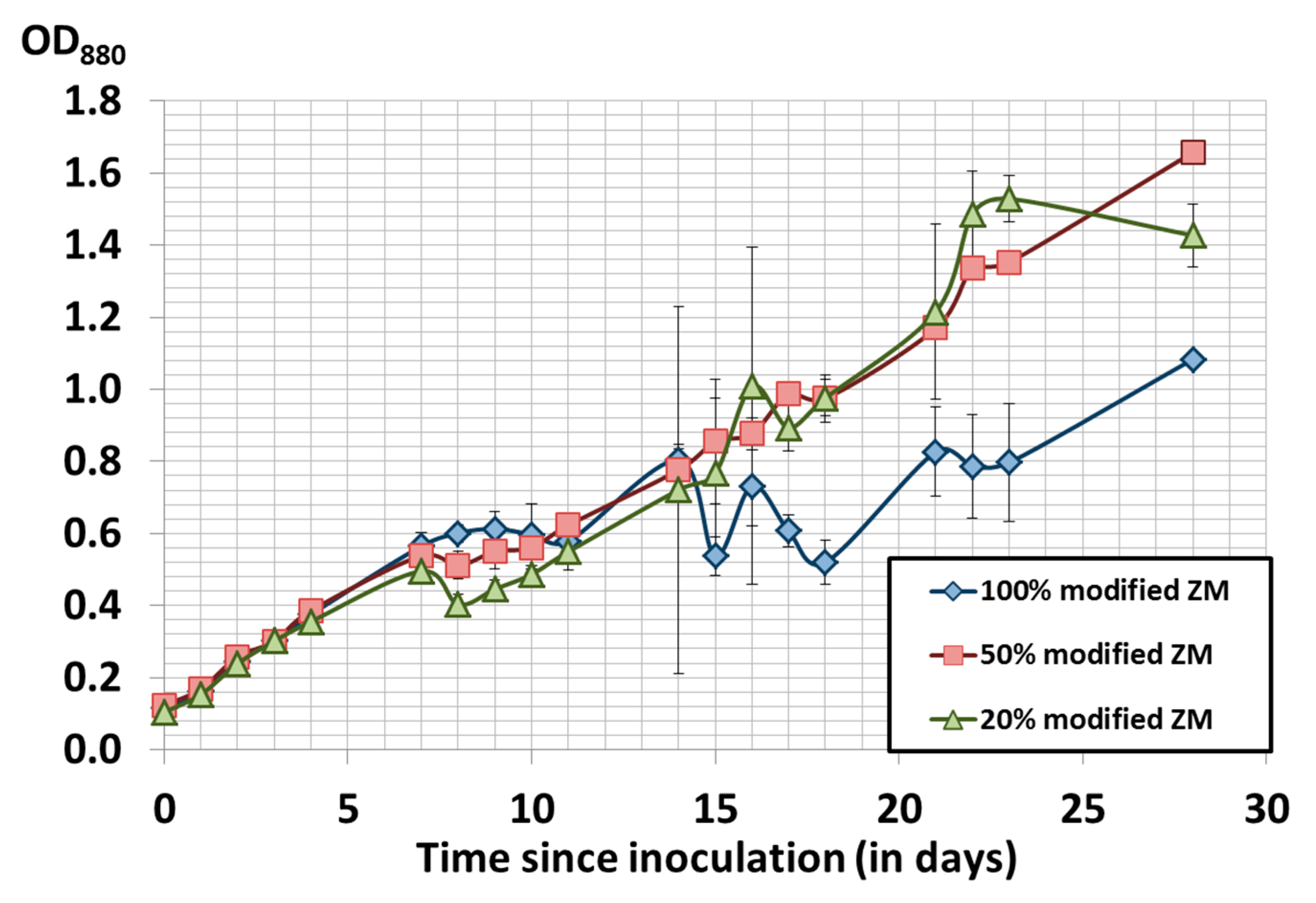
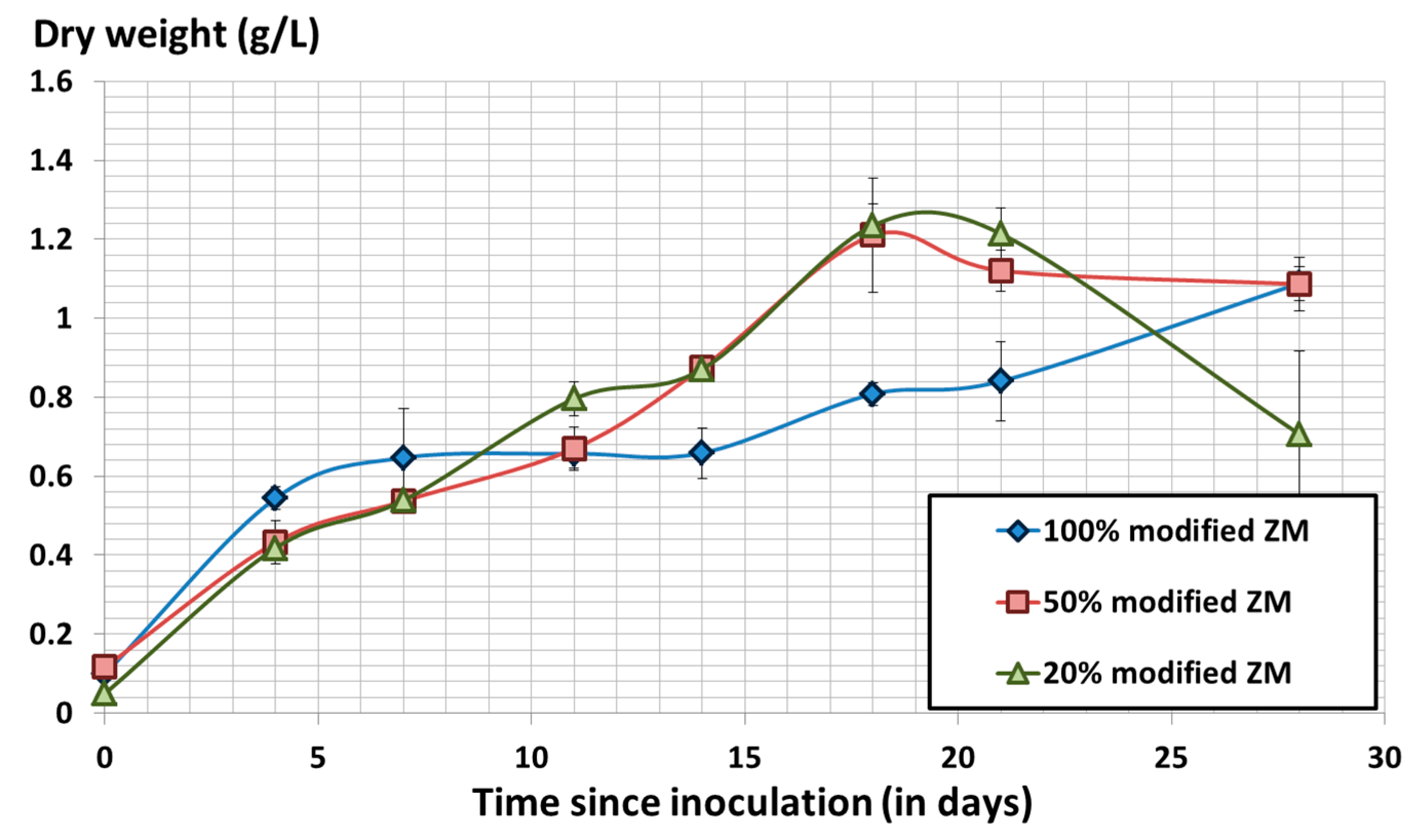
3.3. Cost Optimization of Modified Zarrouk’s Medium Composition
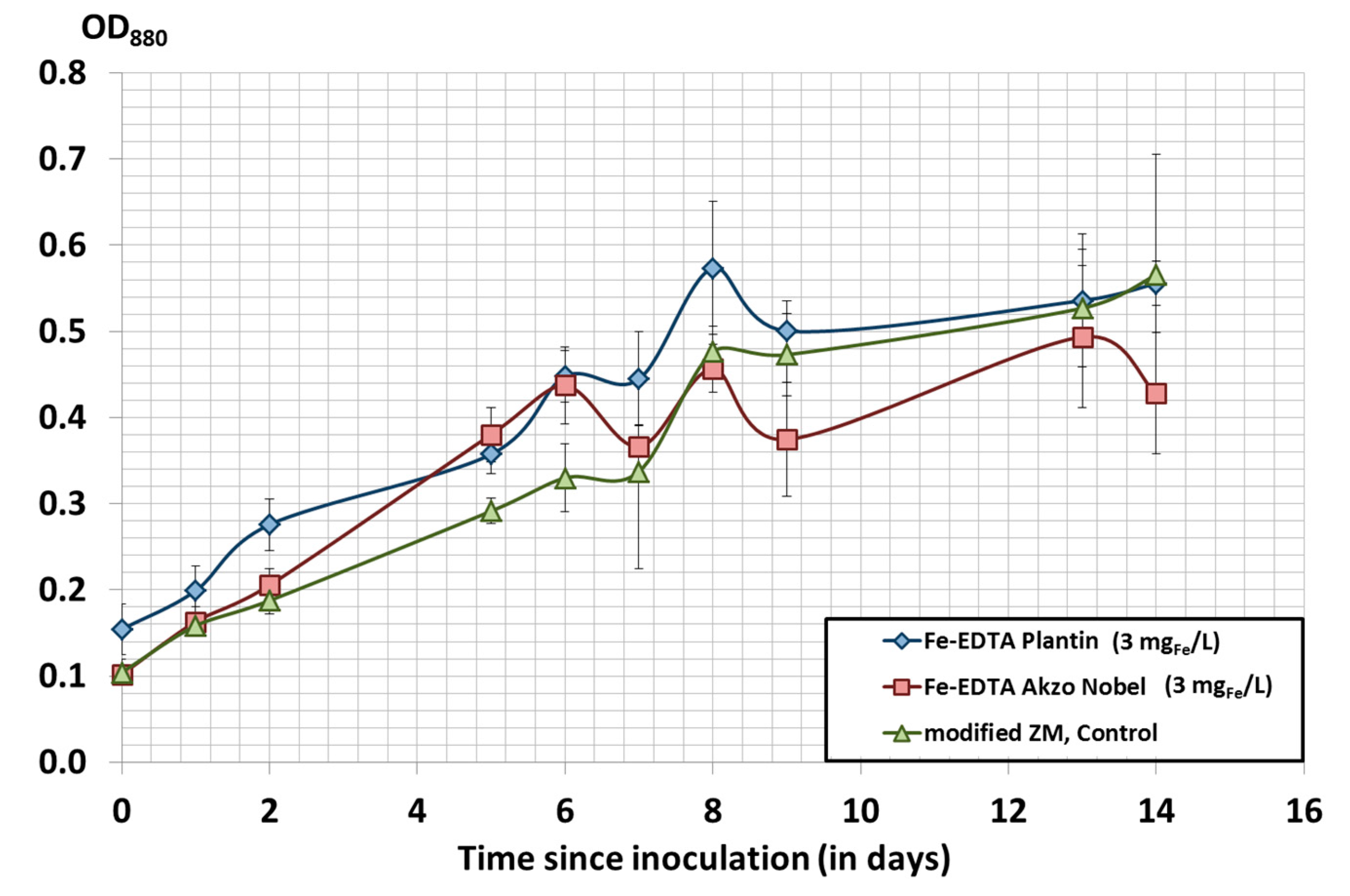
3.4. Iron Source and Iron Content in Spirulina
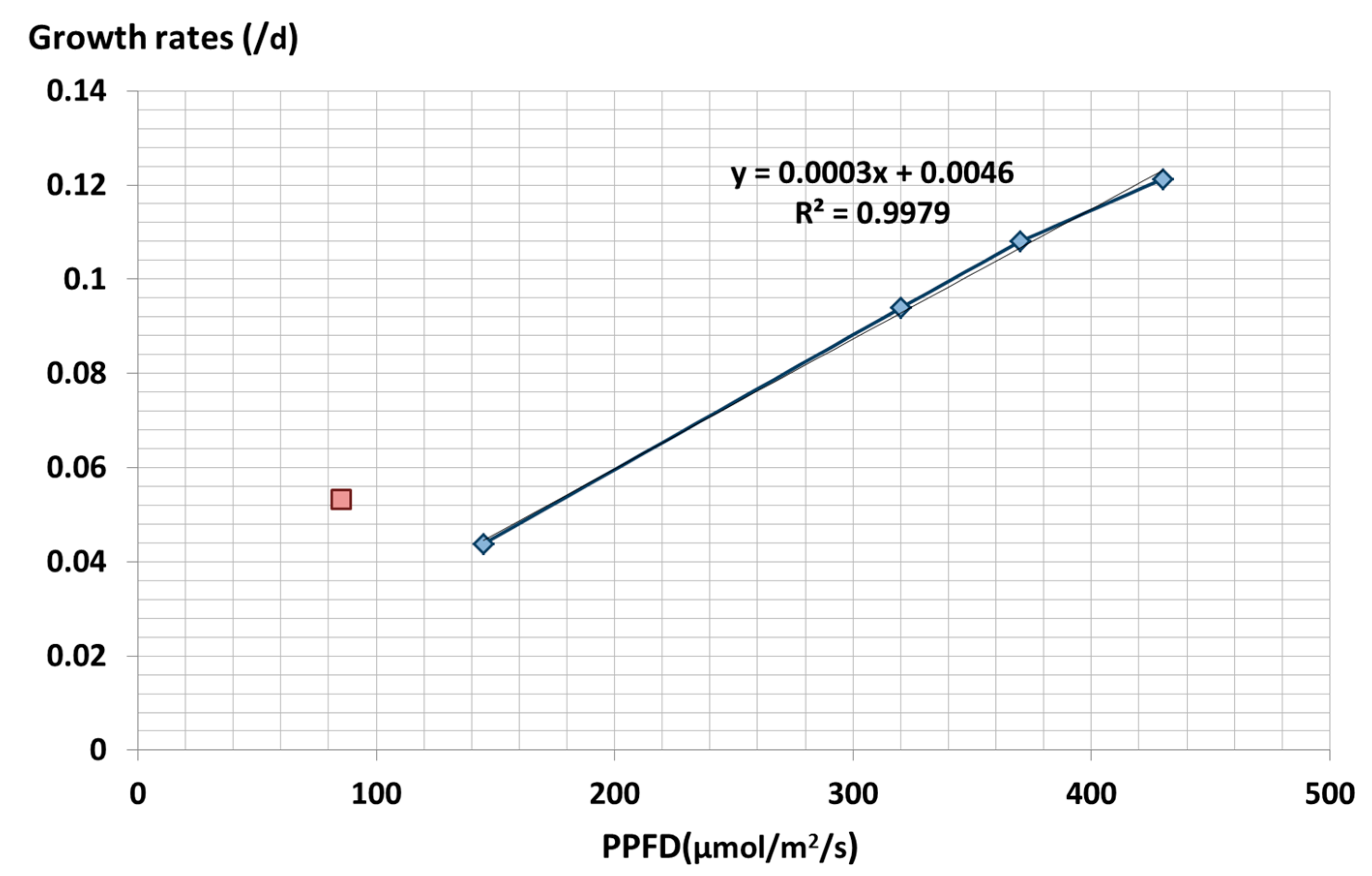
3.5. Effect of Light Intensity on Spirulina Growth
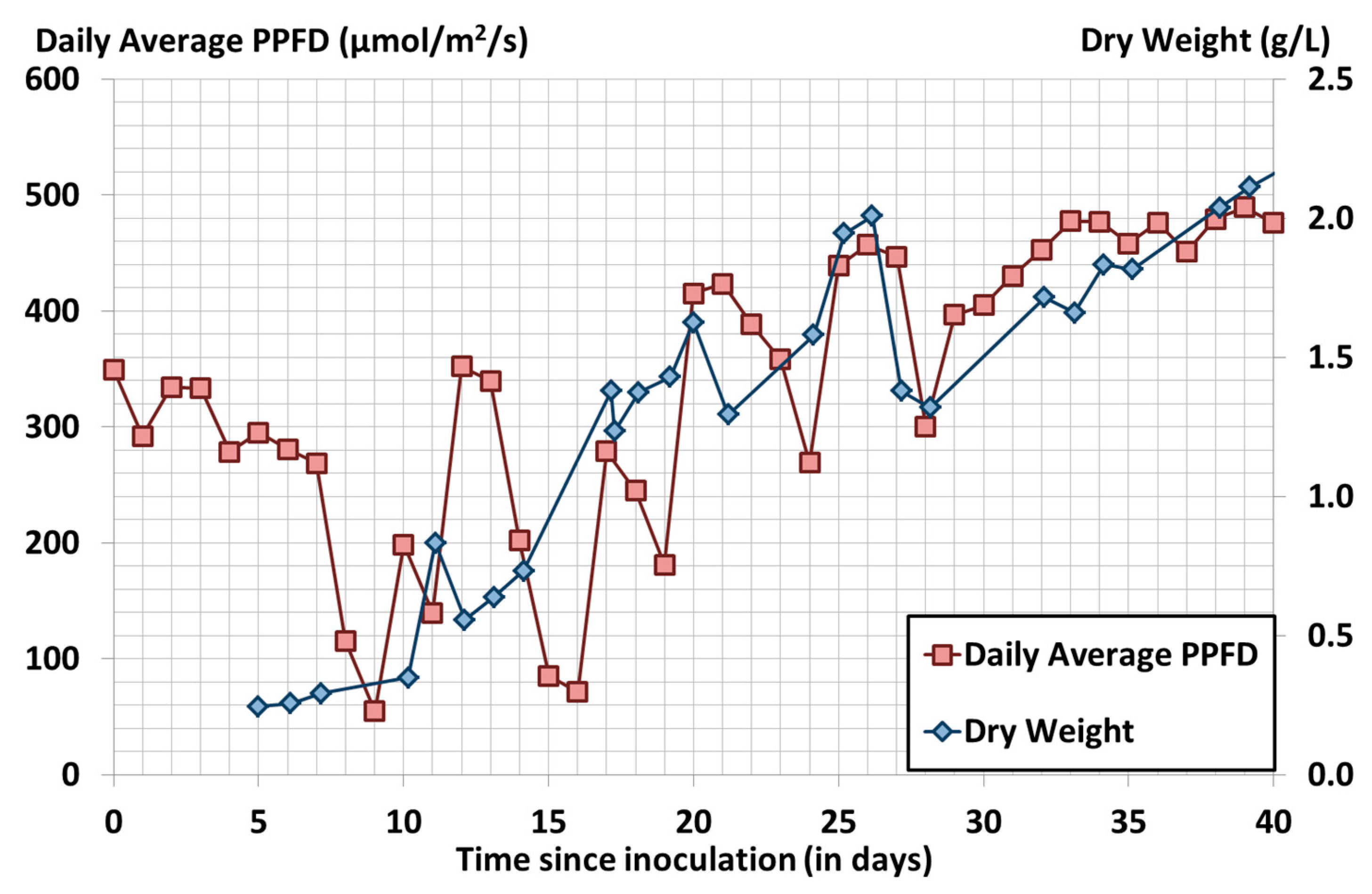
3.6. Spirulina Cultivation Run in a 1000 L Camargue PBR
3.7. Cost Comparison: PBR and Open Ponds
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benemann, J. Microalgae for Biofuels and Animal Feeds. Energies 2013, 6, 5869–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.; Ota, Y.; Miyakawa, K.; Shimamatsu, H. Current knowledge on potential health benefits of Spirulina. J. Appl. Phycol. 1993, 5, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Cossío, B.R.; Labella, D.; Niell, F.X. The Feasibility of industrial production of Spirulina (Arthrospira) in Southern Spain. Aquaculture 2003, 217, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bhowmick, G.; Subramanian, G.; Mishra, S.; Sen, R. Raceway pond cultivation of a marine microalga of Indian origin for biomass and lipid production: A case study. Algal Res. 2014, 6, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, A.L.; Kazamia, E.; Dennis, J.S.; Howe, C.J.; Scott, S.A.; Smith, A.G. Life-cycle assessment of potential algal biodiesel production in the United Kingdom: A comparison of raceways and air-lift tubular bioreactors. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4062–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, A.; Grobbelaar, J.U. Factors affecting the output rate of Spirulina platensis with reference to mass cultivation. Biomass 1986, 10, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonshak, A.; Richmond, A. Mass production of the blue-green alga Spirulina: An overview. Biomass 1988, 15, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelekli, A.; Yavuzatmaca, M. Predictive modeling of biomass production by Spirulina platensis as function of nitrate and NaCl concentrations. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soletto, D.; Binaghi, L.; Lodi, A.; Carvalho, J.C.M.; Converti, A. Batch and fed-batch cultivations of Spirulina platensis using ammonium sulphate and urea as nitrogen sources. Aquaculture 2005, 243, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G.; Chatzipavlidis, I.; Georgakakis, D. Effects of phosphorus concentration and light intensity on the biomass composition of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrez, D.A.; Naguib, M.M.; Sultan, Y.Y.; Daw, Z.Y.; Higazy, A.M. Impact of Culturing Media on Biomass Production and Pigments Content of Spirulina platensis. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 1, 951–961. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, J.P.; Tiwari, A.; Mishra, R.M. Evaluation of biomass production of spirulina maxima on different reported media. J. Algal Biomass Util. 2010, 1, 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrouk, C. Contribution à L’étude D’une Cyanophycée: Influence de Divers Facteurs Physiques et Chimiques sur la Croissance et la Photosynthèse de Spirulina maxima (Setch et Gardner) Geitler. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculté des Sciences de l’Université de Paris, Paris, France, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Doumandji, A.; Boutekrabt, L.; Saidi, N.A.; Doumandji, S.; Hamerouch, D.; Haourai, S. Etude de l’impact de l’incorporation de la spirulinae sur les propriétés nutritionnelles, technologiques et organoleptiques du couscous artisanal. Nat. Technol. 2012, 6, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jourdan, J.P. Manuel de Culture Artisanale Pour la Production de Spiruline; Anteanna Technologies: Genève, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Madkour, F.F.; El-Wahab Kamil, A.; Nasr, H.S. Production and nutritive value of Spirulina platensis in reduced cost media. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sommerfeld, M.R.; Lu, C.; Hu, Q. Combined effect of initial biomass density and nitrogen concentration on growth and astaxanthin production of Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyta) in outdoor cultivation. Algae 2013, 28, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuşoglu, Ö.; Üunal, M.K. Biomass Nutrient Profiles of Three Microalgae: Spirulina platensis, Chlorella vulgaris, and Isochrisis galbana. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Iron Deficiency Anemia. 2001. Available online: http://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/en/ida_assessment_prevention_control.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 20 December 2016).
- Hosseini, S.M.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Mozafari, M.R. Nutritional and medical applications of spirulina microalgae. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy Danesi, E.D.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O.; Sato, S.; Monteiro de Carvalho, J.C. Growth and content of Spirulina platensis biomass chlorophyll cultivated at different values of light intensity and temperature using different nitrogen sources. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutner, S.H.; Provasoli, L.; Schatz, A.; Haskins, C.P. Some approaches to the study of the role of metals in the metabolism of microorganisms. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1950, 94, 152–170. [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Feuga, A.; Lemar, M.; Vermel, E.; Pradelles, R.; Rimbaud, L.; Valiorgue, P. Appraisal of a horizontal two-phase flow photobioreactor for industrial production of delicate microalgae species. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Qiuang, H.; Richmond, A. Photic volume in photobioreactors supporting ultrahigh population densities of the photoautotroph Spirulina platensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Calvo, J.J.; Mazuelos, C.; Hermosin, B.; Saiz-Jimenez, C. Chemical composition of Spirulina and eukaryotic algae food products marketed in Spain. J. Appl. Phycol. 1993, 5, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmann, E.M.; Reinehr, C.O.; Costa, J.A.V. Optimization of the repeated batch cultivation of microalga Spirulina platensis in open raceway ponds. Aquaculture 2007, 265, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-C.; Renc, M.; Ogden, K.L. Statistical optimization of culture media for growth and lipid production of Chlorella protothecoides UTEX 250. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puyfoulhoux, G.; Rouanet, J.M.; Besançon, P.; Baroux, B.; Baccou, J.C.; Caporiccio, B. Iron availability from iron-fortified spirulina by an in-vitro digestion/Caco-2 cell culture model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 49, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, E.; Ahlgren, G. Optimum growth conditions and light utilization efficiency of Spirulina platensis (= Arthrospira fusiformis) (Cyanophyta) from Lake Chitu, Ethiopia. Hydrobiologia 1996, 332, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaizola, M.; Duerr, E.O. Effects of light intensity and quality on the growth rate and photosynthetic pigment content of Spirulina platensis. J. Appl. Phycol. 1990, 2, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrue, F.; Setier, P.A.; Sahut, C.; Cournac, L.; Roubaud, A.; Peltier, G.; Froment, A.K. An economic, sustainability, and energetic model of biodiesel production from microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torr, S.S.; Reddy, H.; Deng, S.; Hoffmann, J.; Spangsmark, D.; Madsen, L.B.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Rosendahl, L.A. Hydrothermal liquefaction of Spirulina and Nannochloropsis salina under subcritical and supercritical water conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
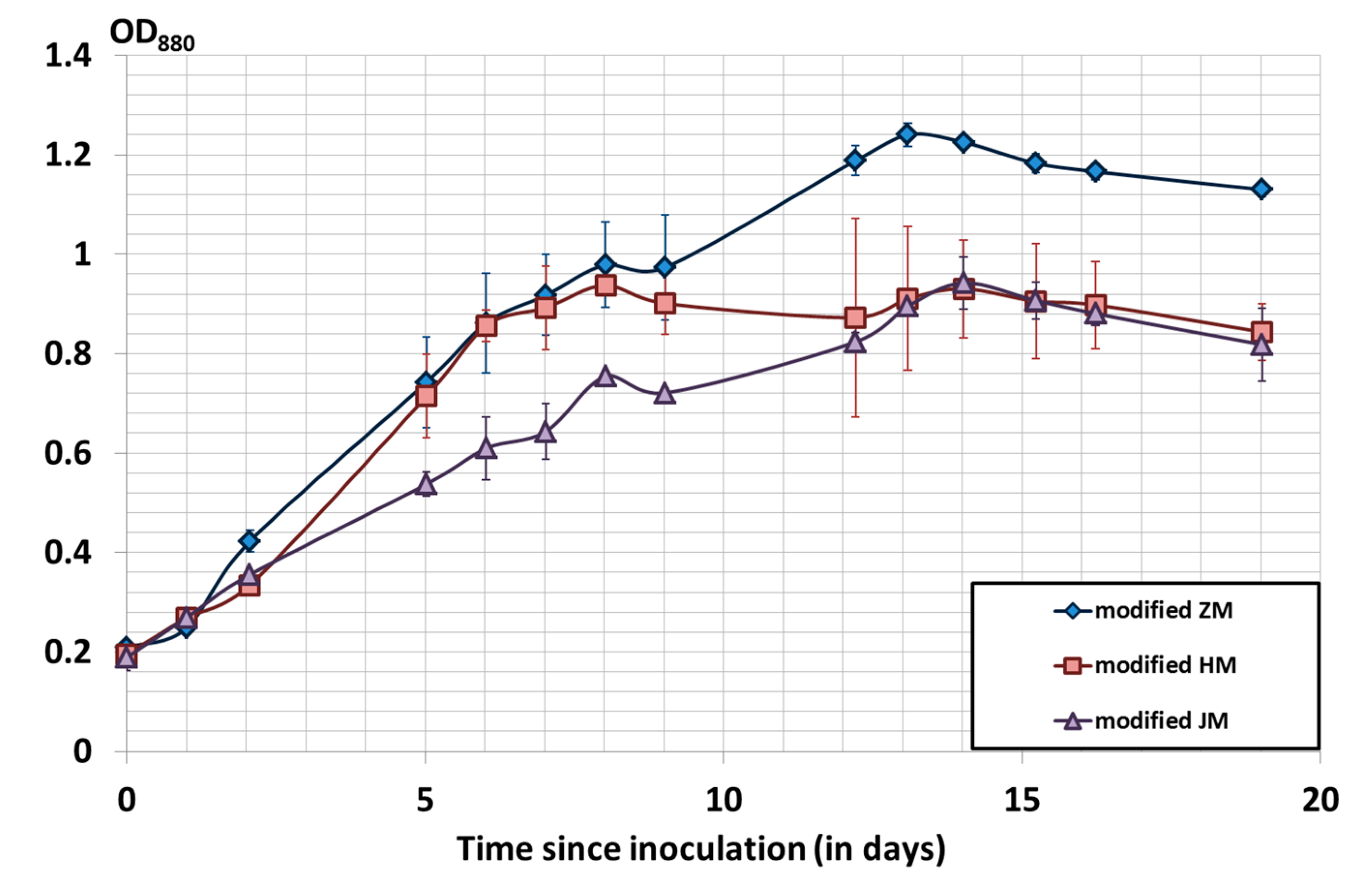


| Chemicals | Modified ZM [13] (g/L) | Modified HM [14] (g/L) | Modified JM [15] (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaHCO3 | 16.8 | 16 | 8 |
| NaCl | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| (NH4)3PO4 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| MgSO4,6H2O | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| FeSO4,6H2O | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| K2SO4 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| CaCl2,2H2O | 0.04 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| CH4N2O | 0 | 0.1 | 0.009 |
| KNO3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| NaNO3 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| K2HPO4 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Hutner’s solution without iron | 1 mL | 1 mL | 1 mL |
| Major Elements Concentrations | Modified ZM [13] (mg/L) | Modified HM [14] (mg/L) | Modified JM [15] (mg/L) |
| Carbonate CO32− | 12,000 | 11,430 | 5710 |
| Nitrogen N | 412 | 47 | 143 |
| Phosphorus P | 89 | 23 | 46 |
| Sulfur S | 238 | 120 | 237 |
| Initial Dry Weight (g/L) | Final Dry Weight (g/L) | Productivity between Day 7 and Day 15 (in mg/L/day) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.35 | 2.76 | 67.7 |
| 0.35 | 2.93 | 67.5 |
| 0.5 | 2.99 | 63.5 |
| 0.7 | 3.07 | 62.5 |
| 1 | 3.40 | 53.2 |
| ZM Proportion | Average Consumption Rate | Average Productivity (mg/L/day) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrate (mgN/L/day) | Phosphate (mgP/L/day) | Sulfate (mgS/L/day) | From Day 0 to Day 21 | From Day 0 to Day 24 | |
| 100% | 7.25 ± 0.10 | 2.38 ± 0.06 | 1.39 ± 0.11 | 36.9 ± 3.2 | 34.4 ± 1.5 |
| 50% | 8.13 ± 0.10 | 0.26 ± 0.24 | 1.06 ± 0.24 | 47.8 ± 2.5 | 34.6 ± 2.4 |
| 20% | 6.42 ± 0.91 | 0.38 ± 0.12 | 0.60 ± 0.71 | 53.5 ± 5.4 | 23.5 ± 7.5 |
| Iron Mass Balance | Residual in Supernatant (mgFe/L) | Adsorbed (mgFe/L) | Internalized (mgFe/L) | Sum (mgFe/L) | Adsorbed (mgFe/g) | Internalized (mgFe/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial iron concentration of 3 mgFe/L | ||||||
| Fe-EDTA Plantin 1 | 0.124 | 2.324 | 0.503 | 2.95 | 2.501 | 0.32 |
| Fe-EDTA Plantin 2 | 0.081 | 2.353 | 0.532 | 2.966 | 2.721 | 0.541 |
| Fe-EDTA Akzo Nobel 1 | 0.062 | 2.359 | 0.424 | 2.845 | 2.507 | 0.451 |
| Fe-EDTA Akzo Nobel 2 | 0.074 | 2.349 | 0.53 | 2.954 | 2.925 | 0.67 |
| Control 1 (2 mgFe/L) | 0.096 | 0.628 | 0.12 | 0.844 | 0.492 | 0.094 |
| Control 2 (2 mgFe/L) | 0.045 | 0.342 | 0.207 | 0.594 | 0.453 | 0.273 |
| Initial iron concentration of 10 mgFe/L | ||||||
| Fe-EDTA Plantin 1 | 8.482 | N.C. | 0.690 | N.C. | N.C. | 2.015 |
| Fe-EDTA Plantin 2 | 5.357 | 1.029 | 0.743 | 7.130 | 3.049 | 2.204 |
| Fe-EDTA Akzo Nobel 1 | 1.557 | 6.011 | 0.461 | 8.030 | 11.702 | 0.898 |
| Fe-EDTA Akzo Nobel 2 | 7.544 | 0.443 | 0.296 | 8.282 | 0.889 | 0.593 |
| Control 1 (2 mgFe/L) | 0.002 | 0.403 | 0.238 | 0.644 | 0.626 | 0.369 |
| Control 2 (2 mgFe/L) | N.C. | N.C. | 0.233 | N.C. | N.C. | 0.357 |
| Techno-Economic Analysis | Productivity (g/m2/day) | Production Cost (€/kg) | Energy Consumption (kWh/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open ponds | 4 | 9.59 | 4.26 |
| 7 | 5.49 | 3.51 | |
| 10 | 3.86 | 3.20 | |
| PBR | 10 | 74.29 | 6.33 |
| 25 | 29.82 | 3.00 | |
| 40 | 18.71 | 2.18 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delrue, F.; Alaux, E.; Moudjaoui, L.; Gaignard, C.; Fleury, G.; Perilhou, A.; Richaud, P.; Petitjean, M.; Sassi, J.-F. Optimization of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) Growth: From Laboratory Scale to Pilot Scale. Fermentation 2017, 3, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation3040059
Delrue F, Alaux E, Moudjaoui L, Gaignard C, Fleury G, Perilhou A, Richaud P, Petitjean M, Sassi J-F. Optimization of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) Growth: From Laboratory Scale to Pilot Scale. Fermentation. 2017; 3(4):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation3040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelrue, Florian, Emilie Alaux, Lagia Moudjaoui, Clément Gaignard, Gatien Fleury, Amaury Perilhou, Pierre Richaud, Martin Petitjean, and Jean-François Sassi. 2017. "Optimization of Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) Growth: From Laboratory Scale to Pilot Scale" Fermentation 3, no. 4: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation3040059





