Administration of the Potential Probiotic Paenibacillus ehimensis NPUST1 Enhances Expression of Indicator Genes Associated with Nutrient Metabolism, Growth and Innate Immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus indie Infections in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Bacterial Strains
2.2. Assay of Hydrolytic Enzymes and Antibiotic Susceptibility to Probiotics
2.3. Feed Preparation and Feeding Experiment
2.4. Determination of Digestive Enzymes in Intestines
2.4.1. Protease Activity Assay
2.4.2. Amylase Activity Assay
2.4.3. Cellulase Activity Assay
2.4.4. Xylanase Activity Assay
2.4.5. Lipase Activity Assay
2.5. Determination of Gene Expression by Real Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real Time Q-PCR)
2.6. Challenge Experiment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
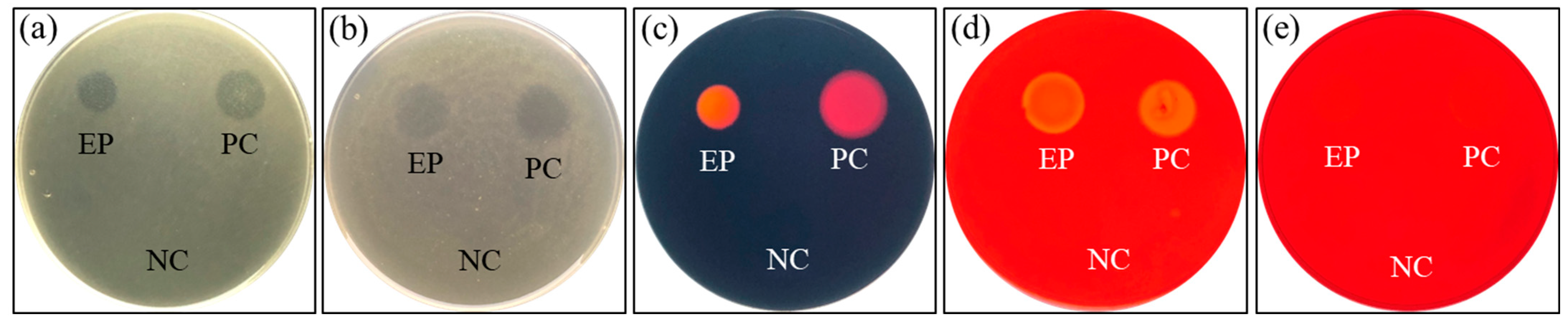
3.1. Characterization of Hydrolytic Enzymes and Antibiotic Susceptibility of P. ehimensis NPUST1
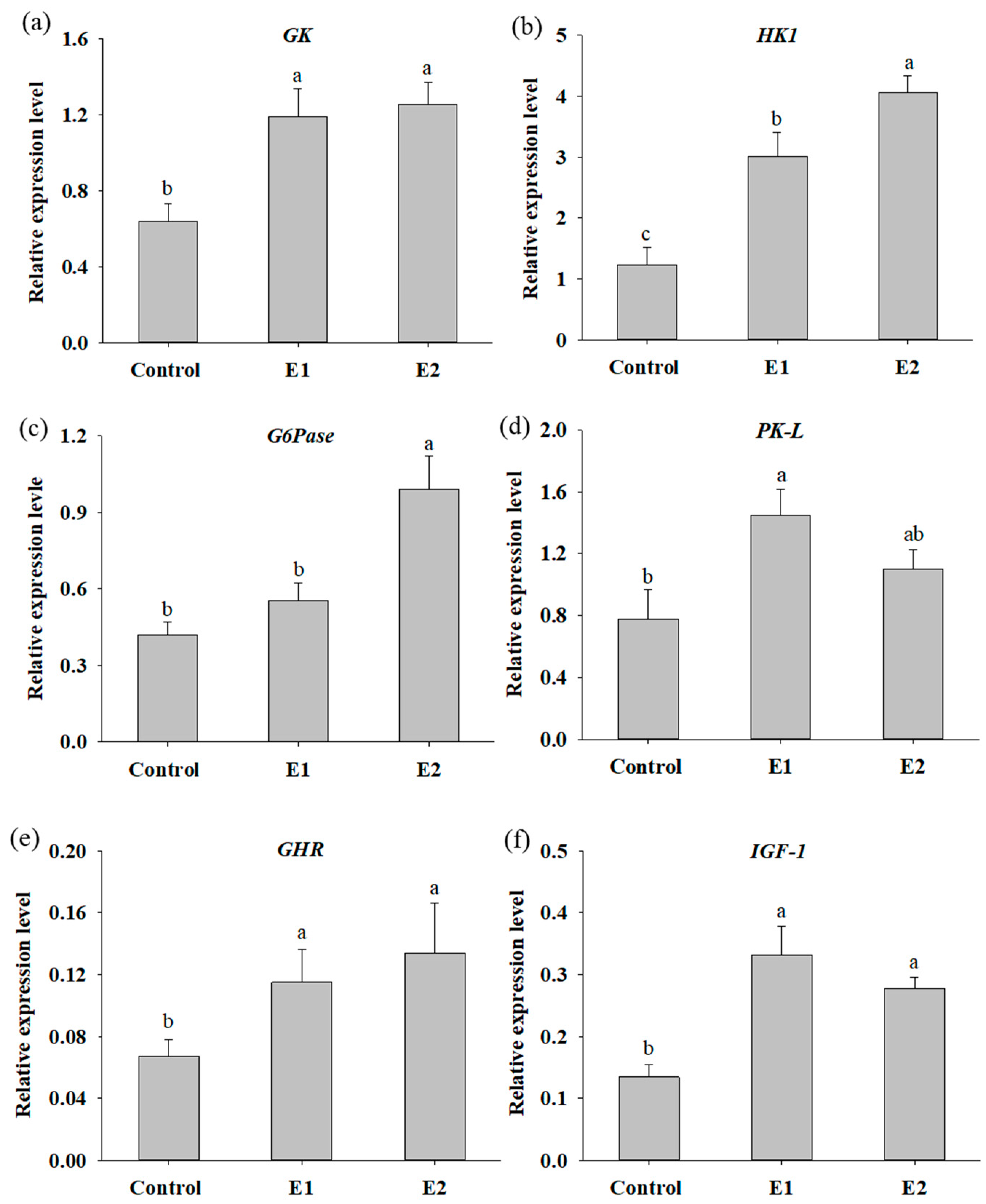
3.2. Dietary Supplementation with P. ehimensis NPUST1 Enhances Digestive Enzyme Activities and Induces the Expression of Genes Involved in Glucose Metabolism and Growth
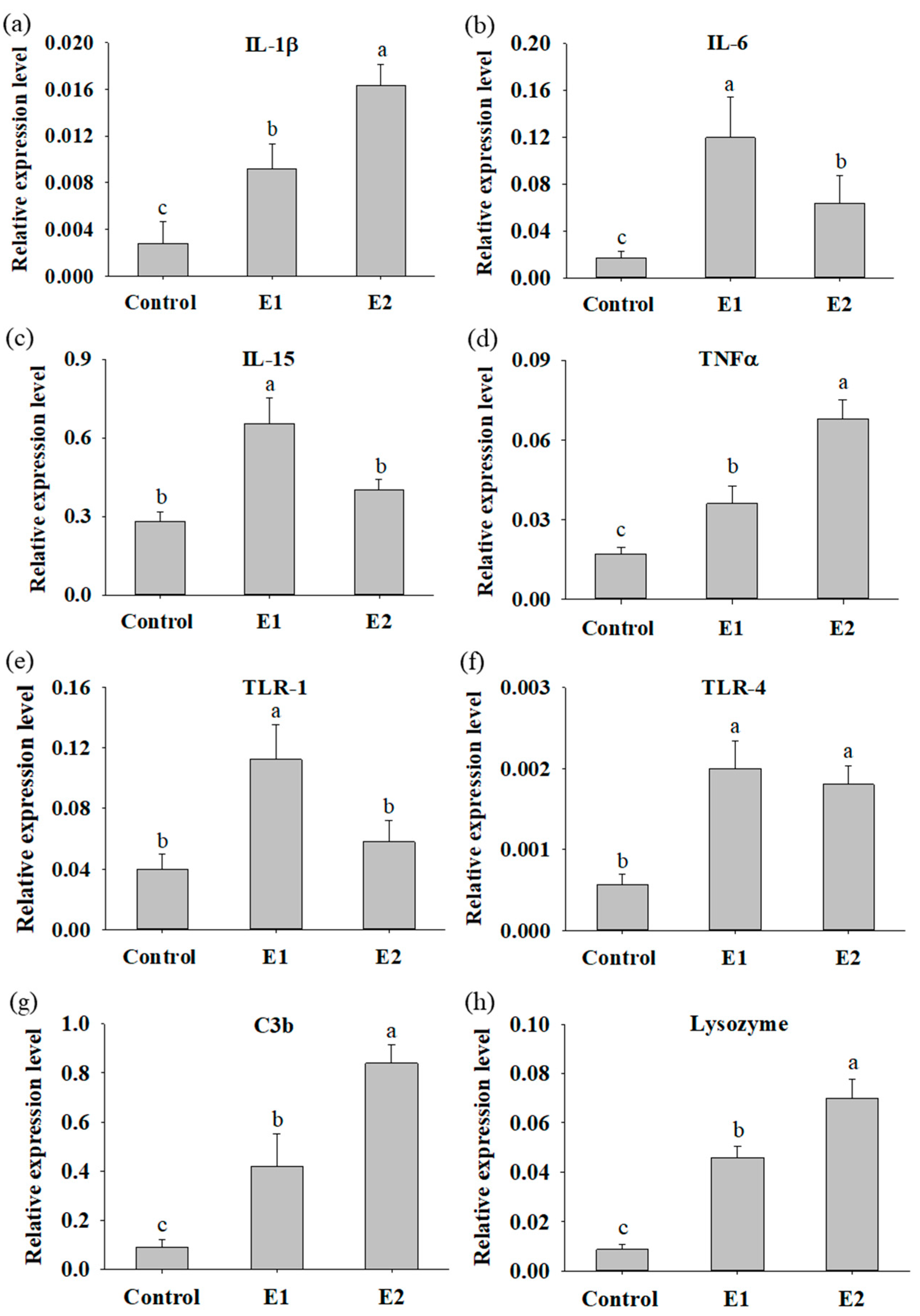
3.3. Fish Supplemented with P. ehimensis NPUST1 Modulate the Expression of Innate Immunity Response Genes
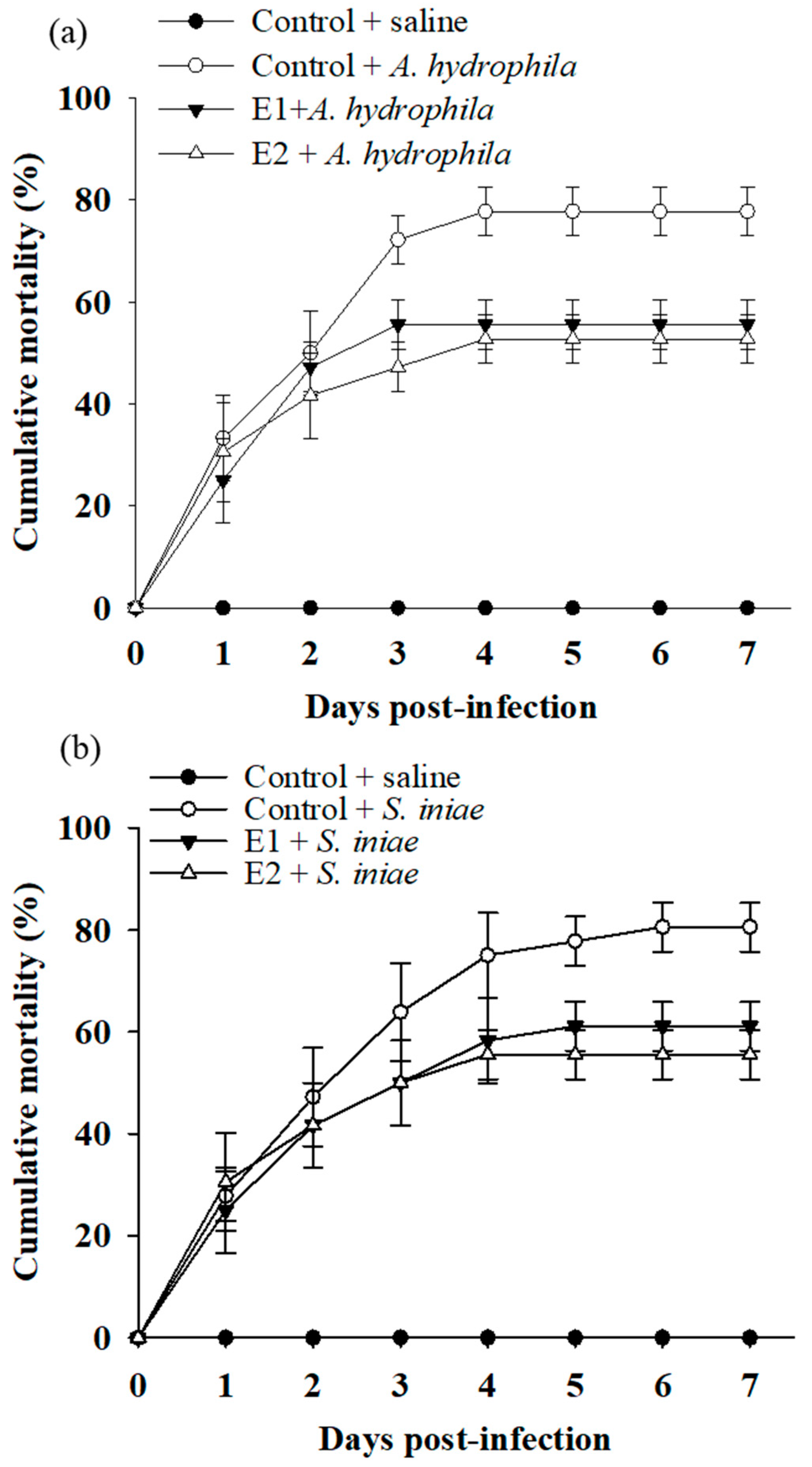
3.4. Dietary Supplementation with P. ehimensis NPUST1 Enhances Disease Resistance against Pathogen Infections
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ksepka, S.P.; Bullard, S.A. Morphology, phylogenetics and pathology of “red sore disease” (coinfection by Epistylis cf. wuhanensis and Aeromonas hydrophila) on sportfishes from reservoirs in the South-Eastern United States. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, C.; Garcia, I.; Irgang, R.; Fajardo, R.; Tapia-Cammas, D.; Acosta, J.; Avendano-Herrera, R. First identification and characterization of Streptococcus iniae obtained from tilapia (Oreochromis aureus) farmed in Mexico. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Valente, C.; Wan, A.H.L. Vibrio and major commercially important vibriosis diseases in decapod crustaceans. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 181, 107527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, S.; Tyagi, A.; Singh, R. Probiotic supplementation as an emerging alternative to chemical therapeutics in finfish aquaculture: A review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringo, E.; Van Doan, H.; Lee, S.H.; Soltani, M.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Harikrishnan, R.; Song, S.K. Probiotics, lactic acid bacteria and bacilli: Interesting supplementation for aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hai, N.V. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.S.; Liu, C.H.; Hu, S.Y. Probiotic Bacillus safensis NPUST1 administration improves growth performance, gut microbiota, and innate immunity against Streptococcus iniae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, F.; Shiu, Y.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Puspitasari, A.W.; Danata, R.H.; Liu, C.H.; Hu, S.Y. Dietary supplementation with xylanase-expressing B. amyloliquefaciens R8 improves growth performance and enhances immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 58, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Vijayaraghavan, P.; Hatamleh, A.A.; Biji, G.D.; Rady, A.M. Host associated mixed probiotic bacteria induced digestive enzymes in the gut of tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathi, C.; Dillibabu, V.; Madhuri, D.K.; Priya, D.M.; Nagalakshmi, C.; Sekaran, G. Dietary inclusion of protease producing novel Pontibacter spp. and Bacillus megaterium as a probiotic enhances immune responses in Labeo rohita. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 17, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Saputra, F.; Chen, Y.C.; Hu, S.Y. Dietary administration of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens R8 reduces hepatic oxidative stress and enhances nutrient metabolism and immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, C.; Priest, F.G.; Collins, M.D. Molecular identification of rRNA group 3 bacilli (Ash, Farrow, Wallbanks and Collins) using a PCR probe test. Proposal for the creation of a new genus Paenibacillus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1993, 64, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olishevska, S.; Nickzad, A.; Deziel, E. Bacillus and Paenibacillus secreted polyketides and peptides involved in controlling human and plant pathogens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1189–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midhun, S.J.; Neethu, S.; Vysakh, A.; Arun, D.; Radhakrishnan, E.K.; Jyothis, M. Antibacterial activity and probiotic characterization of autochthonous Paenibacillus polymyxa isolated from Anabas testudineus (Bloch, 1792). Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktuganov, G.; Melentjev, A.; Galimzianova, N.; Khalikova, E.; Korpela, T.; Susi, P. Wide-range antifungal antagonism of Paenibacillus ehimensis IB-X-b and its dependence on chitinase and beta-1,3-glucanase production. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Liu, C.H.; Hu, S.Y. Dietary administration of probiotic Paenibacillus ehimensis NPUST1 with bacteriocin-like activity improves growth performance and immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus iniae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.C.; Liu, C.H.; Chuang, K.P.; Chang, Y.T.; Hu, S.Y. A potential probiotic Chromobacterium aquaticum with bacteriocin-like activity enhances the expression of indicator genes associated with nutrient metabolism, growth performance and innate immunity against pathogen infections in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.Y.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, C.W.; Lu, J.K.; Chou, H.Y. Complete genome sequence of Streptococcus iniae 89353, a virulent strain isolated from diseased tilapia in Taiwan. Genome Announc. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analyses, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Hu, S.Y. Improvements in the growth performance, immunity, disease resistance, and gut microbiota by the probiotic Rummeliibacillus stabekisii in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, K.; Samayanpaulraj, V.; Narayanadoss, V.; Uthandakalaipandian, R. Isolation of lactic acid bacteria from intestine of freshwater fishes and elucidation of probiotic potential for aquaculture application. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1598–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzon-Atienza, L.; Bravo, J.; Torrecillas, S.; Montero, D.; Canales, A.F.G.; de la Banda, I.G.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Acosta, F. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus velezensis D-18 Strain, as a potential probiotic in European seabass aquaculture. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anokyewaa, M.A.; Amoah, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y.S.; Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Asiedu, B.; Seidu, I. Prevalence of virulence genes and antibiotic susceptibility of Bacillus used in commercial aquaculture probiotics in China. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahm, R.; Geisler, R. Learning from small fry: The zebrafish as a genetic model organism for aquaculture fish species. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.; Hamidoghli, A.; Choi, W.; Bae, J.; Jang, W.J.; Lee, S.; Bai, S.C. Evaluation of potential probiotics Bacillus subtilis WB60, Pediococcus pentosaceus, and lactococcus lactis on growth performance, immune response, gut histology and immune-related genes in whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, W.J.; Lee, J.M.; Hasan, M.T.; Lee, B.J.; Lim, S.G.; Kong, I.S. Effects of probiotic supplementation of a plant-based protein diet on intestinal microbial diversity, digestive enzyme activity, intestinal structure, and immunity in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Wang, S.F.; Cai, Y.; Li, E.C.; Ren, Z.L.; Wu, Y.; Guo, W.L.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y.C. Beneficial effects of a host gut-derived probiotic, Bacillus pumilus, on the growth, non-specific immune response and disease resistance of juvenile golden pompano, Trachinotus ovatus. Aquaculture 2020, 514, 734446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Chun, W.K.; Kim, A.; Kim, N.; Roh, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Yi, M.; Kim, S.; Park, C.I.; Kim, D.H. Dietary probiotic effect of Lactococcus lactis WFLU12 on low-molecular-weight metabolites and growth of olive flounder (Paralichythys olivaceus). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Elsadek, M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Z. The effect of adding Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LSG2-8 in diets on the growth, immune function, antioxidant capacity, and disease resistance of Rhynchocypris lagowskii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 125, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzon-Atienza, L.; Bravo, J.; Fernandez-Montero, A.; Charlie-Silva, I.; Montero, D.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Acosta, F. Dietary supplementation of Bacillus velezensis improves Vibrio anguillarum clearance in European sea bass by activating essential innate immune mechanisms. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 124, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doan, H.; Wangkahart, E.; Thaimuangphol, W.; Panase, P.; Sutthi, N. Effects of Bacillus spp. Mixture on growth, immune responses, expression of immune-related genes, and resistance of nile tilapia against Streptococcus agalactiae infection. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Bae, J.; Hamidoghli, A.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.H.; Min, T.; Bai, S.C. Evaluation of dietary probiotic bacteria and processed yeast (Gropro-aqua) as the alternative of antibiotics in juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Kang, Y.H.; Zhan, S.; Zhao, Z.L.; Jin, S.N.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.Y.; Wang, C.F.; Wang, G.Q.; et al. Effect of Bacillus velezensis on Aeromonas veronii-induced intestinal mucosal barrier function damage and inflammation in crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, K.M.; Reda, R.M. Improvement of immunity and disease resistance in the Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, by dietary supplementation with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Sen, S.S.; Chi, C.; Kim, H.J.; Yun, S.; Park, S.C.; Sukumaran, V. Effect of cellular products of potential probiotic bacteria on the immune response of Labeo rohita and susceptibility to Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragland, S.A.; Criss, A.K. From bacterial killing to immune modulation: Recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrient metabolism and growth-related genes | |||
| Glucokinase (GK) | ATGACCGGCACAGCTGAAAT | 100 | BC122359 |
| ATCCCAGCGGTAGCTTCTTG | |||
| Hexokinase 1 (HK1) | ACTTTGGGTGCAATCCTGAC | 97 | BC067330 |
| AGACGACGCACTGTTTTGTG | |||
| Glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) | ACGCTGTTCCTGCTGTCATTC | 100 | BC164161 |
| TGCACCATTTCTGGGCTTTC | |||
| Pyruvate kinase (PK-L) | TCCTGGAGCATCTGTGTCTG | 104 | BC152219 |
| GTCTGGCGATGTTCATTCCT | |||
| Growth hormone receptor (GHR) | TGAGTCGTTCAGGGTTGCACTT | 100 | NM_001083578 |
| GAAGCTGGTACACCAGACTCA | |||
| Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) | AGTGTACCATGCGCTGTCTC | 100 | NM_131825 |
| CAGCGTCTCCGGCCCCGCCT | |||
| Immune-related genes | |||
| Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) | TGGACTTCGCAGCACAAAATG | 147 | AY340959 |
| CACTTCACGCTCTTGGATGA | |||
| Interleukin-6 (IL-6) | TCAACTTCTCCAGCGTGATG | 73 | JN698962 |
| TCTTTCCCTCTTTTCCTCCTG | |||
| Interleukin-15 (IL-15) | ATGTCATTGGAACTCAGAGGTTTG | 100 | BC162843 |
| CTGTTCTGGATGTCCTGCTTGA | |||
| Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) | AAGGAGAGTTGCCTTTACCG | 152 | BC165066 |
| ATTGCCCTGGGTCTTATGC | |||
| Toll-like receptor-1 (TLR-1) | CAGAGCGAATGGTGCCACTAT | 97 | AY163838 |
| GTGGCAGAGGCTCCAGAAGA | |||
| Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4) | TTTCAGATGCCACATCAGA | 150 | EU551724 |
| TCCACAAGAACAAGCCTTTG | |||
| Lysozyme | CGTGGATGTCCTCGTGTGAAG | 100 | NM_139180 |
| CCAATGGAGAATCCCTCAAA | |||
| Complement component C3b | CGTCTCCGTACACCATCCATT | 100 | NM_131243 |
| GGCGTCTCATCAGGATTTGTTAC | |||
| Elongation factor-1α (EF-1α) | AACAGCTGATCGTTGGAGTCAA | 100 | AY422992 |
| TTGATGTATGCGCTGACTTCCT | |||
| Digestive Enzymes Activities (U/mg Protein) | Control | E1 | E2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amylase | 0.46 ± 0.631 b | 0.68 ± 0.137 b | 1.38 ± 0.212 a |
| Cellulase | 0.11 ± 0.003 b | 0.48 ± 0.023 a | 0.54 ± 0.021 a |
| Lipase | 0.32 ± 0.023 b | 0.92 ± 0.083 a | 0.89 ± 0.113 a |
| Protease | 0.68 ± 0.081 b | 1.72 ± 0.221 a | 1.65 ± 0.192 a |
| Xylanase | 0.19 ± 0.004 b | 0.77 ± 0.038 a | 0.92 ± 0.146 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, P.-H.; Chen, S.-W.; Wen, Z.-H.; Hu, S.-Y. Administration of the Potential Probiotic Paenibacillus ehimensis NPUST1 Enhances Expression of Indicator Genes Associated with Nutrient Metabolism, Growth and Innate Immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus indie Infections in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes 2022, 7, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060386
Lin P-H, Chen S-W, Wen Z-H, Hu S-Y. Administration of the Potential Probiotic Paenibacillus ehimensis NPUST1 Enhances Expression of Indicator Genes Associated with Nutrient Metabolism, Growth and Innate Immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus indie Infections in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes. 2022; 7(6):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060386
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Pei-Hui, Sai-Wei Chen, Zhi-Hong Wen, and Shao-Yang Hu. 2022. "Administration of the Potential Probiotic Paenibacillus ehimensis NPUST1 Enhances Expression of Indicator Genes Associated with Nutrient Metabolism, Growth and Innate Immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus indie Infections in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)" Fishes 7, no. 6: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060386
APA StyleLin, P.-H., Chen, S.-W., Wen, Z.-H., & Hu, S.-Y. (2022). Administration of the Potential Probiotic Paenibacillus ehimensis NPUST1 Enhances Expression of Indicator Genes Associated with Nutrient Metabolism, Growth and Innate Immunity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus indie Infections in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fishes, 7(6), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7060386







