- Article
Effects of Different Application Strategies of Copper-Loaded Montmorillonite on Growth, Intestinal Histology, and Rearing-Water Quality in Penaeus monodon
- Jieyi Wang,
- Yangyang Ding and
- Song Jiang
- + 7 authors
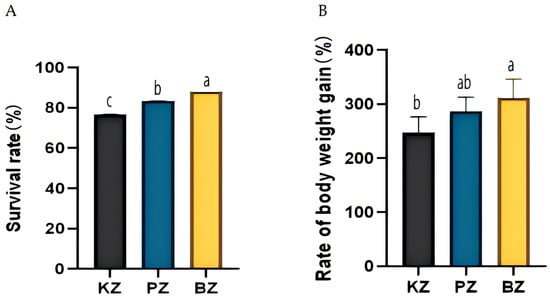
Penaeus monodon is widely cultured in Asia; however, intensive farming practices often result in water-quality deterioration and compromised production performance. Copper-loaded montmorillonite (Cu-MMT) is a functional additive with adsorption and antimicrobial properties, yet the relative effectiveness of different application strategies remains insufficiently evaluated. In this study, 270 shrimp were assigned to three treatments: a control group (KZ), water application of Cu-MMT (PZ), and dietary inclusion of Cu-MMT (BZ). Juvenile Penaeus monodon with an initial body weight of 3.25 ± 0.15 g were used in the trial. Growth performance, intestinal histology, and rearing-water quality were assessed over a 56-day culture period. Shrimp in the BZ group exhibited a significantly higher weight gain rate (311.88 ± 38.17%) and survival rate (88.04%) than those in the KZ (247.45 ± 32.82%; 76.67%) and PZ (286.49 ± 29.78%; 83.33%) groups (p < 0.05). Intestinal histological observations revealed treatment-associated differences in morphology, with more pronounced intestinal enlargement observed in the PZ group, whereas the BZ group exhibited a more moderate intestinal architecture. Water-quality analyses showed that dietary Cu-MMT supplementation was associated with higher dissolved oxygen levels and lower concentrations of total ammonia nitrogen, sulfide, and dissolved iron, particularly during the later stages of the experiment. Overall, these results indicate that dietary inclusion of Cu-MMT provides more favorable outcomes than water application in improving growth performance and rearing-water quality in P. monodon culture under the experimental conditions tested. These findings highlight the importance of application strategy when evaluating functional additives in shrimp aquaculture.
18 January 2026